Capital Cost Project Specification
1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose
This specification outlines the requirements and guidelines for estimating and managing capital costs for the "FutureTech Infrastructure Enhancement" project. It aims to provide a comprehensive framework to ensure accurate cost assessment, budgeting, and financial control throughout the project's lifecycle.
1.2 Scope
This document covers the following aspects of capital cost management:
Cost estimation
Budgeting
Cost control
Financial reporting
2. Definitions and Terminology
2.1 Capital Cost
Capital costs refer to the expenses incurred to acquire, upgrade, or maintain physical assets. These include:
Direct Costs: Costs directly attributable to the project (e.g., construction, equipment).
Indirect Costs: Costs that are not directly tied to the project but are necessary for completion (e.g., administrative expenses).
2.2 Project Lifecycle
The stages of a project from initiation to completion:
Planning: January 2055 - March 2055
Design: April 2055 - June 2055
Execution: July 2055 - December 2056
Completion: January 2057
3. Cost Estimation
3.1 Methodology
Cost estimation for the "FutureTech Infrastructure Enhancement" project will use the following methods:
Analogous Estimating: Leveraging data from similar technology infrastructure projects, such as the "TechCorp Data Center Expansion" project, from 2050.
Parametric Estimating: Applying statistical relationships between variables, such as cost per square foot for construction and equipment installation.
Bottom-Up Estimating: Aggregating costs from detailed work breakdown structures, including individual tasks and resource requirements.
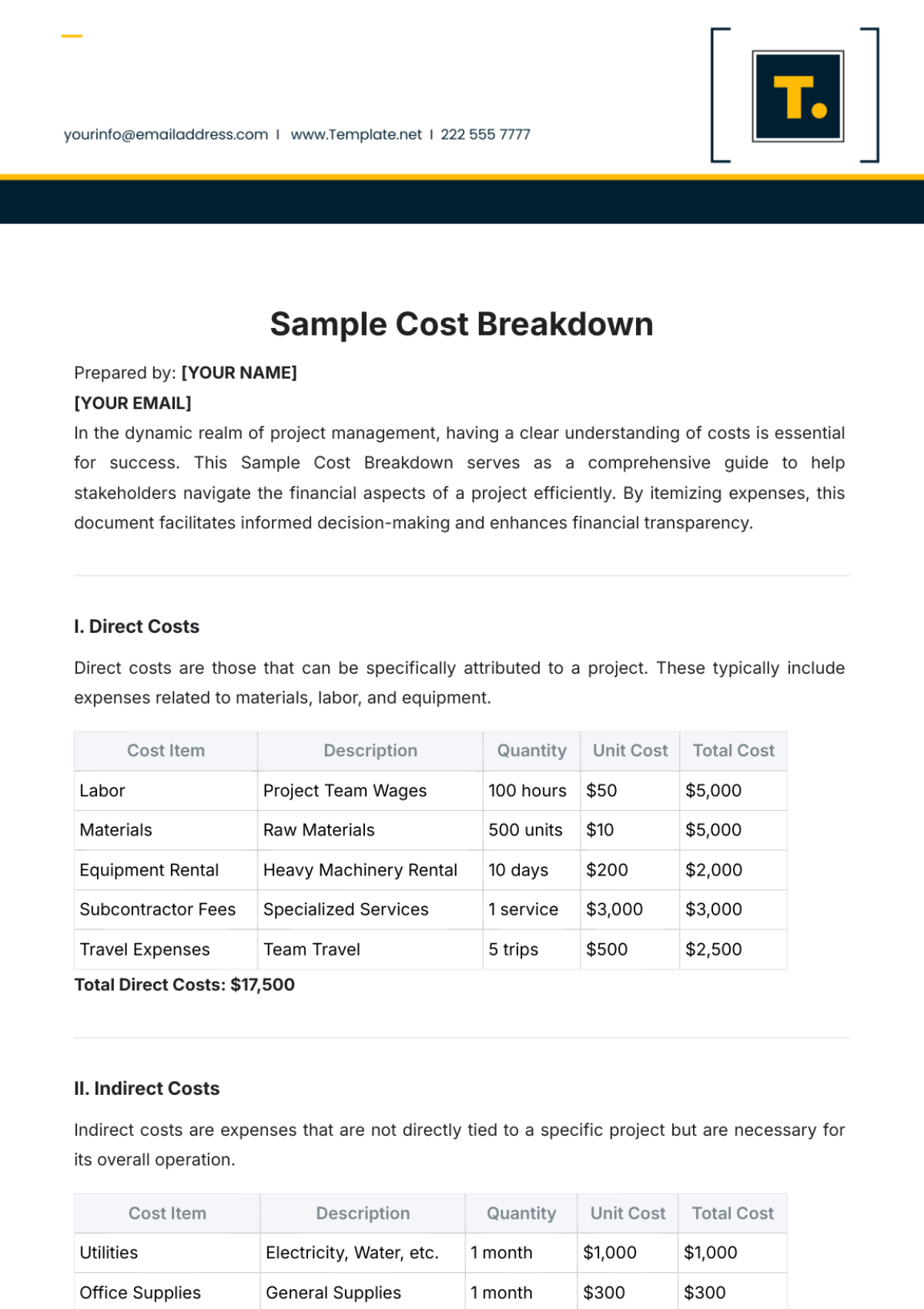
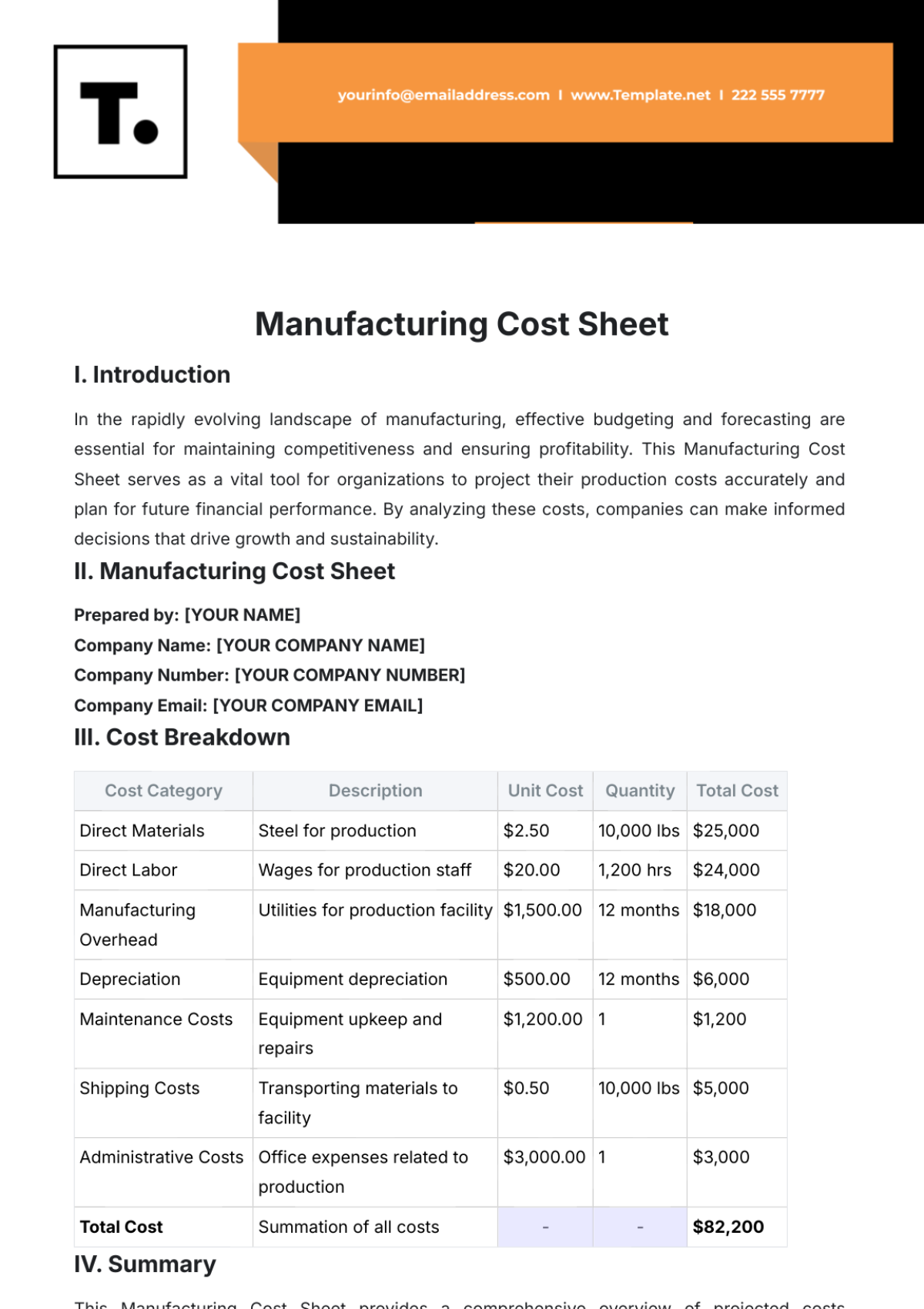
3.2 Cost Breakdown Structure
The cost breakdown structure includes:
Labor Costs: Project management, technical staff, and administrative support.
Materials Costs: Construction materials, high-tech components, and furnishings.
Equipment Costs: Specialized machinery, installation tools, and testing equipment.
Subcontractor Costs: External consulting services, specialized trades, and temporary staffing.
Contingency Costs: Reserved funds for unforeseen expenses and project risks.
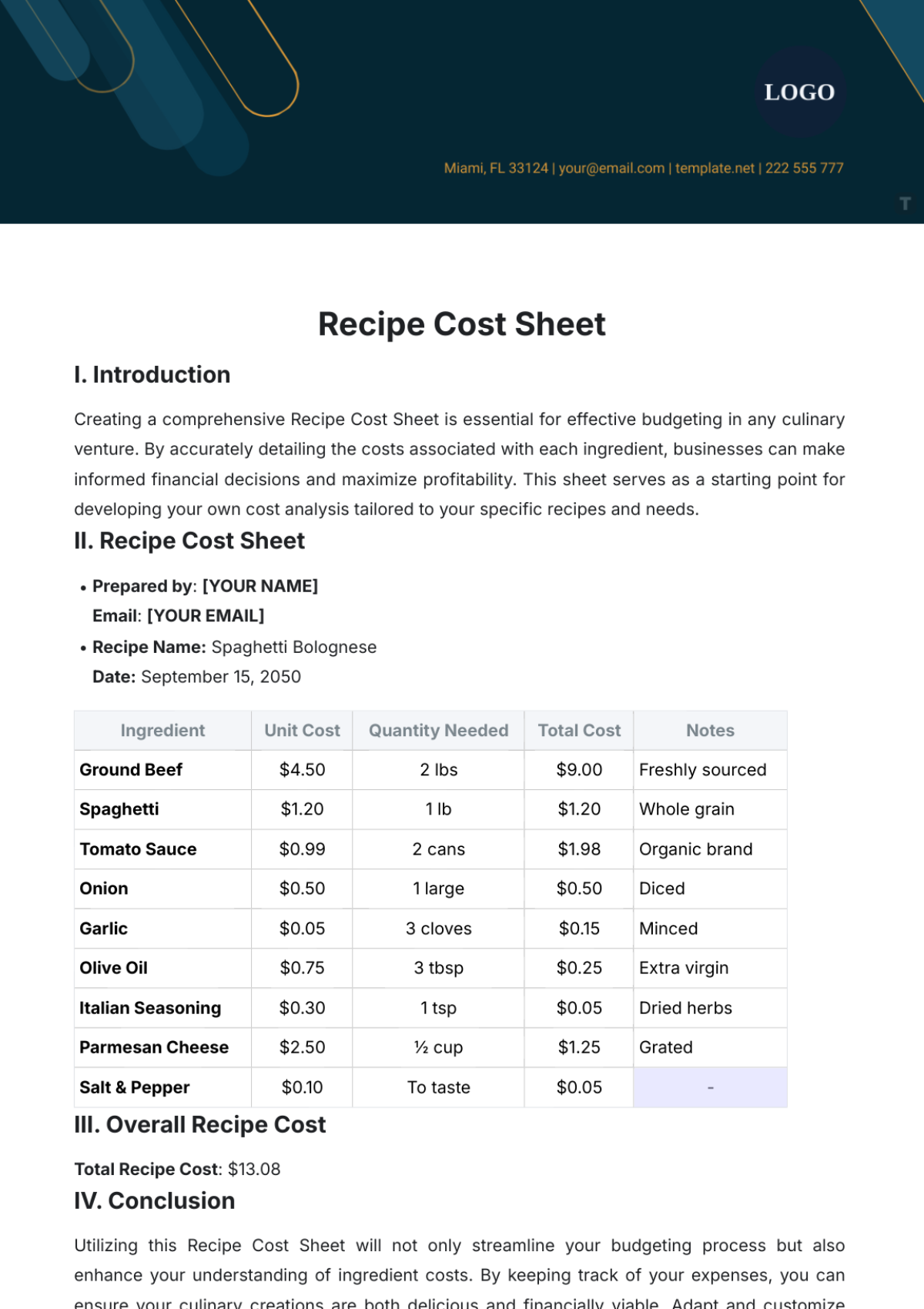
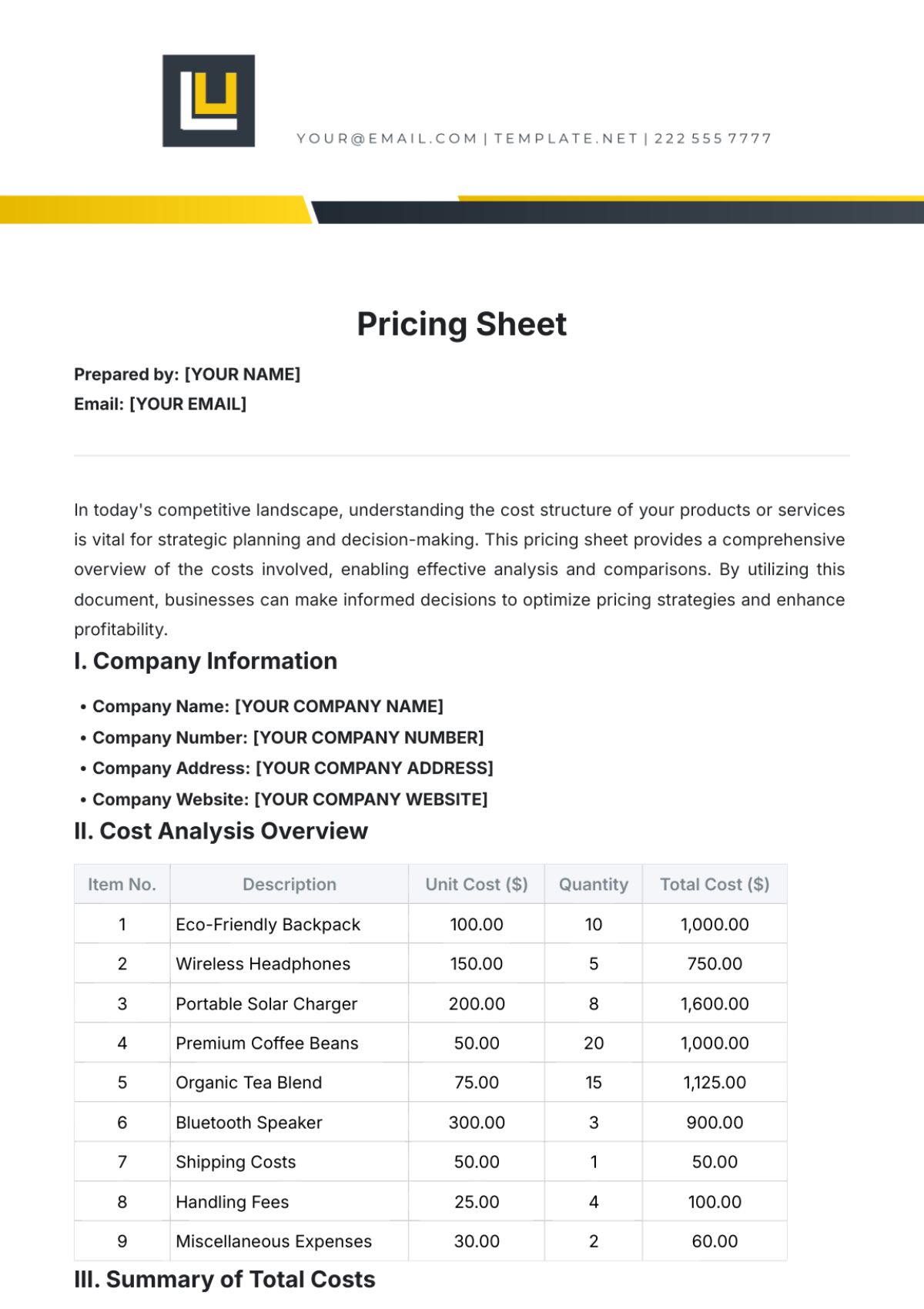
Cost Breakdown Structure
Cost Category | Description | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|
Labor Costs | Wages, salaries, and benefits for project staff | $1,200,000 |
Materials Costs | High-tech components, construction materials | $800,000 |
Equipment Costs | Installation tools, machinery | $500,000 |
Subcontractor Costs | Consulting services, specialized trades | $300,000 |
Contingency Costs | Reserved funds for unexpected expenses | $200,000 |
3.3 Documentation
All cost estimates will be documented, including:
Basis of Estimate: Assumptions, methodologies, and sources of data.
Supporting Data: Quotes from suppliers, historical data, and expert opinions.
Review and Approval: Documentation of reviews and approvals by the project manager and financial controller.
4. Budgeting
4.1 Budget Development
The project budget will be developed based on:
Cost Estimates: As detailed in section 3.
Cash Flow Projections: Timing of cash requirements and expenditures, including initial investment and ongoing operational costs.
4.2 Budget Control
Mechanisms for controlling the budget include:
Regular Monitoring: Monthly reviews of actual expenditures versus budgeted amounts.
Variance Analysis: Quarterly analysis of deviations from the budget, identifying reasons for variances.
Adjustments: Implementing corrective actions as necessary to address budgetary issues.
5. Cost Control
5.1 Cost Tracking
Utilize project management software to track:
Expenditures: Real-time tracking of costs using tools such as "Procore" or "Oracle Primavera".
Budget Performance: Comparison of budgeted versus actual costs, with periodic updates.
5.2 Change Management
Implement a formal change management process to handle:
Scope Changes: Adjustments in project scope, such as additional features or revised requirements, affect costs.
Cost Adjustments: Modifications to budget estimates, including approval processes for changes.
5.3 Risk Management
Identify and manage financial risks through:
Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential cost affects, such as supply chain disruptions or regulatory changes.
Mitigation Strategies: Developing strategies to minimize financial risks, including contingency planning and insurance.
6. Financial Reporting
6.1 Reporting Requirements
Prepare and submit financial reports that include:
Budget Status Reports: Summary of current budget versus actual expenditure.
Cost Forecasts: Predictions of future costs based on current trends and the remaining project scope.
Variance Reports: Detailed explanations of any discrepancies between budgeted and actual costs.
6.2 Frequency of Reporting
Financial reports will be prepared:
Monthly: For regular monitoring and control, including detailed expenditure reports.
Quarterly: For detailed analysis and strategic review, highlighting major variances and corrective actions.
Annually: For comprehensive financial performance review, including overall project cost and budget adherence.
7. Conclusion
7.1 Summary
This specification provides a structured approach to capital cost management for the "FutureTech Infrastructure Enhancement" project. It includes detailed processes for estimation, budgeting, control, and reporting to ensure accurate financial planning and effective management of capital costs.
7.2 Approval
The project sponsor, financial controller, and relevant stakeholders must review and approve this specification before implementation.