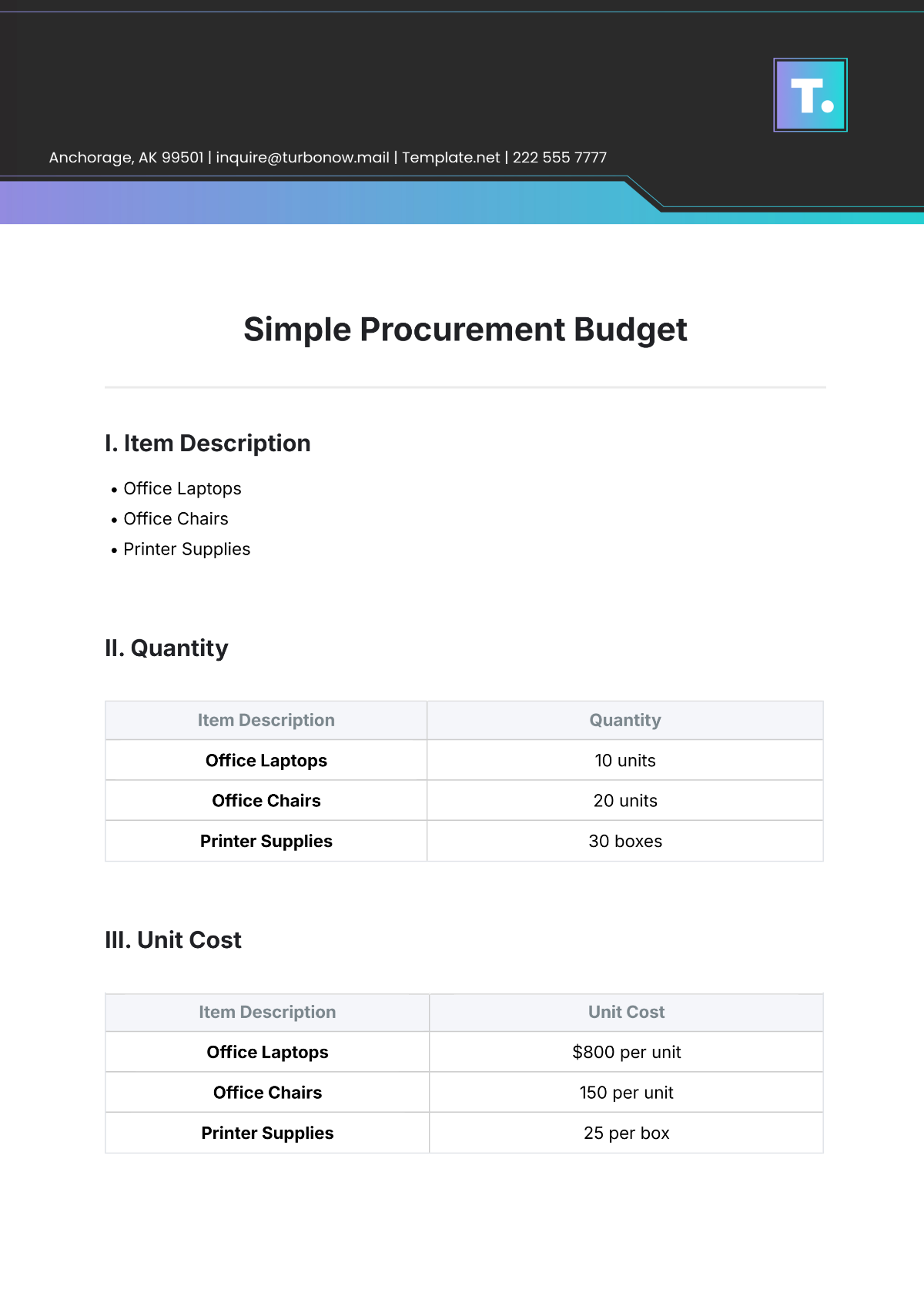
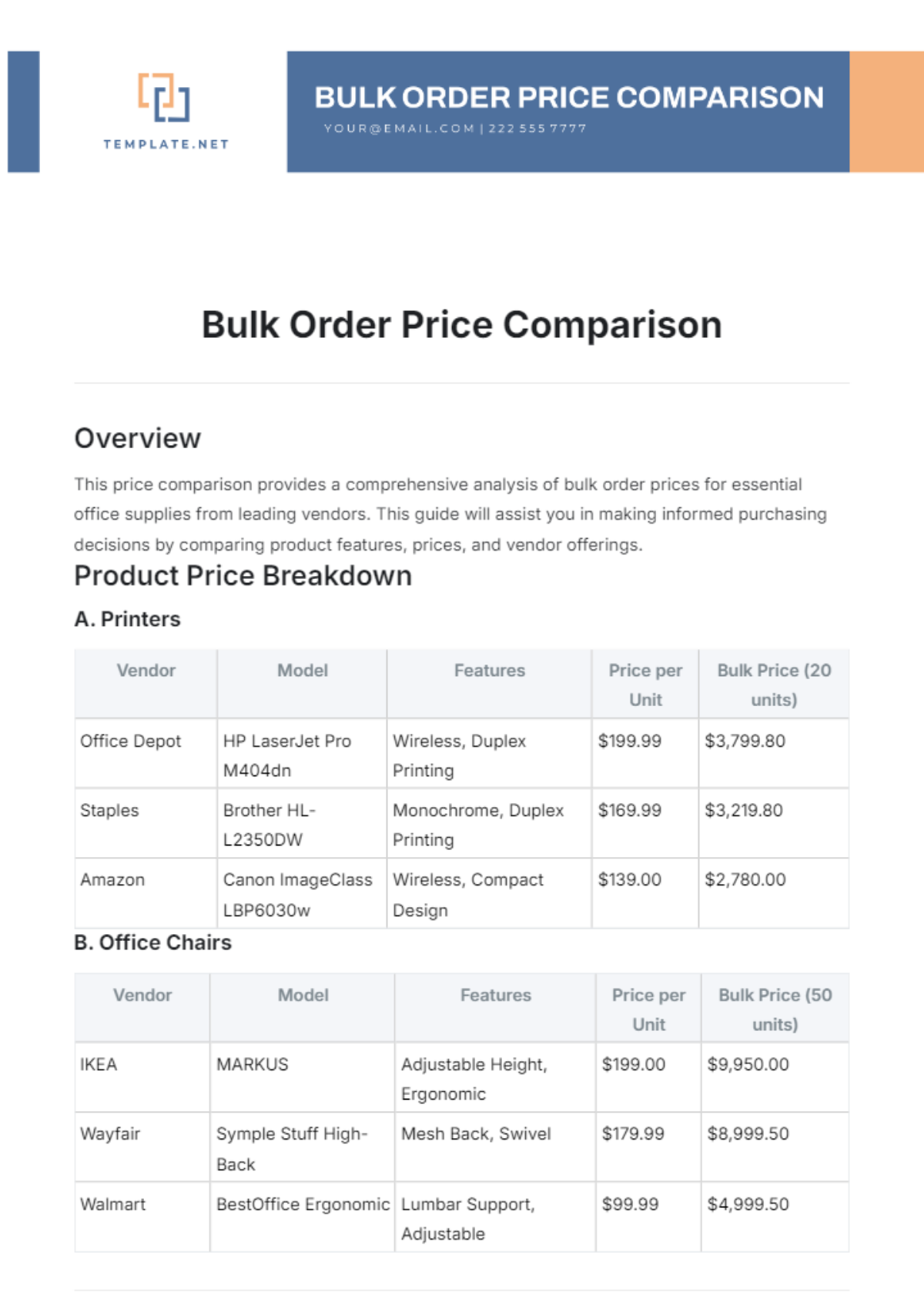
Free Supplier Management Requirements
Optimize supplier relations with Template.net's Supplier Management Requirements Template. Fully customizable and editable, it allows you to address all supplier management criteria. Editable in our Ai Editor Tool, personalize it to meet your organization's needs. Enhance supplier management effortlessly with this comprehensive template from Template.net.