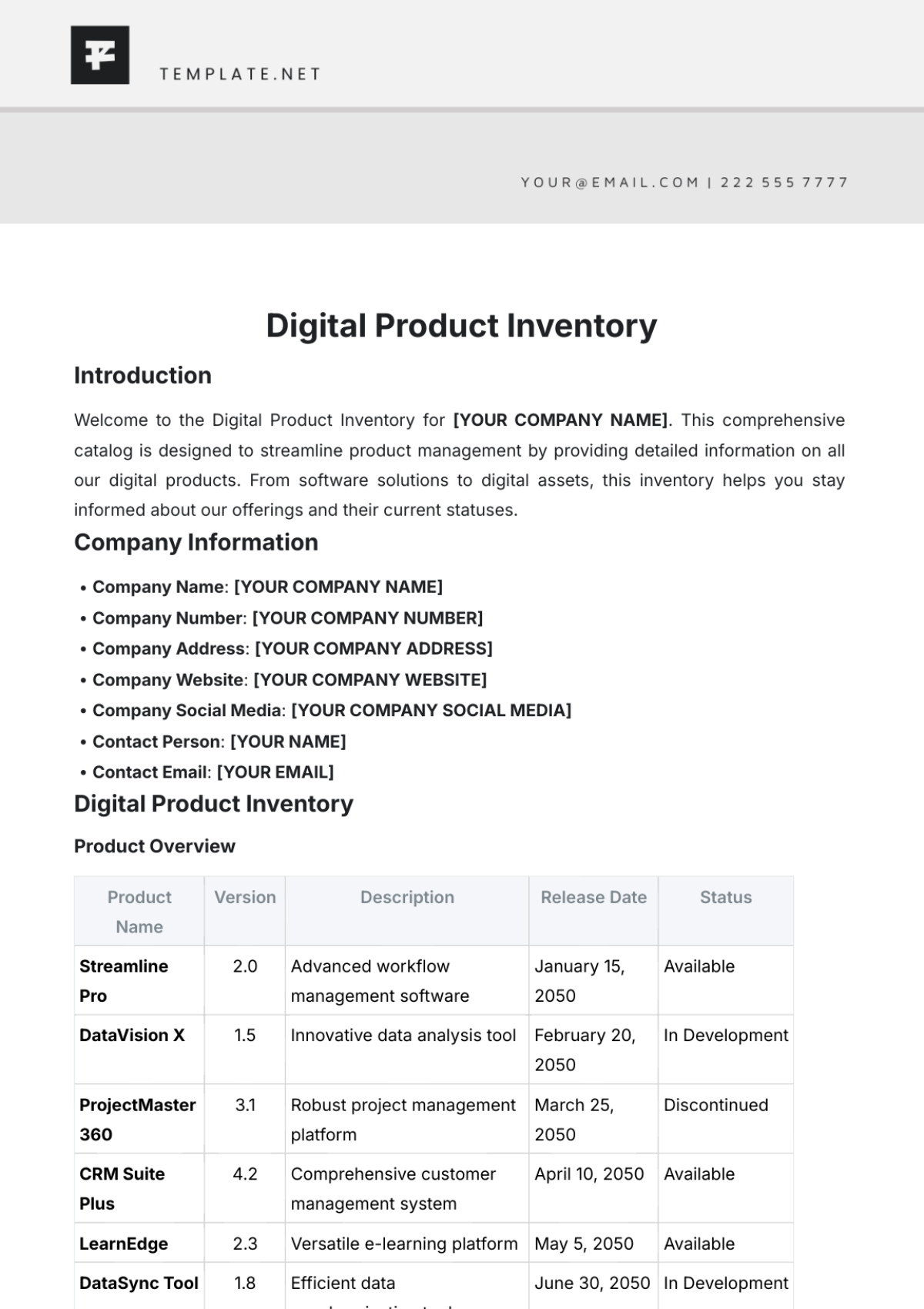
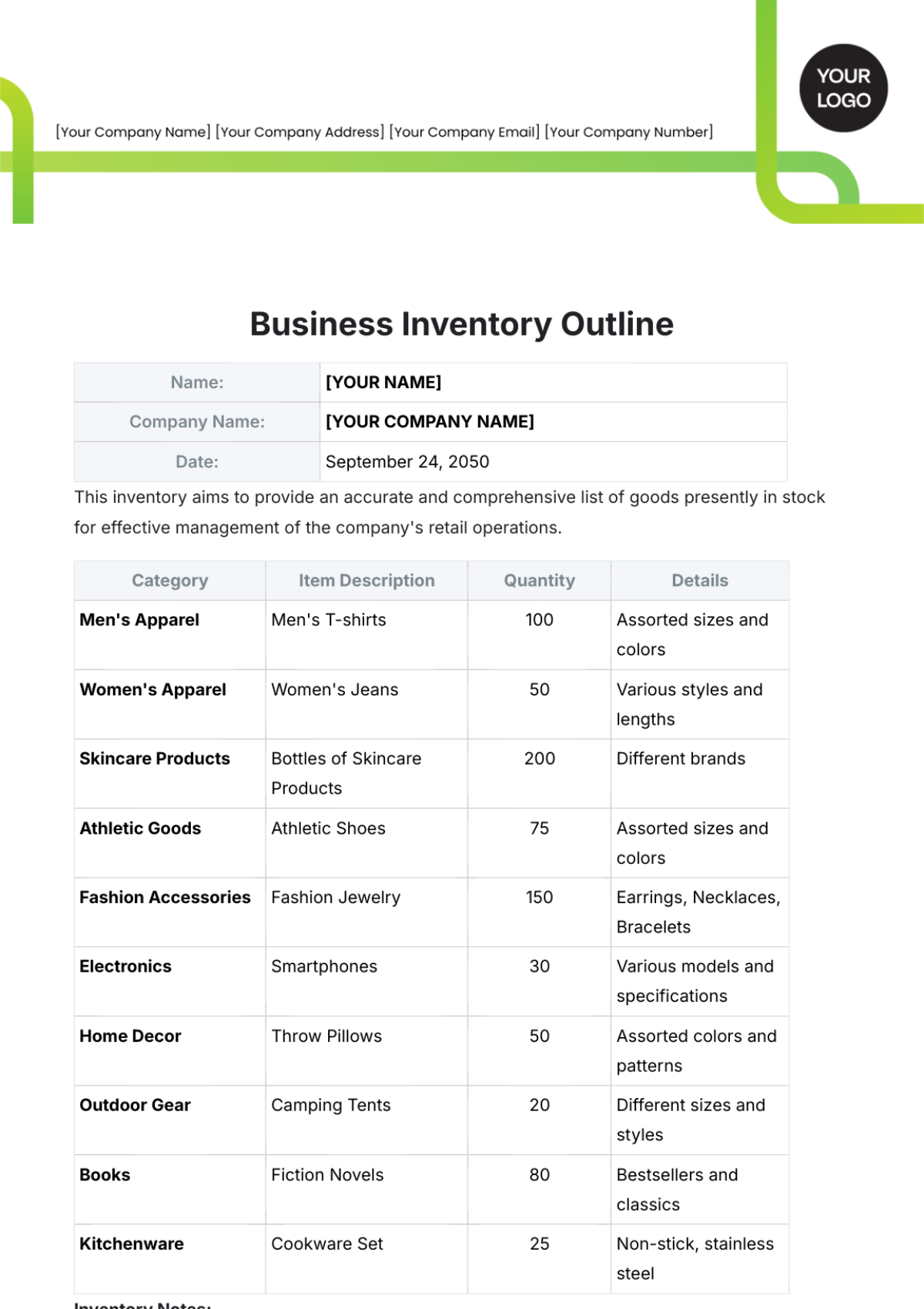
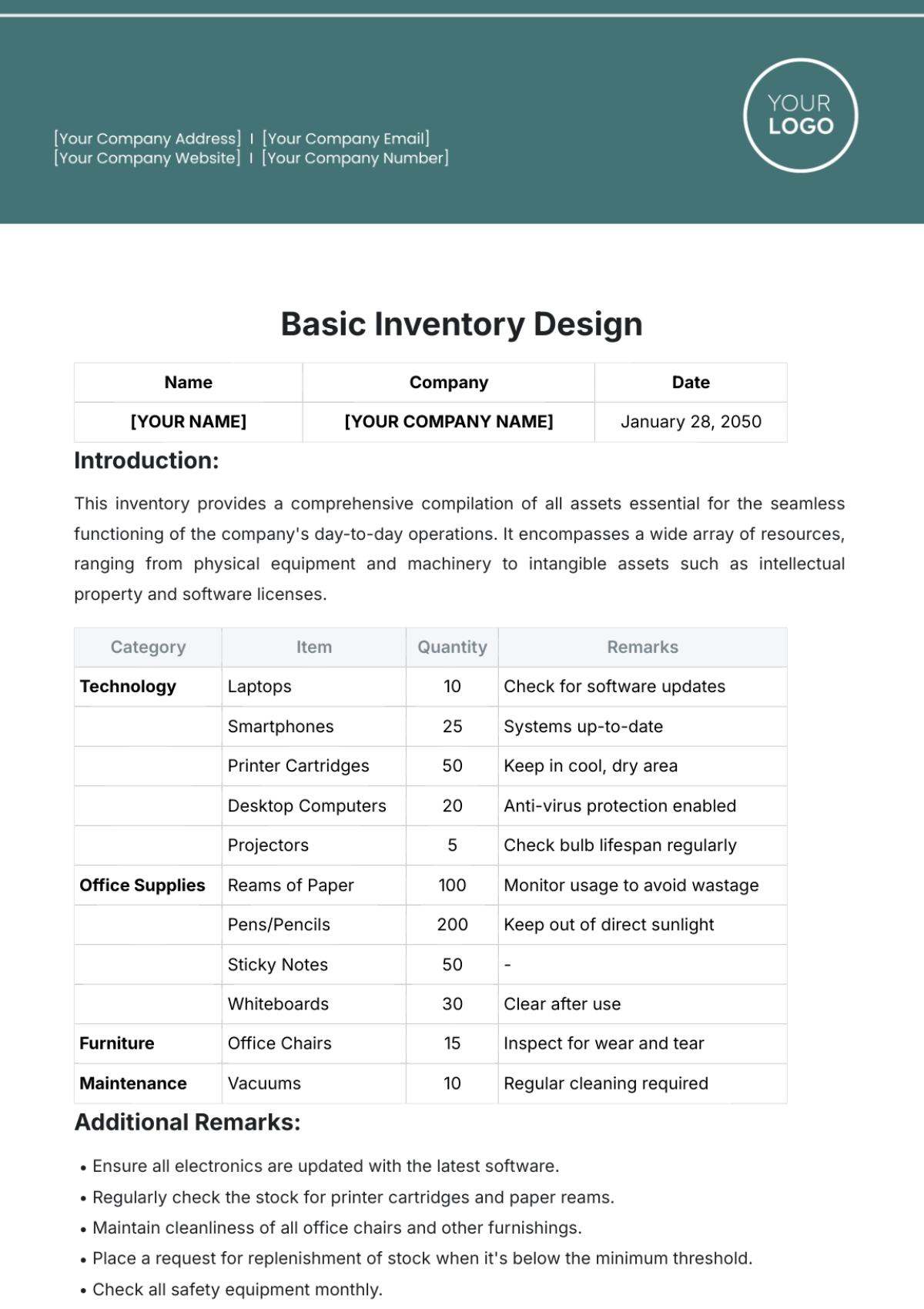
Bakery Inventory SOP
I. Introduction
A. Purpose
The purpose of this Bakery Inventory SOP is to outline the steps and guidelines for managing inventory within [Your Company Name] to ensure accuracy, efficiency, and proper stock levels. This SOP is designed to help staff maintain an organized and effective inventory system, reducing waste and ensuring that the bakery can meet customer demands.
B. Scope
This SOP applies to all staff involved in inventory management at [Your Company Name]. It covers procedures for ordering, receiving, storing, and tracking inventory, as well as conducting regular inventory audits and handling discrepancies.
C. Target Audience
The target audience for this SOP includes inventory managers, purchasing staff, and any other employees responsible for handling and managing inventory at [Your Company Name].
II. Inventory Ordering
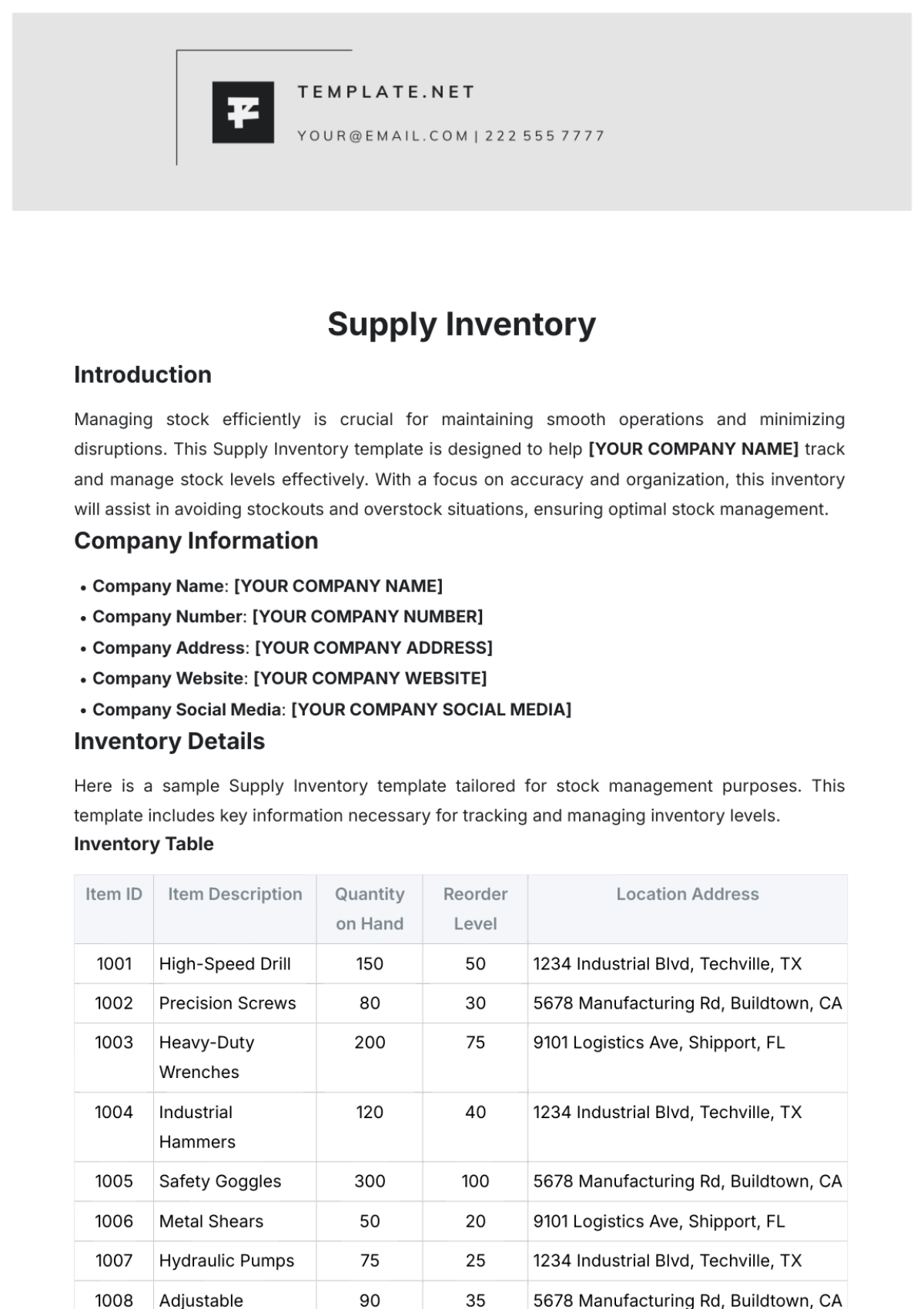
Proper ordering ensures that the bakery has the necessary supplies without overstocking or understocking. The following table provides an overview of the steps for inventory ordering:
No. | Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Assess Needs | Evaluate inventory levels and identify items that need to be reordered. |
2 | Select Suppliers | Choose suppliers based on quality, price, and reliability. |
3 | Place Orders | Submit purchase orders to selected suppliers. |
4 | Confirm Orders | Confirm receipt of purchase orders and expected delivery dates. |
5 | Record Orders | Document order details in the inventory management system. |
A. Assess Needs
Evaluate Inventory Levels: Regularly check inventory levels to determine which items need to be reordered. Keeping track of inventory helps avoid stockouts.
Identify Critical Items: Prioritize ordering of critical items that are essential for daily operations. Ensuring the availability of key ingredients is crucial for uninterrupted production.
Review Usage Patterns: Analyze past usage patterns to predict future inventory needs. Understanding trends helps in making accurate forecasts.
Set Reorder Points: Establish reorder points for each item based on their usage rate. Reorder points trigger automatic replenishment, preventing shortages.
B. Select Suppliers
Quality Assessment: Choose suppliers who provide high-quality products consistently. Quality assurance is key to maintaining product standards.
Price Comparison: Compare prices from different suppliers to get the best deal without compromising quality. Cost efficiency is important for profitability.
Reliability Check: Evaluate suppliers based on their reliability and delivery times. Reliable suppliers ensure timely delivery and reduce operational disruptions.
Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with suppliers for better negotiation and service. Good relationships can lead to better terms and conditions.
C. Place Orders
Submit Purchase Orders: Place orders with selected suppliers using formal purchase orders. Formal orders ensure clarity and accountability.
Order Specifications: Clearly specify the quantity, quality, and delivery date for each item. Detailed specifications prevent misunderstandings.
Order Confirmation: Confirm receipt of the order with the supplier to ensure accuracy. Order confirmation helps verify that the order is correct.
Order Follow-Up: Follow up with suppliers to track the status of orders. Regular follow-ups help ensure timely delivery.
D. Confirm Orders
Receive Order Confirmation: Confirm receipt of purchase orders and expected delivery dates from suppliers. Order confirmation ensures that orders are on track.
Verify Details: Verify the details of the order against the original purchase order. Verification helps ensure accuracy and prevent discrepancies.
Adjust Plans: Adjust inventory plans based on confirmed delivery dates. Planning adjustments help manage stock levels effectively.
Communicate Changes: Communicate any changes in delivery schedules to relevant staff. Effective communication ensures everyone is informed.
E. Record Orders
Document Order Details: Record the details of each order in the inventory management system. Accurate documentation helps maintain organized records.
Track Deliveries: Track deliveries to ensure all orders are received as expected. Delivery tracking helps manage inventory flow.
Update Inventory Levels: Update inventory levels based on received orders. Regular updates ensure inventory records are current.
Review Orders: Periodically review orders and adjust future orders as needed. Regular reviews help improve ordering accuracy.
Maintaining an efficient ordering process is crucial for ensuring that the bakery has the necessary supplies to meet customer demands. Proper ordering practices help prevent stockouts and overstocking, contributing to the overall efficiency of the bakery's operations.
III. Receiving Inventory
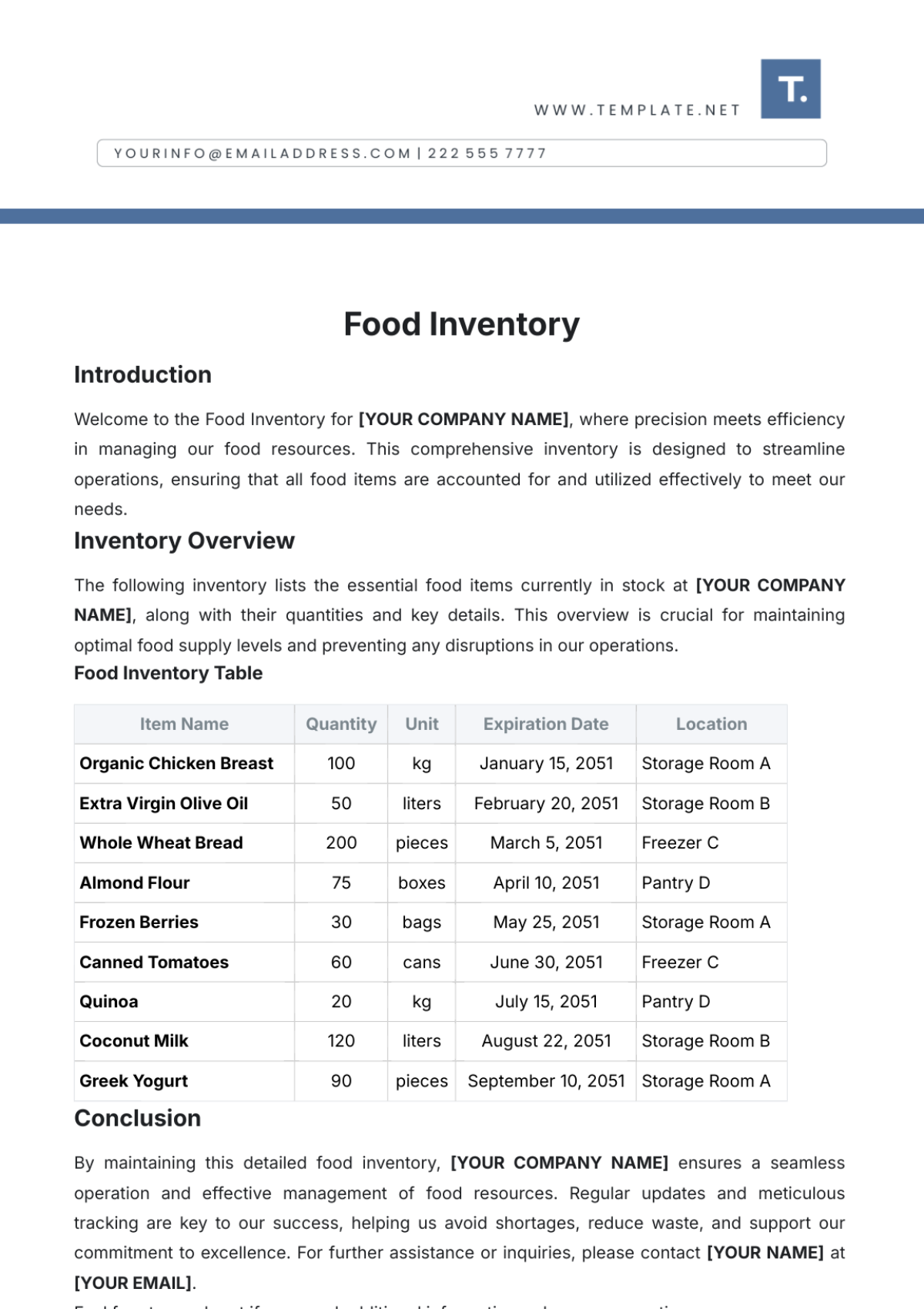
Proper receiving procedures ensure that all items are accurately accounted for and meet quality standards. The following table outlines the steps for receiving inventory:
No. | Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Inspect Deliveries | Examine all incoming shipments for accuracy and quality. |
2 | Verify Quantities | Check the received quantities against the purchase order. |
3 | Record Receipts | Document the receipt of goods in the inventory management system. |
4 | Report Discrepancies | Report any discrepancies or issues to the supplier immediately. |
5 | Store Inventory | Properly store received items in designated areas. |
A. Inspect Deliveries
Examine Shipments: Inspect all incoming shipments for signs of damage or tampering. Careful examination helps ensure product quality.
Check Packaging: Ensure that all packaging is intact and secure. Proper packaging protects the products during transit.
Verify Expiry Dates: Check expiry dates on perishable items to ensure freshness. Ensuring freshness is essential for product quality.
Assess Quality: Evaluate the quality of the received items against set standards. Quality assessment ensures that products meet bakery standards.
Document Findings: Document any issues or concerns during the inspection. Proper documentation helps track and resolve issues.
B. Verify Quantities
Match Quantities: Compare the quantities received against the purchase order. Accurate matching helps prevent discrepancies.
Check Completeness: Ensure that all items listed on the purchase order have been received. Completeness checks prevent missing items.
Address Shortages: Report any shortages or overages to the supplier immediately. Prompt reporting helps resolve issues quickly.
Confirm with Supplier: Confirm received quantities with the supplier if there are discrepancies. Supplier confirmation helps ensure accuracy.
C. Record Receipts
Log Receipts: Enter the details of the received items into the inventory management system. Accurate logging ensures organized records.
Update Inventory Levels: Adjust inventory levels based on the received quantities. Regular updates help maintain current inventory records.
Maintain Records: Keep copies of all delivery documents for future reference. Proper record-keeping ensures accountability.
Review Receipts: Periodically review receipt records for accuracy. Regular reviews help identify and correct errors.
D. Report Discrepancies
Identify Issues: Identify any discrepancies or issues with the received items. Prompt identification helps address problems quickly.
Notify Supplier: Report any discrepancies or issues to the supplier immediately. Timely notification helps resolve issues efficiently.
Document Discrepancies: Document all discrepancies and the actions taken to resolve them. Proper documentation ensures transparency.
Follow Up: Follow up with the supplier to ensure that discrepancies are resolved. Regular follow-ups help maintain good supplier relations.
E. Store Inventory
Proper Storage: Store received items in their designated areas to ensure organization. Proper storage helps maintain order and accessibility.
Temperature Control: Ensure that perishable items are stored at the correct temperatures. Temperature control is crucial for maintaining quality.
Labeling: Label all received items with the date of receipt and any relevant information. Proper labeling helps track inventory.
Rotate Stock: Use the First-In, First-Out (FIFO) method to rotate stock. Stock rotation helps prevent spoilage.
Proper receiving procedures are essential for maintaining accurate inventory records and ensuring product quality. By following these steps, the bakery can effectively manage incoming inventory and address any issues promptly.
IV. Inventory Storage
Effective storage practices ensure that all items are organized, accessible, and maintained at optimal conditions. The following table outlines the steps for proper inventory storage:
No. | Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Designate Storage Areas | Assign specific storage areas for different types of inventory. |
2 | Maintain Cleanliness | Keep storage areas clean and free of debris. |
3 | Control Temperature | Maintain appropriate temperatures for different items. |
4 | Organize Inventory | Organize inventory for easy access and identification. |
5 | Monitor Conditions | Regularly monitor storage conditions to ensure compliance. |
A. Designate Storage Areas
Assign Specific Areas: Assign specific areas for different types of inventory to ensure organization. Designated areas help keep inventory organized and accessible.
Label Storage Areas: Clearly label storage areas for easy identification. Proper labeling helps staff quickly locate items.
Separate Types: Separate different types of inventory to prevent cross-contamination. Separation helps maintain product integrity.
Accessibility: Ensure that frequently used items are stored in easily accessible areas. Easy access improves efficiency.
B. Maintain Cleanliness
Regular Cleaning: Clean storage areas regularly to maintain hygiene. Regular cleaning helps prevent contamination.
Remove Debris: Remove any debris or clutter from storage areas. Keeping areas clear helps maintain order and safety.
Sanitize: Sanitize storage areas periodically to kill germs and bacteria. Sanitization is crucial for maintaining a safe environment.
Inspect for Pests: Regularly inspect storage areas for signs of pests. Pest control helps prevent infestations.
C. Control Temperature
Temperature Settings: Set appropriate temperatures for different storage areas. Proper temperature settings help maintain product quality.
Monitor Regularly: Regularly monitor temperatures to ensure they are within the required range. Monitoring helps detect and address issues promptly.
Adjust as Needed: Adjust temperatures as needed based on inventory requirements. Flexibility in temperature control helps adapt to changing needs.
Record Temperatures: Keep a log of temperature readings for reference. Temperature logs help track compliance.
D. Organize Inventory
Systematic Arrangement: Arrange inventory systematically for easy identification. Systematic arrangement improves efficiency.
Use Shelving: Utilize shelving units to maximize storage space. Shelving helps organize inventory effectively.
Label Items: Label all items with clear, readable labels. Proper labeling helps staff quickly identify items.
Rotate Stock: Use the FIFO method to rotate stock and prevent spoilage. Stock rotation ensures that older items are used first.
E. Monitor Conditions
Regular Checks: Conduct regular checks of storage conditions to ensure compliance. Regular checks help identify and address issues.
Track Expiry Dates: Monitor expiry dates on perishable items to prevent spoilage. Tracking expiry dates helps maintain product quality.
Adjust Storage: Adjust storage conditions as needed to maintain optimal conditions. Flexibility in storage adjustments helps adapt to changes.
Record Findings: Document findings from regular checks for future reference. Proper documentation helps track and resolve issues.
Maintaining proper storage conditions is crucial for preserving the quality and safety of inventory. By following these steps, the bakery can ensure that all items are stored appropriately and remain in optimal condition.
V. Inventory Tracking
Effective tracking practices ensure that inventory levels are accurate and up to date. The following table outlines the steps for tracking inventory:
No. | Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Implement Tracking System | Use an inventory management system to track inventory. |
2 | Conduct Regular Counts | Perform regular inventory counts to verify levels. |
3 | Update Records | Update inventory records based on counts and transactions. |
4 | Monitor Usage | Track usage patterns to identify trends and adjust orders. |
5 | Report Discrepancies | Report any discrepancies found during counts. |
A. Implement Tracking System
Select System: Choose an inventory management system that meets the bakery’s needs. The right system helps streamline tracking.
Train Staff: Train staff on how to use the inventory management system effectively. Proper training ensures accurate usage.
System Integration: Integrate the tracking system with other bakery systems for seamless operation. Integration improves efficiency.
Data Entry: Ensure accurate data entry to maintain reliable records. Accurate entry is crucial for effective tracking.
B. Conduct Regular Counts
Scheduled Counts: Schedule regular inventory counts to verify inventory levels. Regular counts help maintain accuracy.
Count Methods: Use systematic counting methods to ensure thoroughness. Proper methods prevent overlooking items.
Cross-Check Counts: Cross-check counts with inventory records for consistency. Cross-checking helps identify discrepancies.
Adjust Orders: Adjust future orders based on count results. Order adjustments help maintain proper stock levels.
C. Update Records
Timely Updates: Update inventory records promptly based on counts and transactions. Timely updates ensure accuracy.
Record Transactions: Document all inventory transactions, including receipts and issuances. Proper documentation helps track inventory flow.
Adjust Levels: Adjust inventory levels in the system to reflect actual counts. Accurate levels help prevent stockouts.
Review Records: Periodically review inventory records for accuracy. Regular reviews help identify and correct errors.
D. Monitor Usage
Track Patterns: Monitor usage patterns to identify trends and adjust orders. Tracking patterns helps predict future needs.
Analyze Data: Analyze inventory data to make informed decisions. Data analysis helps optimize inventory management.
Forecast Demand: Use usage patterns to forecast future demand. Accurate forecasts help prevent overstocking or understocking.
Adjust Inventory: Adjust inventory levels based on usage trends. Adjustments ensure that inventory meets demand.
E. Report Discrepancies
Identify Discrepancies: Identify any discrepancies found during inventory counts. Prompt identification helps address issues quickly.
Investigate Issues: Investigate the root cause of discrepancies to prevent recurrence. Investigation helps improve processes.
Document Findings: Document findings from investigations for future reference. Proper documentation helps track and resolve issues.
Implement Solutions: Implement solutions to address discrepancies and prevent future occurrences. Effective solutions improve accuracy.
Accurate inventory tracking is essential for maintaining proper stock levels and ensuring efficient operations. By following these steps, the bakery can effectively manage inventory and address any discrepancies promptly.
VI. Inventory Audits
Regular audits help verify the accuracy of inventory records and identify any discrepancies. The following table outlines the steps for conducting inventory audits:
No. | Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Schedule Audits | Plan regular inventory audits to verify accuracy. |
2 | Prepare Audit Team | Assemble a team to conduct the audit. |
3 | Conduct Audit | Perform a thorough inventory count. |
4 | Compare Records | Compare audit results with inventory records. |
5 | Address Discrepancies | Investigate and resolve any discrepancies found. |
A. Schedule Audits
Regular Audits: Plan regular audits to ensure inventory accuracy. Regular audits help maintain organized records.
Audit Frequency: Determine the frequency of audits based on inventory turnover. Appropriate frequency ensures thorough checks.
Audit Calendar: Create an audit calendar to schedule audits in advance. Scheduling helps ensure audits are conducted on time.
Communicate Schedule: Communicate the audit schedule to all relevant staff. Clear communication ensures everyone is informed.
B. Prepare Audit Team
Select Team Members: Choose team members with knowledge of inventory processes. Knowledgeable members ensure effective audits.
Train Team: Train the audit team on audit procedures and expectations. Proper training ensures consistent audits.
Assign Roles: Assign specific roles and responsibilities to team members. Clear roles improve audit efficiency.
Gather Tools: Ensure the team has all necessary tools and materials for the audit. Proper tools help conduct thorough audits.
C. Conduct Audit
Systematic Count: Conduct a systematic inventory count to ensure thoroughness. Systematic counting prevents missed items.
Cross-Check Items: Cross-check items against inventory records for accuracy. Cross-checking helps identify discrepancies.
Document Findings: Document all findings during the audit for future reference. Proper documentation helps track results.
Review Counts: Review counts to ensure accuracy and completeness. Review helps identify any missed items.
D. Compare Records
Match Records: Compare audit results with existing inventory records. Matching helps identify discrepancies.
Identify Differences: Identify any differences between audit counts and records. Identifying differences helps address issues.
Investigate Discrepancies: Investigate the cause of any discrepancies found. Investigation helps prevent recurrence.
Adjust Records: Adjust inventory records to reflect accurate counts. Accurate records help maintain organized inventory.
E. Address Discrepancies
Root Cause Analysis: Conduct a root cause analysis to determine the source of discrepancies. Root cause analysis helps identify underlying issues.
Implement Corrective Actions: Implement corrective actions to resolve discrepancies. Corrective actions help prevent future issues.
Monitor Results: Monitor the results of corrective actions to ensure effectiveness. Monitoring helps ensure issues are resolved.
Report Findings: Report audit findings and corrective actions to management. Reporting helps maintain transparency.
Regular inventory audits are essential for verifying the accuracy of inventory records and identifying any discrepancies. By following these steps, the bakery can maintain accurate records and address any issues promptly.
VII. Inventory Discrepancy Management
Proper management of discrepancies ensures that inventory records are accurate and helps identify and resolve issues. The following table outlines the steps for managing inventory discrepancies:
No. | Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Identify Discrepancies | Recognize any differences between inventory counts and records. |
2 | Investigate Causes | Determine the root causes of discrepancies. |
3 | Implement Solutions | Develop and implement solutions to resolve discrepancies. |
4 | Document Actions | Record all actions taken to address discrepancies. |
5 | Monitor Results | Regularly review the results of implemented solutions. |
A. Identify Discrepancies
Recognize Differences: Identify any differences between inventory counts and records. Recognizing differences helps address issues quickly.
Document Discrepancies: Document all discrepancies found during inventory counts. Proper documentation helps track and resolve issues.
Classify Discrepancies: Classify discrepancies by type and severity. Classification helps prioritize resolution efforts.
Notify Management: Inform management of any significant discrepancies. Notification ensures that management is aware of issues.
B. Investigate Causes
Root Cause Analysis: Conduct a root cause analysis to determine the source of discrepancies. Root cause analysis helps identify underlying issues.
Review Processes: Review inventory processes to identify any potential issues. Process review helps improve accuracy.
Interview Staff: Interview staff involved in inventory management to gather insights. Staff interviews provide valuable information.
Analyze Data: Analyze inventory data to identify patterns and trends. Data analysis helps pinpoint causes.
C. Implement Solutions
Develop Solutions: Develop solutions to address the root causes of discrepancies. Effective solutions help prevent recurrence.
Train Staff: Train staff on new procedures or solutions implemented. Proper training ensures that staff follow new processes.
Implement Changes: Implement changes to inventory processes as needed. Implementation helps resolve discrepancies.
Monitor Implementation: Monitor the implementation of solutions to ensure effectiveness. Monitoring helps track progress.
D. Document Actions
Record Actions: Document all actions taken to address discrepancies. Proper documentation ensures transparency.
Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of discrepancy management efforts. Detailed records help track and review efforts.
Report Actions: Report actions taken to management for review. Reporting helps maintain accountability.
Review Actions: Periodically review actions taken to ensure continued effectiveness. Regular review helps improve processes.
E. Monitor Results
Track Results: Regularly track the results of implemented solutions. Tracking results helps measure effectiveness.
Adjust Solutions: Adjust solutions as needed based on results. Adjustments help improve accuracy.
Report Results: Report the results of discrepancy management efforts to management. Reporting ensures transparency.
Continuous Improvement: Continuously improve inventory processes based on discrepancy management results. Continuous improvement helps maintain accuracy.
Proper management of inventory discrepancies is essential for maintaining accurate records and improving inventory processes. By following these steps, the bakery can effectively address and resolve any discrepancies that arise.
VIII. Inventory Reporting
Accurate and timely reporting helps maintain transparency and supports decision-making. The following table outlines the steps for inventory reporting:
No. | Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Generate Reports | Create regular inventory reports to track levels and usage. |
2 | Review Reports | Analyze inventory reports to identify trends and issues. |
3 | Share Reports | Distribute inventory reports to relevant stakeholders. |
4 | Use Reports | Utilize inventory reports to inform decision-making. |
5 | Archive Reports | Maintain an archive of past inventory reports for reference. |
A. Generate Reports
Regular Reports: Generate regular inventory reports to track levels and usage. Regular reports help maintain organized records.
Report Formats: Use standardized formats for inventory reports to ensure consistency. Standardized formats improve readability.
Accurate Data: Ensure that all data in the reports is accurate and up-to-date. Accurate data is crucial for effective reporting.
Automation: Automate report generation where possible to improve efficiency. Automation helps streamline processes.
B. Review Reports
Analyze Data: Review inventory reports to analyze data and identify trends. Data analysis helps identify patterns and issues.
Identify Issues: Identify any issues or discrepancies in the inventory data. Issue identification helps address problems promptly.
Review Trends: Review trends in inventory levels and usage to forecast future needs. Trend analysis helps improve planning.
Make Recommendations: Make recommendations based on report findings to improve inventory management. Recommendations help guide actions.
C. Share Reports
Distribute Reports: Share inventory reports with relevant stakeholders to ensure transparency. Report distribution helps keep everyone informed.
Tailor Reports: Tailor reports to meet the needs of different stakeholders. Tailoring helps ensure that reports are relevant.
Regular Updates: Provide regular updates on inventory levels and usage to stakeholders. Regular updates help maintain awareness.
Solicit Feedback: Solicit feedback from stakeholders to improve report content and format. Feedback helps improve reporting quality.
D. Use Reports
Informed Decisions: Use inventory reports to make informed decisions about ordering and stocking. Informed decisions help optimize inventory management.
Adjust Orders: Adjust orders based on report findings to maintain proper stock levels. Order adjustments help prevent stockouts and overstocking.
Plan Ahead: Use reports to plan for future inventory needs based on trends and patterns. Planning ahead helps ensure that inventory meets demand.
Monitor Performance: Monitor inventory performance over time using report data. Performance monitoring helps track progress and improvements.
E. Archive Reports
Maintain Archive: Keep an archive of past inventory reports for reference. Maintaining an archive helps track historical data.
Organize Reports: Organize archived reports for easy retrieval. Proper organization improves accessibility.
Review Archive: Periodically review archived reports to identify long-term trends. Archive review helps improve long-term planning.
Secure Storage: Ensure that archived reports are stored securely to protect data integrity. Secure storage helps maintain confidentiality.
Accurate and timely inventory reporting is essential for maintaining transparency and supporting decision-making. By following these steps, the bakery can effectively track and report inventory levels and usage.
IX. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How can discrepancies in inventory be addressed?
A: Discrepancies should be documented, investigated to determine the root cause, and corrective actions should be implemented to resolve the issues and prevent recurrence.
Q: What is the FIFO method and why is it important?
A: The FIFO (First In, First Out) method ensures that older stock is used before newer stock, which is crucial for maintaining the freshness and quality of perishable items.
Q: How can I track inventory levels effectively?
A: Utilize an inventory management system to monitor stock levels, set reorder points, and generate regular reports to keep track of inventory usage and trends.
Q: What should be included in an inventory training program?
A: A comprehensive training program should cover all aspects of inventory management, including procedures for counting, recording, and reporting inventory, as well as handling discrepancies and compliance requirements.
Q: How often should training sessions be conducted for staff?
A: Training sessions should be conducted regularly, with periodic updates to ensure that all staff are aware of the latest inventory management procedures and best practices.
Q: What are some key metrics to monitor for inventory compliance?
A: Key metrics include the accuracy of inventory counts, adherence to FIFO procedures, timely reporting of discrepancies, and overall stock levels compared to targets.
Q: How can automation improve inventory management?
A: Automation can streamline inventory tracking, report generation, and reorder processes, reducing the risk of human error and improving overall efficiency.
Q: What steps should be taken if non-compliance is identified?
A: Identify the causes of non-compliance, implement corrective actions, provide additional training if necessary, and document all actions taken to address the issues.