Bakery Ingredient Handling Guideline Layout
I. Introduction
A. Purpose of the Guideline
(Explain the intent behind the guidelines, emphasizing their role in ensuring ingredient safety and consistency. Outline how adherence to these guidelines benefits both product quality and operational efficiency.)
B. Scope and Applicability
(Define the range of ingredients and processes covered by the guidelines. Specify which areas of the bakery or roles are subject to these standards.)
C. Definitions and Key Terms
(Provide clear definitions for technical terms and jargon used throughout the document. Ensure that all stakeholders have a common understanding of key concepts.)
II. Ingredient Storage
A. General Storage Requirements
(Detail the conditions necessary to maintain ingredient quality, including specific temperature and humidity ranges. Highlight the importance of proper storage to prevent spoilage and maintain ingredient integrity.)
B. Storage Areas
(Describe the designated storage areas, such as dry, refrigerated, and frozen spaces, and their specific requirements. Emphasize the importance of maintaining separate areas to avoid cross-contamination.)
C. Container Specifications
(Outline the types of containers required for different ingredients, including material, design, and labeling. Stress the need for clear identification and proper sealing to prevent contamination.)
III. Ingredient Handling
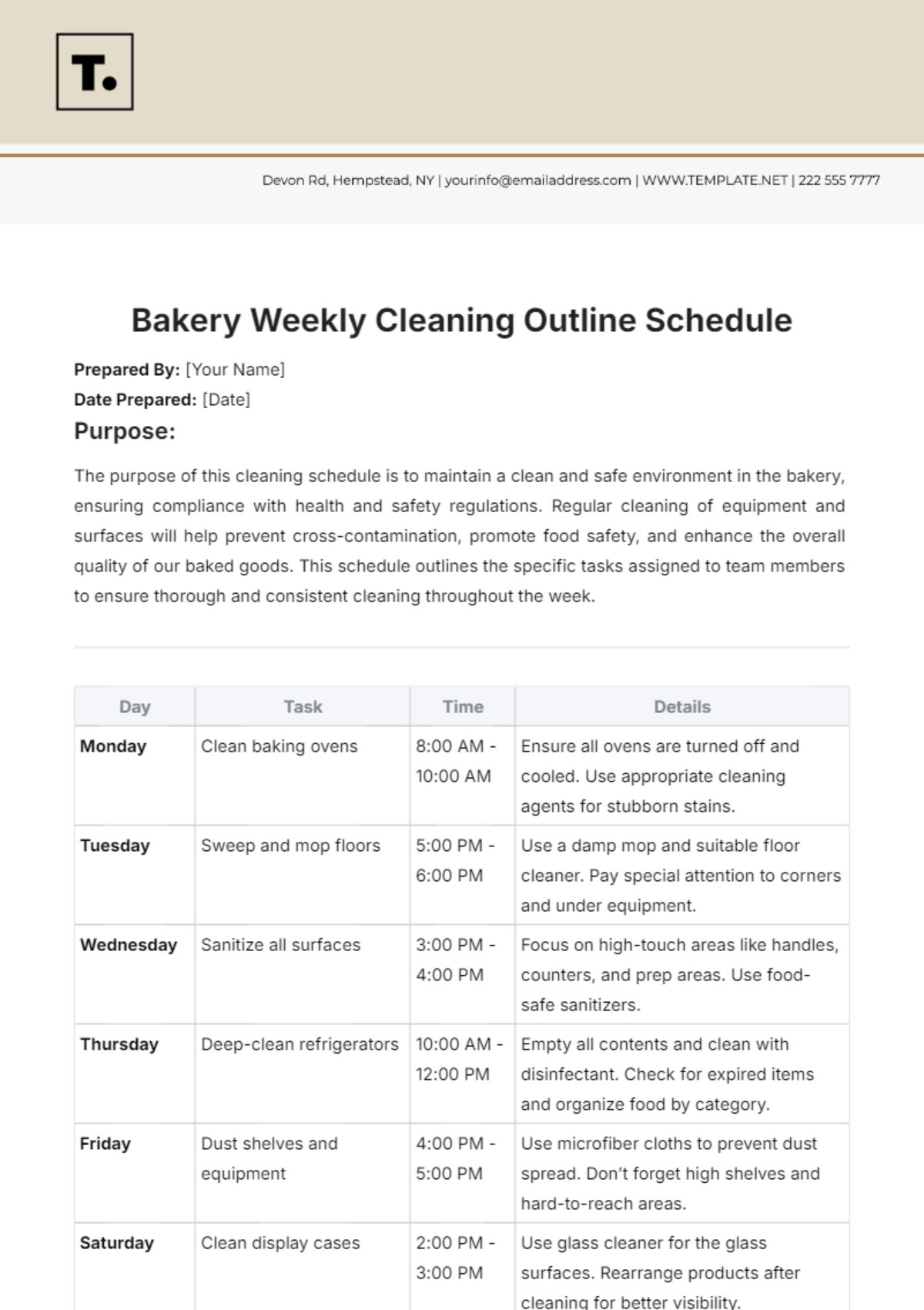
A. Personal Hygiene
(Describe hygiene practices, such as handwashing techniques and use of protective gear. Explain how personal cleanliness contributes to overall food safety.)
B. Handling Procedures
(Detail safe handling techniques to avoid contamination, including proper use of equipment and procedures for transferring ingredients. Emphasize methods to prevent cross-contamination during handling.)
C. Handling Contaminated Ingredients
(Provide steps for identifying and managing contaminated ingredients, including reporting protocols and disposal procedures. Ensure that staff understand how to deal with contamination effectively.)
IV. Ingredient Preparation
A. Measurement Accuracy
(Explain the importance of accurate measurement in ingredient preparation, including the use of calibrated scales and measuring tools. Highlight procedures for ensuring measurement precision.)
B. Mixing and Blending
(Detail the techniques and equipment required for effective mixing and blending of ingredients. Discuss the importance of controlling time and temperature to achieve desired product consistency.)
C. Quality Checks
(Outline procedures for conducting quality checks, including visual inspection, sensory evaluation, and sampling. Ensure that staff know how to identify and address quality issues.)
V. Monitoring and Documentation
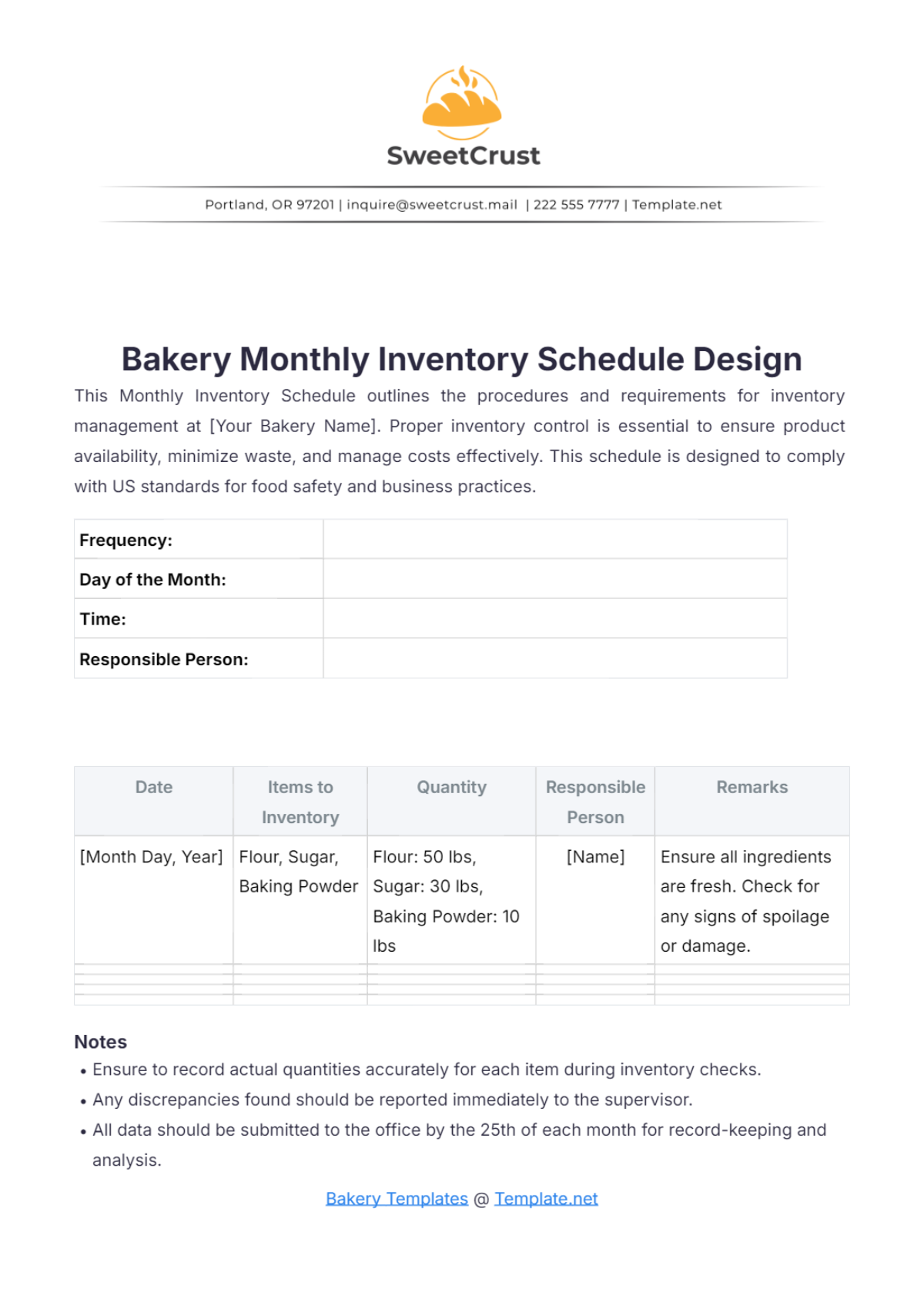
A. Inventory Management
(Describe methods for tracking ingredient usage and managing stock levels, including reorder points and stock rotation practices. Emphasize the need for effective inventory control to minimize waste and ensure availability.)
B. Record Keeping
(Specify the documentation required for ingredient handling, including records of usage, quality checks, and inventory levels. Highlight the importance of maintaining accurate and up-to-date records.)
C. Audits and Inspections
(Provide guidelines for conducting internal audits and external inspections, including procedures for addressing non-compliance. Emphasize the role of regular audits in maintaining high standards.)
VI. Disposal Procedures
A. Disposal of Expired Ingredients
(Detail the procedures for identifying and disposing of expired ingredients, including safe disposal methods and documentation requirements. Stress the importance of proper disposal to prevent contamination and maintain safety.)
B. Handling of Contaminated Ingredients
(Outline procedures for isolating and disposing of contaminated ingredients. Include methods for reporting and documenting incidents to prevent recurrence.)
VII. Training and Education
A. Staff Training Programs
(Describe the training programs for staff, including initial training and ongoing education. Highlight the importance of regular training to ensure staff are knowledgeable about handling procedures.)
B. Training Materials
(Specify the types of training materials used, such as manuals, visual aids, and online resources. Ensure materials are comprehensive and accessible to support effective learning.)
VIII. Compliance and Regulations
A. Regulatory Requirements
(Outline the local, national, and industry-specific regulations relevant to ingredient handling. Emphasize the need for compliance to avoid legal issues and ensure food safety.)
B. Compliance Monitoring
(Describe methods for monitoring compliance with regulations, including regular reviews and checks. Provide guidelines for taking corrective actions when non-compliance is identified.)
IX. Review and Updates
A. Guideline Review Process
(Detail the process for reviewing and updating the guidelines, including the frequency of reviews and responsible personnel. Ensure that guidelines remain current and effective.)
B. Document Control
(Explain the system for managing document versions, including version control, distribution, and archiving. Ensure that all stakeholders have access to the most current version of the guidelines.)