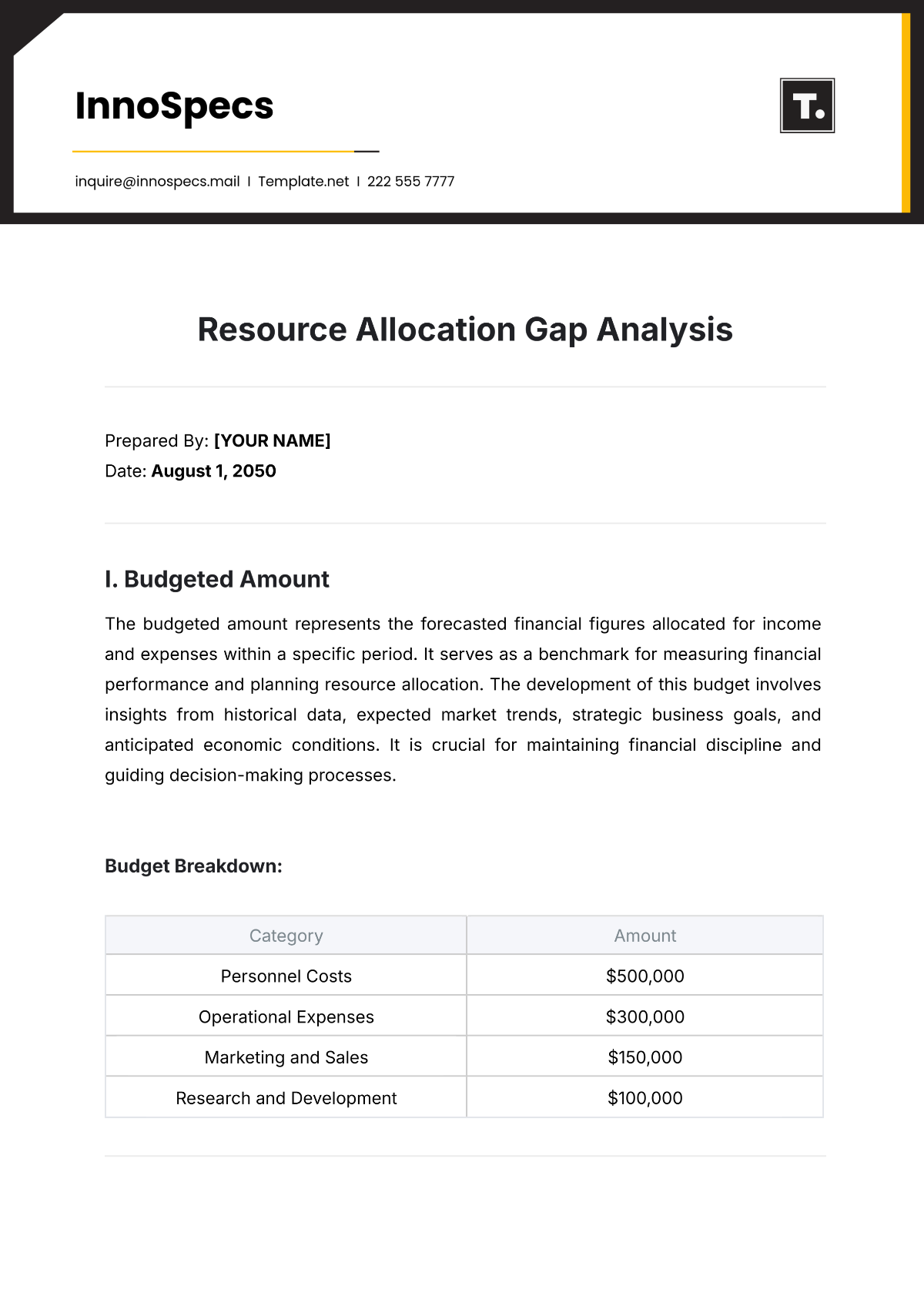
Thematic Analysis in Journalism
Prepared by: [Your Name]
Date: [Date]
1. Introduction
Thematic Analysis in journalism is a qualitative research method used to analyze textual data by identifying, examining, and reporting patterns or themes. This approach provides a structured framework for journalists and researchers to gain a deeper understanding of media content, narrative structures, and the portrayal of various issues. By uncovering recurring themes, thematic analysis helps to reveal underlying messages and trends in journalism, offering insights into how topics are presented and perceived.
2. Methodology
2.1 Data Collection
The data for thematic analysis in journalism is typically collected from various sources, including:
Interviews: Conversations with individuals related to the topic of interest.
News Articles: Reports and features from newspapers, magazines, and online news outlets.
Reports: Investigative or research reports produced by media organizations.
Broadcasts: Transcripts and recordings from television or radio programs.
2.2 Data Analysis
The data analysis process involves several key steps:
Familiarization with Data: Reading and re-reading the data to become thoroughly acquainted with its content.
Generating Initial Codes: Identifying and labeling significant pieces of data that relate to the research question.
Searching for Themes: Grouping codes into potential themes based on their relevance and connection.
Reviewing Themes: Refining and verifying the themes to ensure they accurately represent the data.
Defining and Naming Themes: Clearly defining the themes and assigning appropriate names that capture their essence.
Writing the Report: Presenting the analysis in a structured format, supported by evidence from the data.
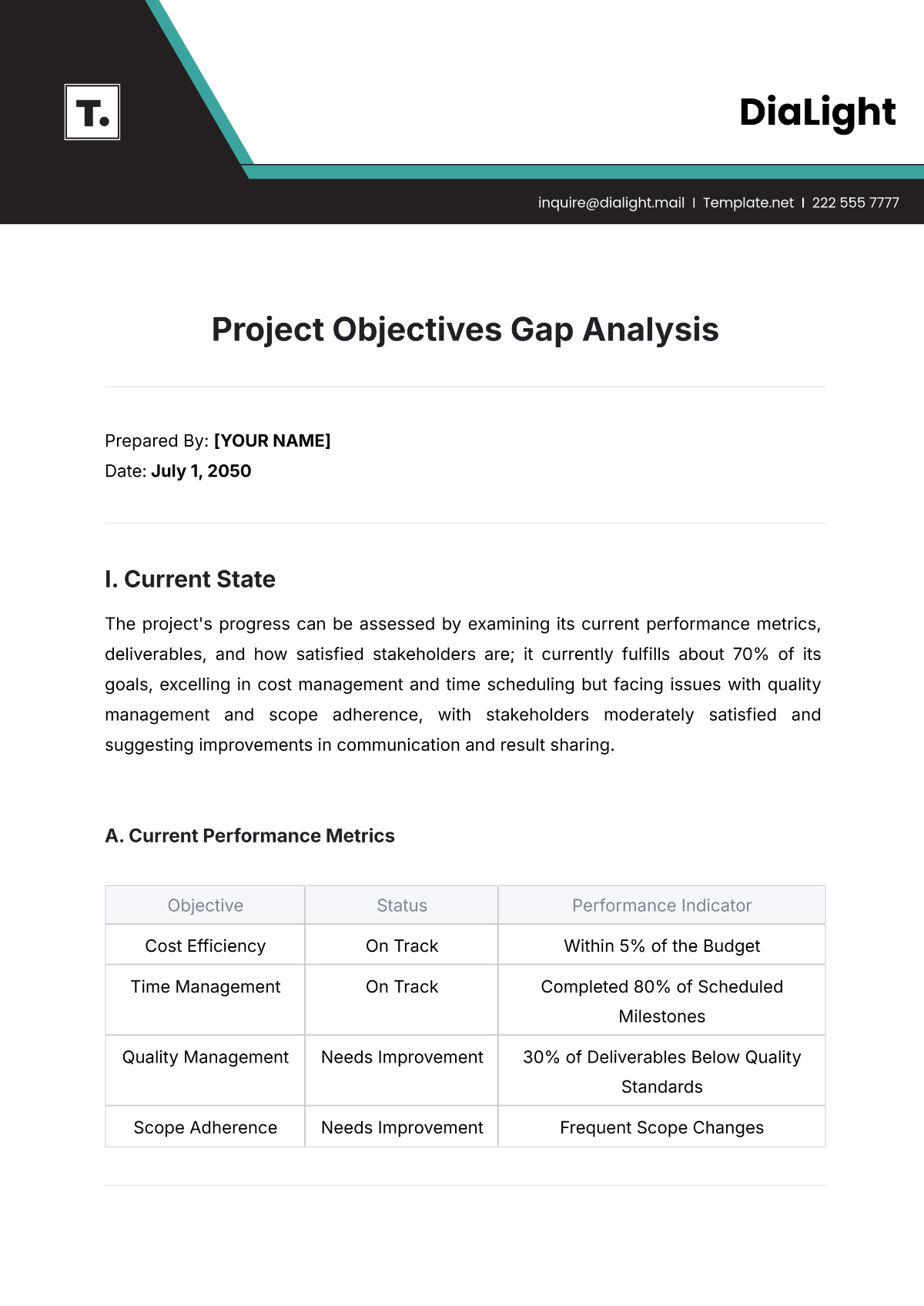
3. Findings
3.1 Identified Themes
The thematic analysis of journalistic content typically reveals several key themes. For example:
Theme | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Media Bias | The presence of partiality or favoritism in reporting. | Favoritism towards political parties. |
Public Perception | How news coverage influences or reflects public attitudes and beliefs. | Shifts in public opinion on social issues. |
Narrative Framing | The way stories are structured to highlight specific aspects and guide interpretation. | Emphasis on certain facts or viewpoints. |
Conflict and Controversy | Reporting on contentious or divisive issues. | Coverage of protests or legal battles. |
3.2 Examples of Data
Example 1: An article on climate change may exhibit a recurring theme of urgency, with multiple sources emphasizing the immediate need for action.
Example 2: Coverage of election campaigns may reveal a theme of polarization, highlighting stark contrasts between opposing candidates.
4. Discussion
4.1 Interpretation of Findings
The findings from the thematic analysis provide valuable insights into the way journalism shapes and reflects public discourse. Key observations include:
Bias and Objectivity: Themes related to media bias highlight how different news outlets may present issues in ways that align with their agendas or perspectives.
Influence on Public Opinion: The analysis shows how media narratives can shape or reinforce public perceptions on various issues.
Narrative Techniques: Understanding narrative framing helps to uncover the strategies used by journalists to guide audience interpretation and engagement.
4.2 Implications for Journalism
The insights gained from thematic analysis can inform best practices in journalism by:
Enhancing Objectivity: Encouraging journalists to be aware of and mitigate biases in their reporting.
Improving Reporting Practices: Providing a framework for more balanced and comprehensive coverage of complex issues.
Guiding Media Literacy: Helping audiences to critically evaluate the media they consume and recognize underlying themes and biases.
5. Conclusion
Thematic Analysis in journalism is a powerful tool for understanding and interpreting media content. By systematically identifying and analyzing themes, journalists, and researchers can gain deeper insights into how issues are represented and perceived. This approach not only enhances the quality of journalism but also contributes to a more informed and critical public.
6. References
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2050). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3(2), 77-101.
Hall, S., Critcher, C., Jefferson, T., Clarke, J., & Roberts, B. (2050). Policing the Crisis: Mugging, the State, and Law and Order. Palgrave Macmillan.
McKee, A. (2050). Textual Analysis: A Beginner's Guide. Sage Publications.