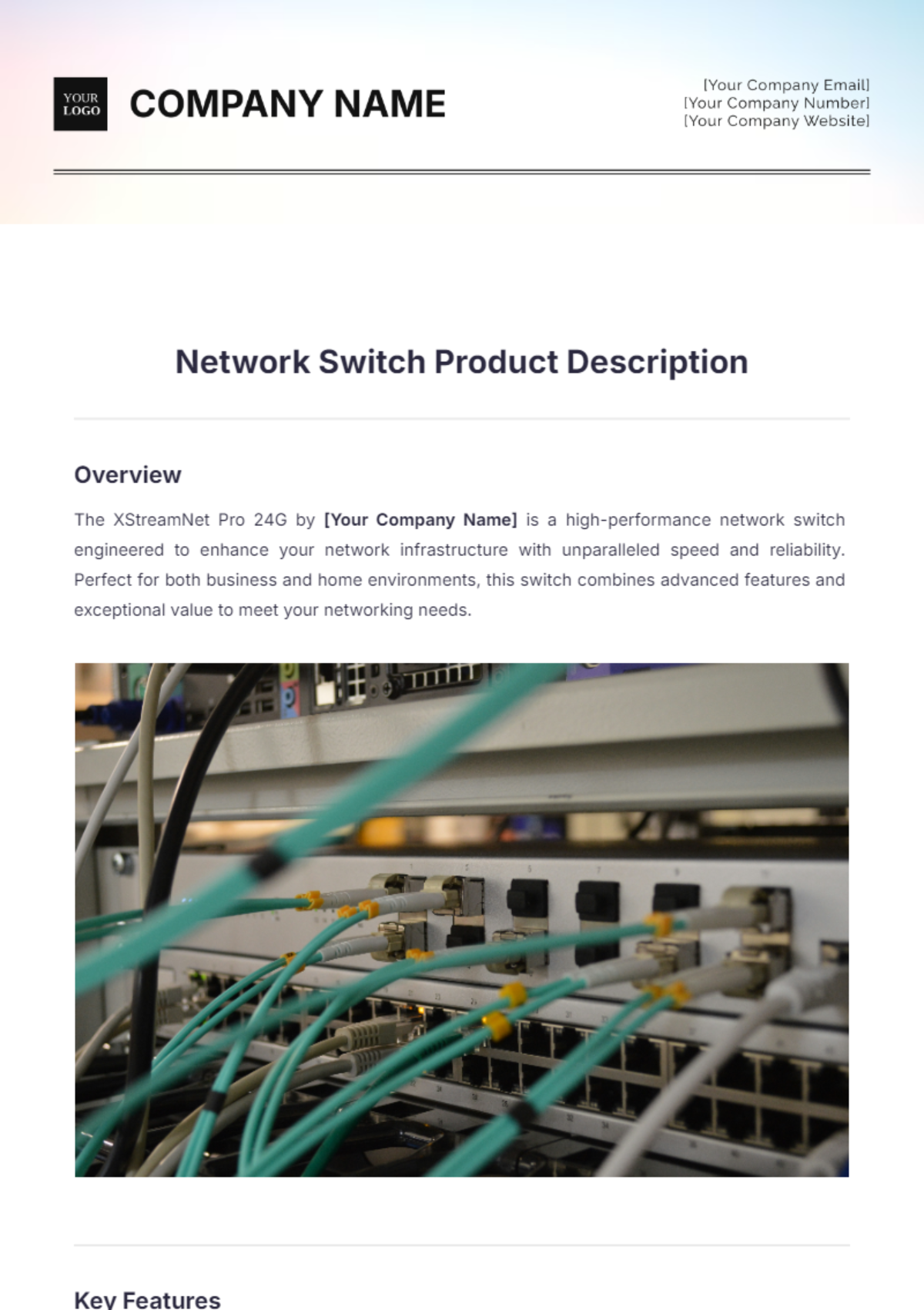
Network Security Protocol
1. Introduction
The objective of this protocol is to ensure comprehensive security across the network infrastructure at [Your Company Name]. This protocol outlines the necessary steps, measures, and best practices for safeguarding the network and minimizing vulnerabilities.
2. Access Control
Implementing strong access control mechanisms is crucial for restricting unauthorized access and ensuring that only legitimate users have access to network resources. The following measures should be applied:
Use of strong, complex passwords.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for critical systems.
Regular review and revision of access permissions.
Implementation of role-based access control (RBAC).
3. Encryption
Encryption ensures the confidentiality and integrity of data in transit and at rest. The following encryption standards and practices should be enforced:
Use of SSL/TLS for securing web traffic.
Deployment of VPNs for secure remote access.
Encryption of sensitive data stored in databases and file systems.
Regular updates to encryption protocols and algorithms.
4. Firewall Configuration
Firewalls act as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks. Proper configuration of firewalls is necessary to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate potential threats. Specific steps include:
Disabling unused services and ports.
Implementing stateful inspection for traffic monitoring.
Configuring rules for both inbound and outbound traffic.
Regular updates and patch management.
5. Intrusion Detection and Prevention
Deploy Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) to monitor network traffic and respond to suspicious activities. Key activities include:
Real-time traffic analysis and alerts.
Automatic blocking of identified threats.
Regular updates to IDS/IPS signatures and rules.
6. Security Policies and Procedures
Security policies and procedures provide a framework for consistently managing network security. Essential components include:
Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) for network resources.
Incident Response Plan (IRP) for handling security breaches.
Regular security training and awareness programs for staff.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery plans.
7. Monitoring and Auditing
Continuous monitoring and regular audits are necessary to ensure ongoing security and compliance. Measures include:
Configuration and use of network monitoring tools.
Regular review of system and network logs.
Conducting periodic security audits and vulnerability assessments.
Implementation of compliance checks against established standards.
8. Conclusion
Maintaining network security is a continuous, evolving process that requires diligent application of these protocols. Regular updates and adherence to best practices will help safeguard network integrity and protect against emerging threats. Ensure ongoing staff training and awareness to support these security measures effectively.