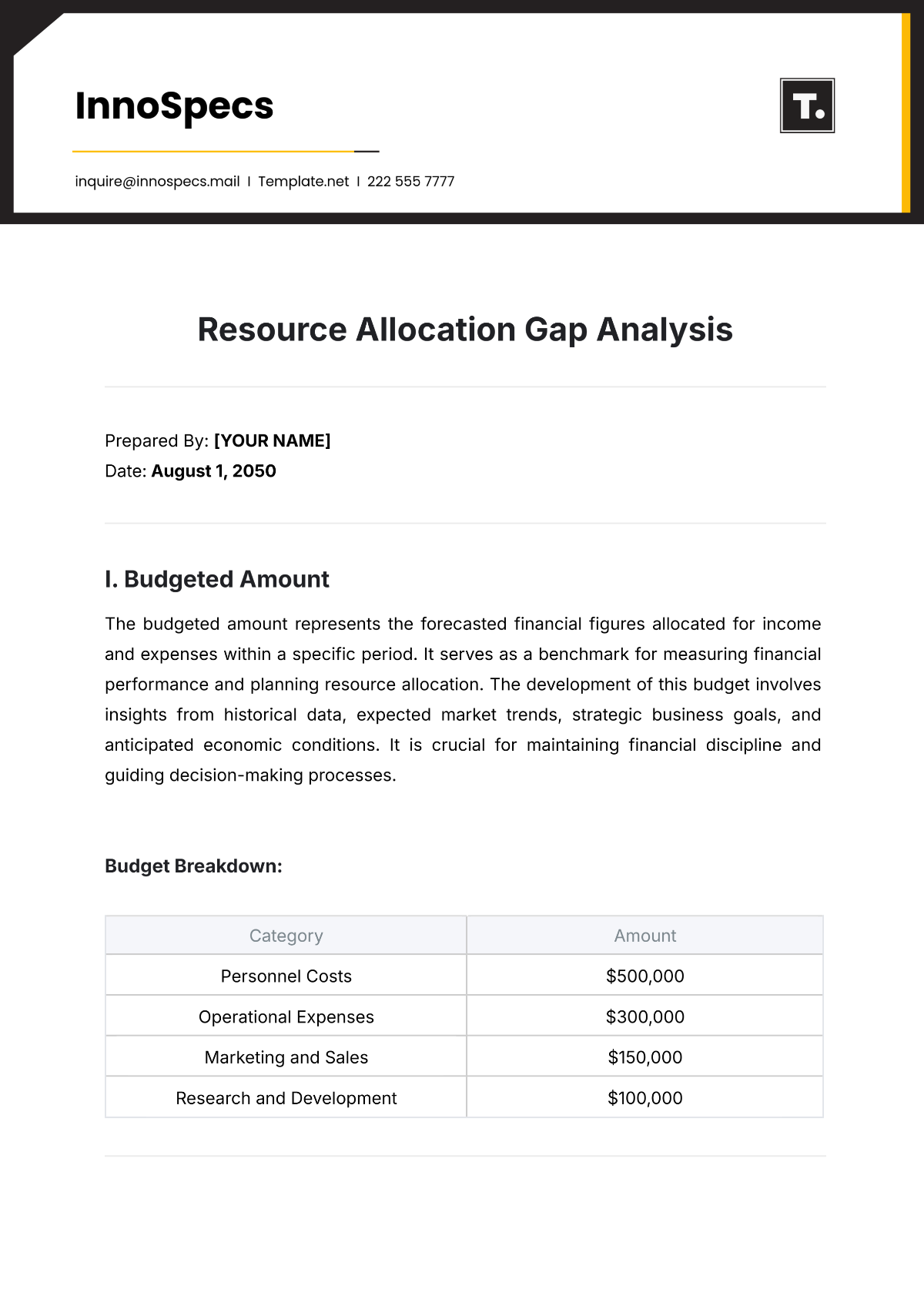
Visual Media Rhetorical Analysis
Prepared by: [YOUR NAME]
Date: [DATE]
I. Introduction
Visual Media Rhetorical Analysis examines how visual elements—such as images, videos, and graphics—communicate messages and persuade audiences. It involves evaluating the use of visual rhetoric, including composition, color, symbolism, and design, to understand how these elements contribute to the overall message and impact.
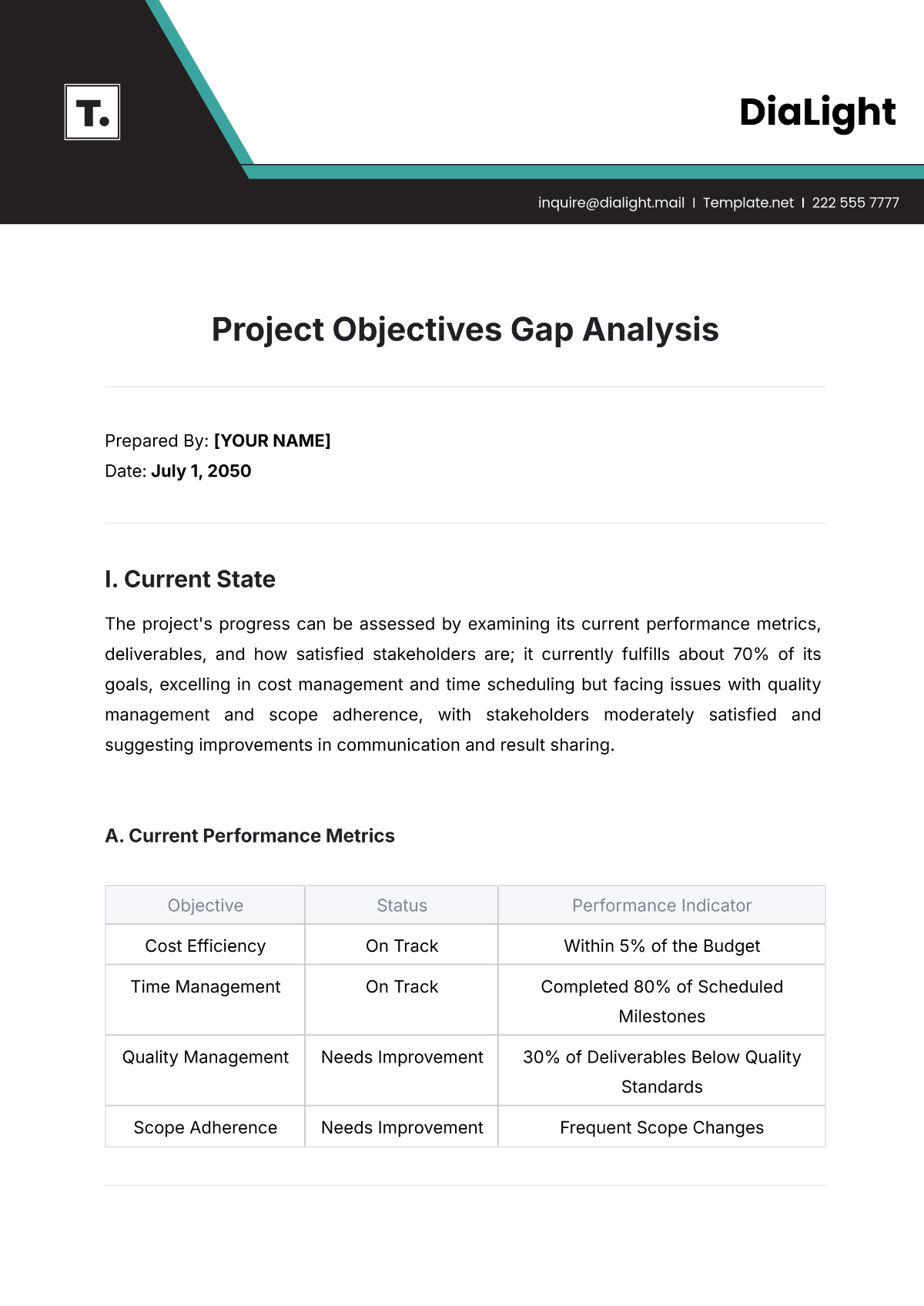
II. Elements of Visual Rhetoric
A. Composition
Composition refers to the arrangement of visual elements within a piece of media. It plays a significant role in guiding the viewer's eye and creating a focal point. Techniques such as the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry are often used to create a balanced and engaging composition.
Technique | Description |
|---|---|
Rule of Thirds | Divide the image into nine equal parts, placing the subject along these lines or at their intersections for a balanced composition. |
Leading Lines | Uses natural lines in the composition to direct the viewer's eye towards the focal point. |
Symmetry | Creates balance in an image by mirroring elements on either side of a central axis. |
B. Color
Color significantly affects the mood and tone of an image. It can evoke emotions, define the atmosphere, and highlight important elements within the frame. Understanding the psychological impact of colors helps in decoding the intended message.
Red: Often associated with passion, urgency, or danger.
Blue: Typically symbolizes calm, trustworthiness, and stability.
Yellow: Conveys happiness, energy, and attention.
Green: Represents nature, growth, and health.
C. Symbolism
Symbolism involves using visual elements to represent abstract ideas or concepts.
Iconography: Specific symbols or icons carry meaning beyond their literal representation. For instance, a heart symbol commonly represents love or compassion.
Metaphors: Visual metaphors use imagery to convey complex ideas or themes. For example, an image of a broken chain might symbolize freedom or liberation.
Cultural Significance: Symbols can have different meanings across cultures. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective communication.
D. Design
Design encompasses the overall aesthetic and functionality of visual media, including layout, typography, and user interface elements.
Layout: Organizes content in a visually appealing and functional manner. Effective layout guides the viewer through the information logically and intuitively.
Typography: The style and arrangement of text influence readability and visual appeal. Font choice, size, and spacing contribute to the overall design.
User Interface: In digital media, UI design affects how users interact with content. A well-designed interface ensures ease of use and enhances user experience.
III. Case Studies
A. Advertising Campaigns
Advertising campaigns often rely heavily on visual rhetoric to persuade consumers. By analyzing various campaigns, we can see how composition, color, and symbolism are used to align with brand messaging and market products effectively.
B. Film and Television
In film and television, visual elements are crucial in storytelling and attracting the audience's emotions. Cinematography techniques, color grading, and set design all contribute to the narrative and the viewer's experience.
C. Social Media Graphics
Social media graphics are designed to catch the eye quickly and concisely convey messages. Visual elements like bold colors, clear typography, and engaging imagery are key to achieving high engagement on platforms such as Instagram and Twitter.
IV. Conclusion
Visual Media Rhetorical Analysis is an invaluable tool for understanding how images, videos, and graphics communicate and persuade. By evaluating composition, color, symbolism, and design, one can gain insights into the effectiveness and impact of visual media. This analysis not only enhances our appreciation of visual art but also equips us with the skills to create compelling visual content.