Verbs for Literary Analysis
Prepared By: [Your Name]
Date: [Date]
1. Introduction
In literary analysis, examining the use of verbs within a text provides crucial insights into the narrative, characters, and thematic elements. Verbs, being central to action and description, play a significant role in shaping a literary work’s meaning and emotional impact. This document outlines a comprehensive approach to analyzing verbs, detailing their influence on narrative progression, character development, and thematic exploration.
2. Thematic Analysis of Verbs
2.1 Understanding Thematic Elements
Verbs often reflect the core themes of a literary work by revealing underlying ideas and concerns. By analyzing how verbs contribute to thematic development, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the text's message and implications.
Action and Theme
Active Verbs: Actions that drive the plot forward often reflect the central themes. For example, in Shakespeare's "Macbeth," verbs like "murder," "ambition," and "regret" are central to exploring themes of power and guilt.
Recurrent Verbs: The repeated use of certain verbs can emphasize key thematic concerns. For instance, in Orwell's "2050," verbs related to surveillance and control underline the theme of authoritarianism.
2.2 Emotional Impact of Verbs
Verbs contribute significantly to the emotional tone of a text. By analyzing verbs associated with emotions, readers can uncover how the author conveys mood and character feelings.
Verbs and Character Emotions
Descriptive Verbs: Verbs that describe emotional states (e.g., "weep," "despair," and "exult") help convey the psychological depth of characters. In "Pride and Prejudice," Jane Austen uses verbs like "plead" and "admire" to depict romantic tension.
Action Verbs: Actions that reflect internal emotions (e.g., "tremble," "shout") reveal characters’ psychological struggles. In "The Catcher in the Rye," verbs such as "complain" and "struggle" illustrate Holden Caulfield's internal conflict.
3. Analysis of Verbal Patterns
3.1 Narrative Function
Examining the function of verbs within the narrative structure reveals how they influence the progression and pacing of the story.
Verb Usage and Plot Development
Plot Advancement: Verbs that denote significant actions drive the plot forward. In "The Great Gatsby," verbs like "chase," "wait," and "envision" are pivotal in advancing the narrative and highlighting key plot points.
Pacing: The choice of verbs can affect the pacing of the narrative. Short, sharp verbs can create tension, while longer, descriptive verbs may slow the narrative down for reflection.
3.2 Character Development
Verbs also play a crucial role in character development, revealing attributes and motivations through their actions and interactions.
Verbs and Character Traits
Dynamic Verbs: Verbs that show change or development in characters, such as "evolve," "transform," or "mature," illustrate character growth. In "Jane Eyre," verbs like "rebel" and "resist" reflect Jane's evolution from a submissive child to an assertive woman.
Static Verbs: Verbs indicating stability or unchangeability (e.g., "remain," "persist") highlight characters’ fixed traits or ongoing struggles. In "Wuthering Heights," verbs like "brood" and "haunt" emphasize Heathcliff’s unchanging bitterness.
4. Comparative Analysis
4.1 Verbs Across Different Texts
Comparing verb usage across different literary works can reveal similarities and differences in thematic exploration, character portrayal, and narrative techniques.
Case Studies
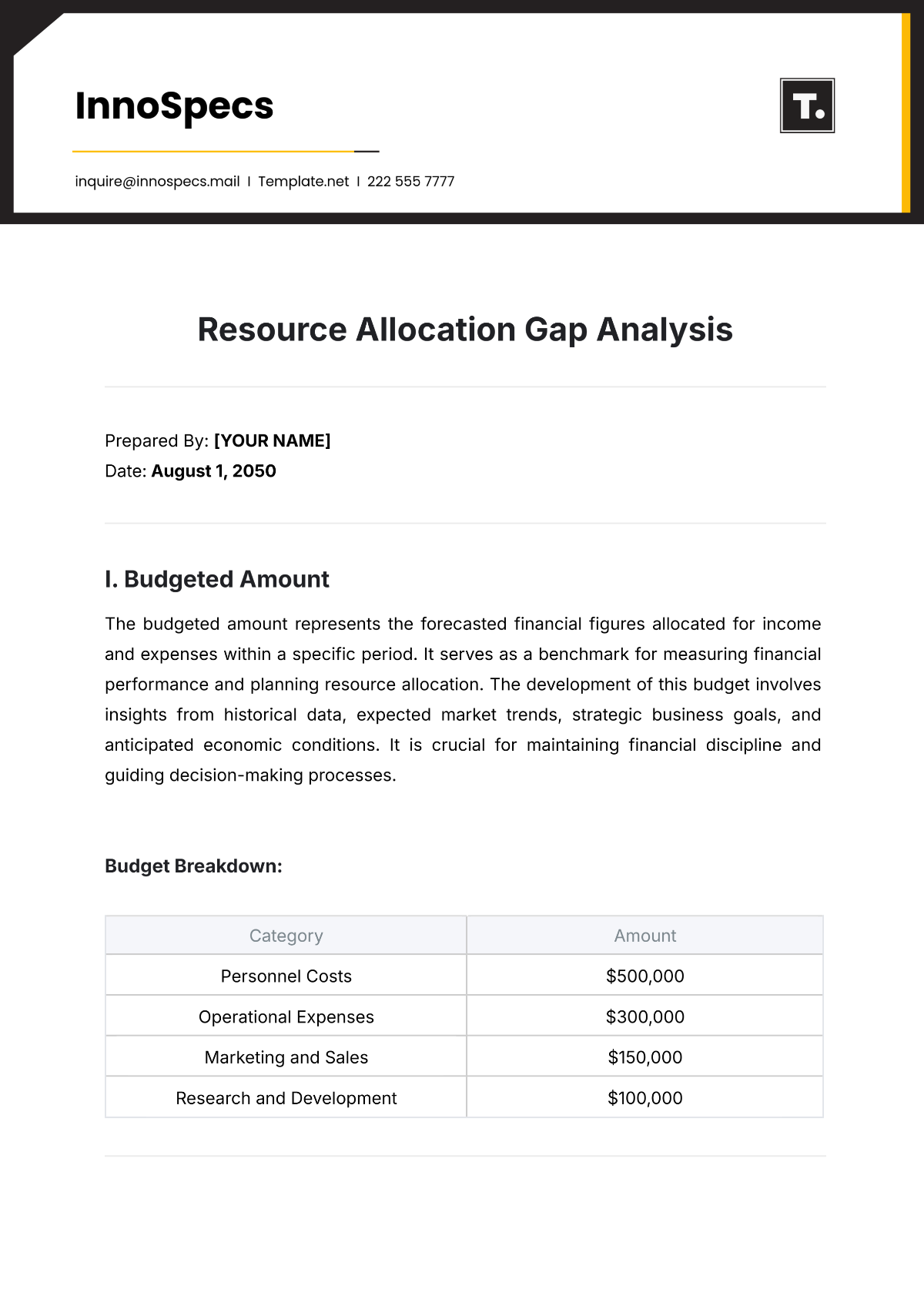
Literary Work | Central Verbs | Thematic Focus | Character Development |
|---|---|---|---|
Shakespeare's "Macbeth" | "Murder," "ambition," "regret" | Power, guilt | Macbeth's descent into tyranny |
Orwell's "2050" | "Surveil," "control," "manipulate" | Authoritarianism, control | Winston Smith's struggle against oppression |
4.2 Insights from Comparative Analysis
Thematic Insights: Comparing verbs helps identify how different authors handle similar themes. For instance, both Orwell and Huxley explore totalitarianism but use distinct verb choices to convey their respective dystopian visions.
Character Analysis: Analyzing verbs used to describe characters in various texts can provide insights into how different authors approach character development and psychological depth.
5. Conclusion
The analysis of verbs within a literary text provides a profound understanding of the narrative’s structure, thematic depth, and character dynamics. By examining how verbs influence these elements, literary scholars and readers can gain a richer appreciation of the text’s overall impact and significance. This comprehensive approach to verb analysis enhances our ability to interpret and appreciate the complexities of literary works.