Free SMART Goals for Employees

SMART Goals Overview
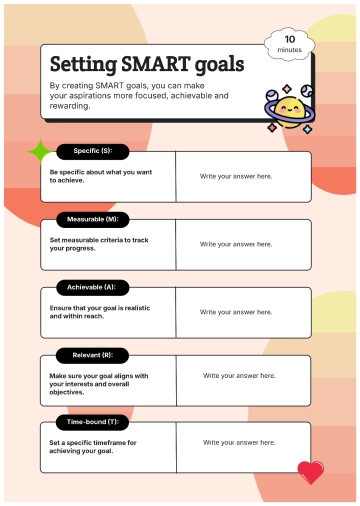
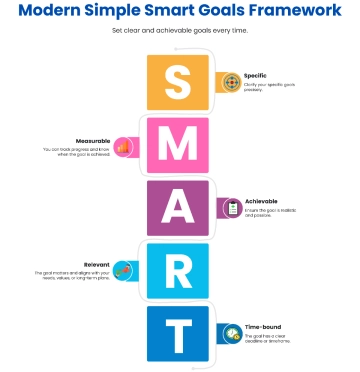
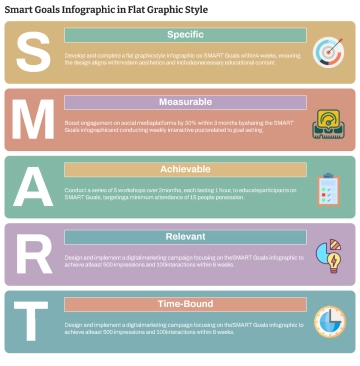
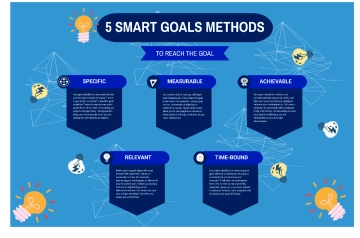
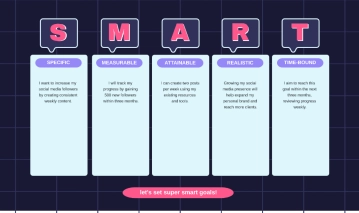
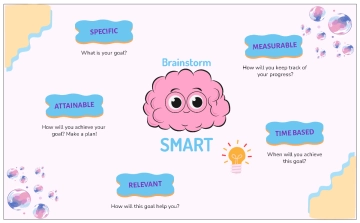
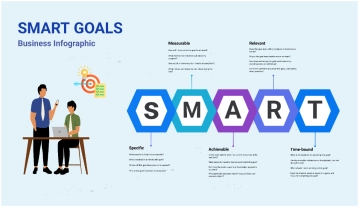
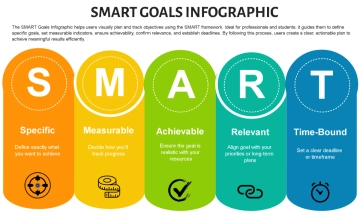
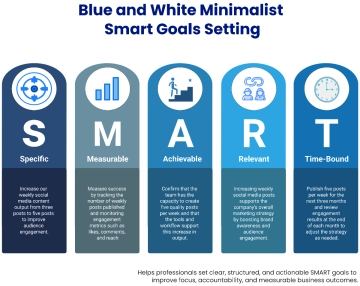
Specific |
|---|
Define clear, specific goals that detail what needs to be accomplished. For example: "Increase customer satisfaction ratings by 10% over the next six months." |
Measurable |
Ensure each goal includes criteria for measuring progress and achieving targets. For example: "Complete 5 professional development courses by the end of the year." |
Achievable |
Set realistic and attainable goals based on available resources and constraints. For example: "Increase sales by 15% by implementing a new marketing strategy." |
Relevant |
Align goals with broader business objectives and employee roles. For example: "Develop a social media campaign that aligns with our brand's voice and increases online engagement by 20%." |
Time-bound |
Set deadlines or time frames within which goals should be accomplished. For example: "Launch the new product line by the end of Q3." |
Action Plan
Identify Key Tasks: Break down each SMART goal into actionable tasks.
Example: For increasing customer satisfaction, the tasks may include conducting surveys, training staff, and improving response times.Allocate Resources: Determine the necessary resources, such as time, budget, and personnel, required to complete each task.
Set Milestones: Establish interim deadlines and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress towards the final goal.
Implement Strategy: Execute the action plan, ensuring all team members are aware of their responsibilities and deadlines.
Monitor Progress: Regularly review progress against milestones and make adjustments to the plan as needed.
Accountability
Individual Accountability: Assign each goal to specific employees or teams, making them responsible for its completion.
Example: The marketing team is responsible for the development and execution of the new social media campaign.
Leadership Support: Ensure that managers provide the necessary support, guidance, and resources to employees.
Example: The sales manager oversees the implementation of the new marketing strategy to increase sales.
Regular Check-ins: Schedule regular meetings to discuss progress, address challenges, and provide feedback.
Example: Weekly team meetings to review customer satisfaction survey results and adjust strategies.
Documentation: Keep records of progress, challenges, and outcomes to assess performance and provide a basis for future goal-setting.
Notes
Risk Management: Identify potential risks that could hinder the achievement of goals and develop contingency plans.
Example: If the marketing strategy fails to generate the expected sales increase, a backup plan involving a different promotional approach may be needed.
Continuous Improvement: Encourage employees to seek opportunities for improvement throughout the goal achievement process.
Example: Employees can propose new ideas to enhance customer satisfaction beyond the initial target.
Feedback Loop: Implement a system for ongoing feedback from employees and management to refine goals and strategies.
Example: After launching the new product line, gather customer and employee feedback to assess its success and make adjustments.
Conclusion
Summary of Expectations
Achievement: Employees are expected to meet their SMART goals within the specified time frames.
Support: Management will provide the necessary resources and support to help employees achieve their goals.
Evaluation: Performance will be evaluated based on the successful completion of goals, with consideration for any challenges encountered.
Next Steps
Begin the implementation of the action plan immediately.
Schedule the first progress check-in meeting within two weeks.
Continuously monitor and adjust goals as necessary to ensure alignment with business objectives.
Prepared by: [YOUR NAME]
Date: August 22, 2050
Department: Human Resources Department
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Boost employee performance with the SMART Goals for Employees Template from Template.net. Fully customizable and editable in our Ai Editor Tool, it’s perfect for performance reviews, career development, and ensuring alignment with company objectives. This template is an essential tool for driving employee engagement, productivity, and success in the workplace.