Blank Root Cause Analysis
Prepared by: [YOUR NAME]
Date: July 8, 2060
I. Introduction
The introduction should provide a brief explanation of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and its purpose. It sets the context for the document by outlining the importance of identifying the underlying causes of problems rather than just addressing symptoms.
II. Purpose and Objectives
A. Purpose
Clearly define the primary purpose of conducting the RCA, which is to investigate and address the root cause of the identified issue.
B. Objectives
List the specific goals of the RCA. These should guide the process of problem identification, data collection, analysis, and solution development.
Identify the Problem: Define the issue that needs to be analyzed.
Gather and Analyze Data: Collect data from various sources to help identify root causes.
Determine Root Causes: Use analytical tools to trace the problem's origins.
Develop Corrective Actions: Propose solutions to eliminate the root causes.
Implement and Monitor: Ensure solutions are applied and monitored for effectiveness.
III. Problem Identification
A. Problem Statement
Describe the problem clearly and concisely. This should include key details such as when the issue occurred, where it was observed, and the conditions that led to its identification.
B. Impact of the Problem
Explain the consequences of the problem on various aspects such as finance, operations, safety, and customer satisfaction. Use a table to quantify and categorize the impacts.
IV. Data Collection
A. Data Sources
Identify and list all sources of information you will use in your analysis. These could include incident reports, historical data, interviews, or real-time observations.
B. Data Collection Methods
Describe the methods used to gather data. Examples include surveys, direct observation, and interviews. Explain why these methods were selected.
C. Data Analysis
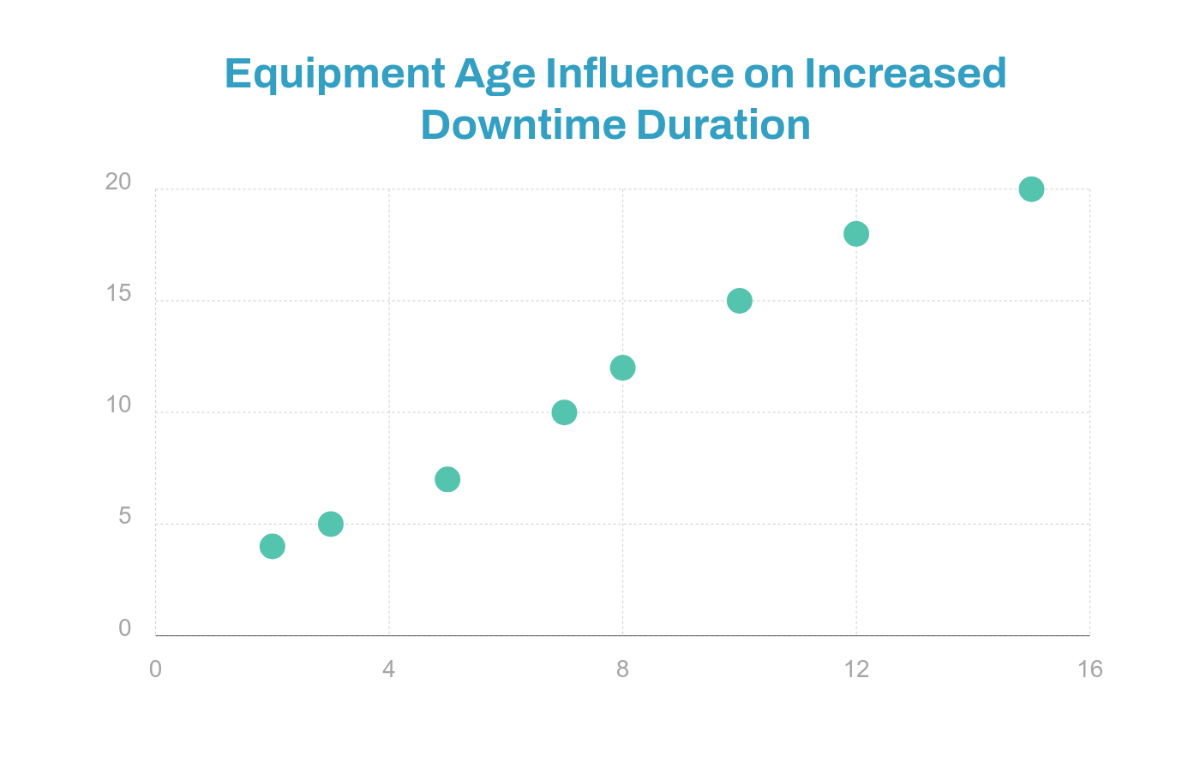
Present the collected data and analyze it. Use charts, graphs, or tables to summarize and interpret the data. Highlight any trends or patterns that emerge.
V. Root Cause Identification
A. Tools and Techniques
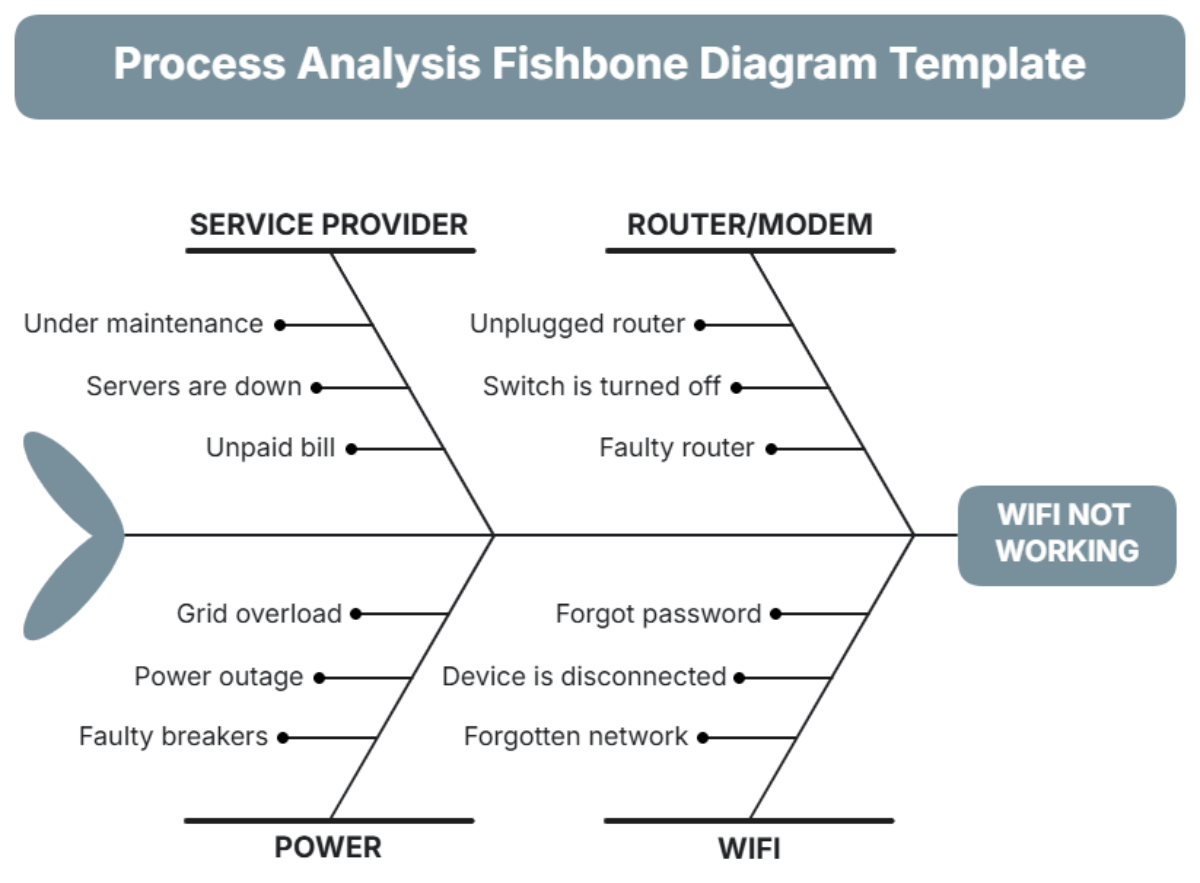
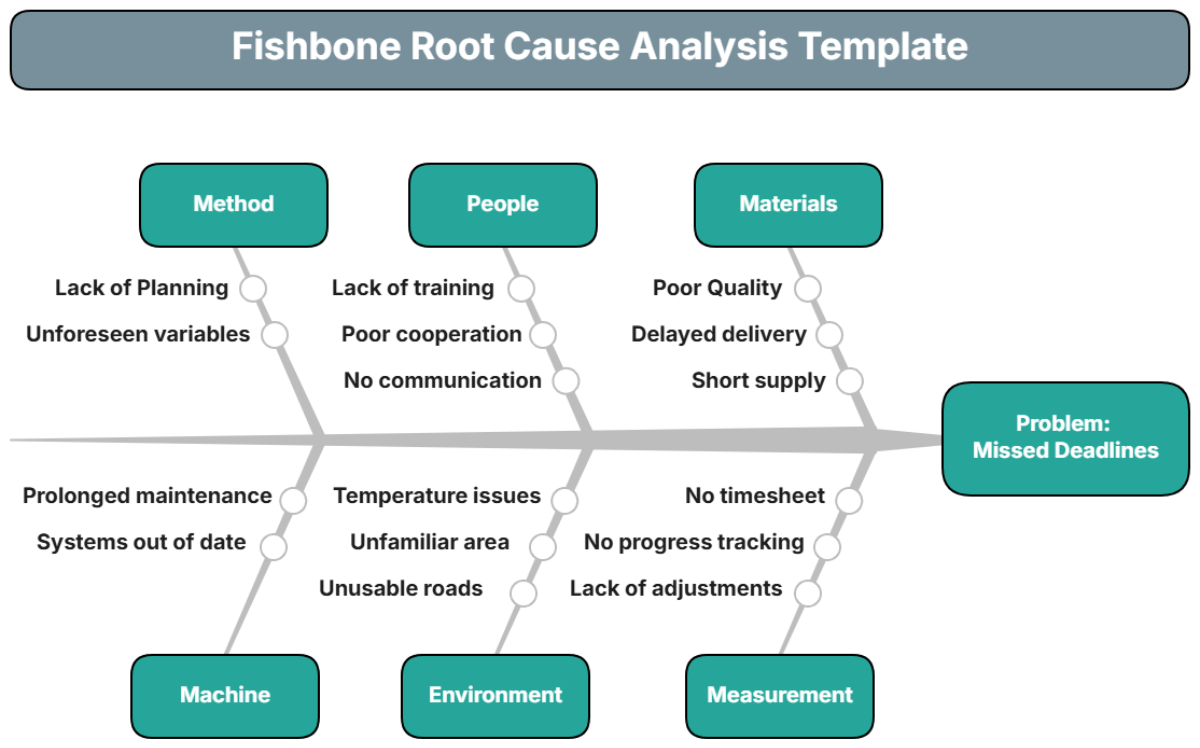
List and explain the tools you will use to identify the root causes of the problem. Common tools include the "Five Whys," Fishbone Diagram, and Pareto Analysis.
B. Analysis Process
Explain how each of the selected tools was applied to trace the issue back to its root causes.
C. Root Cause Summary
Provide a summary of the root causes identified in the analysis. For each cause, include supporting evidence.
VI. Corrective Actions
A. Proposed Solutions
List the corrective actions designed to address each root cause. Ensure that these actions are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound).
B. Action Plan
Outline the steps needed to implement each corrective action. Include timelines, resources, and monitoring mechanisms to ensure each action is effective.
VII. Implementation and Monitoring
A. Implementation Process
Describe the process for putting the corrective actions into practice. Assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and explain how the actions will be integrated into day-to-day operations.
B. Monitoring and Evaluation
Explain how you will monitor the implementation and evaluate the effectiveness of the corrective actions. List specific metrics to track, such as production downtime or safety incidents.
VIII. Conclusion
A. Summary of Findings
Recap the main findings from the RCA, including the root causes and proposed solutions. Emphasize why these actions are critical to preventing future issues.
B. Lessons Learned
Share key insights gained during the analysis process, including any lessons about the organization's operations or practices that contributed to the problem.
C. Next Steps
Outline the next steps to finalize the implementation of corrective actions. This may include further monitoring, follow-up analyses, or additional resources required.