Bibliography Guide Journal Article
Prepared by: [Your Name]
Date: [Date]
1. Introduction
In academic writing, creating a precise and organized bibliography is essential for ensuring the credibility and traceability of research. A well-constructed bibliography acknowledges the sources of information and enhances the reliability of academic work. This article provides an in-depth guide to bibliography creation, covering various citation styles, formatting guidelines, and common practices. By following these comprehensive guidelines, researchers and students can ensure their work adheres to the highest standards of academic integrity.
2. Understanding Citation Styles
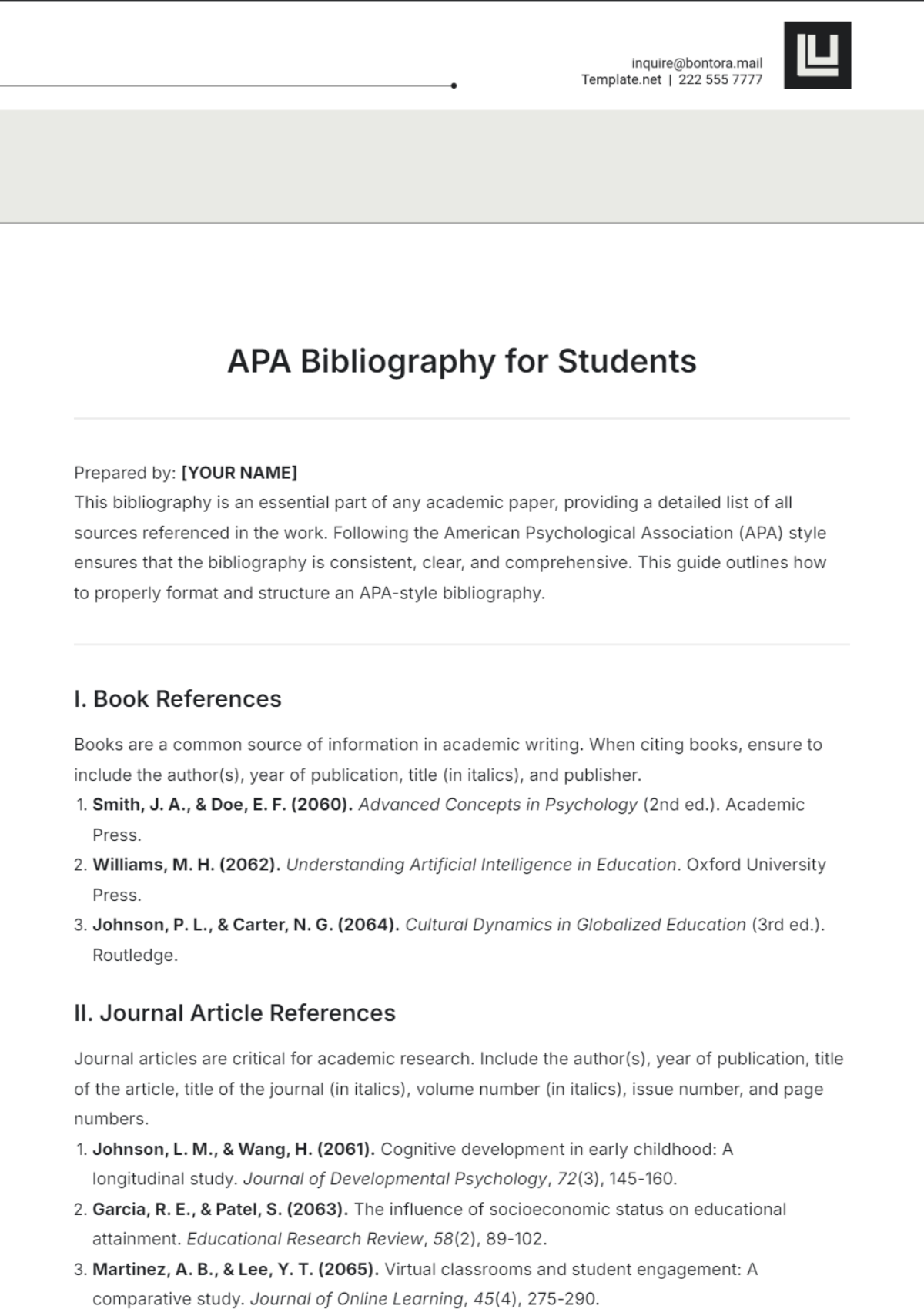
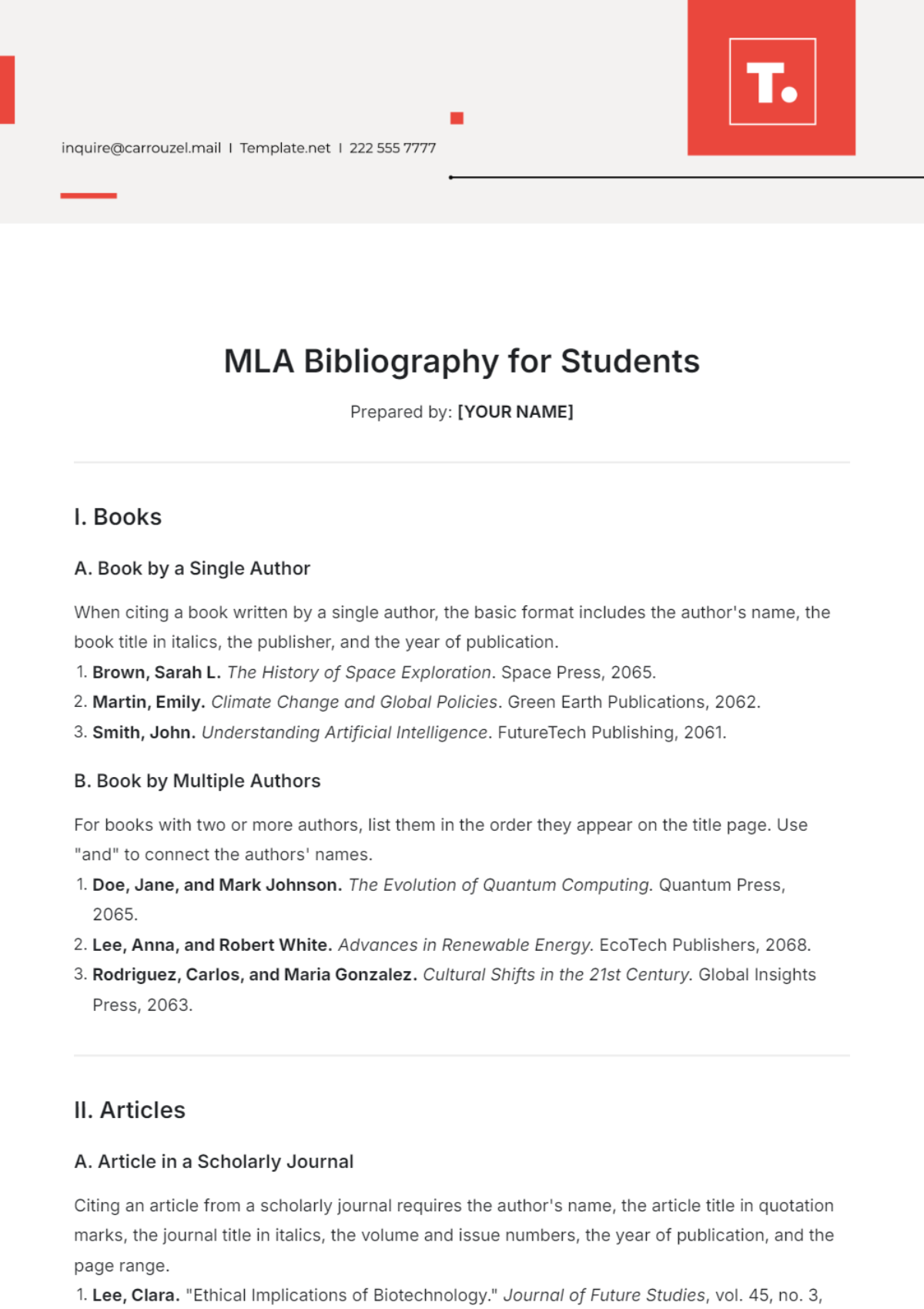
2.1. APA (American Psychological Association)
The APA citation style is widely used in the social sciences, such as psychology, sociology, and education. It emphasizes the author's name and the date of publication, which helps readers locate the most recent research.
Key Features:
In-text citations include the author's last name and the publication year (e.g., Smith, 2053).
The author's last name is organized alphabetically in the reference list.
Specific formats are used for different source types, including books, journal articles, and electronic resources.
Example Entry: Smith, J. (2053). Understanding psychology. Academic Press.
2.2. MLA (Modern Language Association)
The MLA style is commonly used in the humanities, particularly in literature, philosophy, and the arts. It focuses on the author's name and the page number, reflecting the importance of textual evidence in these fields.
Key Features:
In-text citations include the author's last name and page number (e.g., Smith 23).
The author's last name is organized alphabetically in the Works Cited.
Each entry includes detailed information such as publication city and publisher.
Example Entry: Smith, John. Understanding Psychology. Academic Press, 2053.
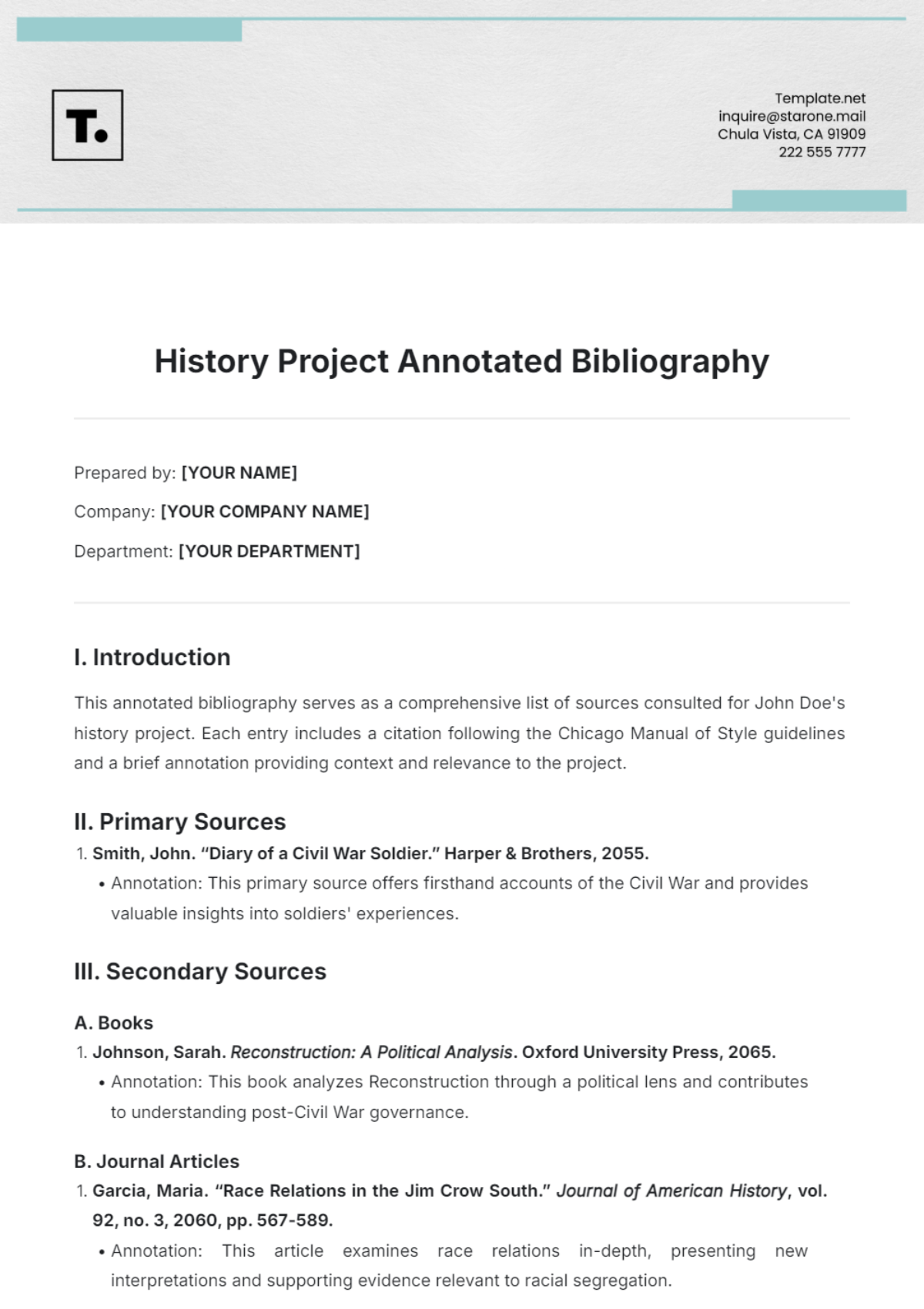
2.3. Chicago Manual of Style
The Chicago style is versatile, and used in various disciplines, including history and the social sciences. It offers two systems: the Notes and Bibliography system and the Author-Date system.
Key Features:
The Notes and Bibliography system uses footnotes or endnotes with a bibliography.
The Author-Date system includes parenthetical citations and a reference list.
Detailed guidelines are provided for various source types and their specific requirements.
Example Entry (Author-Date): Smith, John. 2053. Understanding Psychology. Academic Press.
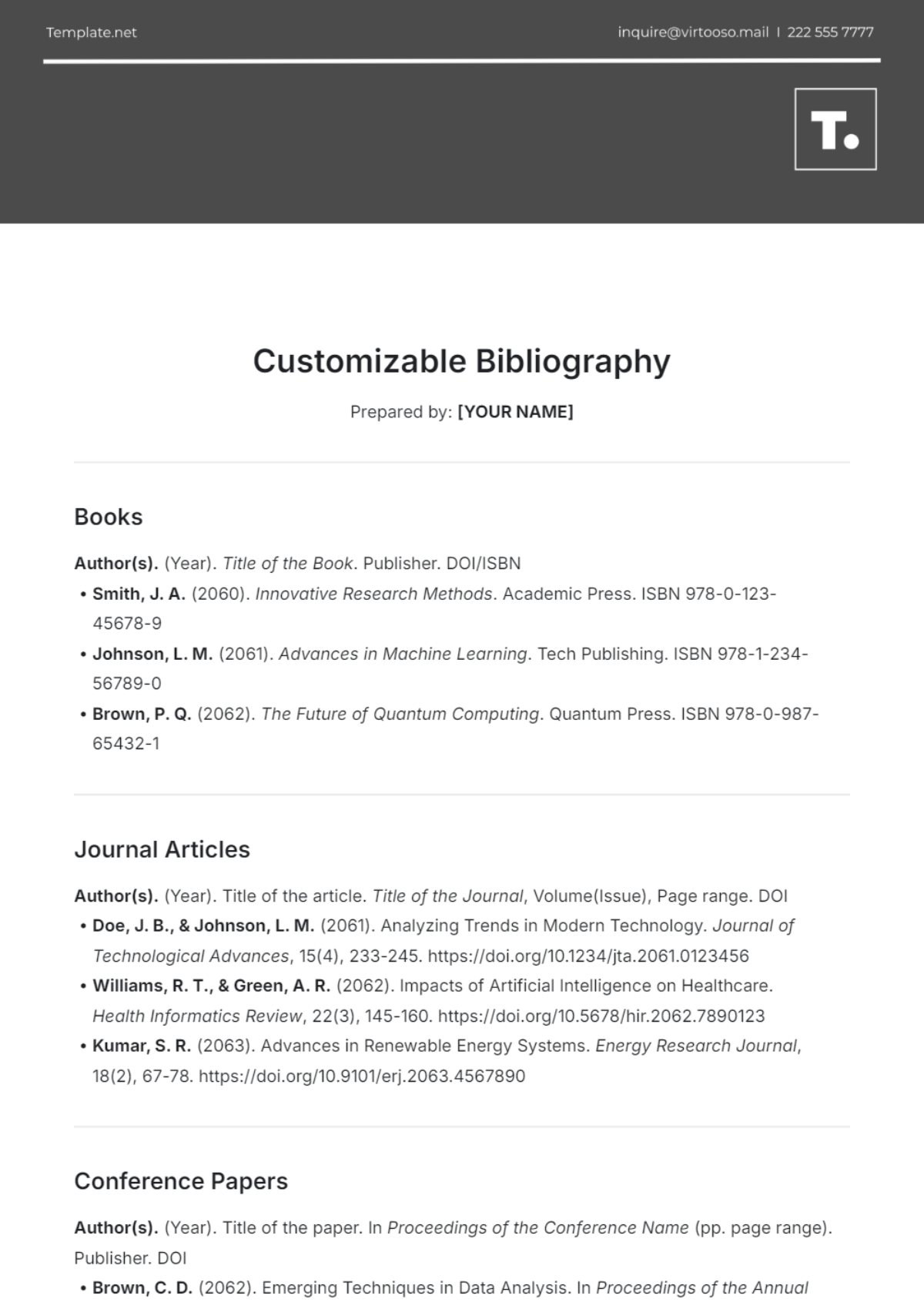
3. Formatting Guidelines
3.1. General Formatting Principles
Consistency: Maintain uniformity in the font, size, and spacing across the bibliography, with most styles advising the use of a standard font such as Times New Roman and a size like 12-point.
Hanging Indentation: For most citation styles, use a hanging indent format where the first line of each reference is flush left, and subsequent lines are indented by half an inch.
Alphabetical Order: Organize entries alphabetically by the author's last name or the title of the work if the author is unknown.
3.2. Specific Formatting Requirements
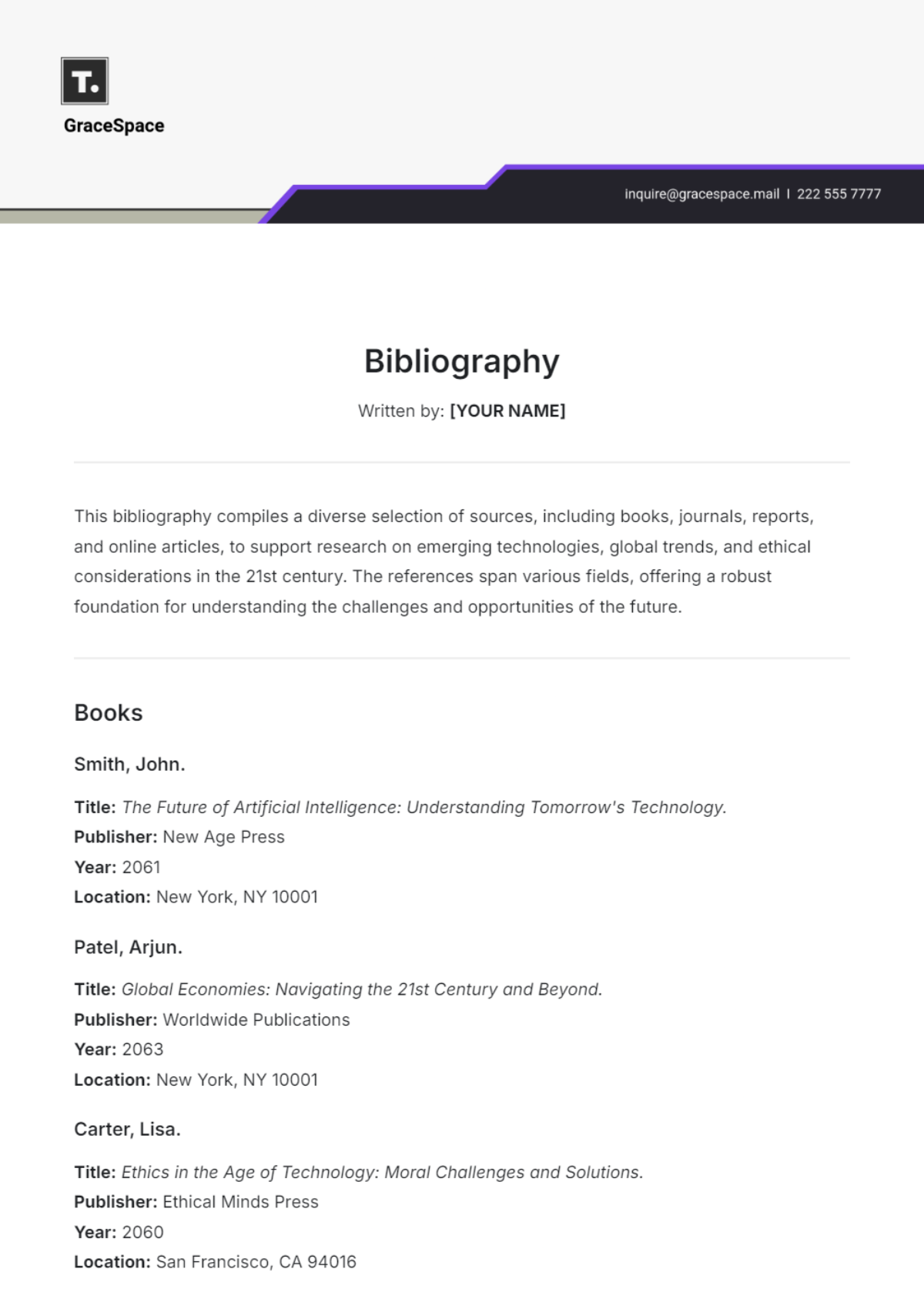
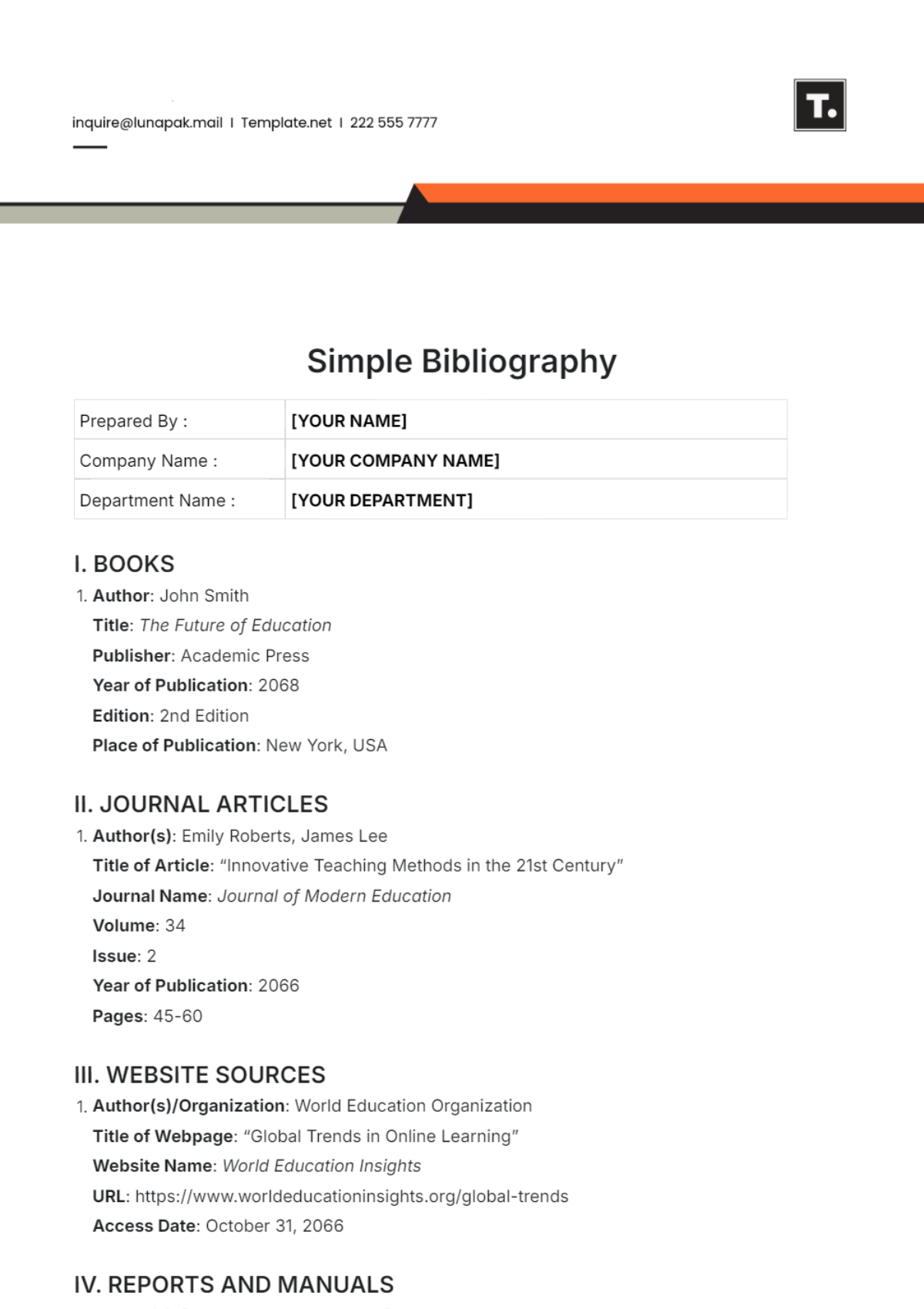
Books:
Include the author's name, title of the book in italics, place of publication, publisher, and year of publication.
Journal Articles:
Include the author's name, title of the article in quotation marks, title of the journal in italics, volume number, issue number, page range, and year of publication.
Websites:
Include the author's name (if available), the title of the webpage, the name of the website, the URL, and the date of access.
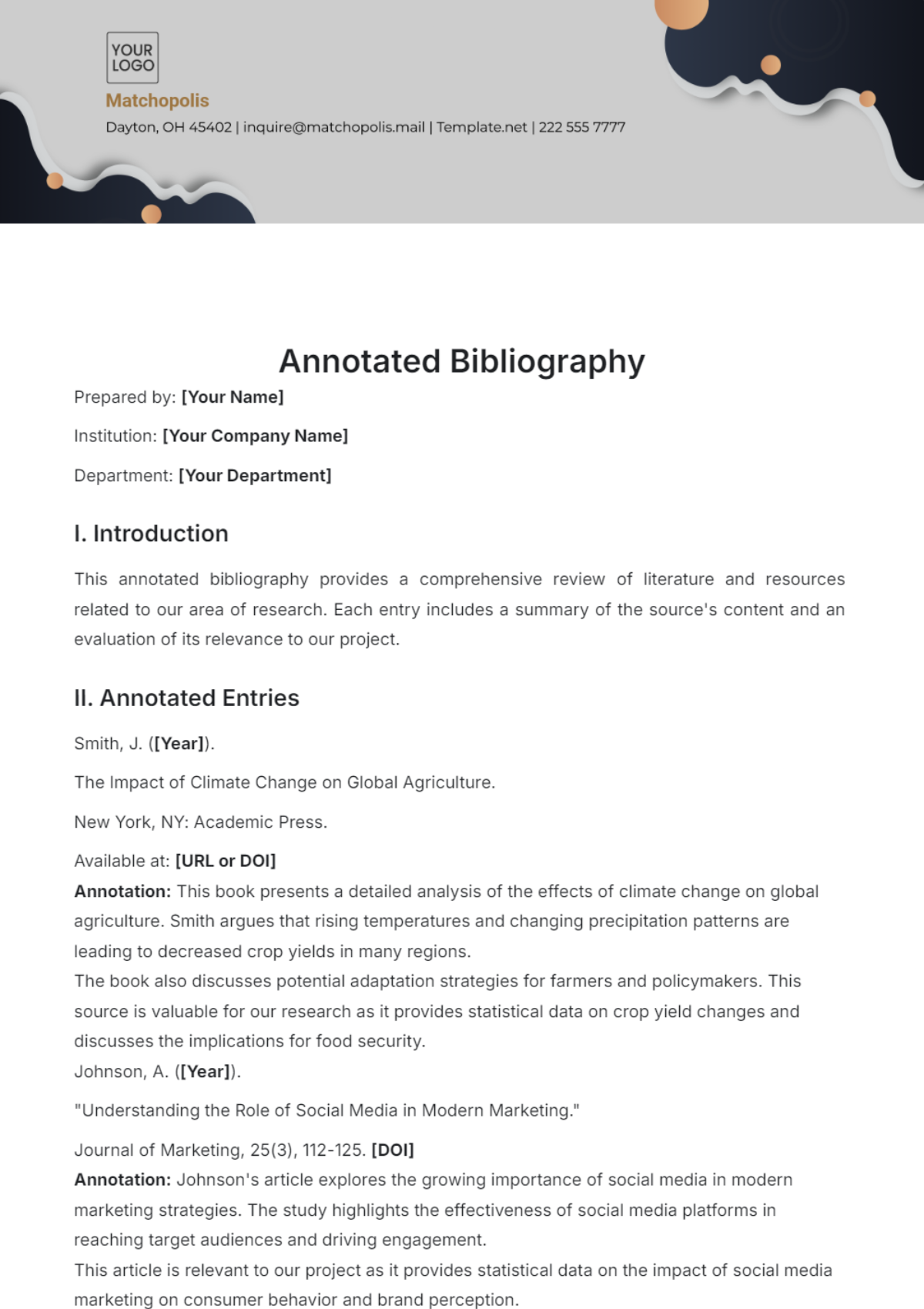
4. Common Errors and How to Avoid Them
4.1. Inconsistent Formatting
Issue: Inconsistent formatting can undermine the professionalism of a bibliography.
Solution: Adhere strictly to the formatting guidelines of the chosen citation style and use citation management tools to ensure uniformity.
4.2. Incorrect or Missing Information
4.3. Plagiarism
Issue: Failure to properly cite sources can result in plagiarism.
Solution: Always provide complete and accurate citations for all sources used in your work, and follow the citation style guidelines closely.
5. Conclusion
Creating a thorough and correctly formatted bibliography is a fundamental aspect of academic writing that ensures the credibility and traceability of research. By understanding and applying various citation styles, following detailed formatting guidelines, and avoiding common errors, researchers can produce high-quality bibliographies that contribute to the integrity of their scholarly work. For additional resources, consider using citation management software and consulting style guides for further assistance.
6. References:
American Psychological Association. (2050). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). American Psychological Association.
Modern Language Association. (2050). MLA Handbook (9th ed.). Modern Language Association.
The Chicago Manual of Style. (2050). The Chicago Manual of style (17th ed.). University of Chicago Press.
Journal Article Templates @ Template.net