Free Cardiac SBAR

Prepared by: Dr. [Your Name]
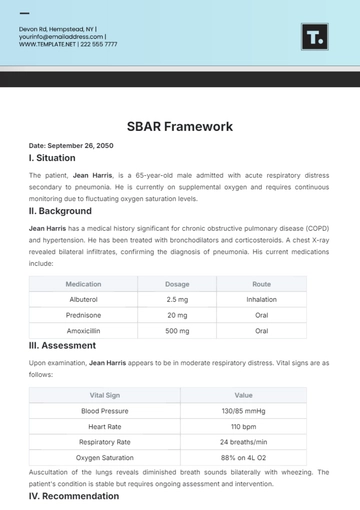
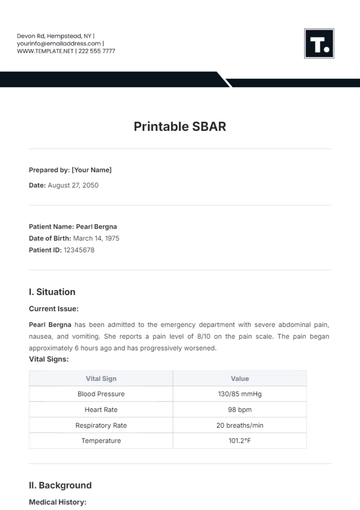
I. Situation
Patient Name: Mrs. Eleanor White
Age: 62
Gender: Female
Date: August 27, 2050
Time: 14:30
Location: Roome 505, [Your Company Address]
Mrs. Eleanor White, a 62-year-old female, presented with acute chest pain, shortness of breath, and sweating. The symptoms began approximately 30 minutes prior to her arrival. Vital signs upon admission indicated elevated blood pressure and an irregular heart rate.
II. Background
Mrs. White has a medical history notable for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. She has been receiving treatment for hypertension for the past 10 years and has been managing her hyperlipidemia with statins for the past 3 years. Her current medications include Amlodipine 10 mg daily and Atorvastatin 20 mg daily. No known drug allergies.
Her last cardiovascular assessment was about 18 months ago, which indicated stable coronary artery disease. She has no previous history of myocardial infarction or significant arrhythmias.
III. Assessment
Vital Signs:
Vital Sign | Value |
|---|---|
Blood Pressure | 155/92 mmHg |
Heart Rate | 108 bpm (irregular) |
Respiratory Rate | 24 breaths/min |
Temperature | 98.4°F |
Oxygen Saturation | 93% |
Clinical Findings:
Chest pain was described as crushing and radiating to the left shoulder
Severe dyspnea and anxiety present
Sweating noted
An electrocardiogram (ECG) shows ST-segment elevation in the inferior leads
Clinical Judgment:
The patient’s presentation is consistent with acute myocardial infarction (MI). Immediate intervention and further diagnostic evaluation are essential.
IV. Recommendation
Immediate Actions:
Administer aspirin 325 mg orally
Initiate intravenous access and administer nitroglycerin to alleviate pain and decrease myocardial oxygen demand
Continuously monitor cardiac rhythm and prepare for potential advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) measures
Further Evaluation:
Conduct urgent coronary angiography to evaluate for possible coronary artery blockages
Consider thrombolytic therapy if coronary angiography indicates significant blockage
Consultation:
Refer to cardiology for immediate assessment and intervention
Inform the patient’s family about her condition and discuss possible treatment options
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
The Cardiac SBAR Template offered by Template.net is designed for precise communication in cardiac care. This customizable, downloadable template is both printable and editable with the help of our AI Editor Tool, ensuring accurate and efficient documentation of patient information. Use this tool to enhance clarity and streamline communication with healthcare professionals.