Project Implementation Methodology
Prepared by: [YOUR NAME]
Date: [DATE]
1. Introduction
A Project Implementation Methodology is a structured approach that outlines the processes, procedures, and practices necessary to successfully execute and complete a project. It serves as a roadmap, detailing each phase of the project from initiation to closure, ensuring that goals are met efficiently and effectively.
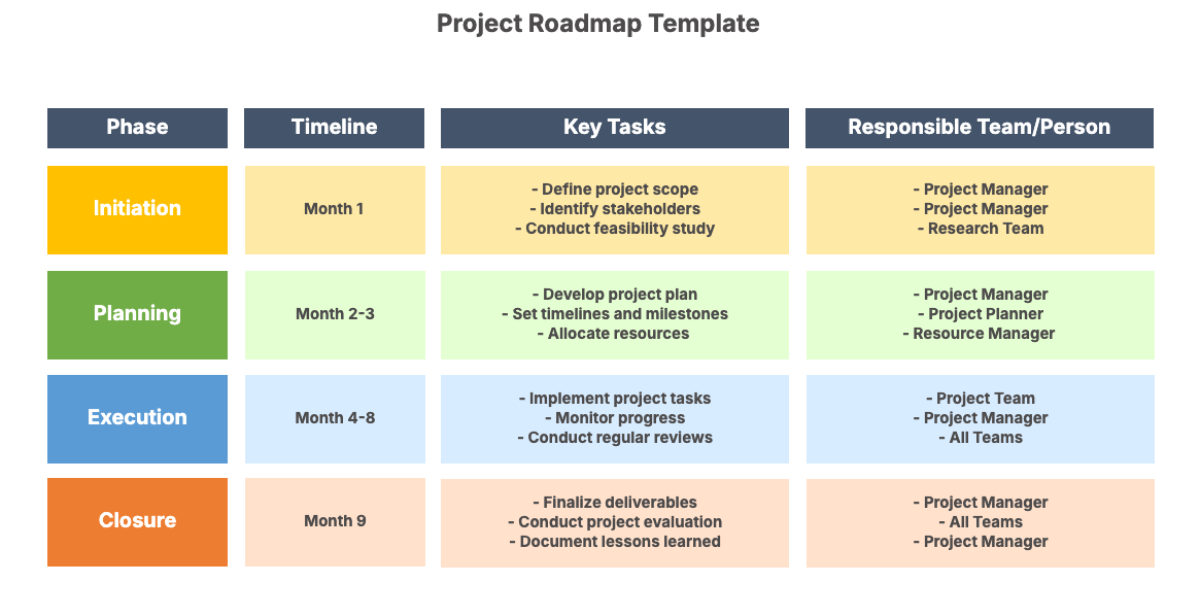
2. Phase 1: Initiation
2.1. Project Proposal
The project proposal is the first step, which includes:
Identifying project objectives
Outlining deliverables
Estimating timelines and resources
Stakeholder analysis
2.2. Feasibility Study
Conducting a feasibility study to evaluate:
Technical feasibility
Economic feasibility
Operational feasibility
Legal and regulatory compliance
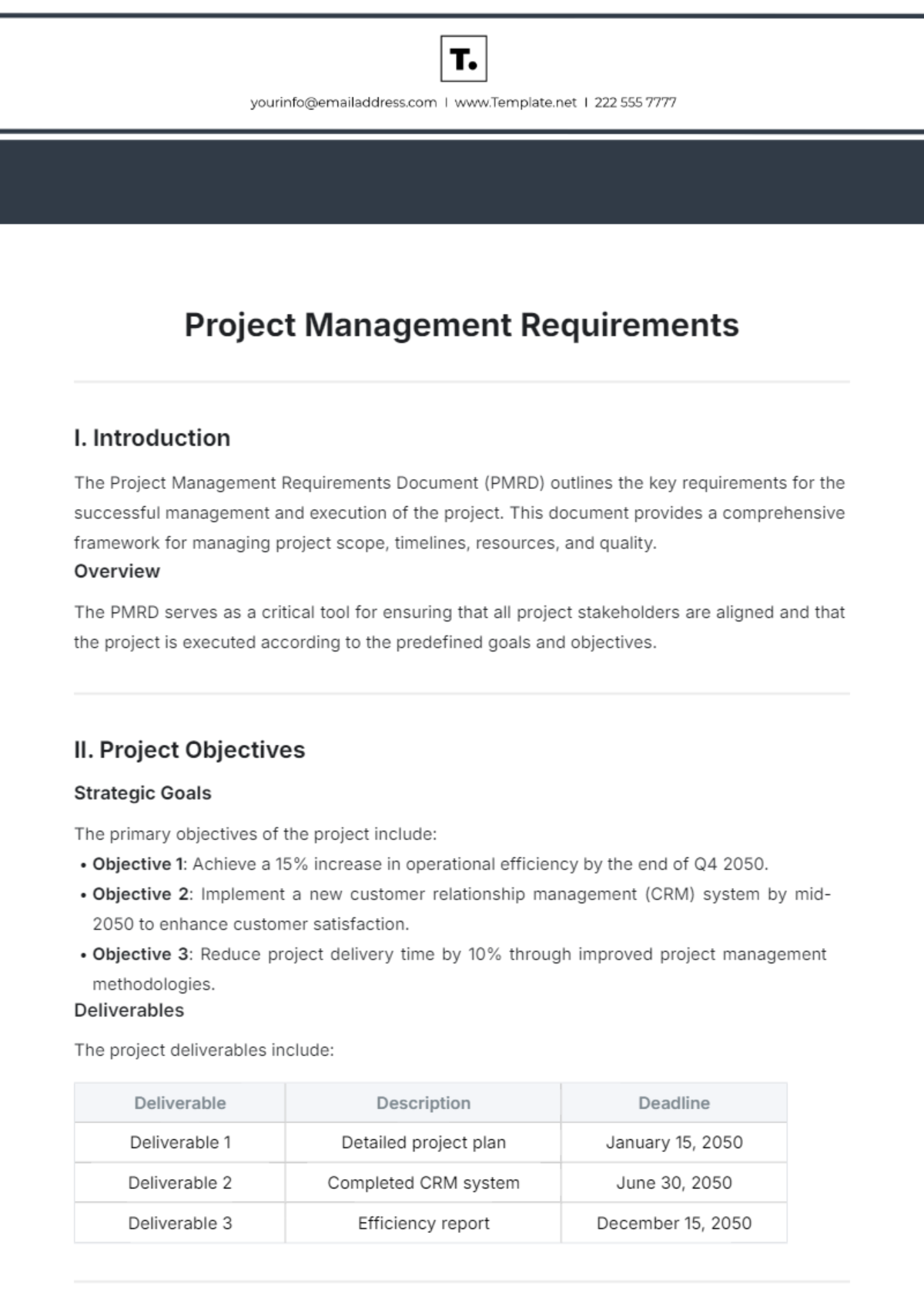
2.3. Project Charter
Developing a project charter that includes:
Project title and description
Objectives and deliverables
Scope
Stakeholders
Timeline and milestones
Budget estimates
3. Phase 2: Planning
3.1. Project Plan
Creating a comprehensive project plan that outlines:
Work breakdown structure (WBS)
Resource allocation
Task assignments
Schedule development
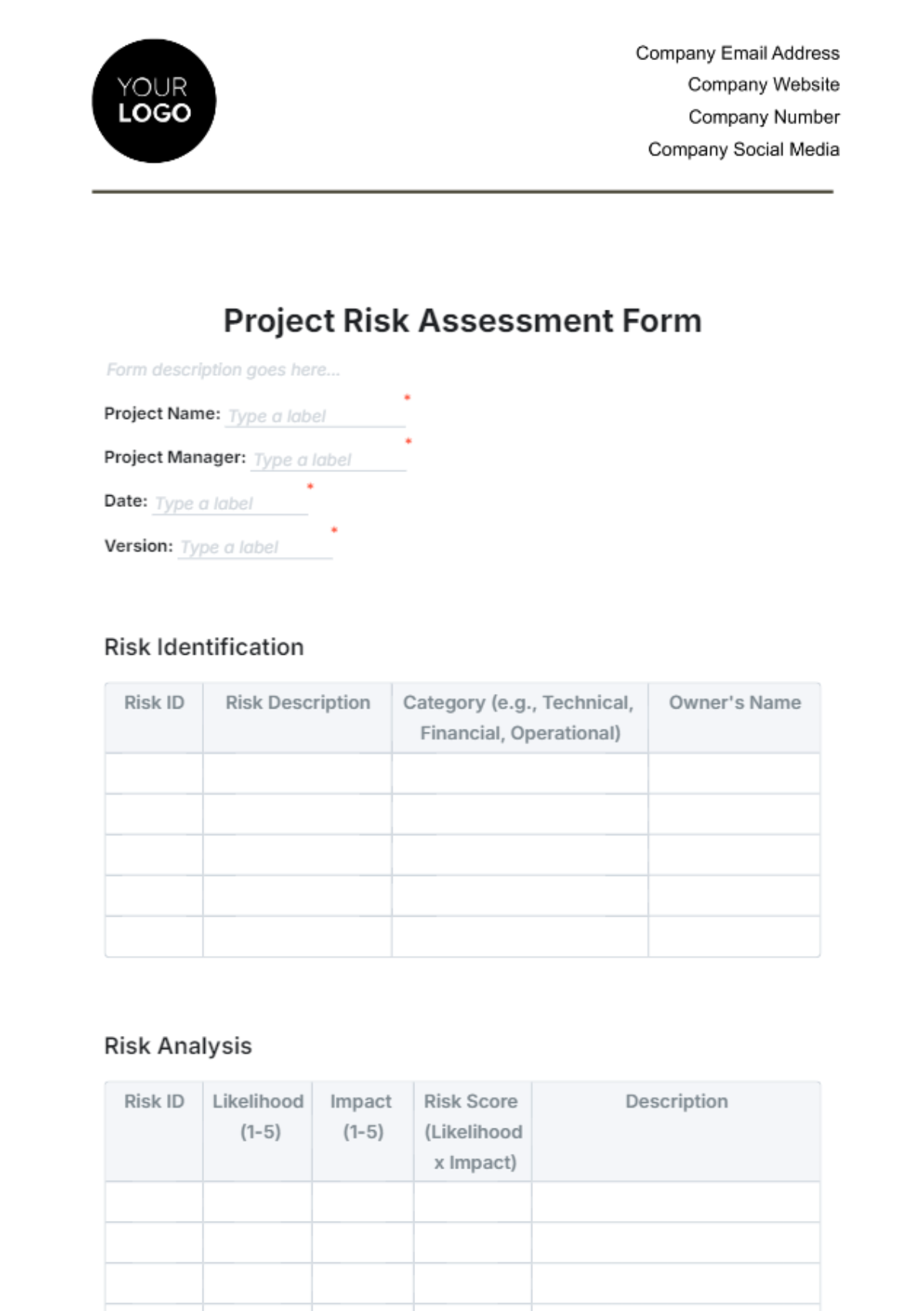
3.2. Risk Management Plan
Developing a risk management plan to identify and mitigate risks, including:
Risk identification
Risk assessment (impact and probability)
Risk response strategies
Risk monitoring and control
3.3. Communication Plan
Formulating a communication plan to ensure effective information dissemination:
Stakeholder communication requirements
Communication methods and tools
Frequency and timing of communications
3.4. Quality Management Plan
Creating a quality management plan that includes:
Quality objectives
Quality assurance processes
Quality control measures
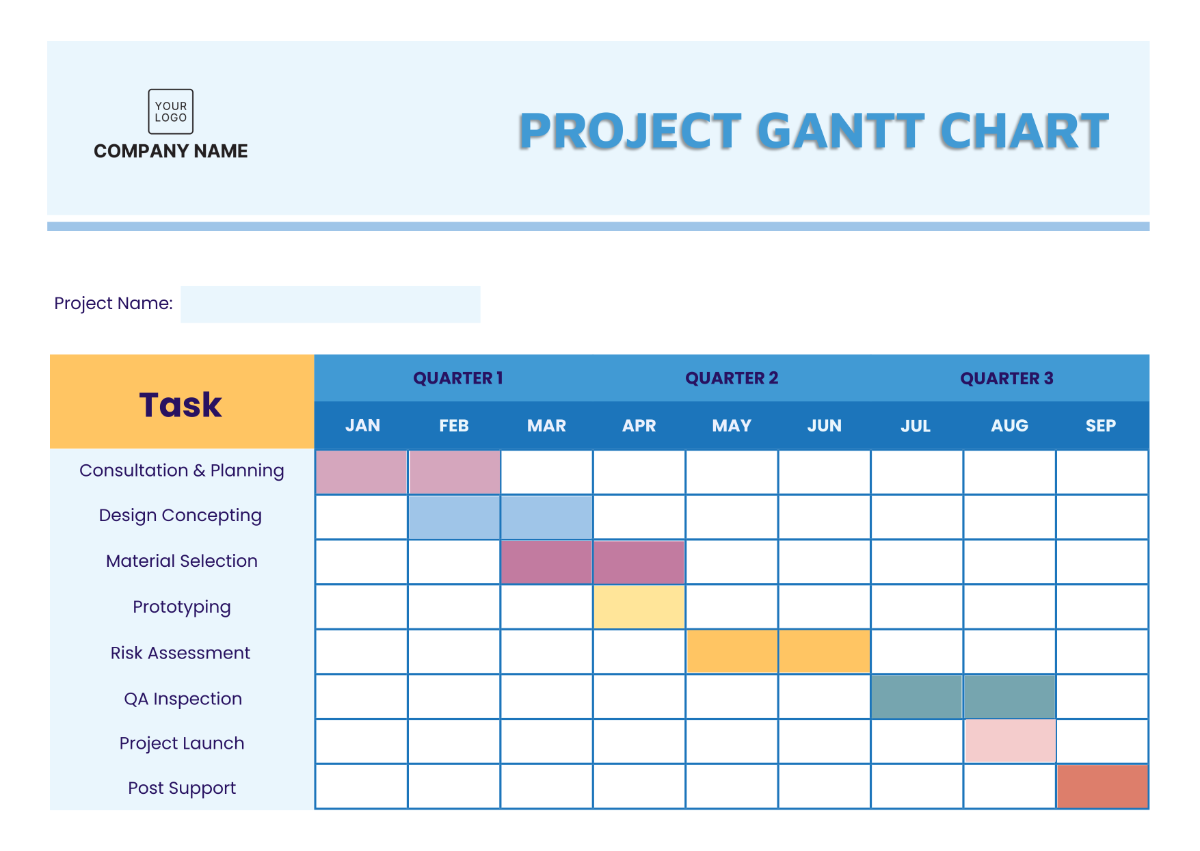
4. Phase 3: Execution
4.1. Task Implementation
Executing the project plan by:
Allocating resources
Performing tasks and activities
Coordinating team efforts
Ensuring quality standards
4.2. Progress Monitoring
Monitoring the progress of the project by:
Regular status updates
Performance metrics
Scheduled reviews
Tracking timelines and budgets
4.3. Issue Management
Managing issues as they arise by:
Identifying issues
Documenting and tracking issues
Resolving issues promptly
Escalating issues when necessary
5. Phase 4: Monitoring and Controlling
5.1. Performance Reporting
Regularly reporting on project performance, focusing on:
Progress against milestones
Variance analysis (schedule, cost, scope)
Risk status
Quality metrics
5.2. Change Management
Implementing a change management process to handle changes in scope, schedule, or resources:
Change request documentation
Impact analysis
Approval workflows
Implementation of changes
5.3. Quality Control
Ensuring the project meets quality standards by:
Conducting quality inspections
Performing quality audits
Documenting and addressing non-conformities
6. Phase 5: Closure
6.1. Final Deliverables
Ensuring all project deliverables are completed and handed over to stakeholders by:
Verifying completion of project tasks
Obtaining stakeholder acceptance
6.2. Project Documentation
Completing all project documentation, including:
Final reports
Lessons learned
Project performance analysis
6.3. Post-Implementation Review
Conducting a post-implementation review to analyze the project's success and areas for improvement:
Reviewing project objectives
Assessing project performance
Identifying lessons learned
6.4. Project Handover and Closure
Formally closing the project by:
Transferring project deliverables to operations
Releasing project resources
Closing project accounts
7. Conclusion
A well-defined Project Implementation Methodology is essential for project success. It systematically guides all phases, aiding in resource management, timeline adherence, and quality control. This approach helps navigate complexities, mitigate risks, and meet stakeholder expectations. By addressing project objectives, planning, execution, and issue management, it ensures efficiency and continuous improvement, ultimately leading to successful outcomes and stakeholder satisfaction.