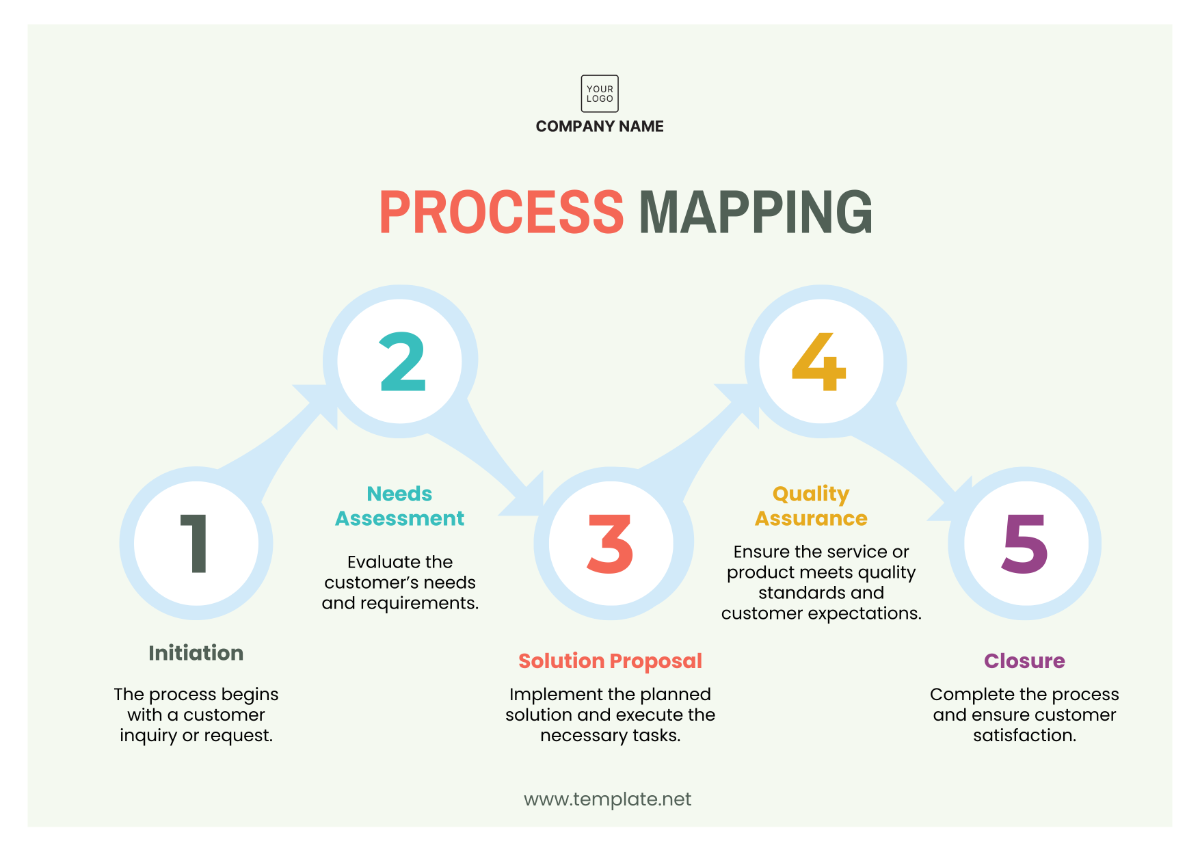
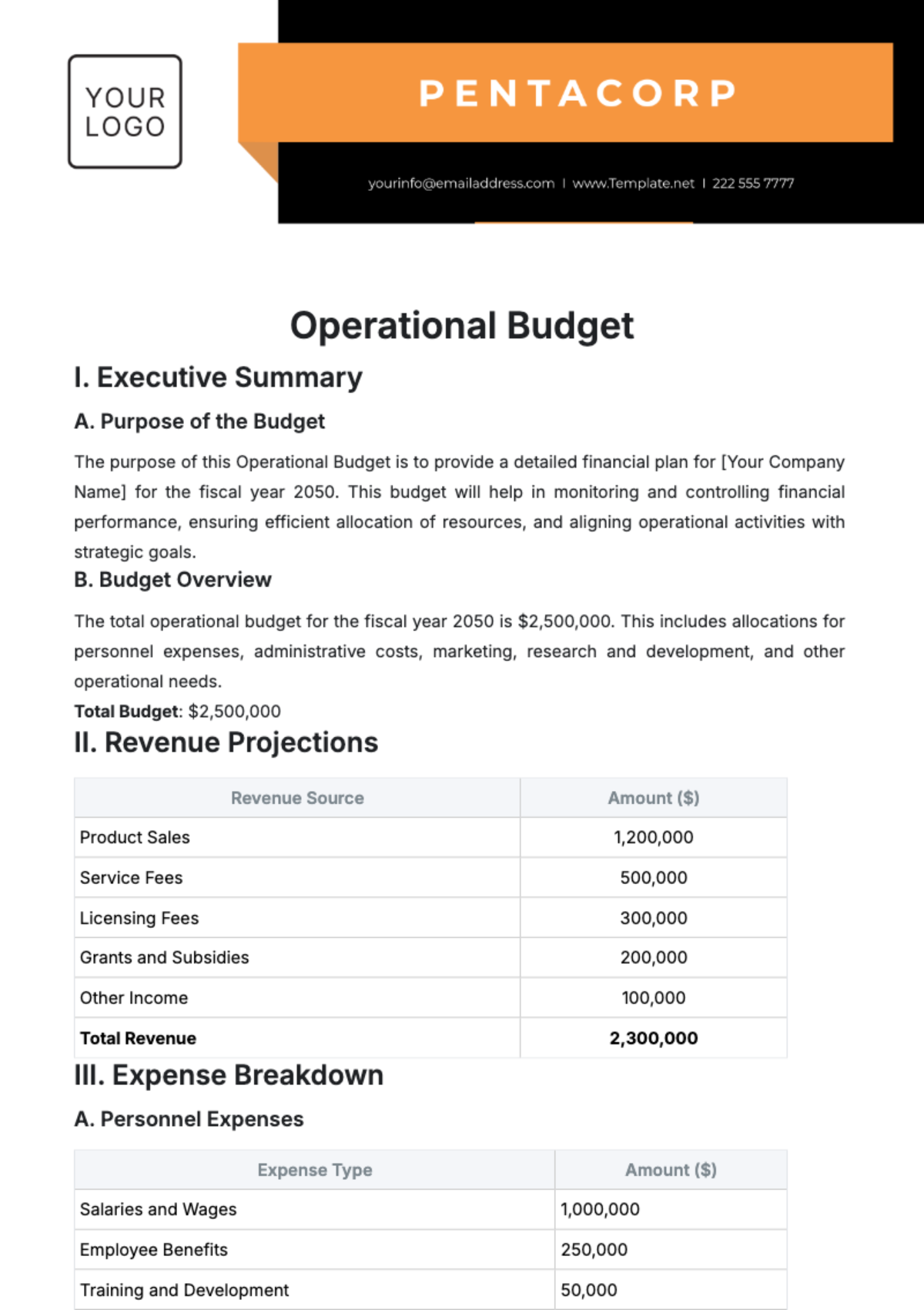
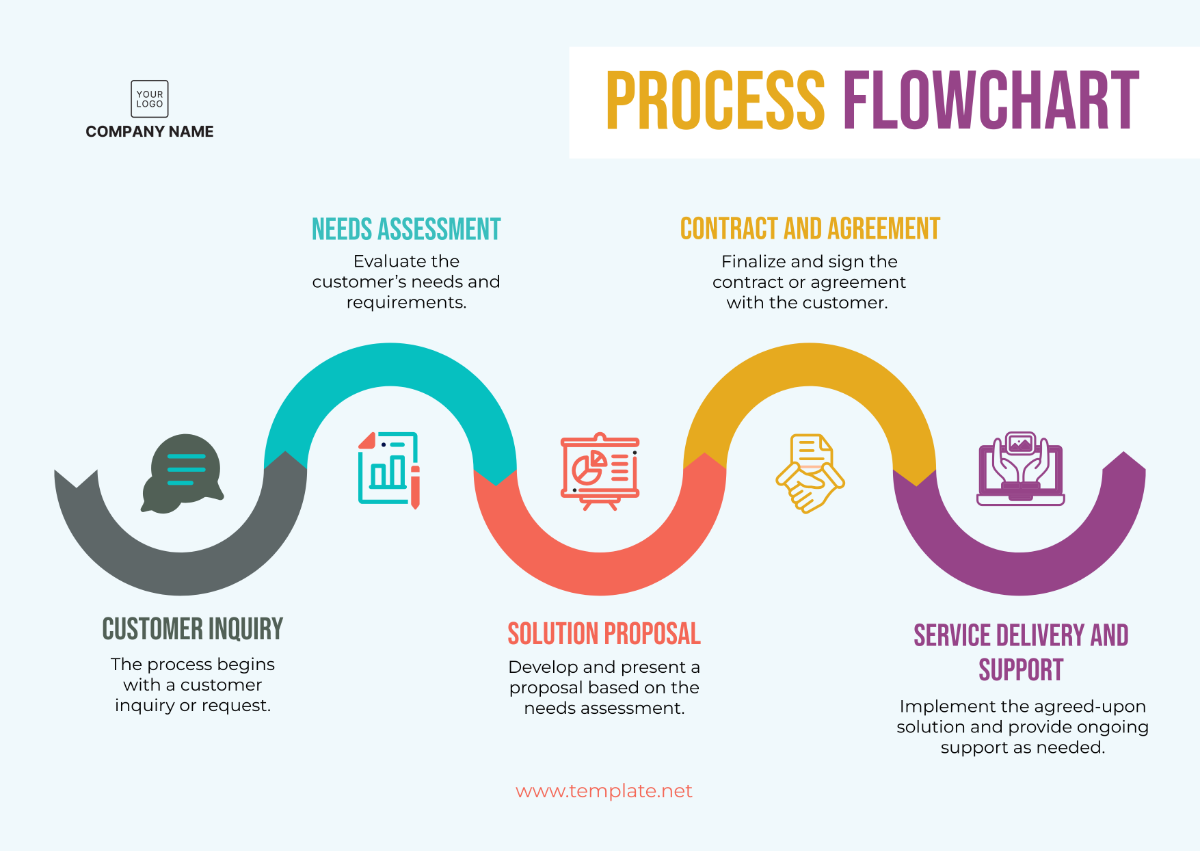
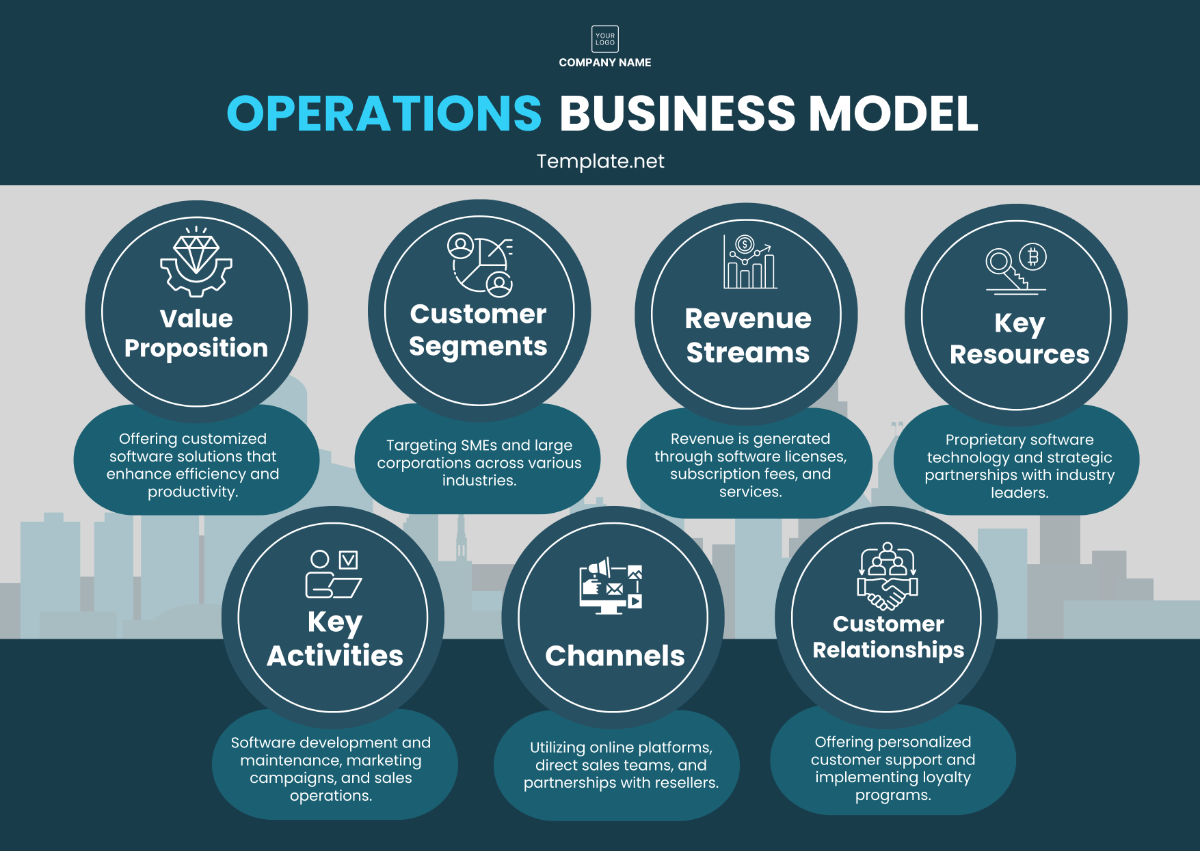
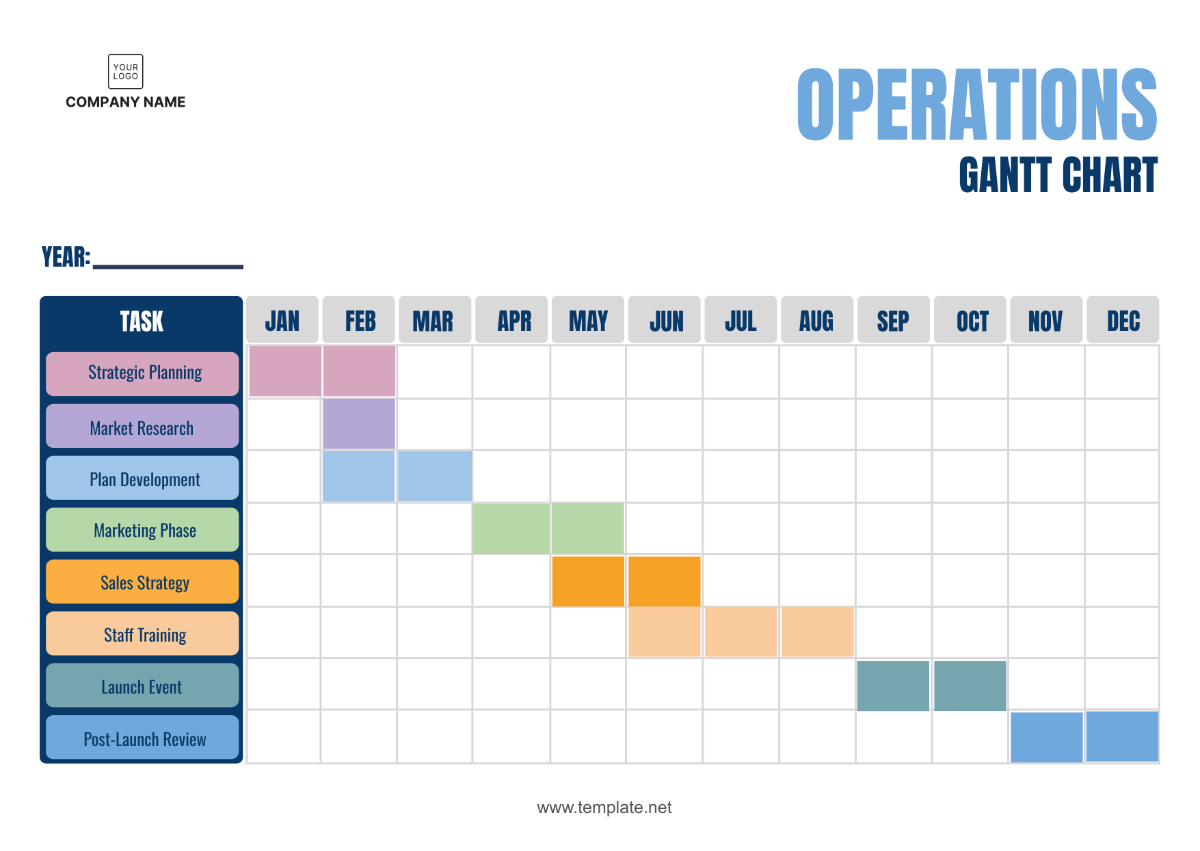
Operations Supply Chain Management
I. Introduction
Welcome to the Operations Supply Chain Management guide for [Your Company Name]. In today’s dynamic business environment, effective supply chain management is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring operational efficiency. Our supply chain is a network of processes that integrates suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers, aiming to deliver products and services in a timely, cost-effective, and high-quality manner. This guide outlines our approach to managing these processes and highlights the strategic importance of aligning our supply chain operations with our overall business goals.
At [Your Company Name], we are committed to fostering robust supply chain practices that not only meet regulatory requirements but also drive sustainable growth. Our operations are designed to be agile and resilient, adapting to market changes and customer demands while optimizing resource utilization. By adhering to industry best practices and leveraging advanced technologies, we ensure that our supply chain functions efficiently and effectively. This introduction sets the stage for understanding the key components of our supply chain management strategy, offering insights into our operational priorities and the principles guiding our supply chain activities.
II. Key Components of Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management is constituted by various elements that work together to ensure the seamless production and delivery of goods and services. These key components include:
Component | Description |
|---|---|
Sourcing and Procurement | The process of finding and acquiring goods and services from suppliers. This involves evaluating suppliers, negotiating contracts, and ensuring the quality and cost-effectiveness of purchased items. |
Production Planning | Coordinating the manufacture of products, which includes scheduling production runs, allocating resources, and managing production workflows to meet demand and optimize efficiency. |
Inventory Management | Supervision of non-capitalized assets and stock items, including managing inventory levels, forecasting demand, and ensuring that products are available when needed while minimizing excess stock. |
Warehouse Management | Controlling the storage, organization, and movement of materials within a warehouse. This involves managing space utilization, inventory accuracy, and the efficiency of order fulfillment processes. |
Logistics and Transportation | Planning and executing the movement of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption. This includes optimizing transportation routes, managing shipping schedules, and ensuring timely delivery. |
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) | Managing the company's interactions with current and potential customers. This involves maintaining customer records, analyzing customer data, and improving service quality to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. |
III. Strategies for Effective Supply Chain Management
Implementing effective supply chain strategies is essential for enhancing efficiency and productivity. Key strategies include:
Lean Manufacturing: Streamlining processes to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
Just-In-Time (JIT): Inventory strategy to increase efficiency and reduce waste by receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process.
Six Sigma: A set of techniques and tools for process improvement aimed at reducing defects and variability.
Total Quality Management (TQM): An organization-wide approach to embedding quality in every aspect of the business.
Global Sourcing: Procuring goods and services from international markets to leverage global efficiencies.
IV. Technological Tools in Supply Chain Management
Technology plays a crucial role in modern supply chain management, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and reliability across various processes. Here’s a look at some key technological tools that are transforming supply chains:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): ERP systems are integrated software platforms that unify core business processes across an organization. These systems facilitate real-time data sharing and communication between departments, ensuring seamless coordination in areas such as procurement, production, and inventory management. By consolidating data into a single source, ERP systems improve decision-making, reduce errors, and streamline operations, providing a comprehensive view of the supply chain from end to end.
Supply Chain Management Software (SCMS): SCMS solutions offer a broad range of functionalities tailored to the planning, execution, and monitoring of supply chain activities. These tools enable businesses to manage supply chain activities such as demand forecasting, supply planning, order fulfillment, and logistics. SCMS solutions often include features for tracking performance metrics, optimizing routes, and managing supplier relationships, all of which contribute to more efficient and responsive supply chain operations.
Advanced Analytics: Leveraging big data analytics, businesses can gain valuable insights into their supply chain operations. Advanced analytics involves the use of statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling to interpret large volumes of data. By analyzing patterns and trends, companies can make data-driven decisions to enhance forecasting accuracy, identify potential disruptions, and optimize inventory levels. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities within the supply chain.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID): RFID technology uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags can store information about the items they are attached to, such as product details, location, and movement history. RFID enhances inventory management by providing real-time visibility into stock levels and reducing manual data entry errors. It also improves tracking of goods throughout the supply chain, from production to delivery, leading to more efficient operations and better accuracy.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records and verifies transactions across a network of computers. In supply chain management, blockchain technology enhances transparency and security by providing an immutable record of transactions. This technology allows for secure and verifiable tracking of goods as they move through the supply chain, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring the authenticity of products. By enabling end-to-end traceability, blockchain enhances trust among supply chain partners and improves overall operational integrity.
These technological tools collectively contribute to more streamlined, transparent, and efficient supply chain operations, driving significant improvements in performance and competitiveness.
V. Challenges in Supply Chain Management
Supply chain managers often face numerous challenges that can impede operational efficiency. Common challenges include:
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Globalization | Managing supply chains that span multiple countries and continents introduces complexities related to different time zones, cultural differences, and varying business practices. Global supply chains require coordination across diverse regulatory environments and logistical frameworks, complicating oversight and management. |
Risk Management | Mitigating risks associated with supply chain disruptions, such as natural disasters, political instability, or supplier failures, is crucial. Effective risk management involves identifying potential threats, assessing their impact, and developing contingency plans to minimize disruptions and ensure business continuity. |
Compliance and Regulation | Adhering to varying regulatory requirements across different regions poses a significant challenge. This includes compliance with local laws, international standards, environmental regulations, and industry-specific guidelines. Navigating these diverse requirements demands thorough knowledge and constant vigilance to avoid legal issues and penalties. |
Cost Control | Balancing cost-efficiency with quality and service is a persistent challenge. Supply chain managers must find ways to minimize costs while maintaining high standards of product quality and customer service. This involves optimizing procurement processes, reducing waste, and negotiating favorable terms with suppliers without compromising value. |
Technology Integration | Integrating new technologies into existing supply chain processes can be complex and resource-intensive. Challenges include ensuring compatibility with legacy systems, managing data integration, and training staff on new tools. Successful technology integration requires careful planning and execution to realize the benefits of enhanced efficiency and accuracy. |
VI. Case Study: Apple Inc.
The supply chain management practices of Apple Inc. provide a pertinent example of how effective SCM contributes to business success. Key aspects of Apple’s SCM include:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Sourcing | Apple sources components from multiple suppliers to ensure quality and mitigate risks. |
Production | Apple employs Just-In-Time production methodologies to minimize inventory costs. |
Inventory Management | Advanced forecasting and inventory management systems to align supply with demand. |
Logistics | Utilizes efficient logistics networks to distribute products worldwide rapidly. |
Technology | Incorporates cutting-edge technology, such as RFID and advanced analytics, for real-time insights. |
VII. Conclusion
Effective supply chain management is essential for the success of [Your Company Name]. By understanding and addressing the key components of supply chain management, from sourcing and procurement to customer relationship management, we ensure that our operations are streamlined, efficient, and aligned with our business objectives. The integration of advanced technological tools such as ERP systems, SCMS, advanced analytics, RFID, and blockchain technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing the accuracy, transparency, and responsiveness of our supply chain. These tools not only facilitate smoother operations but also empower us to make informed decisions, manage risks, and adapt to changing market conditions.
Despite the benefits, we recognize that challenges such as globalization, risk management, regulatory compliance, cost control, and technology integration must be proactively addressed. By continuously monitoring these challenges and implementing effective strategies, we can maintain a resilient and agile supply chain that supports our growth and meets the needs of our customers. At [Your Company Name], we are committed to leveraging best practices and innovative solutions to overcome these challenges and drive operational excellence. Our ongoing focus on supply chain management ensures that we remain competitive and capable of delivering exceptional value to our stakeholders.