Balanced Scorecard Methodology
1. Introduction
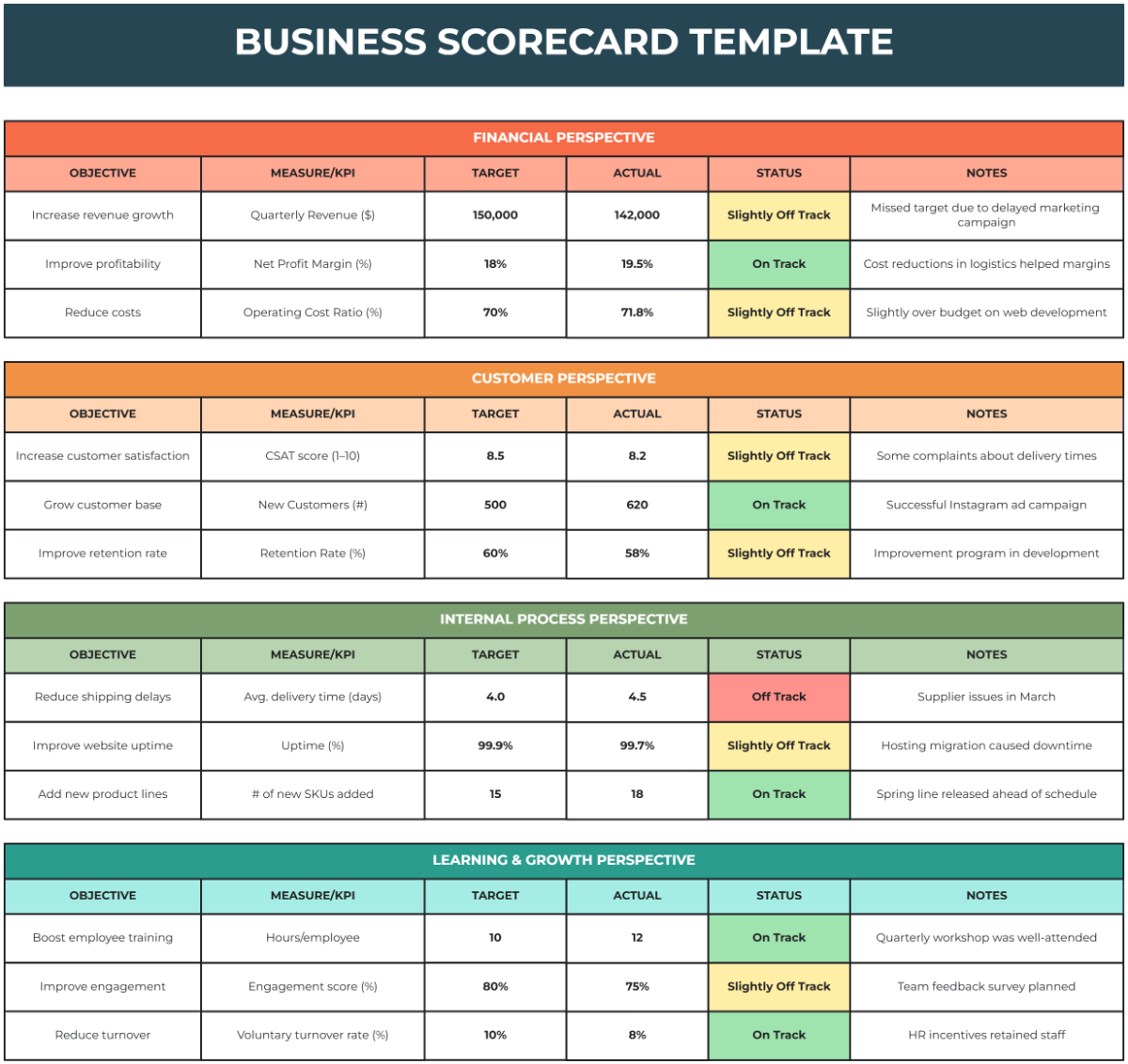
The Balanced Scorecard Methodology is a strategic planning and management tool used by organizations to align business activities with their vision and strategy. It focuses on four key perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth. By implementing this methodology, organizations can measure performance, monitor progress, and achieve their strategic goals.
2. Key Perspectives
2.1 Financial Perspective
The financial perspective focuses on the financial objectives of the organization and helps to answer the question: "How do we look to our shareholders?" This perspective typically includes objectives and measures related to profitability, revenue growth, cost management, and return on investment.
Profitability
Revenue Growth
Cost Management
Return on Investment (ROI)
2.2 Customer Perspective
The customer perspective emphasizes customer satisfaction and retention, aiming to answer the question: "How do our customers see us?" Key objectives and measures often involved in this perspective include customer satisfaction scores, market share, and customer loyalty.
Customer Satisfaction Scores
Market Share
Customer Loyalty
2.3 Internal Processes Perspective
This perspective focuses on internal operational goals and strives to answer the question: "What must we excel at?" Key objectives and measures in this area target process efficiency, quality, and cycle time reduction. Implementing best practices and optimizing internal processes are crucial for achieving excellence in this dimension.
Process Efficiency
Quality Improvement
Cycle Time Reduction
Best Practices Implementation
2.4 Learning & Growth Perspective
The learning and growth perspective aims to foster continuous improvement and innovation. It answers the question: "How can we continue to improve and create value?" This perspective deals with employee training, organizational culture, and the company’s ability to innovate and grow. Key objectives and measures include employee satisfaction, skill development, and technology adoption.
Employee Satisfaction
Skill Development
Technology Adoption
Organizational Culture
3. Implementing the Balanced Scorecard
3.1 Step 1: Define Vision and Strategy
The first step in implementing the Balanced Scorecard is to clearly define the organization's vision and strategy. This involves setting long-term goals and identifying the core values that guide the company's direction. Senior leadership should be involved in crafting a vision statement that is both inspiring and achievable.
3.2 Step 2: Develop Strategic Objectives
Next, develop specific strategic objectives for each of the four perspectives. These objectives should be aligned with the overall vision and strategy of the organization. Each objective should be actionable and measurable.
Define objectives for the Financial Perspective
Set goals for the Customer's Perspective
Identify key internal processes to be optimized
Determine areas for learning and growth
3.3 Step 3: Establish Measures and Targets
Once strategic objectives have been identified, the next step is to establish specific measures and targets for each objective. Measures should be quantitative and allow the organization to track progress over time. Targets provide benchmarks for success and help ensure that objectives are met.
3.4 Step 4: Align Initiatives and Resources
After setting measures and targets, align organizational initiatives and resources with the strategic objectives. This involves allocating budgets, assigning responsibilities, and ensuring that all departments are working towards the common goals outlined in the Balanced Scorecard.
3.5 Step 5: Monitor and Review
Regular monitoring and review are essential for the success of the Balanced Scorecard. Organizations should conduct periodic reviews to assess performance against targets and make any necessary adjustments. This helps to ensure that the strategy remains relevant and that the organization continues to move toward its long-term goals.
4. Benefits of the Balanced Scorecard
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard methodology offers several benefits:
Improved strategic alignment
Enhanced performance measurement
Better organizational focus
Increased accountability
Greater agility and adaptability
5. Conclusion
The Balanced Scorecard methodology provides a comprehensive framework for translating an organization's vision and strategy into actionable objectives and measurable outcomes. By focusing on four key perspectives—Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth—organizations can more effectively align their activities with their strategic goals, monitor performance, and drive continuous improvement.