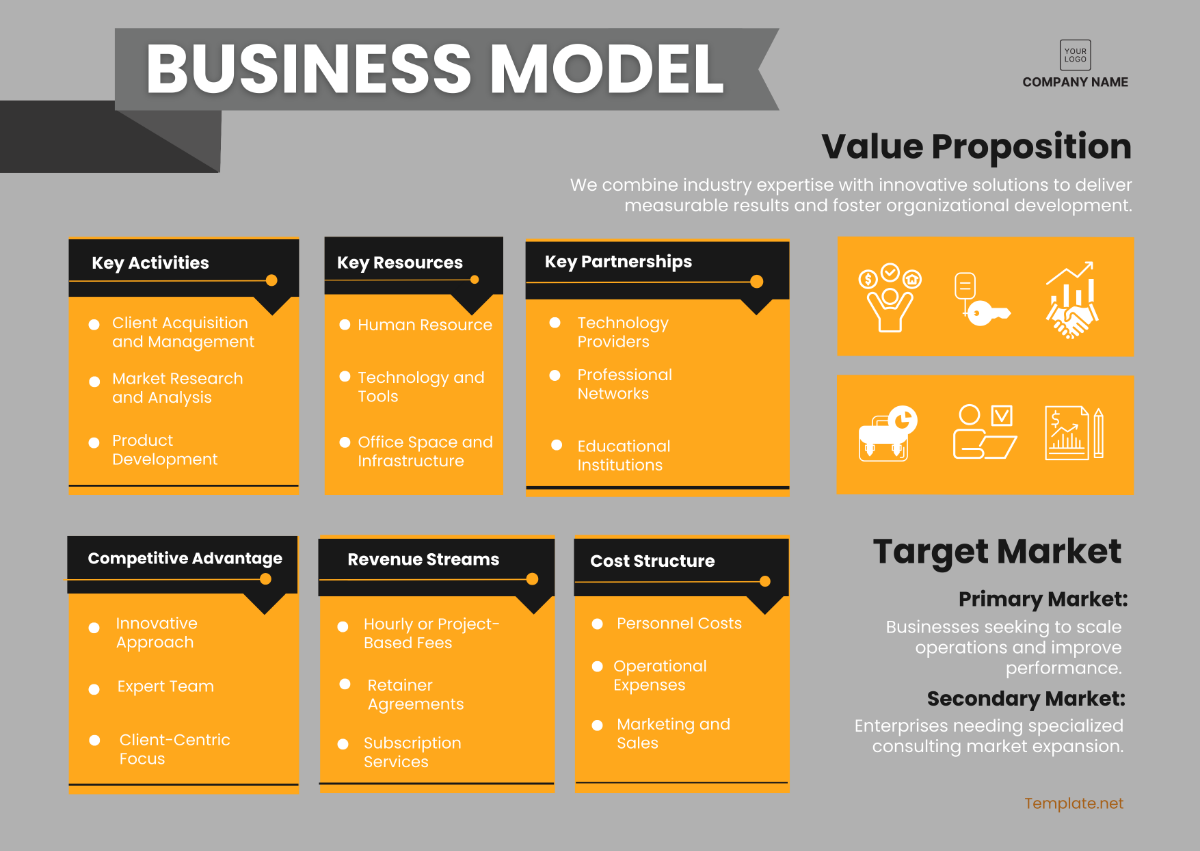
Lean Startup Methodology
1. Introduction
The Lean Startup Methodology offers a strategic approach for launching and managing new products. By focusing on rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative development, this methodology aims to reduce risk and improve the chances of startup success. Through this structured approach, businesses can quickly adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs. At [Your Company Name], we leverage the Lean Startup Methodology to help our clients streamline their product development processes, ensuring they achieve market fit efficiently and effectively.
2. Problem Identification
Objective: Define the core problem and target market for the project management tool.
Problem Statement: Small businesses often struggle with inefficient project management due to the lack of a simple, affordable tool. Existing solutions are either too complex or too expensive, leading to wasted resources and suboptimal project outcomes.
Target Market: Small business owners and project managers in the tech and service sectors who need a straightforward, cost-effective solution for managing projects, tracking progress, and coordinating teams.
3. Solution Hypothesis
Objective: Propose a solution and explain its value proposition.
Proposed Solution: Develop a cloud-based project management tool designed specifically for small businesses. The tool will offer essential features such as task management, team collaboration, and basic reporting at a competitive price point.
Value Proposition: This tool provides small businesses with a user-friendly, affordable solution that integrates seamlessly into their existing workflows. It simplifies project management tasks, enhances team collaboration, and provides actionable insights through basic reporting features.
4. Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Objective: Create and test an initial version of the product to gather feedback.
MVP Description: The MVP will include core features like task creation and assignment, progress tracking, and basic reporting functionalities. This version aims to validate the essential value propositions without extensive development.
Features:
Task Creation and Assignment: Allows users to create tasks, assign them to team members, and set deadlines.
Progress Tracking: Visual indicators to show task status and overall project progress.
Basic Reporting: Simple reports to track task completion rates and project milestones.
Testing Plan: Launch the MVP to a group of 50 small businesses for a three-month trial period. Collect feedback through surveys and direct interviews to assess usability, feature relevance, and overall satisfaction.
5. Validated Learning
Objective: Analyze feedback to refine the product and business model.
Feedback Collection Methods:
Surveys: Distribute questionnaires to MVP users to gauge their experience and gather detailed feedback on features.
Interviews: Conduct in-depth interviews with a subset of users to gain qualitative insights into their needs and challenges.
Usage Analytics: Monitor feature usage and user behavior through built-in analytics tools to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
Data Analysis: Evaluate survey responses, interview insights, and usage data to determine which features are most valuable and identify any issues or gaps.
Learnings: Based on the feedback, the product may need adjustments, such as adding requested features or improving existing functionalities.
6. Pivot or Persevere
Objective: Decide the next steps based on validated learning.
Pivot Strategy: If feedback suggests that users need advanced features (e.g., integration with other tools), consider developing a more robust version of the product that includes these capabilities while maintaining a focus on affordability.
Persevere Plan: If the MVP meets user needs and receives positive feedback, continue to enhance the product by addressing any minor issues and expanding its features in response to user requests.
7. Metrics and Measurement
Objective: Track progress and measure success through key metrics.
Key Metrics:
User Engagement: Monitor metrics such as active users, frequency of feature use, and user retention rates.
Customer Satisfaction: Use Net Promoter Score (NPS) to measure overall satisfaction and likelihood of recommending the product.
Conversion Rates: Track the rate of users transitioning from the free trial to paid subscriptions.
Measurement Methods: Employ analytics tools to collect data on user behavior, conduct regular surveys to assess satisfaction, and analyze conversion metrics to evaluate growth and success.
8. Iterative Development
Objective: Continuously improve the product based on ongoing feedback.
Development Cycle: Implement a two-week sprint cycle to develop and test new features or improvements. Each sprint will focus on addressing feedback from the previous cycle and implementing necessary changes.
Update Plan: Release updates every two weeks, incorporating user feedback and addressing any issues identified. After each release, collect new feedback and iterate accordingly to ensure the product continues to meet user needs effectively.
9. Conclusion
The Lean Startup Methodology offers a dynamic approach to product development and business innovation by emphasizing rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative improvement. It helps identify genuine customer needs, test solutions efficiently with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), and make informed decisions based on real feedback. This methodology fosters a customer-centric mindset, enabling businesses to adapt quickly, track progress through key metrics, and enhance their chances of long-term success.