Agile Sprint Management
I. Introduction
Agile Sprint Management is a dynamic approach to project management that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and iterative progress. In 2060, the methodologies and best practices have evolved, but the core principles remain essential for successful project execution. This document outlines a comprehensive Agile Sprint Management process tailored to modern needs.
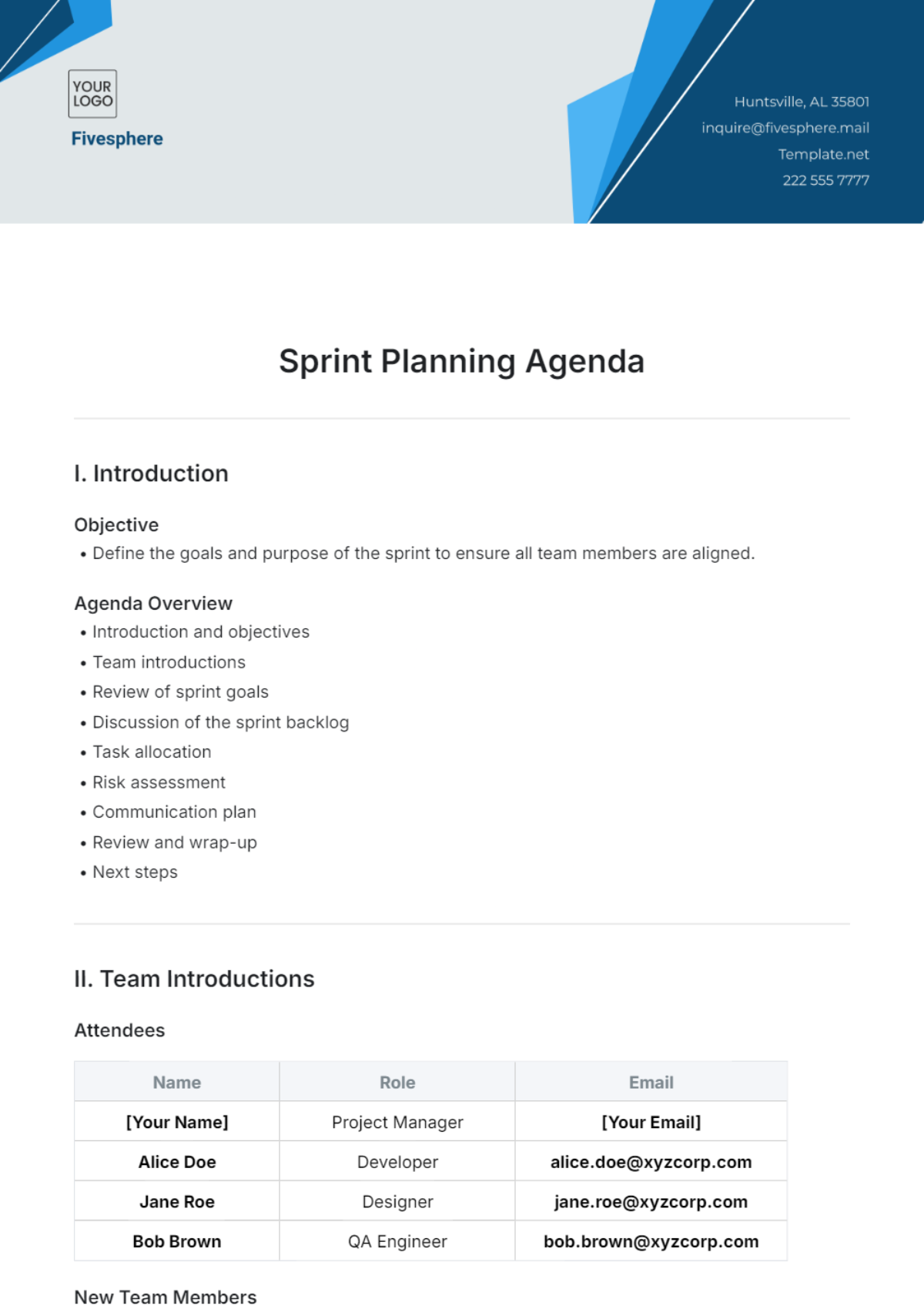
II. Sprint Planning
Objective Setting
In this phase, the primary goal is to define the objectives for the upcoming sprint. This involves setting clear, actionable goals aligned with the project's overall vision.
Example Objective:
Objective: Develop a new user interface for the client portal.
Outcome: Deliver a functional prototype with basic user interactions.
Backlog Refinement
Refine the product backlog by prioritizing tasks and ensuring they are well-defined. This step helps the team understand the scope and requirements of the sprint.
Backlog Example:
Task ID | Task Description | Priority | Estimated Effort | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Design wireframes | High | 8 hours | Pending |
2 | Implement login functionality | Medium | 12 hours | Pending |
3 | Integrate API for data fetch | Low | 6 hours | Pending |
III. Sprint Execution
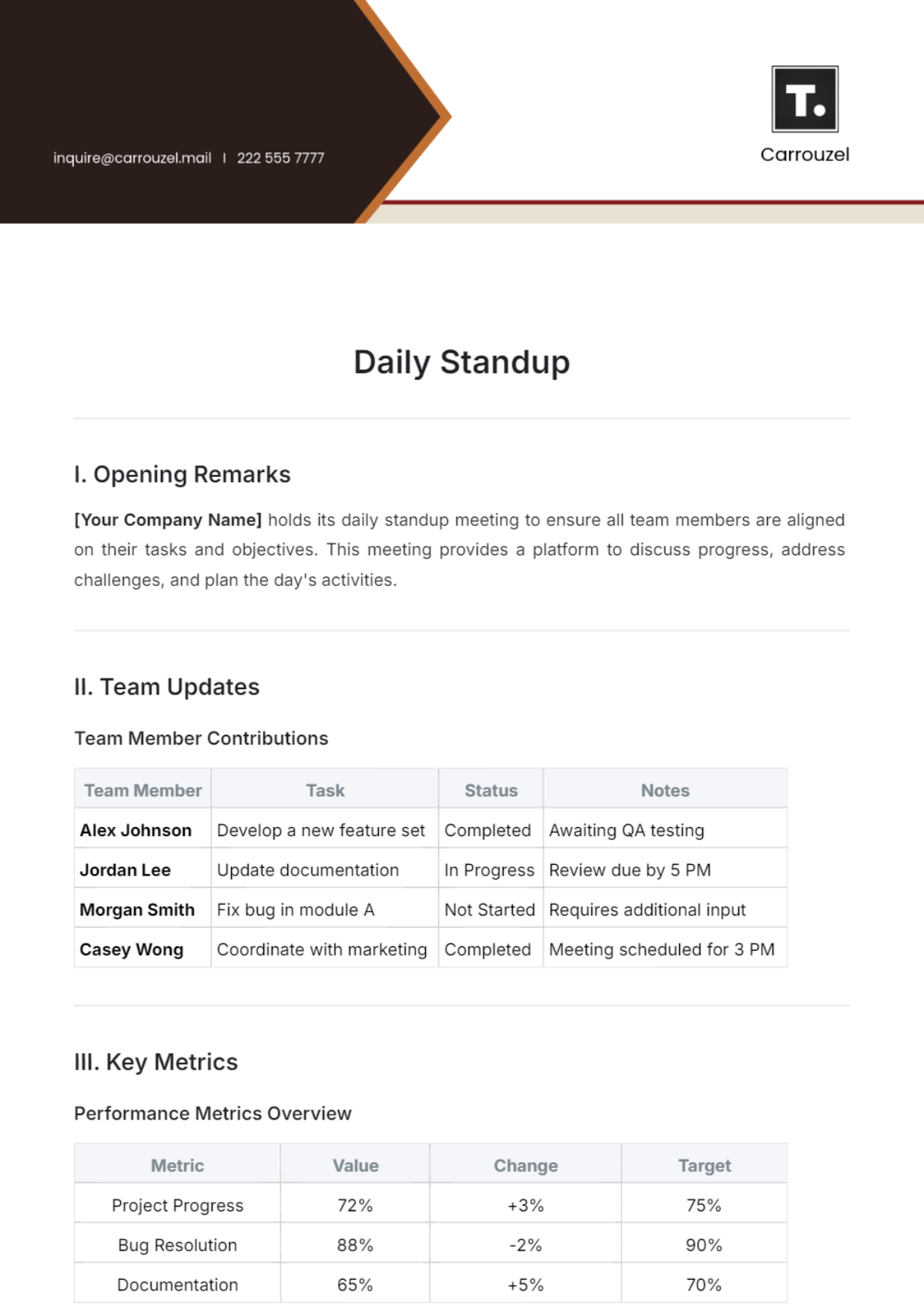
Daily Stand-Ups
Daily stand-up meetings are crucial for tracking progress, identifying roadblocks, and ensuring team alignment. These meetings are brief, typically lasting no more than 15 minutes.
Stand-Up Agenda:
What did you accomplish yesterday?
What will you work on today?
Are there any obstacles or issues?
Task Management
Utilize tools to track task progress and ensure that the team adheres to the sprint schedule. Tools like Kanban boards or digital task trackers can be beneficial.
Task Management Tools:
Tool Name | Description | Use Case | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
Jira | Comprehensive project tracking | Task management | Active |
Trello | Visual task management | Kanban boards | Active |
Asana | Project management and collaboration | General task tracking | Active |
IV. Sprint Review
Demonstration
At the end of the sprint, demonstrate the completed work to stakeholders. This session is crucial for gathering feedback and ensuring that the project aligns with stakeholder expectations.
Demonstration Checklist:
Complete Features: Verify that all planned features are demonstrated.
Feedback Collection: Gather feedback from stakeholders.
Action Items: Document any new tasks or changes requested.
Retrospective
Conduct a sprint retrospective to review what went well, what could be improved, and how the team can enhance performance in future sprints.
Retrospective Topics:
Topic | Discussion Points | Action Items |
|---|---|---|
What went well? | List successes and effective practices | Document successful strategies |
What could be improved? | Identify areas for improvement | Develop action plan for enhancements |
What will we do differently? | Discuss changes for future sprints | Assign tasks for implementation |
V. Conclusion
Agile Sprint Management remains a vital approach for managing projects in 2060. By adhering to the outlined steps—sprint planning, execution, review, and retrospective—teams can ensure a structured yet flexible approach to achieving project goals. For more information or assistance, please contact:
[Your Company Name]
Email: [Your Company Email]
Phone: [Your Company Number]
Address: [Your Company Address]
Contact Person: [Your Name]
Email: [Your Email]