Free Health & Safety Strategy

I. Executive Summary
In an era where workplace health and safety is paramount, [Your Company Name] is committed to establishing and maintaining a comprehensive Health & Safety Strategy that not only meets but exceeds industry standards. This strategy outlines our approach to ensuring the well-being of our employees, contractors, visitors, and the broader community. It is designed to mitigate risks, foster a culture of safety, and promote the continuous improvement of health and safety practices across all levels of our organization.
The strategy is structured to address current needs while also anticipating future challenges, particularly as we move toward the year 2050 and beyond. This forward-looking approach ensures that [Your Company Name] remains a leader in health and safety, adapting to emerging risks and regulatory changes with agility and foresight.
II. Health & Safety Objectives
A. Primary Objectives
Zero Harm Goal:
[Your Company Name] aims to achieve a Zero Harm environment where no employee, contractor, or visitor experiences injury or illness due to workplace activities. This objective is central to our Health & Safety Strategy and is pursued through rigorous risk assessment, preventive measures, and continuous education.Compliance with Regulations:
Compliance with local, national, and international health and safety regulations is a non-negotiable aspect of our strategy. By 2050, [Your Company Name] aims to lead the industry in compliance, setting benchmarks for others to follow.Fostering a Safety Culture:
A strong safety culture is essential for long-term success. [Your Company Name] is dedicated to embedding health and safety into the corporate culture, where every individual understands their role in maintaining a safe workplace and is empowered to act on it.
B. Long-Term Goals
Sustainability and Safety Integration:
By 2050, [Your Company Name] aims to integrate sustainability with health and safety practices fully. This includes reducing environmental hazards that can impact health and safety and ensuring that all operations are conducted with minimal ecological impact.Technological Advancement in Safety:
Embracing technology is crucial for the evolution of workplace safety. We aim to implement advanced safety technologies, such as wearable devices for real-time monitoring and AI-driven predictive analytics, to identify potential risks before they lead to incidents.Global Health & Safety Leadership:
[Your Company Name] aspires to be recognized globally as a leader in health and safety by 2050. This includes setting industry standards, influencing policy, and sharing best practices across borders.
III. Health & Safety Governance
A. Leadership and Accountability
Executive Oversight:
The Health & Safety Committee, led by a senior executive, will have the overall responsibility for implementing and monitoring the strategy. This committee will report directly to the Board of Directors, ensuring that health and safety remain a top priority at the highest levels of the organization.Roles and Responsibilities:
Every employee at [Your Company Name] has a role in ensuring health and safety. Clear roles and responsibilities will be defined, from top management to front-line workers, with specific accountability measures in place.Health & Safety Champions:
[Your Company Name] will designate Health & Safety Champions within each department. These individuals will act as the first point of contact for safety concerns and will play a key role in promoting safety culture within their teams.
B. Policy and Procedure Framework
Comprehensive Health & Safety Policy:
A detailed Health & Safety Policy will be maintained, outlining the company’s commitment to safety, the standards to be upheld, and the procedures to be followed. This policy will be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in regulations, industry practices, and organizational needs.Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
SOPs will be developed for all high-risk activities, ensuring that tasks are performed consistently and safely. These procedures will be made accessible to all employees and will be included in regular training programs.Emergency Response Plan:
An Emergency Response Plan will be in place to address potential incidents such as fires, chemical spills, or medical emergencies. This plan will be tested regularly through drills and will be updated based on the outcomes of these tests.
C. Continuous Improvement
Annual Health & Safety Audits:
Regular audits will be conducted to assess compliance with health and safety policies and procedures. These audits will identify areas for improvement, and action plans will be developed to address any gaps.Feedback Mechanisms:
Employees will be encouraged to provide feedback on health and safety practices. A formal feedback mechanism will be established, allowing for anonymous submissions and ensuring that all concerns are addressed promptly.Innovation in Safety Practices:
[Your Company Name] will foster a culture of innovation, encouraging employees to propose new ideas and solutions for improving health and safety. Successful innovations will be recognized and implemented company-wide.
IV. Risk Management
A. Risk Assessment Process
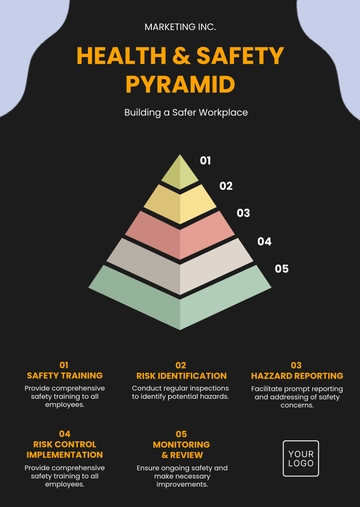
Hazard Identification:
A thorough process for identifying potential hazards in the workplace will be established. This will include regular inspections, employee reporting, and analysis of incident data to pinpoint areas of concern.Risk Evaluation and Prioritization:
Once hazards are identified, they will be evaluated based on their potential impact and likelihood. Risks will be prioritized, and resources will be allocated accordingly to address the most critical issues first.Control Measures:
Appropriate control measures will be implemented to mitigate identified risks. These measures will be categorized into engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment (PPE) to ensure a comprehensive approach to risk management.
B. Incident Management
Incident Reporting System:
[Your Company Name] will implement an efficient incident reporting system that allows for quick and accurate reporting of all incidents, near-misses, and unsafe conditions. This system will be accessible to all employees and will facilitate prompt corrective action.Incident Investigation Protocol:
Every reported incident will be thoroughly investigated to determine the root cause. A structured protocol will be followed, including gathering evidence, interviewing witnesses, and analyzing contributing factors.Lessons Learned and Communication:
The outcomes of incident investigations will be communicated across the organization to prevent recurrence. A “lessons learned” database will be maintained, and regular briefings will be held to share insights and best practices.
C. Monitoring and Review
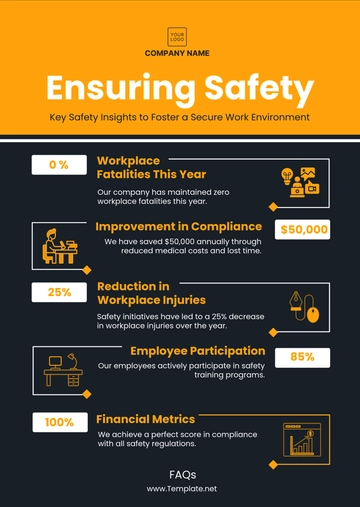
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
A set of KPIs will be established to monitor the effectiveness of health and safety initiatives. These KPIs will include metrics such as the number of incidents, near-misses, and days lost due to injury, allowing for ongoing performance evaluation.Regular Reviews and Updates:
The Health & Safety Strategy will be reviewed annually to ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness. This review will consider changes in the operating environment, emerging risks, and feedback from employees and stakeholders.Benchmarking:
[Your Company Name] will benchmark its health and safety performance against industry leaders to identify areas for improvement. Benchmarking will involve comparing KPIs, best practices, and innovative approaches to ensure that we remain at the forefront of health and safety.
V. Health & Safety Training
A. Training Programs
Induction Training:
All new employees will undergo comprehensive health and safety induction training. This training will cover the company’s policies, procedures, and the specific hazards associated with their role. Refresher courses will be mandatory every two years.Role-Specific Training:
Tailored training programs will be developed for different roles within the organization. For example, employees working with hazardous materials will receive specialized training on safe handling procedures, while office staff will focus on ergonomic practices.Emergency Preparedness Training:
Regular emergency preparedness drills will be conducted to ensure that all employees are familiar with the procedures to follow in case of an emergency. This training will cover evacuation procedures, first aid, and the use of emergency equipment.
B. Competency Management
Training Needs Assessment:
A formal training needs assessment will be conducted annually to identify gaps in employee knowledge and skills. This assessment will guide the development of training programs and ensure that all employees are competent in their roles.Certification and Accreditation:
Employees involved in high-risk activities will be required to obtain relevant certifications and accreditations. [Your Company Name] will provide support for employees to attain these qualifications, ensuring that they meet industry standards.Continuous Professional Development (CPD):
[Your Company Name] will promote continuous professional development by offering opportunities for employees to attend workshops, seminars, and conferences on health and safety. This will ensure that our workforce remains knowledgeable and up-to-date with the latest industry developments.
C. Training Evaluation
Feedback and Assessment:
After each training session, participants will provide feedback to assess the effectiveness of the training. This feedback will be used to refine and improve future training programs.Training Outcomes and Impact Analysis:
The impact of training programs on health and safety performance will be monitored through KPIs and incident data. This analysis will help to determine whether training is leading to measurable improvements in safety.Recognition and Incentives:
[Your Company Name] will recognize and reward employees who demonstrate exceptional commitment to health and safety. Incentive programs will be introduced to encourage ongoing participation in training and adherence to safety protocols.
VI. Health & Safety Communication
A. Internal Communication
Regular Safety Meetings:
Regular safety meetings will be held at all levels of the organization to discuss health and safety performance, share updates on ongoing initiatives, and address any emerging concerns. These meetings will ensure that health and safety remain a priority throughout [Your Company Name].Safety Bulletins and Alerts:
Safety bulletins and alerts will be issued to communicate important safety information, such as changes to procedures, updates on regulatory requirements, and lessons learned from incidents. These communications will be distributed through multiple channels to ensure they reach all employees.Employee Engagement:
[Your Company Name] will actively engage employees in health and safety discussions through forums, surveys, and suggestion boxes. This will create a two-way communication channel, allowing employees to contribute to safety initiatives and feel invested in the outcomes.
B. External Communication
Stakeholder Communication:
[Your Company Name] will maintain open communication with external stakeholders, including regulatory bodies, industry associations, and the local community. Regular updates will be provided on our health and safety performance and initiatives, ensuring transparency and building trust.Health & Safety Reports:
Annual Health & Safety Reports will be published, detailing our performance against objectives, key achievements, and areas for improvement. These reports will be shared with stakeholders and made available on our website.Crisis Communication Plan:
In the event of a major incident, a Crisis Communication Plan will be activated to manage communication with the public, media, and other stakeholders. This plan will ensure that accurate information is disseminated quickly and that [Your Company Name] maintains control of the narrative.
VII. Health & Safety Performance
A. Performance Measurement
Data Collection and Analysis:
Comprehensive data on health and safety performance will be collected and analyzed regularly. This data will include incident reports, audit findings, and employee feedback, providing a robust foundation for performance measurement.Trend Analysis:
Trend analysis will be conducted to identify patterns in health and safety performance over time. This analysis will help to predict potential issues and inform proactive measures to address emerging risks.Continuous Monitoring:
Real-time monitoring systems will be implemented to track key safety metrics continuously. This will enable rapid response to any deviations from safety standards and ensure that potential issues are addressed before they escalate.
B. Performance Reporting
Monthly and Quarterly Reports:
Health and safety performance will be reported monthly and quarterly to the Health & Safety Committee and the Board of Directors. These reports will provide detailed insights into performance against KPIs, progress on initiatives, and any areas of concern.Annual Health & Safety Review:
An annual review will be conducted to assess the overall effectiveness of the Health & Safety Strategy. This review will include a comprehensive evaluation of performance, lessons learned, and recommendations for the coming year.Benchmarking Reports:
[Your Company Name] will produce benchmarking reports comparing our health and safety performance with industry peers. These reports will help to identify best practices and areas where we can improve our performance.
C. Continuous Improvement
Root Cause Analysis:
Root cause analysis will be conducted for all significant incidents and near-misses. This analysis will identify underlying causes and inform the development of preventive measures to avoid recurrence.Action Plans:
Action plans will be developed to address any issues identified through audits, reviews, and feedback mechanisms. These plans will include clear timelines, responsible parties, and progress monitoring to ensure that improvements are implemented effectively.Recognition of Success:
[Your Company Name] will recognize and celebrate success in health and safety performance. Achievements will be highlighted in internal communications, and awards will be given to teams and individuals who have made significant contributions to improving safety.
VIII. Future Considerations
A. Adapting to New Risks
Climate Change and Health:
As we approach 2050, climate change will present new health and safety challenges. [Your Company Name] will proactively address these challenges by incorporating climate resilience into our strategy, such as preparing for extreme weather events and their impact on workplace safety.Emerging Technologies:
The rapid development of new technologies, such as AI and robotics, will introduce both opportunities and risks. [Your Company Name] will stay ahead of these trends by integrating new technologies into our safety practices while also managing any associated risks.Global Health Trends:
Global health trends, such as pandemics and the rise of chronic diseases, will have implications for workplace safety. [Your Company Name] will monitor these trends closely and adapt our Health & Safety Strategy to ensure that we are prepared for any eventualities.
B. Strategic Partnerships
Collaboration with Industry Leaders:
[Your Company Name] will seek to establish strategic partnerships with industry leaders in health and safety. These partnerships will allow us to share knowledge, adopt best practices, and stay at the forefront of safety innovation.Engagement with Regulators:
We will actively engage with regulators to influence the development of health and safety policies. By participating in industry forums and working groups, [Your Company Name] will help shape the future of workplace safety.Community Involvement:
[Your Company Name] will continue to engage with the communities where we operate, supporting local safety initiatives and contributing to broader societal well-being.
C. Investment in Health & Safety
Budget Allocation:
A dedicated budget for health and safety initiatives will be maintained, ensuring that sufficient resources are available to implement our strategy effectively. This budget will be reviewed annually and adjusted based on evolving needs and priorities.Investment in Technology:
Significant investment will be made in safety-related technologies, such as advanced monitoring systems, AI-driven analytics, and innovative PPE. These investments will ensure that [Your Company Name] remains at the cutting edge of safety.Long-Term Planning:
Health and safety considerations will be integrated into [Your Company Name]'s long-term strategic planning. This includes anticipating future risks, aligning with global safety trends, and ensuring that our strategy remains relevant and effective as we move toward 2050 and beyond.
IX. Conclusion
[Your Company Name] is dedicated to ensuring the health and safety of all employees, contractors, visitors, and the wider community. Our Health & Safety Strategy is a dynamic document designed to evolve in response to changing conditions and emerging risks. As we look toward 2050 and beyond, [Your Company Name] will continue to lead by example, fostering a culture of safety, investing in innovation, and striving for excellence in all aspects of health and safety management. This strategy not only protects our people but also strengthens our reputation as a responsible and forward-thinking organization.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Develop a robust health and safety strategy with the Health & Safety Strategy Template from Template.net. This customizable template aids in outlining your organization's safety goals and objectives. Editable in our AI Editor Tool, it supports you in creating a proactive approach to health and safety management. Download now to elevate your safety strategy!