Free Safety Observational Study

Prepared by: [Your Name]
Date: [Date]
1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose
This Safety Observational Study aims to identify unsafe behaviors and environmental hazards within the workplace. The study aims to provide recommendations that improve safety standards, reduce accidents, and ensure regulatory compliance by analyzing these factors.
1.2 Scope
This study was conducted over three months in various departments of a manufacturing plant. The focus was on high-risk areas such as the assembly line, machine operation zones, and material handling sections, where safety incidents are more likely to occur.
1.3 Objective
To assess the compliance of employees with safety protocols.
To identify environmental and operational hazards that could lead to accidents.
To provide actionable recommendations for improving safety standards.
2. Methodology
2.1 Observation Strategy
A non-intrusive, real-time observational approach was utilized to capture authentic workplace behaviors and conditions. The study was designed to avoid influencing the actions of workers and to provide a clear view of actual safety practices in the field.
2.2 Sample Population
The study observed a total of 100 employees across various shifts, focusing on machine operators, assembly workers, and material handlers.
2.3 Duration
The observations were conducted over 12 weeks, covering all operational hours, including day and night shifts.
2.4 Data Collection Tools
Observation checklists: Used to monitor compliance with safety rules.
Photographs: Captured unsafe conditions for further analysis.
Interviews: Conducted with employees to gain insights into their perception of safety in the workplace.
2.5 Observation Criteria
The following criteria were used to assess safety compliance:
Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
Machine operation safety
Proper lifting techniques
Adherence to signage and safety barriers
Dangers in the environment, such as spills and blocked pathways.
3. Observations and Findings
3.1 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Compliance
A. PPE Use
Observation:
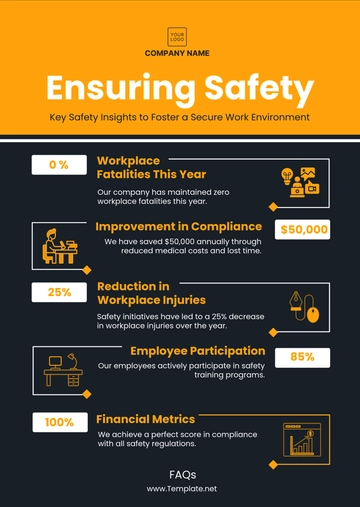
PPE use was inconsistent, with 20% of employees failing to wear hard hats in high-risk areas, and 15% of workers neglecting to wear gloves while handling hazardous materials.
B. Non-Compliance by Department
Department | PPE Non-Compliance Rate (%) |
|---|---|
Assembly Line | 25% |
Machine Operations | 15% |
Material Handling | 20% |
Finding:
A significant portion of employees did not fully comply with PPE requirements, particularly in the Assembly Line department. The reasons cited for non-compliance included discomfort, lack of training, and poor enforcement by supervisors.
3.2 Machine Operation Safety
A. Machinery Handling Practices
Observation:
25% of machine operators did not follow proper lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance or troubleshooting activities, significantly increasing the risk of accidents.
List of Unsafe Machine Practices Observed:
Failure to use LOTO procedures
Operating machinery without guards in place
Overriding safety mechanisms for efficiency
Finding:
Inconsistent application of machine safety protocols, particularly LOTO procedures, poses a serious risk to workers. The primary reasons identified were a lack of refresher training and a focus on production speed over safety.
3.3 Proper Lifting Techniques
A. Lifting and Handling Injuries
Observation:
25% of employees involved in material handling lifted items incorrectly, leading to a higher risk of musculoskeletal injuries. Observers noted that employees often bent their backs instead of using their legs to lift heavy objects.
B. Training Deficiencies
Finding:
Workers in material handling had insufficient training in proper lifting techniques. This gap resulted in frequent violations of safe lifting protocols, particularly during high-pressure periods when productivity was prioritized.
3.4 Environmental Hazards
A. Obstructed Walkways and Spills
Observation:
Several environmental hazards were observed, including obstructed walkways (30% of inspected areas), improper storage of materials, and spills that were not immediately cleaned.
List of Common Environmental Hazards:
Walkways obstructed by tools and materials
Spills of lubricants and other liquids
Inadequate signage for slippery surfaces
Finding:
Environmental hazards were frequently observed, particularly in high-traffic areas. These hazards posed significant risks for slips, trips, and falls, which could result in serious injuries.
4. Analysis
4.1 Behavioral Patterns
The study identified several key behavioral patterns contributing to safety violations. In particular, a culture of “short-cutting” safety procedures for the sake of productivity was prevalent, especially in departments with tight production deadlines. A lack of enforcement exacerbated this by supervisors.
Key Factors Impacting Safety:
Lack of consistent safety training
Poor supervision and enforcement
Pressure to maintain high productivity
Inadequate reporting and addressing of environmental hazards
4.2 Trends
The most common safety issues revolved around PPE non-compliance and improper handling of machinery. Additionally, environmental hazards like spills and obstructed walkways were pervasive and often went unaddressed, creating a cycle of neglect.
5. Recommendations
5.1 Strengthen PPE Compliance
Action: Conduct regular PPE inspections and implement penalties for non-compliance.
Rationale: Ensuring that employees wear the proper protective gear can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
5.2 Reinforce Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures
Action: Provide refresher training on LOTO procedures and audit compliance weekly.
Rationale: Proper LOTO procedures are critical for preventing machine-related injuries and should be strictly enforced.
5.3 Provide Ergonomic Training for Material Handlers
Action: Provide instruction on proper lifting methods and supply necessary equipment, such as back supports.
Rationale: Preventing musculoskeletal injuries through proper lifting methods can reduce lost workdays and increase overall worker safety.
5.4 Improve Environmental Hazard Management
Action: Implement stricter housekeeping policies, including immediate cleanup of spills and routine inspection of walkways.
Rationale: Addressing environmental hazards promptly will reduce accidents related to slips, trips, and falls.
6. Conclusion
This Safety Observational Study revealed several safety concerns, particularly in PPE use, machine handling practices, and environmental hazard management. These findings highlight the need for more rigorous training, enforcement, and accountability measures within the workplace. Implementing the recommended actions will probably result in a safer working environment, reduce accidents, and promote a culture of safety compliance.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Ensure thorough safety assessments with the Safety Observational Study Template from Template.net. This fully customizable and editable template allows you to document and analyze safety observations easily. Editable in our Ai Editor Tool, it offers a user-friendly experience, helping you tailor content to meet your specific requirements for efficient and professional safety studies.