Observational Study Methods
Principal Investigator: [Your Name]
Affiliation: [Your Company Name]
Date: [Date]
1. Introduction
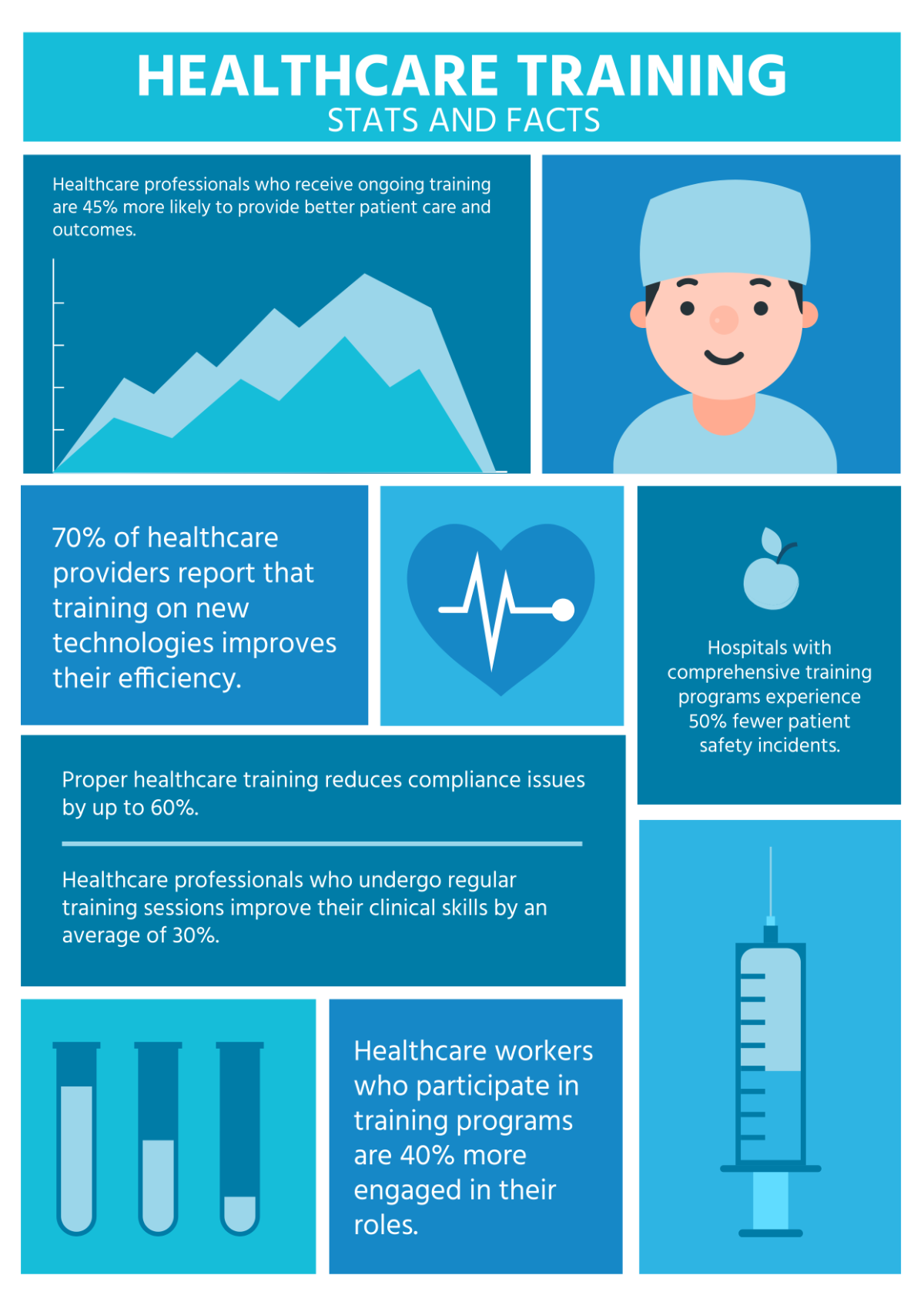
This observational study aims to understand customer behavior in a retail environment, focusing on how customers interact with store layouts, products, and staff. By observing customers in their natural shopping environment, the study seeks to identify patterns and preferences that can inform store design and improve customer service.
2. Methodology
2.1 Definition and Purpose
This study involves observing and recording customer behavior within a retail store without intervening or altering the shopping experience. The purpose is to gather authentic data on how customers navigate the store, select products, and interact with staff.
2.2 Types of Observational Study Methods
Naturalistic Observation
Description: Observe customers as they shop in the store without any interference or manipulation.
Example: Watching customers' routes through the store to identify common pathways and areas of high traffic.
Example: Noting how customers interact with product displays and in-store promotions.
Structured Observation
Description: Using a systematic approach with predefined criteria to record specific customer behaviors.
Example: Employing a checklist to track how often customers use self-checkout stations versus traditional checkout lanes.
Example: Using a coding system to classify types of customer interactions with sales associates (e.g., asking for help, making a purchase).
2.3 Data Collection Techniques
Direct Observation
Description: Observing and noting customer behavior in real-time without recording devices.
Example: Watching customers in different sections of the store and recording their actions and interactions.
Example: Taking notes on how long customers spend in specific areas of the store.
Video Recording
Description: Using cameras to capture customer behavior for later analysis.
Example: Installing cameras in key areas (e.g., entrance, checkout lanes) to record customer movement and interactions.
Example: Reviewing footage to analyze customer reactions to in-store displays and promotions.
Field Notes
Description: Documenting observations in detailed notes during or immediately after the observation period.
Example: Recording observations on customer behavior and interactions in a notebook.
Example: Writing reflections on patterns noticed during the observation sessions.
3. Results
3.1 Data Analysis
Quantitative Analysis
Description: Analyzing numerical data to identify patterns and trends.
Example: Calculating the average time customers spend in different sections of the store.
Example: Analyzing the frequency of customer interactions with staff to determine service needs.
Section | Average Time Spent | Customer Interactions |
|---|---|---|
Entrance | 5 minutes | 10 interactions/hour |
Electronics | 15 minutes | 5 interactions/hour |
Checkout | 7 minutes | 20 interactions/hour |
Qualitative Analysis
Description: Examining narrative data to understand the context and meaning behind customer behaviors.
Example: Analyzing how customers respond to promotional displays based on video recordings and field notes.
Example: Identifying common themes in customer feedback and interactions with staff.
3.2 Patterns Identified
High Traffic Areas: Customers frequently visit electronics and checkout sections.
Promotional Impact: Customers show increased interest in products featured in end-of-aisle displays.
Customer Service Needs: A high interaction rate in checkout areas suggests a need for additional staff or improved self-checkout options.
4. Discussion
4.1 Implications
Understanding customer behavior provides valuable insights for improving store layout, product placement, and customer service. By addressing observed patterns and preferences, stores can enhance the shopping experience and potentially increase sales.
4.2 Limitations
Observer Bias: The presence of observers may influence customer behavior.
Generalizability: Findings may be specific to the observed store and may not apply to all retail environments.
4.3 Recommendations
Optimize Store Layout: Reorganize high-traffic areas to improve customer flow and accessibility.
Enhance Promotions: Increase visibility and placement of promotional displays to capture customer interest.
Improve Customer Service: Address identified needs for additional staff or support in high-interaction areas.
5. Conclusion
This observational study provides a detailed analysis of customer behavior in a retail environment. The insights gained can guide store improvements and enhance the overall shopping experience. Future studies should consider expanding to different store types and locations to validate and extend these findings.
6. References
Doe, M. J. (2050). Understanding consumer behavior. Academic Press.
Retail Insights. (2052, August 10). Analyzing customer behavior: Best practices. Retrieved from https://www.retailinsights.com/customer-behavior-analysis