Concept of Operations (CONOPS)
1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose
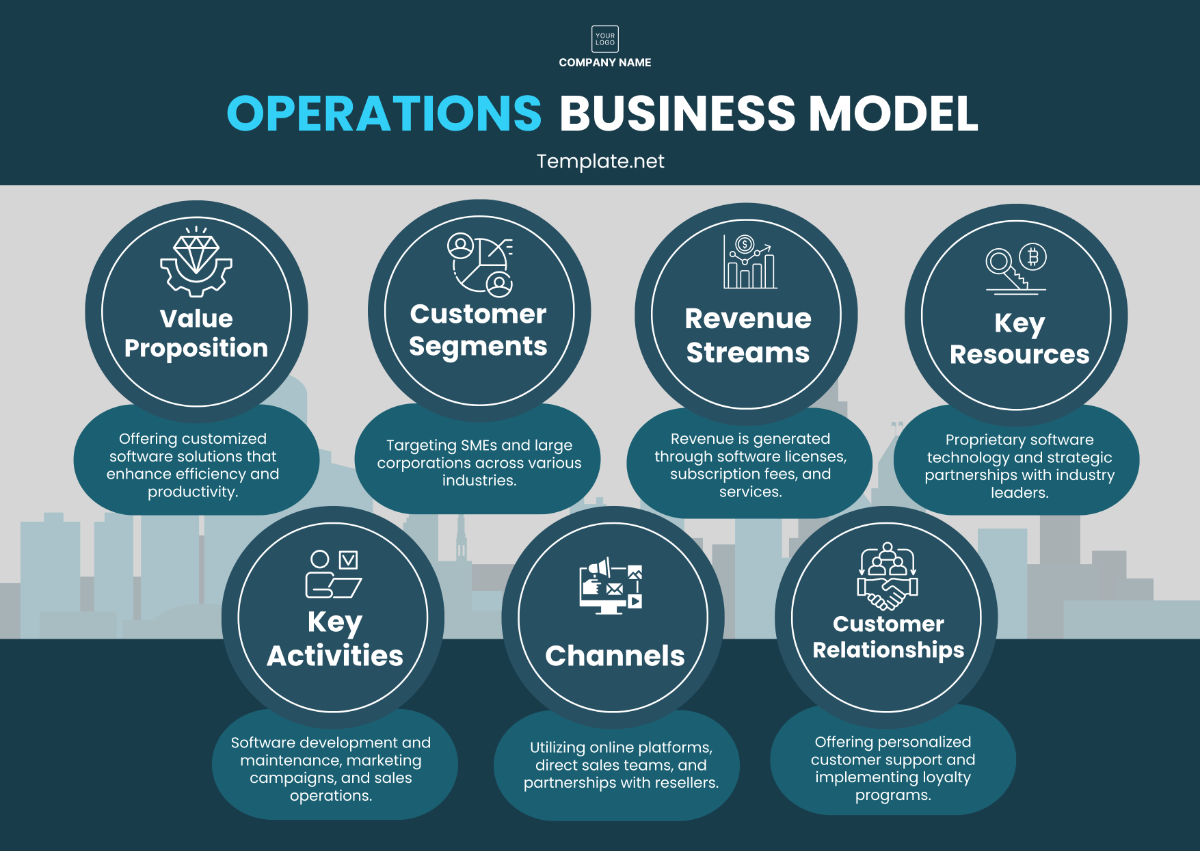
The Concept of Operations (CONOPS) serves as a foundational document for [Your Company Name], providing a comprehensive overview of our operational framework and strategic approach from 2050 onwards. This document is designed to ensure that all organizational processes, from high-level strategy to daily operational activities, are clearly defined and aligned with the company’s vision and goals. The CONOPS will guide the development, implementation, and management of our operational activities, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and effectiveness across all levels of the organization.
The purpose of this CONOPS is not only to outline the operational strategies but also to facilitate communication and understanding among stakeholders, including employees, partners, and customers. By detailing the operational processes, roles, responsibilities, and resources, this document aims to provide a clear and actionable plan for achieving our strategic objectives. The CONOPS will evolve as [Your Company Name] grows and adapts to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and regulatory requirements.
1.2 Scope
The scope of this CONOPS encompasses the entirety of [Your Company Name]'s operational activities, including but not limited to:
Core Services: Detailed descriptions of the products and services offered, including delivery methods and customer engagement strategies.
Customer Relationship Management: Strategies for managing customer interactions, maintaining satisfaction, and fostering loyalty.
Supply Chain Logistics: Processes related to sourcing, procurement, inventory management, and distribution.
Financial Operations: Budgeting, financial planning, revenue management, and expense tracking.
Information Technology Systems: Integration and management of technology infrastructure, cybersecurity measures, and data management.
Human Resources Management: Recruitment, training, performance management, and employee retention strategies.
This CONOPS will cover operational strategies from 2050 to 2100, incorporating future trends and predictions to ensure long-term relevance and adaptability. The document will outline key milestones, expected challenges, and mitigation strategies to guide the company through its growth and evolution.
2. Operational Objectives
2.1 Short-term (2050-2060)
2.1.1 Sustainability and Environmental Compliance
Objective: To achieve significant reductions in environmental impact and align with global sustainability initiatives.
Strategies:
Renewable Energy Transition: Implementing solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources across all operational sites. By 2055, all facilities will be powered by renewable energy.
Carbon Footprint Reduction: Adopting energy-efficient technologies and practices to reduce carbon emissions by [40%] from current levels.
Waste Management: Enhancing recycling programs and adopting zero-waste policies to minimize landfill use and waste generation.
2.1.2 Technological Integration
Objective: To leverage cutting-edge technologies to streamline operations and enhance productivity.
Strategies:
Automation: Integrating robotics and AI-driven automation systems to optimize manufacturing, logistics, and customer service processes.
Data Analytics: Utilizing big data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, operational performance, and market trends.
Smart Infrastructure: Implementing IoT (Internet of Things) devices to monitor and control operational processes in real time.
2.1.3 Market Expansion
Objective: To establish a stronger presence in emerging markets and increase global market share.
Strategies:
Regional Partnerships: Forming strategic alliances with local companies to facilitate market entry and expansion.
Product Localization: Adapting products and services to meet the specific needs and preferences of new regional markets.
Brand Awareness Campaigns: Launching targeted marketing campaigns to build brand recognition and attract customers in new markets.
2.2 Long-term (2061-2100)
2.2.1 Global Market Leadership
Objective: To become a leading global player in the industry, setting benchmarks for excellence and innovation.
Strategies:
Global Presence: Expanding operations into new geographic regions, focusing on high-growth areas such as Africa and Southeast Asia.
Innovation Hub: Establishing research and development centers to drive innovation and maintain competitive advantage.
Customer-Centric Approach: Continuously evolving products and services to meet changing customer needs and preferences.
2.2.2 Human Capital Development
Objective: To build a highly skilled and motivated workforce capable of driving the company’s growth and success.
Strategies:
Continuous Learning: Implementing ongoing training and development programs to keep employees updated on the latest industry trends and technologies.
Leadership Development: Fostering a culture of leadership and career progression through mentorship and leadership training programs.
Employee Well-being: Enhancing employee benefits and work-life balance initiatives to improve job satisfaction and retention.
2.2.3 Customer-Centric Innovations
Objective: To deliver innovative solutions that are highly responsive to customer needs and preferences.
Strategies:
Personalized Offerings: Utilizing AI and machine learning to create personalized product recommendations and services.
Enhanced Customer Experience: Implementing advanced customer support systems, including virtual assistants and chatbots, to provide real-time assistance.
Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing robust mechanisms for collecting and analyzing customer feedback to drive continuous improvement.
3. Operational Structure
3.1 Organizational Hierarchy
The organizational hierarchy at [Your Company Name] is structured to ensure clear communication, efficient decision-making, and effective execution of operational strategies. The hierarchy includes multiple levels, each with distinct roles and responsibilities.
3.1.1 Executive Leadership
The Executive Leadership team provides strategic direction and oversight for the entire organization. Key roles include:
Chief Executive Officer (CEO): Sets the overall strategic vision and ensures alignment with long-term goals.
Chief Financial Officer (CFO): Oversees financial planning, budgeting, and reporting, ensuring financial stability and growth.
Chief Operating Officer (COO): Manages daily operations, including supply chain, production, and service delivery.
Chief Technology Officer (CTO): Leads technology strategy and implementation, driving innovation and digital transformation.
3.1.2 Middle Management
Middle management serves as the bridge between executive leadership and operational teams. Responsibilities include:
Department Heads: Oversee specific functional areas such as marketing, sales, and human resources, ensuring alignment with overall strategy.
Regional Managers: Manage operations within designated geographic areas, implementing company policies and strategies locally.
3.1.3 Operational Teams
Operational teams are responsible for executing daily tasks and achieving operational goals. Key roles include:
Team Leaders: Supervise and coordinate the activities of team members, ensuring adherence to processes and standards.
Employees: Carry out specific operational tasks, including customer service, production, and logistics.
3.2 Roles and Responsibilities
3.2.1 CEO
Role: The CEO is responsible for the overall strategic direction and leadership of [Your Company Name].
Responsibilities:
Strategic Vision: Defining the company’s long-term goals and strategies.
Stakeholder Relations: Building and maintaining relationships with key stakeholders, including investors, partners, and government agencies.
Performance Oversight: Monitoring the company’s performance and making high-level decisions to drive growth and sustainability.
3.2.2 COO
Role: The COO is responsible for the efficient execution of daily operations and the implementation of strategic initiatives.
Responsibilities:
Operational Efficiency: Streamlining processes and ensuring that operational activities are conducted efficiently and effectively.
Team Management: Leading and supporting middle management and operational teams.
Technology Integration: Overseeing the implementation of new technologies and systems to enhance operational performance.
3.2.3 CFO
Role: The CFO is responsible for managing the financial health of the company.
Responsibilities:
Financial Planning: Developing and managing budgets, financial forecasts, and investment plans.
Compliance: Ensuring compliance with financial regulations and standards.
Reporting: Providing accurate and timely financial reports to stakeholders and executive leadership.
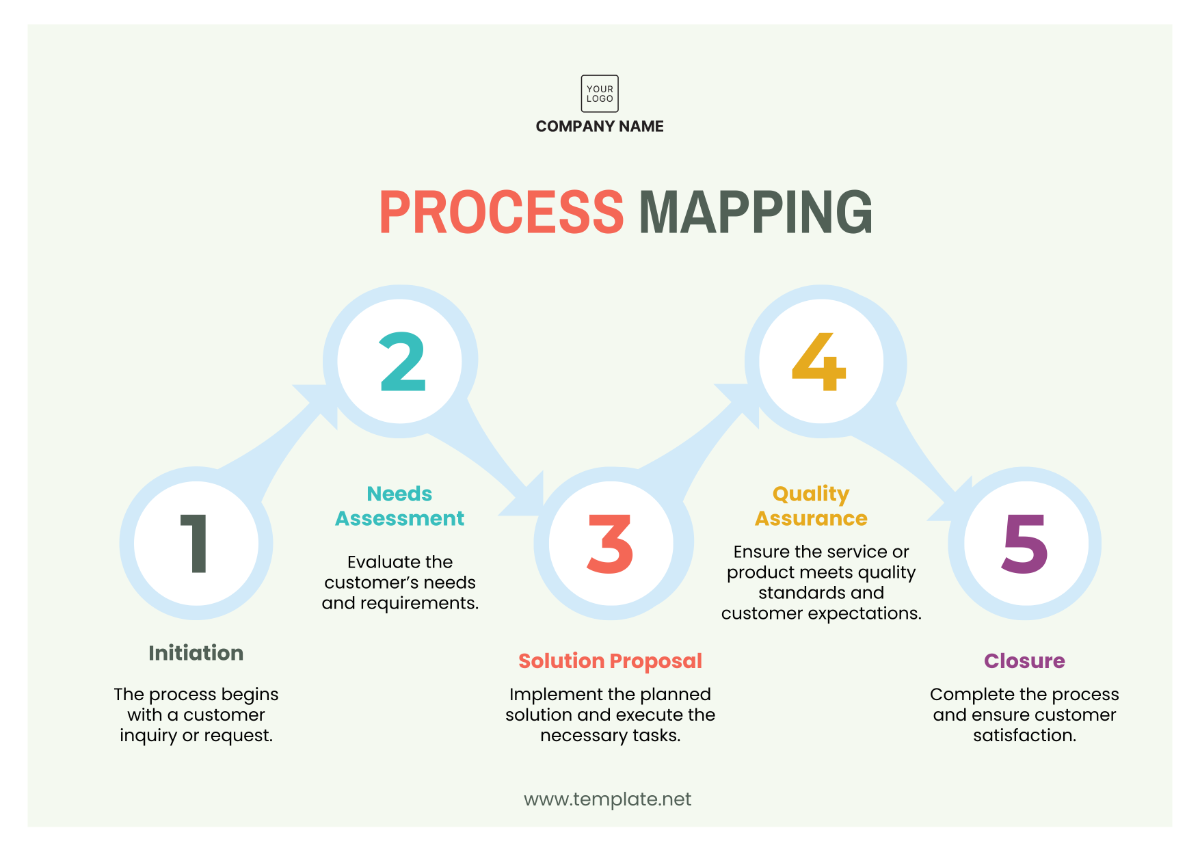
4. Operational Processes
4.1 Core Processes
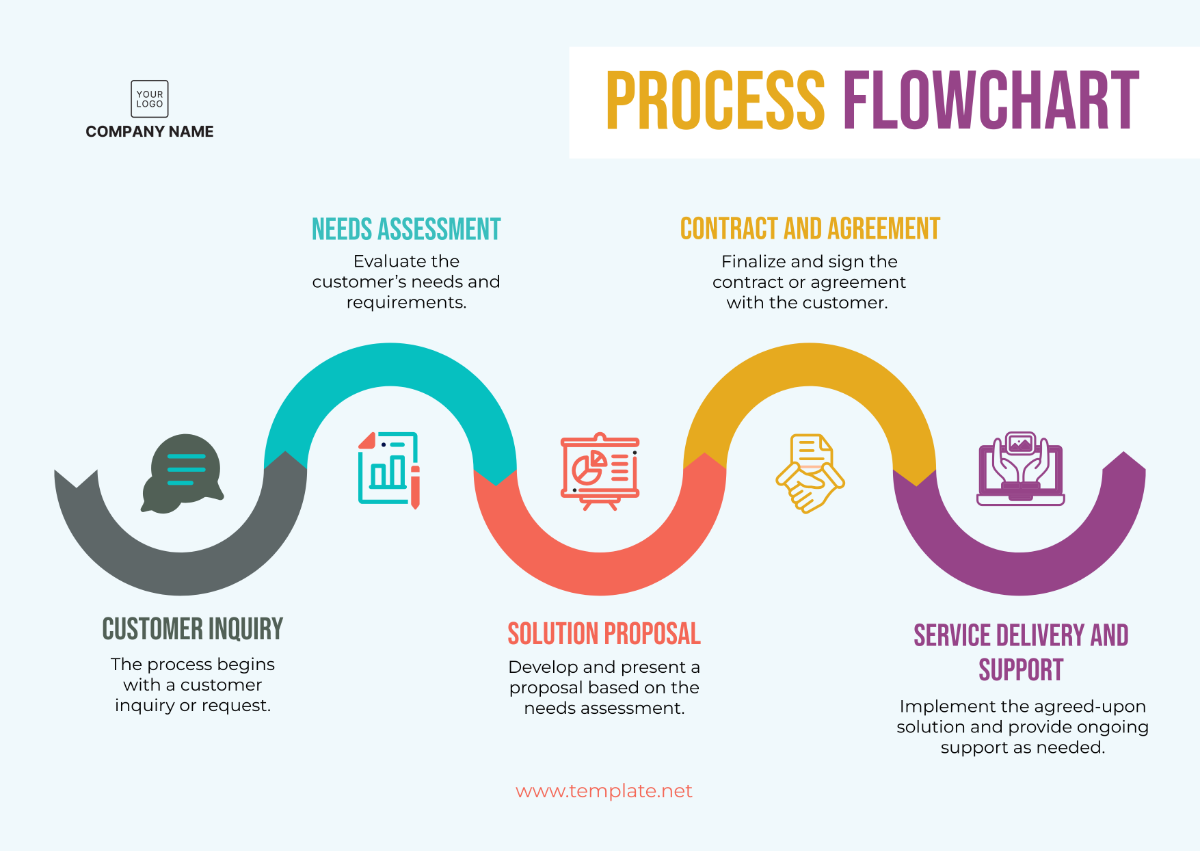
4.1.1 Service Delivery
Service delivery is a critical component of [Your Company Name]'s operations, encompassing all aspects of product and service provision to customers.
Processes:
Order Management: Handling customer orders from receipt to fulfillment, ensuring timely and accurate delivery.
Customer Support: Providing assistance and resolving issues through various channels, including phone, email, and live chat.
Quality Assurance: Implementing quality control measures to ensure that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations.
4.1.2 Supply Chain Management
The supply chain management process involves the coordination of activities from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to customers.
Processes:
Sourcing: Identifying and selecting suppliers based on quality, cost, and sustainability criteria.
Procurement: Purchasing raw materials and components required for production.
Logistics: Managing the transportation and warehousing of goods to ensure efficient and timely delivery.
Inventory Management: Monitoring stock levels and managing inventory to prevent shortages and overstocking.
Process | Technology Integration (2050-2100) | Sustainability Focus |
|---|---|---|
Sourcing | AI-driven supplier selection | Preferential sourcing from eco-friendly suppliers |
Procurement | Automated procurement platforms | Green procurement practices |
Logistics | Autonomous vehicles and drones for delivery | Reducing carbon emissions through optimized routes |
Inventory Management | Real-time inventory tracking systems | Minimizing waste through advanced forecasting |
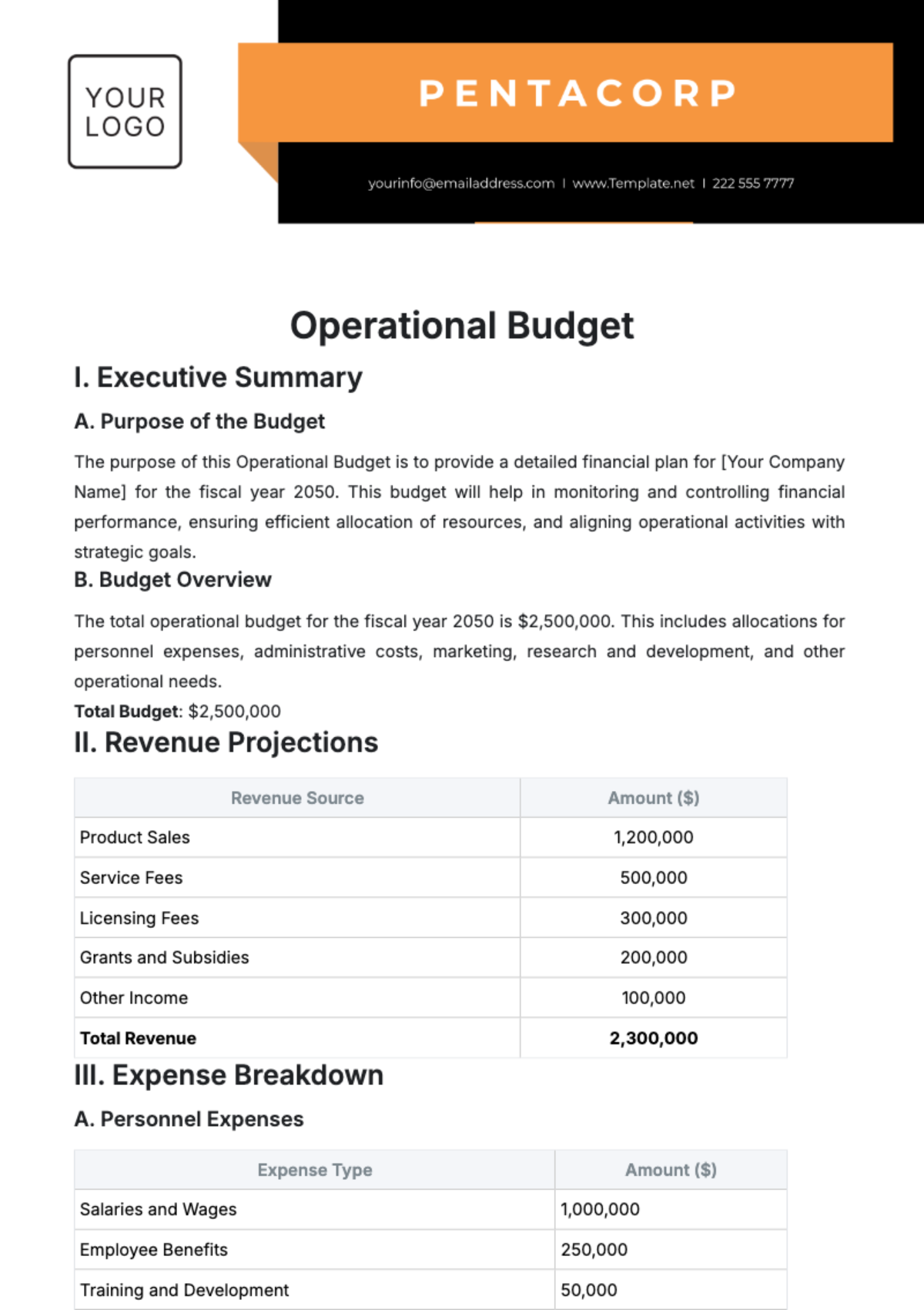
4.1.3 Financial Management
Financial management encompasses all activities related to budgeting, financial planning, and reporting.
Processes:
Budgeting: Developing annual budgets and financial forecasts to guide operational and strategic decisions.
Expense Tracking: Monitoring and controlling expenses to ensure alignment with budgetary constraints.
Revenue Management: Managing revenue streams and ensuring accurate billing and collections.
4.2 Supporting Processes
4.2.1 Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is integral to the operation and management of [Your Company Name]'s systems and processes.
Processes:
IT Infrastructure: Implementing and maintaining hardware and software systems to support operational activities.
Cybersecurity: Protecting the company’s data and systems from cyber threats through advanced security measures.
Data Management: Managing and analyzing data to support decision-making and operational efficiency.
4.2.2 Human Resources
Human resources (HR) management focuses on recruiting, developing, and retaining a talented workforce.
Processes:
Recruitment: Attracting and hiring qualified candidates to fill open positions.
Training and Development: Providing employees with the skills and knowledge needed to perform their roles effectively.
Performance Management: Evaluating employee performance and providing feedback and development opportunities.
4.2.3 Marketing and Sales
Marketing and sales processes are essential for promoting [Your Company Name]'s products and services and driving revenue growth.
Processes:
Marketing Campaigns: Developing and executing marketing strategies to build brand awareness and attract customers.
Sales Strategies: Implementing sales tactics and techniques to drive revenue and achieve sales targets.
Customer Relationship Management: Managing interactions with customers to enhance satisfaction and loyalty.
5. Performance Measurement
5.1 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are metrics used to evaluate the effectiveness of [Your Company Name]'s operational activities and strategic initiatives.
KPIs:
Customer Satisfaction: Measured through surveys and feedback mechanisms to assess the quality of products and services.
Operational Efficiency: Evaluated based on metrics such as cycle time, production yield, and cost per unit.
Financial Performance: Monitored through financial ratios, revenue growth, and profitability metrics.
5.1.1 Customer Satisfaction
Metrics: Customer satisfaction scores, Net Promoter Score (NPS), and customer retention rates.
Targets: Achieve a customer satisfaction score of [90%] or higher and a retention rate of [85%] or higher.
5.1.2 Operational Efficiency
Metrics: Cycle time, production yield, and cost per unit.
Targets: Reduce cycle time by [20%] and improve production yield to [95%] or higher.
5.1.3 Financial Performance
Metrics: Revenue growth, profit margins, and return on investment (ROI).
Targets: Achieve annual revenue growth of [10%] and maintain a profit margin of [15%] or higher.
5.2 Monitoring and Reporting
Monitoring and reporting processes ensure that KPIs are tracked, analyzed, and reported regularly to support decision-making and performance improvement.
Processes:
Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources, including operational systems, customer feedback, and financial reports.
Performance Analysis: Analyzing data to identify trends, issues, and opportunities for improvement.
Reporting: Providing regular performance reports to stakeholders, including executive leadership, department heads, and operational teams.
6. Risk Management
6.1 Risk Identification
Risk identification involves recognizing potential risks that could impact [Your Company Name]'s operations and strategic objectives.
Types of Risks:
Operational Risks: Risks related to day-to-day operations, such as equipment failure, supply chain disruptions, and workforce issues.
Financial Risks: Risks related to financial performance, including cash flow issues, investment losses, and regulatory changes.
Strategic Risks: Risks related to the achievement of strategic goals, including market competition, technological changes, and geopolitical events.
6.2 Risk Assessment
Risk assessment involves evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks to determine their potential effect on the organization.
Assessment Criteria:
Likelihood: The probability of the risk occurring, categorized as low, medium, or high.
Impact: The potential consequences of the risk, categorized as minor, moderate, or severe.
6.2.1 Operational Risks
Assessment: Assess the likelihood of equipment failure and its impact on production schedules. Evaluate the potential impact of supply chain disruptions on inventory levels and customer delivery.
6.2.2 Financial Risks
Assessment: Assess the risk of cash flow issues due to unexpected expenses or revenue shortfalls. Evaluate the impact of investment losses on financial stability and growth.
6.2.3 Strategic Risks
Assessment: Evaluate the likelihood of market competition affecting market share and profitability. Assess the impact of technological changes on operational processes and product offerings.
6.3 Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation involves developing and implementing strategies to minimize or eliminate identified risks.
Mitigation Strategies:
Operational Risks: Implement preventive maintenance programs, diversify suppliers, and develop contingency plans for operational disruptions.
Financial Risks: Maintain financial reserves, conduct regular financial audits, and diversify investments to mitigate financial risks.
Strategic Risks: Monitor market trends, invest in research and development, and develop flexible strategies to adapt to changing conditions.
7. Conclusion
The Concept of Operations (CONOPS) for [Your Company Name] provides a detailed and comprehensive overview of our operational framework, strategic objectives, and processes. This document is designed to guide the company’s activities from 2050 to 2100, ensuring that all operational aspects are aligned with our long-term goals and vision.
By outlining our operational strategies, organizational structure, processes, performance measurement, and risk management practices, the CONOPS serves as a roadmap for achieving operational excellence and sustaining long-term growth. As [Your Company Name] evolves and adapts to changing conditions, this document will be updated to reflect new developments, emerging trends, and strategic priorities.
The successful implementation of this CONOPS will enable [Your Company Name] to navigate the complexities of the future business environment, deliver exceptional value to customers, and achieve our strategic objectives. We are committed to continuous improvement and innovation, ensuring that our operations remain efficient, effective, and aligned with our vision for the future.