Operations Project Management
1. Introduction
Operations Project Management is the systematic planning, organization, and execution of projects that improve a company’s operations. For [Your Company Name], effective operations management is essential in ensuring seamless execution of processes, reducing waste, increasing productivity, and achieving sustainable growth. This Operations Project Management Plan provides the roadmap for managing projects that enhance operational efficiency, ensuring that they are completed on time, within budget, and in alignment with strategic objectives. The timeline for this project spans from 2050 to 2053 and includes critical operational upgrades aimed at achieving long-term sustainability goals.
This plan will address various aspects of project management such as scope, deliverables, roles and responsibilities, risk management, budget allocation, and quality assurance. By following this structured approach, [Your Company Name] aims to future-proof its operations by adopting the latest technological advancements and best practices in operational management.
2. Project Scope and Objectives
2.1 Project Scope
The scope of the Operations Project Management initiative focuses on modernizing [Your Company Name]'s operational framework. Key components of the scope include:
System Automation: Introduction of AI and machine learning-based solutions across production, logistics, and supply chain management. This will enhance the ability to manage inventory in real time, predict demand, and optimize supply chain activities.
Process Optimization: Revising existing workflows to eliminate redundant processes, improve efficiency, and reduce errors. This will be achieved by integrating intelligent software systems that streamline decision-making and reduce the need for manual intervention.
Sustainability Integration: Incorporation of energy-efficient technologies and practices, such as renewable energy sources and waste reduction initiatives, to align with long-term environmental goals.
Customer-Centric Operations: Redesign of customer service processes to provide faster response times, automate support ticket management, and personalize customer interactions through the use of advanced customer relationship management (CRM) tools.
2.2 Project Objectives
The objectives of this project focus on both short-term operational improvements and long-term sustainability. These objectives include:
Achieve a [20%] increase in production efficiency through automation and process improvements. This target will be measured through key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production cycle time, output per labor hour, and machine utilization rates.
Reduce operational costs by [15%] over the next three years (2050-2053) by optimizing the supply chain, adopting lean manufacturing principles, and reducing energy consumption. This will involve regular audits of energy use, procurement practices, and production waste.
Increase customer satisfaction levels by [25%], as measured by net promoter score (NPS) and customer retention rates. This will be achieved by improving response times and delivering more personalized customer service through data-driven insights.
Achieve carbon neutrality by 2055 by transitioning to renewable energy sources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions by [50%] by the end of 2053.
These objectives will position [Your Company Name] as a leader in operational excellence, driving business growth while promoting environmental stewardship.
3. Operations Overview
3.1 Key Operational Areas
The key operational areas at [Your Company Name] will be the focus of this project. These areas are interdependent and require streamlined processes to ensure efficiency and productivity:
Supply Chain Management: This area deals with the procurement of raw materials, vendor management, inventory control, and transportation logistics. Optimizing the supply chain will involve leveraging AI-driven tools for real-time inventory management, demand forecasting, and route optimization.
Production: The heart of [Your Company Name]'s operations, production involves manufacturing goods and ensuring quality standards. The implementation of smart factory technologies will allow for predictive maintenance, machine learning-based production scheduling, and real-time data analytics to monitor production performance.
Customer Service: Customer service operations encompass managing inquiries, resolving complaints, and delivering a seamless customer experience. The adoption of AI-powered chatbots, automated support ticket systems, and predictive analytics will enhance customer satisfaction by reducing wait times and offering personalized solutions.
Logistics and Distribution: Effective logistics and distribution ensure that products are delivered to customers in a timely and cost-efficient manner. Optimizing this area involves using machine learning to predict shipping patterns, minimizing fuel consumption, and reducing lead times.
3.2 Operational Resources
The success of this project will depend on the effective utilization of resources across various departments. These resources include:
Human Resources: Skilled teams in operations, engineering, IT, and customer service will be instrumental in executing the project. The HR department will also oversee training programs to upskill employees in using new technologies.
Technology: The project will require cutting-edge technology solutions, such as AI-driven automation systems, advanced data analytics platforms, IoT devices for smart manufacturing, and renewable energy technology.
Capital: A comprehensive project budget of [$50 million] has been allocated to cover all expenses related to system upgrades, training, energy-efficient solutions, and contingency planning over the next three years (2050-2053).
4. Project Deliverables
4.1 Major Deliverables
The Operations Project Management initiative at [Your Company Name] will deliver a number of tangible outputs:
Fully automated operational systems: AI-driven solutions will be deployed across production, supply chain, and customer service departments by the end of 2051. This will include the use of robotic process automation (RPA) for handling repetitive tasks, thus freeing human workers to focus on higher-value activities.
Energy-efficient solutions: By 2052, the project will deliver renewable energy installations, such as solar power, to reduce operational reliance on fossil fuels. In addition, smart energy monitoring systems will be implemented to track and optimize energy consumption.
Process optimization reports: Detailed process optimization reports will be produced at key milestones throughout the project, highlighting areas of improvement, cost savings achieved, and recommendations for further efficiency gains.
4.2 Milestones
Key project milestones have been established to track progress and ensure timely delivery:
Milestone | Description | Due Date |
|---|---|---|
Project Kickoff | Formal project approval and initiation | October 2050 |
Initial Systems Review | Comprehensive review of current systems and processes | December 2050 |
Automation Implementation | Deployment of automated systems in key departments | June 2051 |
Mid-Project Evaluation | Progress review against key performance indicators | June 2052 |
Final System Integration | Completion of system integration and energy solutions | December 2052 |
Project Closeout | Submission of final deliverables and project review | December 2053 |
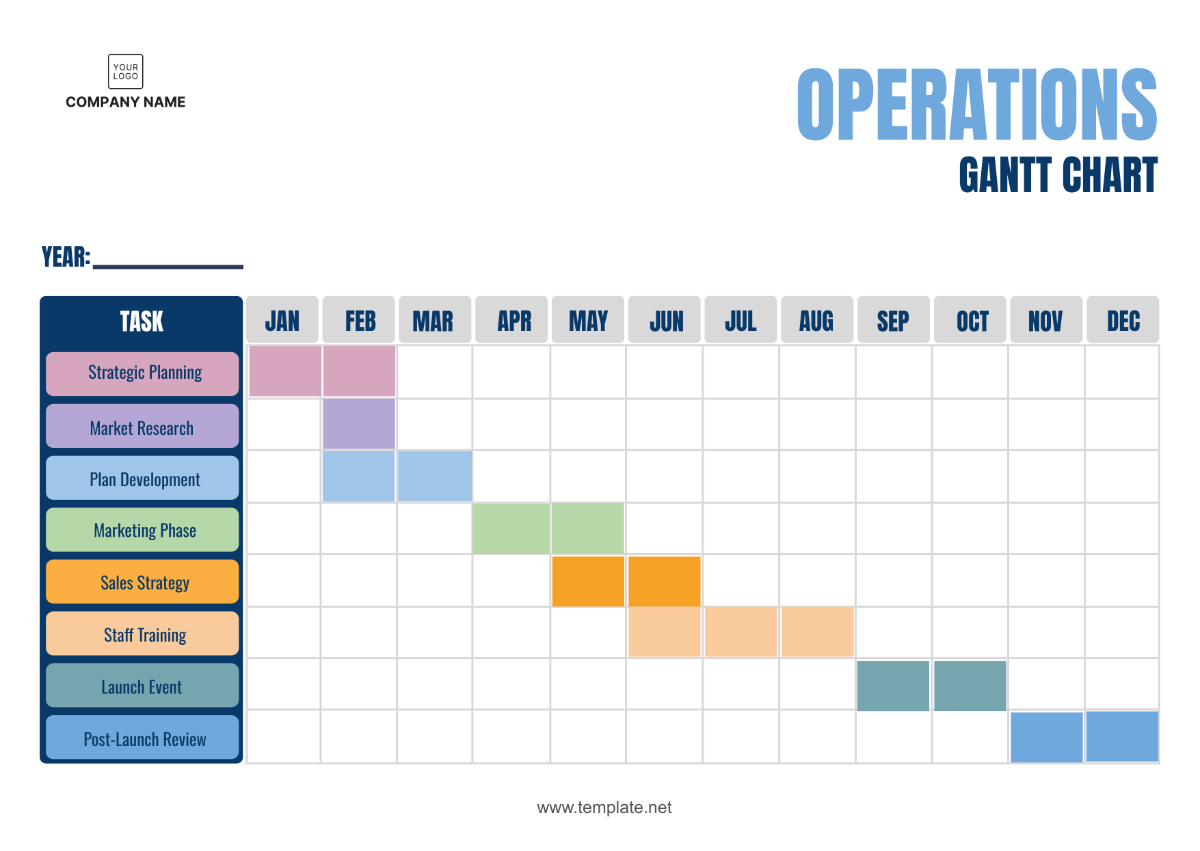
5. Project Schedule and Timeline
5.1 Phases of the Project
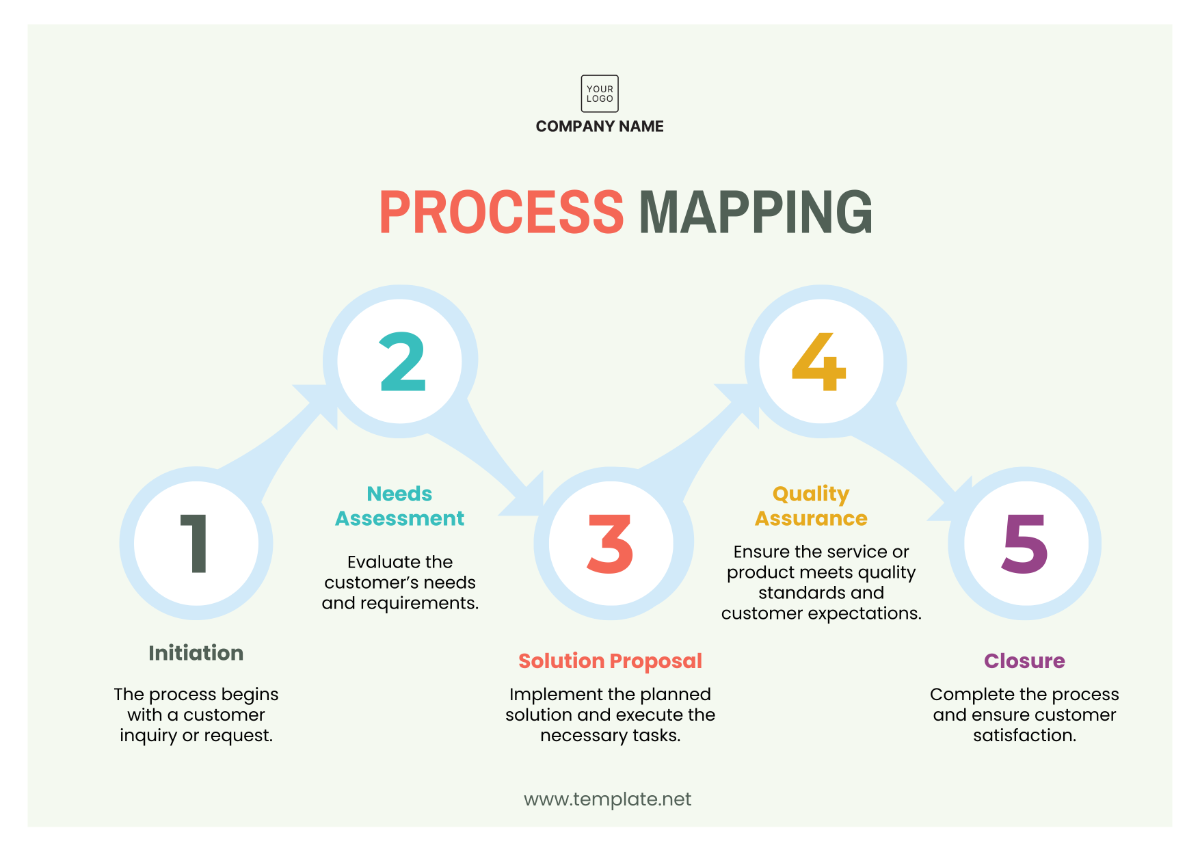
The project will be executed in five distinct phases, each focusing on specific activities:
Initiation Phase: This phase includes the formal approval of the project, the development of the project charter, and the assignment of key project roles. The primary activities include stakeholder meetings, risk assessment, and budget approval.
Planning Phase: The planning phase focuses on defining the project scope, creating detailed schedules, and finalizing the resource allocation. Key activities include project team training, software and system design, and securing vendor contracts for technology procurement.
Execution Phase: During this phase, the project team will implement the deliverables, including system automation, sustainability initiatives, and process optimization. The focus will be on installing the technology, training personnel, and closely monitoring initial outcomes.
Monitoring and Controlling Phase: This phase will run in parallel with the execution phase, as ongoing performance tracking is essential. Real-time data collection and performance analytics will be used to ensure that the project is meeting its objectives, milestones, and staying within budget.
Closure Phase: The final phase involves handing over completed systems and processes to the operations teams, conducting final quality checks, and preparing a post-project review to assess overall success and identify lessons learned.
5.2 Timeline
The timeline for the Operations Project Management initiative spans from October 2050 to December 2053. Below is a detailed schedule with specific activities and deadlines:
Phase | Activity | Start Date | End Date | Responsible Parties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Initiation Phase | Project Kickoff Meeting | October 1, 2050 | October 15, 2050 | Project Manager, Stakeholders |
Project Charter Development | October 16, 2050 | October 31, 2050 | Project Manager, Planning Team | |
Stakeholder Engagement | October 16, 2050 | October 31, 2050 | Project Manager, HR Department | |
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Planning | October 16, 2050 | October 31, 2050 | Risk Management Team | |
Planning Phase | Detailed Project Plan Development | November 1, 2050 | November 30, 2050 | Project Manager, Planning Team |
Resource Allocation and Procurement | November 1, 2050 | December 15, 2050 | Procurement Team, IT Department | |
Technology and System Design | November 15, 2050 | December 31, 2050 | IT Department, External Consultants | |
Training Program Development | November 15, 2050 | December 15, 2050 | Training Department | |
Execution Phase | Automation System Deployment | January 2, 2051 | June 30, 2051 | IT Department, Operations Team |
Energy-Efficient Solutions Installation | January 2, 2051 | December 31, 2052 | Facilities Management Team, External Contractors | |
Process Optimization Implementation | February 1, 2051 | August 31, 2051 | Operations Team, Process Improvement Specialists | |
Customer Service Technology Integration | March 1, 2051 | December 31, 2051 | IT Department, Customer Service Team | |
Monitoring and Controlling Phase | Performance Tracking and Reporting | January 2, 2051 | December 31, 2053 | Project Manager, Monitoring Team |
Budget and Schedule Review | Monthly | Monthly | Project Manager, Financial Analyst | |
Risk Management and Adjustment | As Needed | As Needed | Risk Management Team | |
Closure Phase | Final System Integration | October 1, 2052 | December 31, 2052 | IT Department, Operations Team |
Quality Assurance and Final Checks | October 1, 2052 | December 15, 2052 | Quality Assurance Team | |
Project Handover and Documentation | December 16, 2052 | December 31, 2052 | Project Manager, Documentation Specialist | |
Post-Project Review and Lessons Learned | December 1, 2053 | December 15, 2053 | Project Manager, Evaluation Team |
6. Budget and Financial Management
6.1 Project Budget Overview
The total budget for the Operations Project Management initiative is allocated at [$50 million]. This budget covers all project phases, including planning, execution, and closure. It is divided among various expenditure categories to ensure that all aspects of the project are adequately funded.
6.2 Cost Breakdown
The cost breakdown is detailed below:
Category | Estimated Cost (USD) | Description |
|---|---|---|
Technology Procurement | [$20,000,000] | Costs for purchasing AI-driven systems, automation tools, and renewable energy technologies. |
Training and Development | [$5,000,000] | Includes costs for employee training programs, workshops, and certifications. |
Consulting Services | [$7,000,000] | Fees for external consultants specializing in process optimization, technology integration, and sustainability. |
System Integration | [$8,000,000] | Expenses related to system installation, integration, and initial testing. |
Operational Costs | [$4,000,000] | Day-to-day expenses including utilities, facility management, and ongoing maintenance. |
Contingency Fund | [$3,000,000] | Reserved funds for unexpected costs and risk management. |
Project Management | [$3,000,000] | Costs for project management team salaries, administrative expenses, and documentation. |
This detailed budget ensures comprehensive coverage of all project needs and provides a financial buffer to handle unforeseen challenges. Regular financial reviews will be conducted to ensure adherence to the budget and timely allocation of funds.
7. Risk Management
7.1 Risk Identification
Identifying potential risks early in the project lifecycle is crucial for effective management. The following types of risks will be considered:
Technological Risks: Risks associated with the implementation of new technologies, such as system failures, software incompatibility, or integration issues.
Financial Risks: Risks related to budget overruns, unexpected costs, or funding shortfalls.
Operational Risks: Risks arising from process inefficiencies, supply chain disruptions, or changes in operational requirements.
Regulatory Risks: Risks related to changes in regulations or compliance requirements that may impact project implementation.
7.2 Risk Mitigation Strategies
To manage and mitigate identified risks, the following strategies will be employed:
Technological Risks: Conduct thorough testing and validation of all new systems before full-scale implementation. Engage experienced consultants and technical experts to ensure successful technology integration.
Financial Risks: Establish a robust financial management plan with regular budget reviews and cost controls. Maintain a contingency fund to address unexpected expenses.
Operational Risks: Develop and implement comprehensive operational procedures and contingency plans. Regularly review and update processes to address potential inefficiencies and disruptions.
Regulatory Risks: Stay informed about regulatory changes and engage legal experts to ensure compliance. Incorporate flexibility in project plans to accommodate changes in regulations.
8. Project Roles and Responsibilities
8.1 Project Manager Role
The Project Manager is responsible for overseeing the entire project from initiation to closure. Key responsibilities include:
Planning and Scheduling: Develop and manage the project plan, schedule, and milestones. Ensure that all project activities are aligned with the defined scope and objectives.
Resource Allocation: Allocate resources efficiently and manage the project budget. Ensure that all team members have the necessary tools and support to perform their tasks.
Stakeholder Communication: Serve as the primary point of contact for stakeholders. Provide regular updates on project progress, risks, and issues.
Risk Management: Identify and manage project risks, implementing mitigation strategies as needed.
8.2 Team Members and Stakeholders
The project team consists of various roles, each with specific responsibilities:
IT Department: Responsible for the deployment and integration of technology solutions, including automation systems and energy-efficient technologies.
Operations Team: Works on process optimization, system implementation, and ensuring that operational improvements are effectively integrated.
Training Department: Develops and delivers training programs to upskill employees and ensure smooth adoption of new technologies and processes.
Quality Assurance Team: Monitors and ensures that all deliverables meet the required quality standards. Conducts final checks and validations.
Stakeholders: Includes senior management, department heads, and external partners who have a vested interest in the project’s success. Stakeholders provide input, review project progress, and approve key decisions.
9. Communication Plan
9.1 Internal Communication
Effective internal communication is essential for project success. Key elements of the internal communication plan include:
Regular Meetings: Schedule weekly project team meetings to review progress, address issues, and plan upcoming activities. Include bi-weekly updates for stakeholders.
Project Management Software: Utilize project management software for tracking tasks, deadlines, and project milestones. Ensure that all team members have access to this platform and regularly update their progress.
Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of project plans, decisions, and changes. Ensure that all relevant information is easily accessible to team members.
9.2 External Communication
External communication focuses on keeping stakeholders and external partners informed about the project:
Status Reports: Prepare and distribute monthly status reports to stakeholders, outlining project progress, achievements, and any issues encountered.
Stakeholder Updates: Provide quarterly updates to stakeholders through meetings or written reports. Include key performance indicators, financial status, and risk assessments.
Public Announcements: Coordinate with the PR department for any public announcements related to project milestones or achievements.
10. Quality Management
10.1 Quality Assurance Process
Quality assurance is critical to ensure that all project deliverables meet the required standards. The quality assurance process includes:
Quality Standards: Define and document quality standards for each deliverable, including technological systems, process improvements, and customer service enhancements.
Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing and validation of all new systems and processes. Ensure that all solutions meet predefined criteria and performance benchmarks.
Continuous Improvement: Implement a continuous improvement process to regularly review and enhance quality standards based on feedback and performance data.
10.2 Quality Control Procedures
Quality control procedures ensure that project deliverables are consistently monitored and maintained:
Inspections: Perform regular inspections of completed work to ensure compliance with quality standards and specifications.
Feedback Mechanism: Establish a feedback mechanism for team members and stakeholders to report quality issues and suggest improvements.
Corrective Actions: Implement corrective actions to address any identified quality issues promptly and effectively.