Free Argumentative Essay on Food Labeling

Written By: [Your Name]
Introduction
In an era where consumer awareness about nutrition and health is on the rise, food labeling has become a critical tool in the marketplace. Food labels are designed to provide essential information to consumers, helping them make informed choices about their diet. However, the practice of food labeling comes with its controversies and challenges. This essay delves into the pros and cons of food labeling, evaluates its effectiveness in promoting public health, and examines its impact on consumer choices. Through a balanced presentation of arguments and evidence, this essay aims to advocate for a stance on the necessity and effectiveness of comprehensive food labeling.
Literature Review or Background
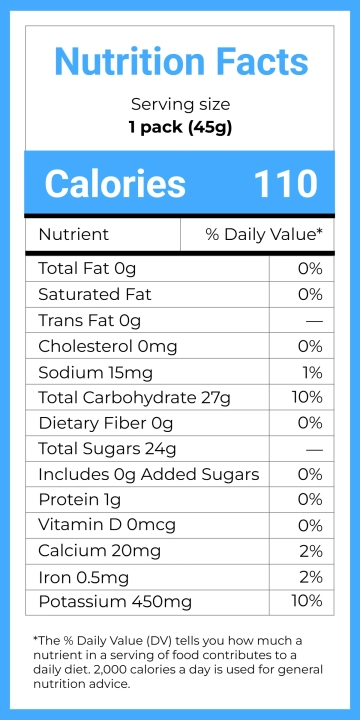
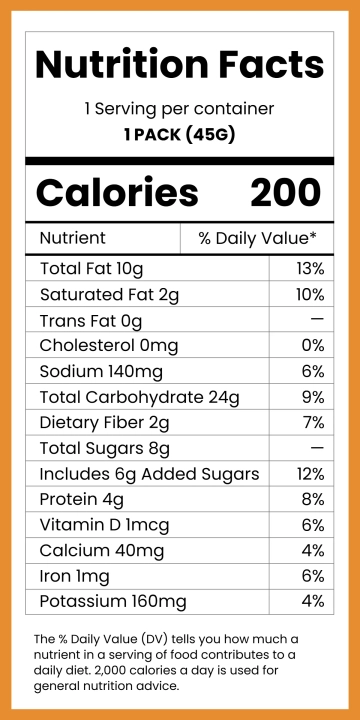
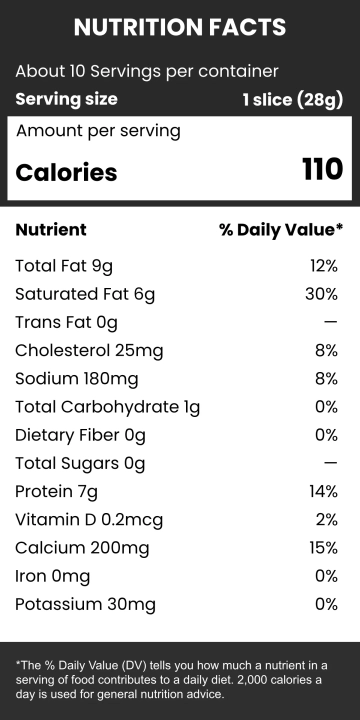
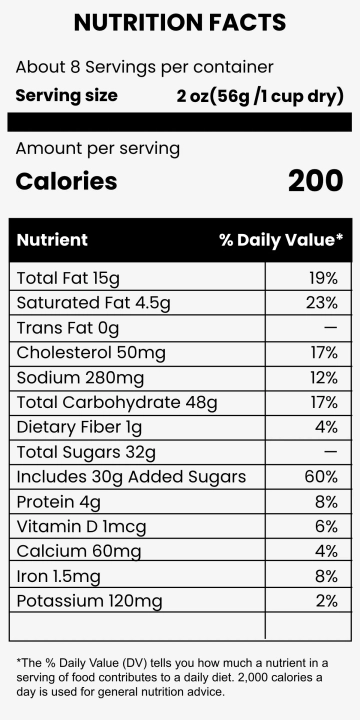
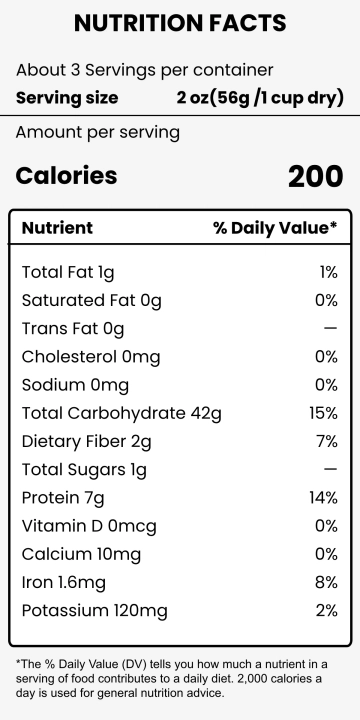
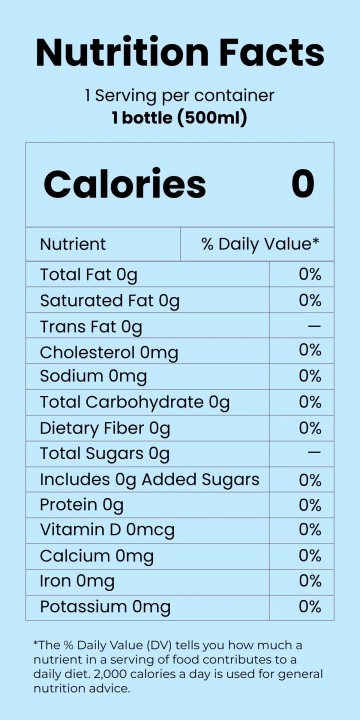
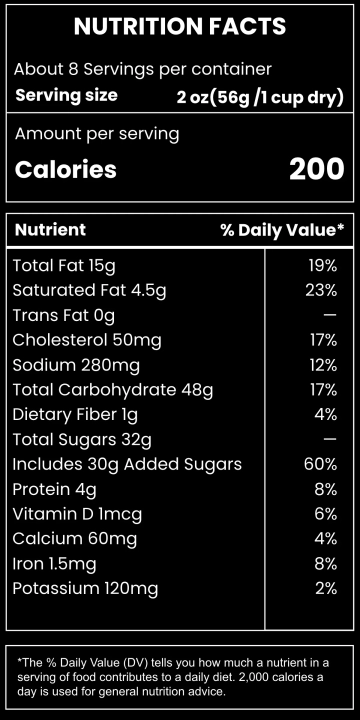
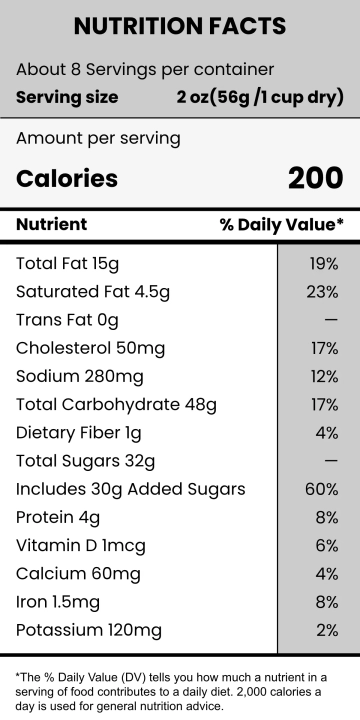
Food labeling has a long history that traces back to the early 20th century when regulations were first introduced to ensure food safety and quality. The advent of nutritional labeling marked a significant stride towards transparency in the food industry. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), mandatory labeling provides consumers with information critical to their dietary choices (FDA, 2050). Recent studies have shown that consumers increasingly depend on food labels to manage their nutritional intake and avoid allergens (Campos, Doxey, & Hammond, 2051). Despite these advances, questions about the accuracy, understandability, and overall impact of food labeling persist.
Arguments and Evidence
Accuracy of Nutritional Information
One of the primary benefits of food labeling is the accuracy of nutritional information provided to the consumer. Accurate labeling can help individuals monitor their intake of crucial nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and calories, aiding in weight management and overall health. A study published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics found that individuals who read nutritional labels exhibit healthier eating behaviors (Graham & Laska, 2052). This underscores the importance of precise and comprehensive food labeling in fostering public health.
Impact on Consumer Choices
Food labels significantly influence consumer choices, encouraging healthier eating habits. According to a survey by the International Food Information Council Foundation, 59% of consumers often read food labels before purchasing (IFIC, 2050). Labels that highlight low levels of sugar, fat, or sodium can steer consumers toward products that contribute to a healthier diet. Furthermore, labels indicating organic or non-GMO ingredients cater to the preferences of health-conscious consumers, thereby impacting purchasing decisions.
Effectiveness in Promoting Public Health
The role of food labeling in promoting public health cannot be overstated. Labels serve as a critical defense against diet-related diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease by educating consumers about the content of their food. The implementation of clear and prominent calorie counts on fast food menus, as mandated by the FDA, exemplifies how labeling can act as a preventive measure against overeating (Pomeranz & Brownell, 2051). Such initiatives underscore the public health benefits derived from transparent food labeling practices.
Counterarguments
Despite the advantages, there are notable counterarguments against food labeling. Critics argue that food labels can be confusing or misleading, potentially causing more harm than good. The complexity of nutritional information can overwhelm consumers, rendering labels ineffective. Additionally, loopholes in regulations may allow manufacturers to present their products more favorably than is justified. According to Freedman and Brody (2051), the overemphasis on specific nutrients like fats or sugars can lead to a skewed perception of food healthiness, ignoring the holistic quality of the diet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while food labeling is a beneficial tool for consumer education and public health promotion, it is not without its pitfalls. The accuracy of nutritional information, the influence on consumer choices, and the overall effectiveness in fostering healthier lifestyles are substantial advantages. However, addressing the concerns related to the potential for confusing or deceptive information is essential to maximize the benefits of food labeling. Continued efforts to improve label clarity, accuracy, and comprehensiveness will be crucial in ensuring that food labels serve their intended purpose effectively and equitably.
Bibliography
Campos, S., Doxey, J., & Hammond, D. (2051). Nutrition labels on pre-packaged foods: a systematic review. Public Health Nutrition, 14(8), 1496-1506.
FDA. (2050). Food Labeling & Nutrition. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition
Freedman, M. R., & Brody, T. (2051). Truth claims and labeling: how the law can be changed to better protect consumers. Nutrition Today, 46(5), 229-235.
Graham, D. J., & Laska, M. N. (2052). Nutrition label use partially mediates the relationship between attitude toward healthy eating and overall dietary quality among college students. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 112(3), 414-418.
IFIC. (2050). 2020 Food and Health Survey. International Food Information Council Foundation. Retrieved from https://foodinsight.org/2020-food-and-health-survey/
Pomeranz, J. L., & Brownell, K. D. (2051). Legal and public health considerations affecting the success, reach, and impact of menu-labeling laws. American Journal of Public Health, 101(3), 546-551.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
The Food Labeling Argumentative Essay Template from Template.net offers a clear and well-structured format for crafting persuasive essays on food labeling. This template is fully editable and customizable to suit your specific arguments and preferences. Plus, it's editable in our AI Editor Tool, allowing for effortless personalization and professional-quality results.