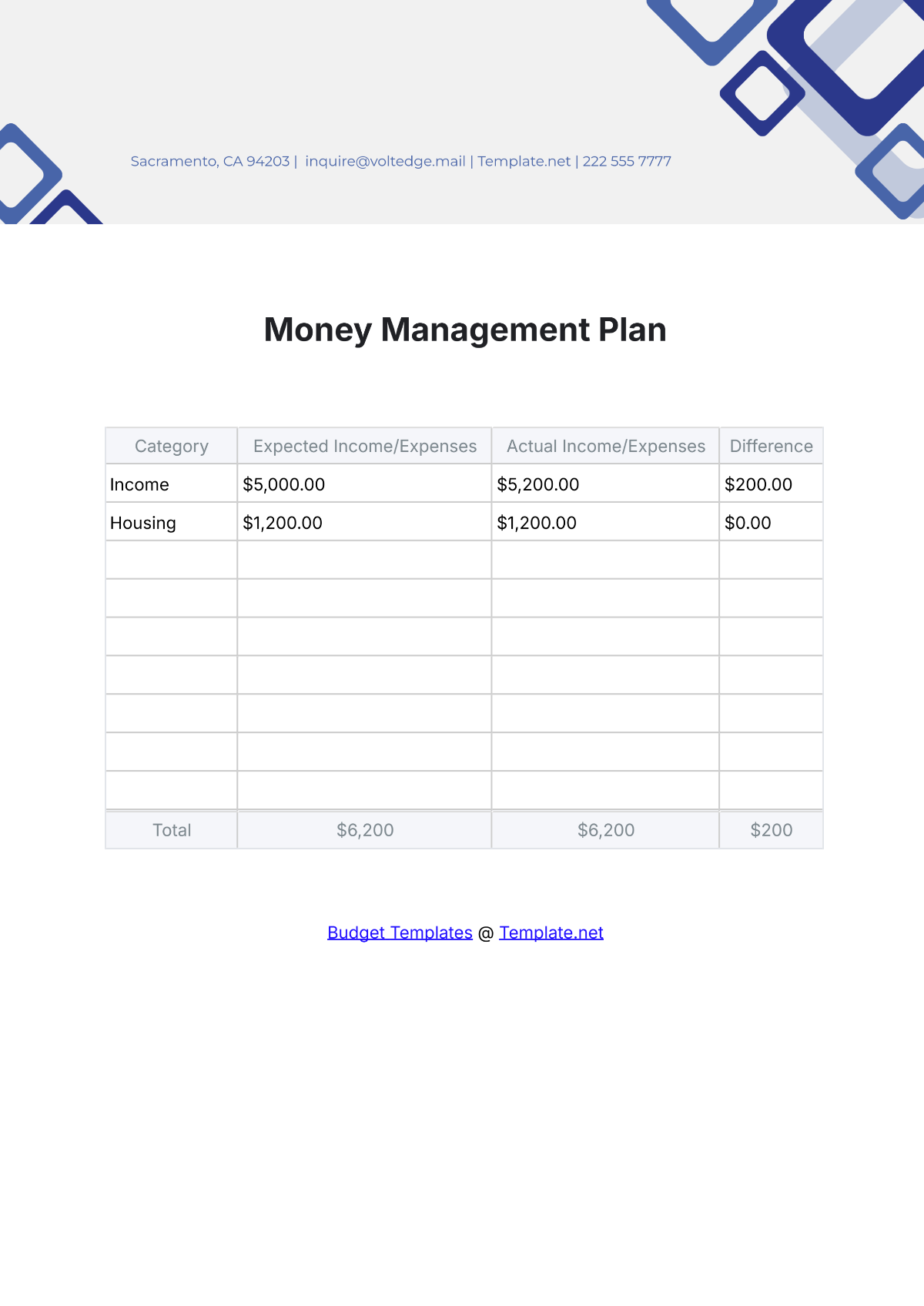
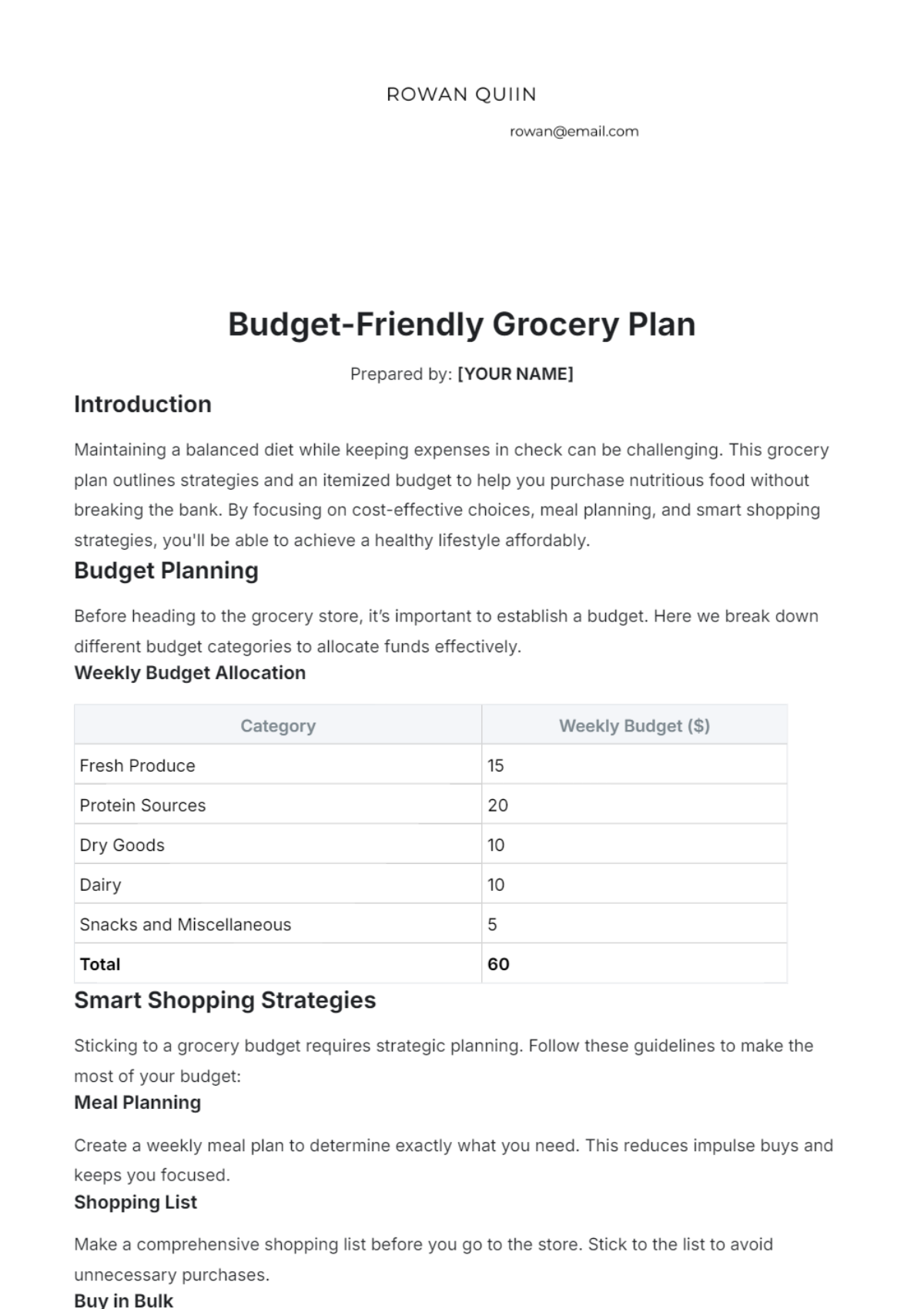
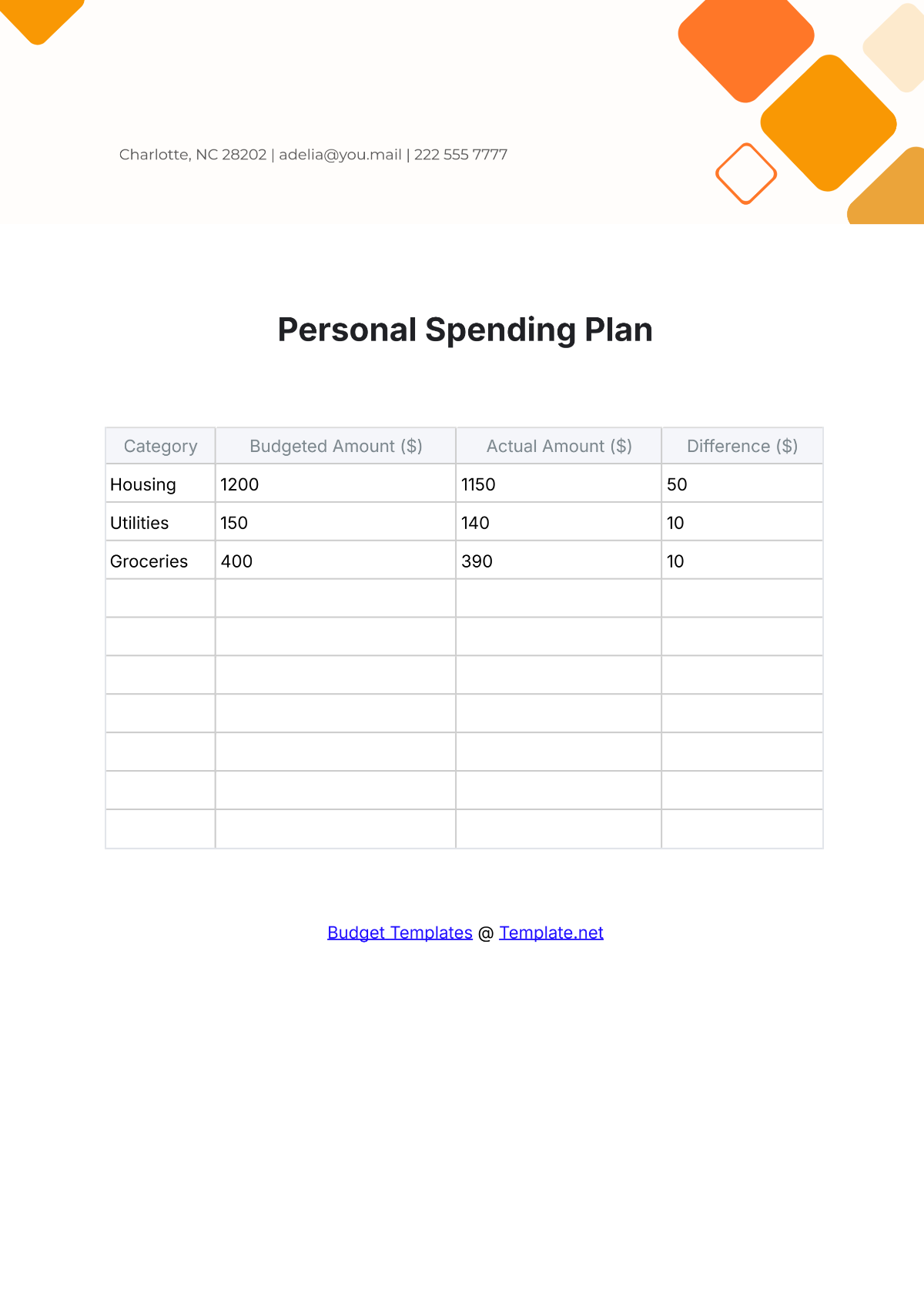
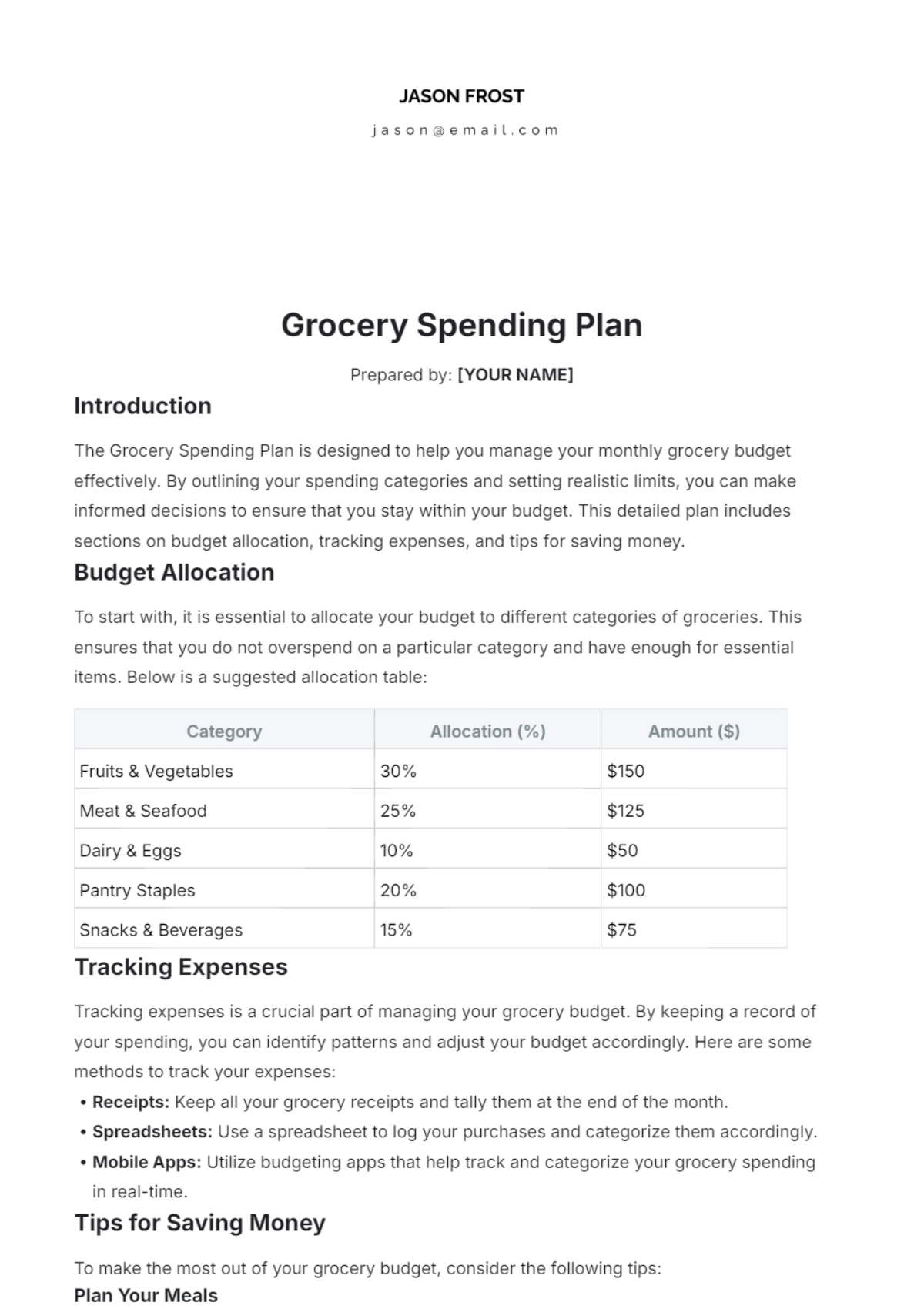
Free Architecture Budget Plan
Manage your firm's finances efficiently with the Architecture Budget Plan Template from Template.net. This editable and customizable template helps you plan and allocate your budget for projects and operations. Fully editable in our Ai Editor Tool, it provides a professional and organized format to ensure accurate financial planning for your architecture firm.