ISO 9001 Internal Audit
1. Introduction
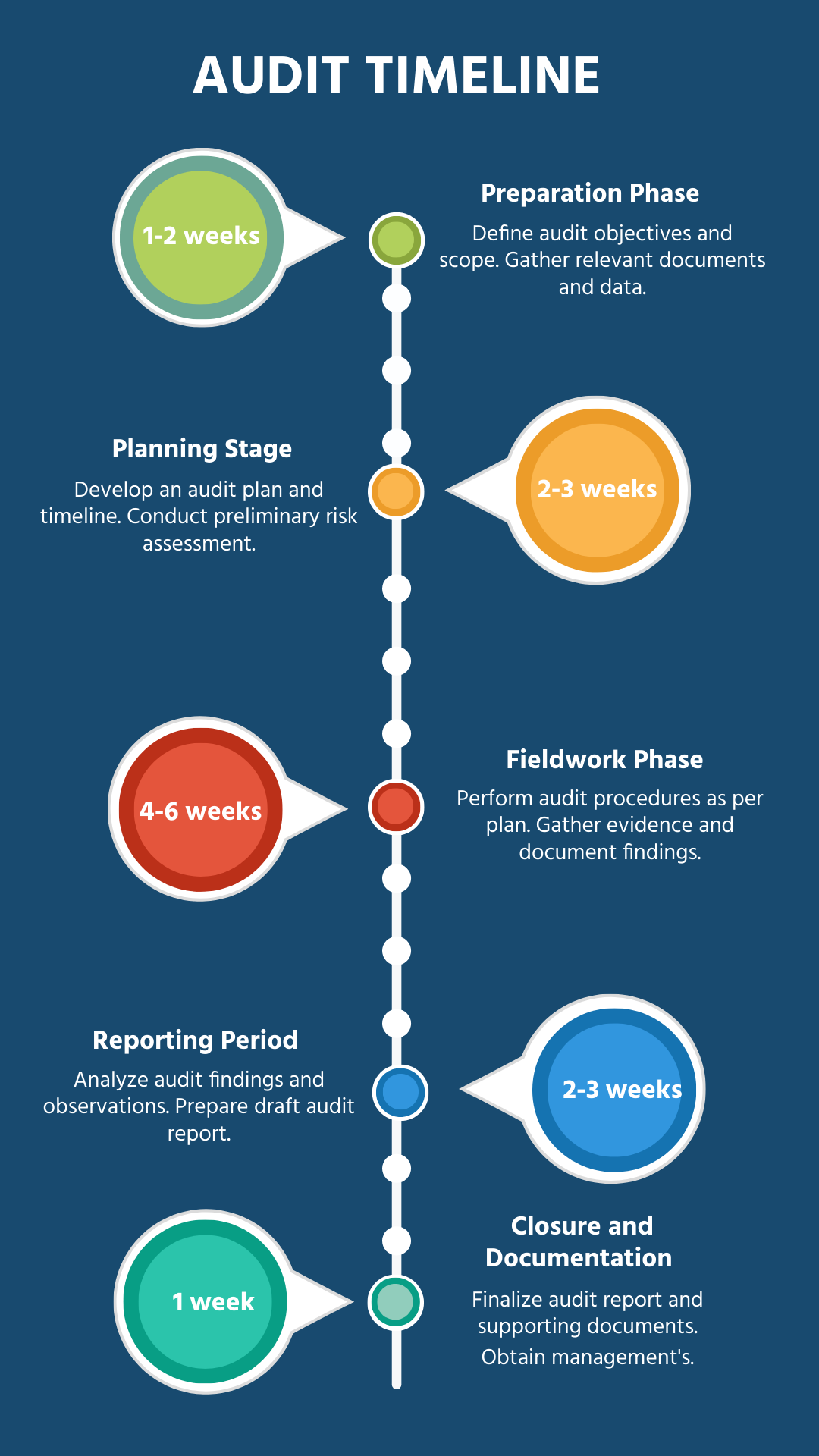
This document presents a comprehensive report on the internal audit conducted at [Your Company Name]. The primary purpose of this audit is to assess compliance with the ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System (QMS) standards. Additionally, this audit aims to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the organization’s processes are aligned with best practices for continual enhancement and customer satisfaction.
2. Audit Scope and Objectives
The scope of the audit covers all critical processes and departments within [Your Company Name], including but not limited to Production, Procurement, Human Resources, Sales, Quality Control, and Logistics. The key objectives of this audit are as follows:
Verify the effectiveness of the Quality Management System (QMS) across all operational levels.
Identify non-conformities, partial compliance, and potential opportunities for continual improvement.
Ensure compliance with ISO 9001:2015 standards and assess how well the QMS is implemented and maintained.
Evaluate risk management practices, including the organization’s ability to mitigate potential risks to quality.
3. Audit Team
The internal audit was conducted by a qualified team of auditors with extensive experience in ISO 9001 standards and QMS. The team members included:
Lead Auditor: John Anderson – Certified ISO 9001 Lead Auditor with 10+ years of experience in auditing and quality management systems.
Auditor: Sarah Mitchell – Senior Auditor specializing in operational audits and process efficiency.
Auditor: David Collins – Auditor with expertise in compliance and risk management.
4. Audit Findings and Observations
The following table outlines key findings and observations from the audit, detailing the department or process audited, the level of conformity, and any required corrective actions:
Finding No. | Department/Process | Description | Conformity Level | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Procurement | Non-conformity in document control | Non-Conformity | Implement a centralized document management system. Deadline: 30 days. |
2 | Production | Partial compliance with the internal audit schedule | Partial Compliance | Improve internal audit scheduling and tracking. Deadline: 45 days. |
3 | Human Resources | Full compliance with employee training documentation | Compliant | No action required. |
4 | Logistics | Non-conformity in risk assessment procedures | Non-Conformity | Develop a formal risk assessment plan for logistics. Deadline: 30 days. |
5 | Quality Control | Partial compliance with process monitoring documentation | Partial Compliance | Ensure all process monitoring data is properly recorded and stored. Deadline: 60 days. |
5. Key Observations
During the audit, several strengths, areas for improvement, and potential risks were observed:
Strengths:
Process Optimization: The Production Department demonstrated excellent process control with minimal deviations from established protocols. Continuous improvement initiatives have led to increased output efficiency by 12% over the last year.
Employee Engagement: Employees in the Quality Control department showed a high level of awareness and commitment to the QMS, with training records indicating above-average compliance rates across the department.
Opportunities for Improvement:
Document Control: Inconsistent document handling was observed in the Procurement department, necessitating a review of the current document management system to ensure timely updates and accessibility across all departments.
Training Programs: Training on ISO 9001 requirements could be expanded for the Logistics and Procurement departments to ensure full understanding and adherence to quality and risk management practices.
Risks:
Risk of Non-Compliance: The lack of documented evidence for risk management procedures in the Logistics department presents a potential risk of non-compliance with ISO 9001 standards. This could result in future operational inefficiencies or quality-related issues.
Operational Bottlenecks: Delays in the procurement process were identified due to inconsistent supplier evaluation methods, which could negatively impact production schedules and customer satisfaction.
6. Recommendations
Based on the audit findings and observations, the following recommendations are made to enhance the QMS and address identified issues:
Corrective Actions:
Implement corrective actions for non-conformities identified, particularly in Procurement and Logistics. A centralized document management system should be introduced in Procurement, and a risk management plan should be formalized in Logistics.
Training Enhancements:
Develop targeted training programs for the Procurement and Logistics departments. This should focus on ISO 9001:2015 standards, with specific attention to document control, supplier evaluation, and risk management protocols.
Ongoing Monitoring and Auditing:
Establish a more frequent internal audit schedule, particularly for departments that showed partial compliance. This will help in early identification and rectification of potential issues.
Risk Mitigation:
Implement a comprehensive risk management strategy in the Logistics department to address operational bottlenecks and mitigate the risks of non-compliance. Supplier evaluations should be standardized to prevent delays in procurement.
7. Conclusion
The internal audit of [Your Company Name]. was completed by ISO 9001:2015 standards. Several areas of non-conformity and partial compliance were identified, particularly in Procurement and Logistics, which require immediate corrective actions. However, the overall effectiveness of the Quality Management System remains strong, particularly in Production and Quality Control. Continued efforts to enhance training, improve document management, and strengthen risk management processes will further solidify compliance and operational efficiency.
8. Auditor Sign-off
Lead Auditor: | Date: June 20, 2050 |
|
Auditor: | Date: June 20, 2050 |
|
Auditor: | Date: June 20, 2050 |
|