Free Sample Procurement Audit

Prepared by: [Your Name]
I. Executive Summary
This document offers a comprehensive example of a procurement audit, detailing a structured framework for assessing procurement processes, practices, and policies. Designed as a reference for organizations, it focuses on ensuring effective purchasing strategies, regulatory compliance, vendor management, and cost efficiency. The audit provides actionable insights into procurement operations to support continuous improvement and risk mitigation.
II. Audit Objectives
The key objectives of this procurement audit are outlined below to guide the evaluation process:
A. Evaluate Efficiency and Effectiveness
To assess how well the current procurement processes contribute to the organization's operational goals and whether they achieve the desired results without unnecessary delays or resource wastage.
B. Ensure Compliance
To verify adherence to applicable legal standards, industry regulations, and internal policies governing procurement activities.
C. Review Vendor Management
To evaluate the adequacy of vendor selection criteria, negotiation practices, and ongoing management to ensure sustainable and beneficial relationships.
D. Identify Cost-Saving Opportunities
To analyze current expenditure patterns and recommend strategies for cost control and financial efficiency.
III. Scope of the Audit
This procurement audit focuses on the following critical areas of the procurement lifecycle:
A. Purchasing Strategies
Analyzing the methods and criteria used to make purchasing decisions and their alignment with organizational objectives.
B. Vendor Selection
Evaluating the processes and criteria for selecting vendors, including fairness, transparency, and quality benchmarks.
C. Contract Management
Assessing the negotiation, approval, and monitoring of contracts to ensure clarity, compliance, and performance.
D. Compliance Assessment
Reviewing adherence to internal policies and external regulations to identify any gaps or risks of non-compliance.
E. Cost Management
Examining cost-tracking mechanisms and expenditure patterns to uncover inefficiencies or unexploited savings opportunities.
IV. Methodology
A comprehensive approach combining qualitative and quantitative techniques was employed in this audit:
A. Document Review
Procurement manuals, policies, contracts, vendor lists, and transaction records were meticulously examined to understand existing practices.
B. Interviews
Key personnel, including procurement managers, finance officers, and department heads, were interviewed to gather insights into daily operations, challenges, and perceptions of the current system.
C. Data Analysis
Procurement data, including transaction histories, budget allocations, and expense reports, were analyzed to identify patterns, anomalies, and trends.
D. Testing and Validation
A selective review of specific procurement transactions and contracts was conducted to ensure adherence to defined policies and procedures.
V. Findings and Observations
The audit revealed various strengths and improvement areas in the organization's procurement operations:
A. Strengths
Clear purchasing strategies aligned with organizational goals.
Effective vendor management practices, ensuring timely delivery and quality.
Strong initial compliance framework covering most regulatory requirements.
B. Areas for Improvement
Documentation of procurement activities lacks consistency, creating risks of mismanagement.
The vendor base is limited, potentially affecting supply chain flexibility.
Cost monitoring and tracking mechanisms need enhancement to capitalize on potential savings.
VI. Risk Assessment
The audit identified significant risks that could affect procurement efficiency and compliance:
A. Vendor Dependence
Over-reliance on a small pool of vendors increases vulnerability to supply chain disruptions.
B. Compliance Monitoring
A lack of regular audits and monitoring mechanisms could lead to inadvertent non-compliance.
C. Inconsistent Documentation
Fragmented documentation practices increase the risk of errors, inefficiencies, and non-compliance with legal or policy requirements.
VII. Recommendations
Based on the audit findings, the following recommendations are proposed:
A. Standardize Documentation
Implement a centralized system for consistent documentation of procurement activities, including templates for purchase orders and contracts.
B. Expand Vendor Base
Encourage diversification by onboarding additional suppliers to mitigate risks associated with vendor dependency.
C. Establish Compliance Monitoring
Develop a robust compliance monitoring framework with periodic audits, checklists, and real-time tracking of procurement activities.
D. Enhance Cost Control Measures
Introduce advanced cost analysis tools and regular reviews of procurement expenditures to identify and implement savings strategies.
VIII. Compliance Evaluation
The audit assessed procurement activities for alignment with relevant policies and regulations. While most processes comply with the required standards, the following areas require improvement:
Updating internal policies to align with recent regulatory changes.
Providing targeted staff training to enhance awareness of compliance requirements.
IX. Appendices
Supporting materials for the audit include:
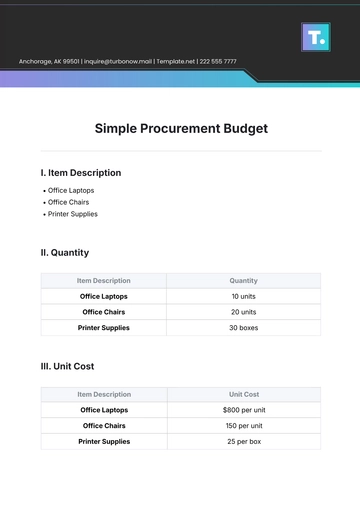
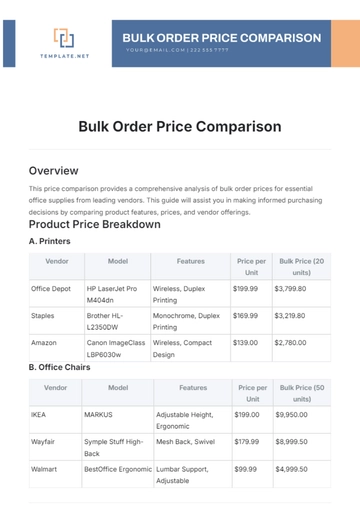
Procurement Data Analysis: Detailed tables and graphs illustrating trends and anomalies in procurement spending.
Interview Summaries: Notes and highlights from discussions with key stakeholders.
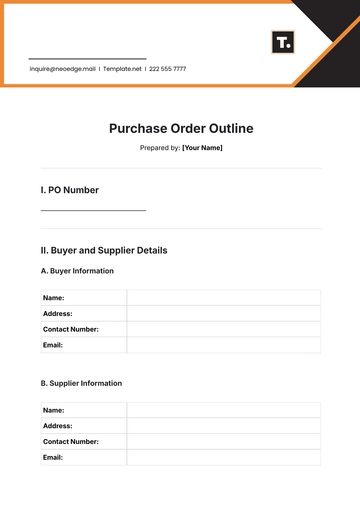
Sample Documentation: Examples of purchase orders, vendor agreements, and policy documents reviewed during the audit.
Compliance Checklist: A checklist outlining the criteria used to assess regulatory and policy adherence.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Ensure compliance and accuracy with our Sample Procurement Audit Template at Template.net. This customizable and editable tool is perfect for auditing procurement procedures, identifying inefficiencies, and maintaining transparency. Editable in our Ai Editor Tool, you can adapt it to meet specific organizational requirements, making it a practical solution for effective auditing.