Simple Group Study Class Notes
Prepared by: [Your Name]
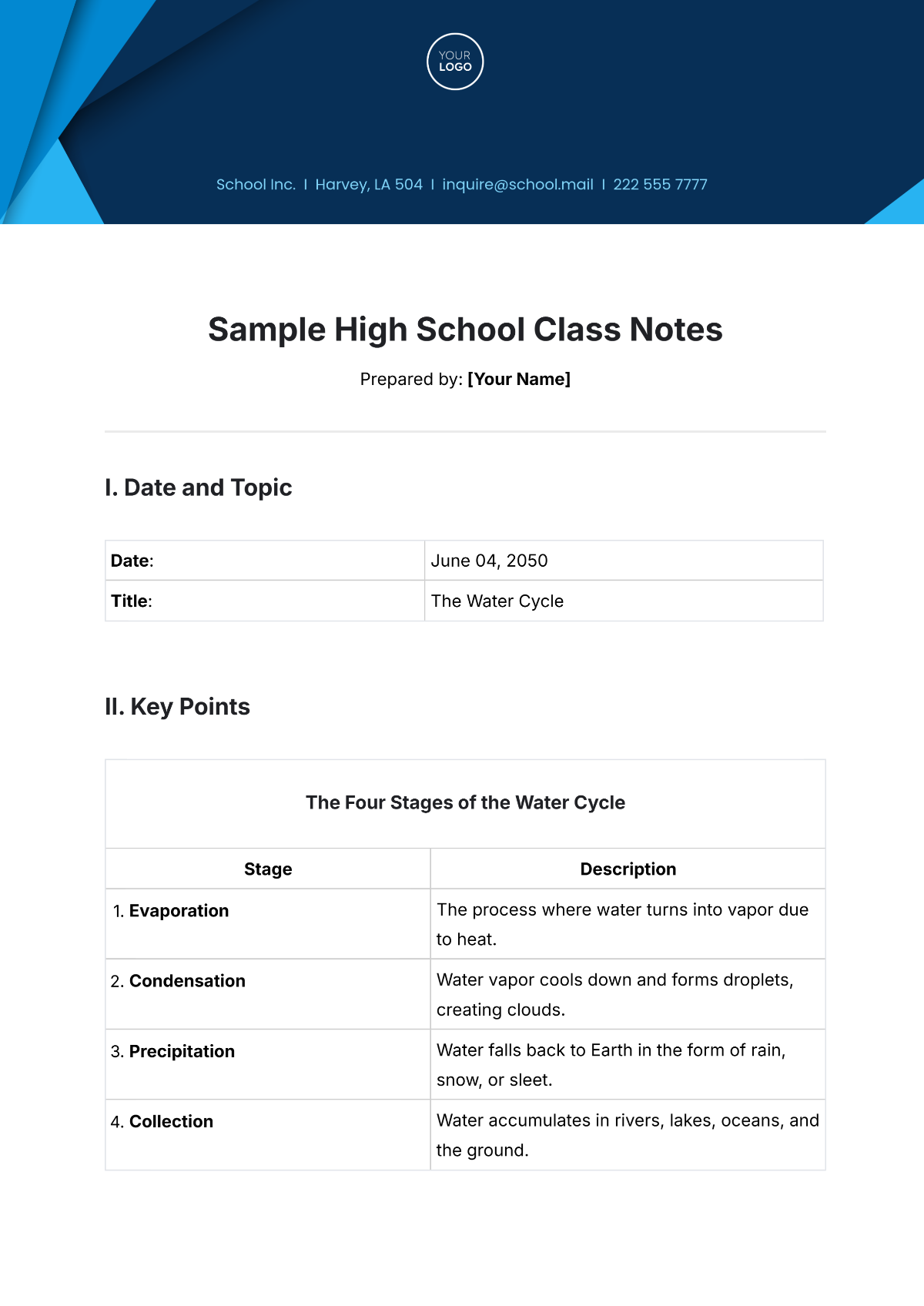
Date: | April 05, 2050 |
Title: | Introduction to Biology |
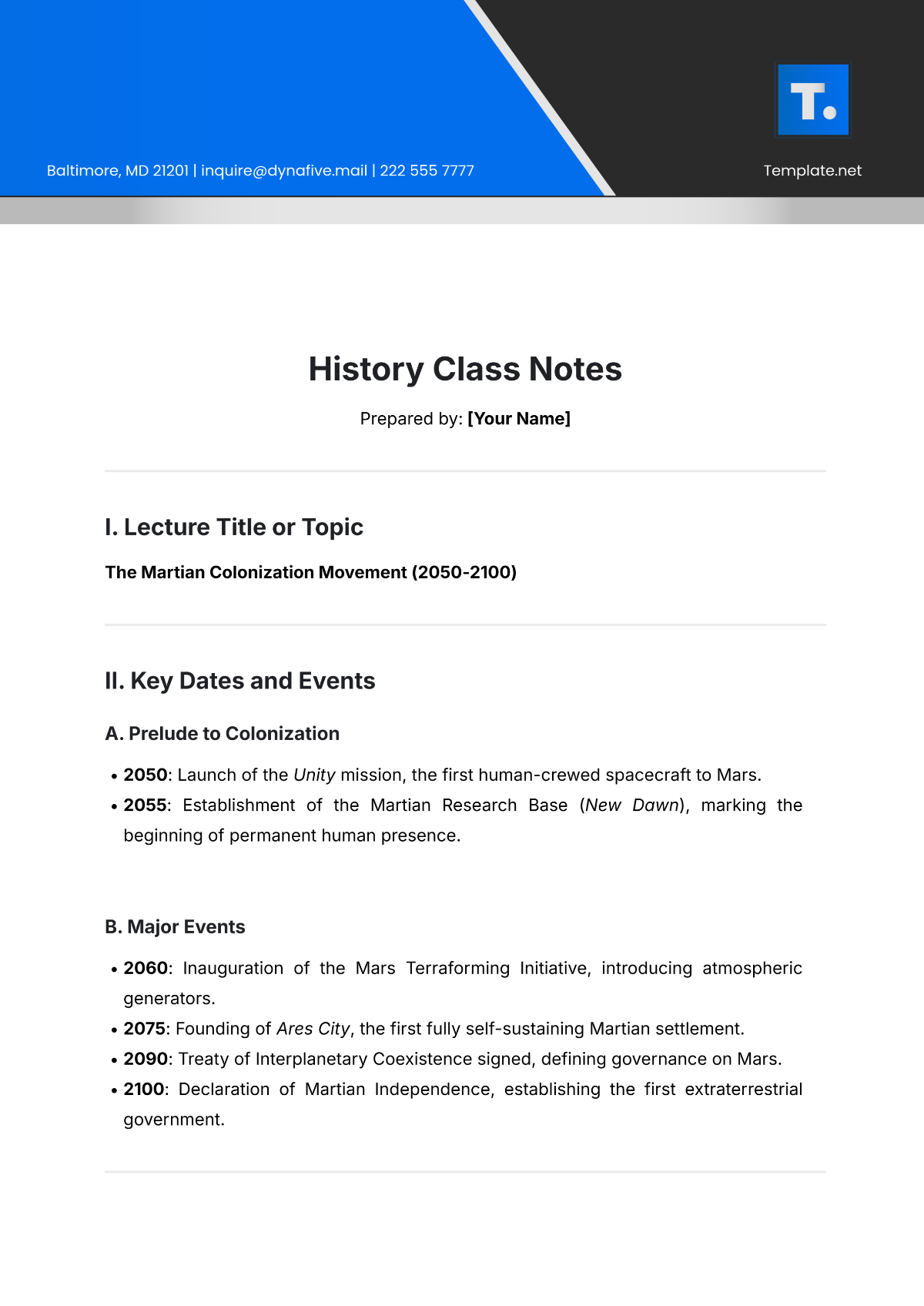
I. Key Concepts/Definitions
|
II. Main Ideas
Cell Theory | Structure of Prokaryotic Cells | Structure of Eukaryotic Cells |
|
|
|
III. Summary
In summary, all living organisms are composed of cells, with two primary types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack membrane-bound organelles, whereas eukaryotic cells are more complex and contain specialized structures to perform various functions. The understanding of cell structures and their functions is critical for studying biological processes. |
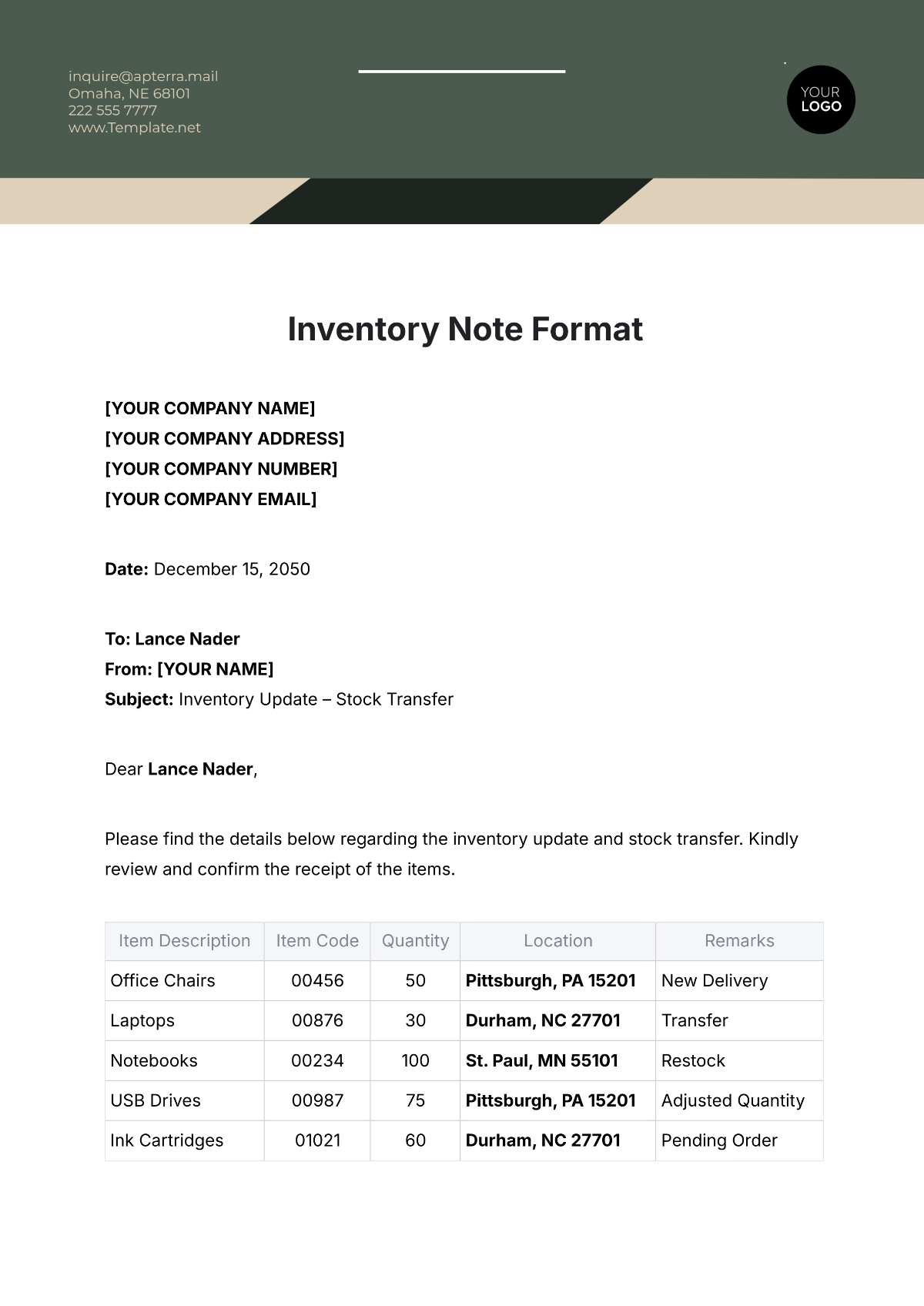
IV. Diagrams/Charts
|
V. Discussion Points
|