Printable Class Notes
Prepared by: [Your Name]
Date: | April 10, 2050 |
Title: | The Structure of the Atom |
I. Key Concepts
A. What is an Atom?
The basic unit of matter consists of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Atoms combine to form molecules, which make up all substances in the universe.
B. Parts of an Atom
Nucleus: The central core of the atom, containing protons and neutrons.
Electron Cloud: The area surrounding the nucleus where electrons are located.
II. Definitions
A. Protons
Positively charged particles are found in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons defines the element.
B. Neutrons
Neutrally charged particles are found in the nucleus, helping to stabilize the atom.
C. Electrons
Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells.
III. Examples
Example 1: Hydrogen Atom
A hydrogen atom consists of one proton, one neutron (in some isotopes), and one electron. It’s the simplest atom in the periodic table.
Example 2: Oxygen Atom
An oxygen atom has eight protons, eight neutrons, and eight electrons. It plays a key role in the composition of water and is essential for respiration.
IV. Diagrams/Charts
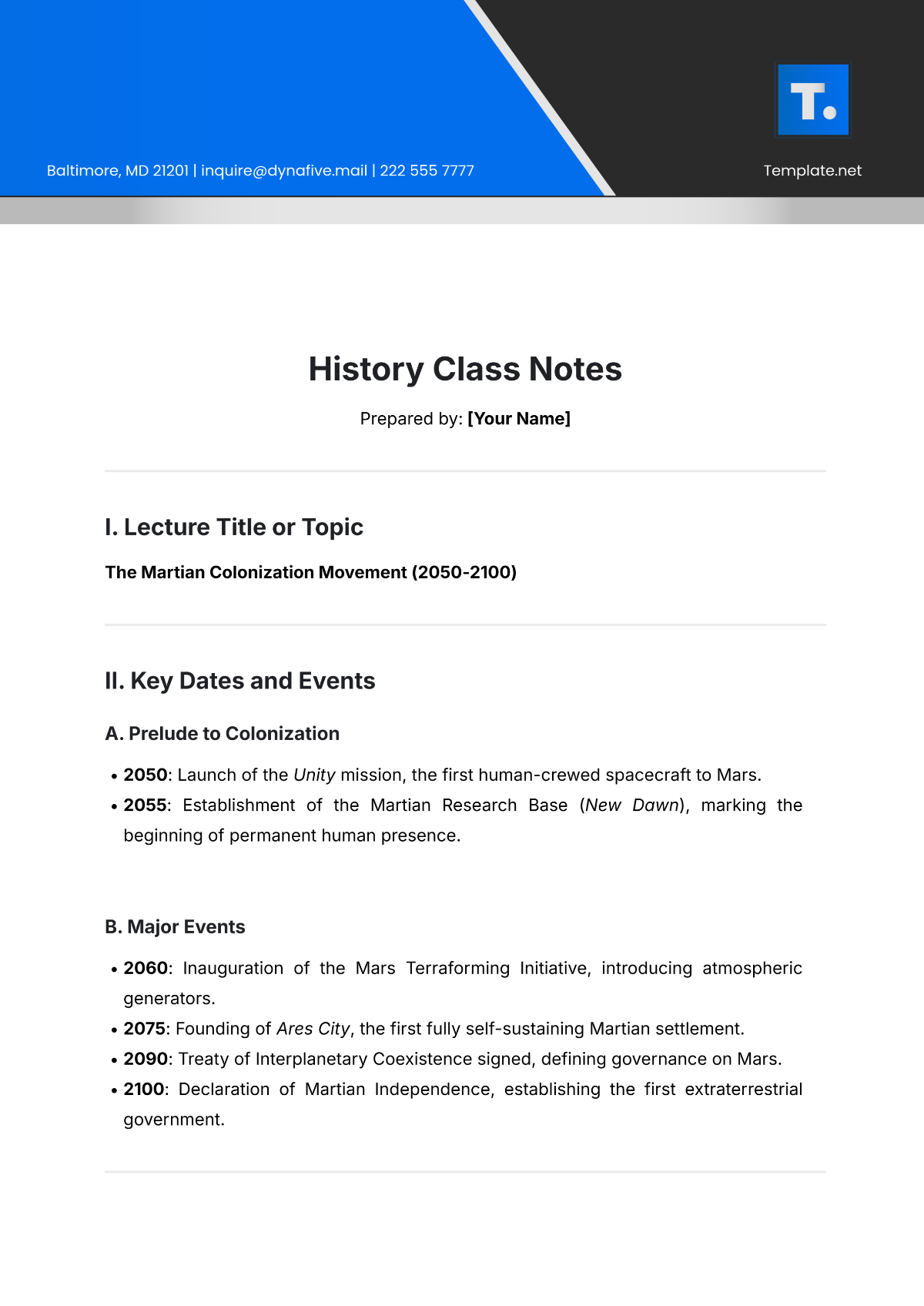
Atom Structure Diagram
A simple diagram illustrating:
The nucleus (containing protons and neutrons) is at the center, with electrons orbiting in energy shells around it.
V. Important Dates/Events
A. Discovery of the Atom
In the early 19th century, John Dalton proposed the atomic theory, which states that matter is made of indivisible atoms.
B. Development of Atomic Models
In the early 20th century, scientists like Ernest Rutherford and Niels Bohr developed models of the atom that led to a deeper understanding of atomic structure.
VI. Summary
An atom is the fundamental building block of matter, made up of a central nucleus (containing protons and neutrons) and orbiting electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus defines the element. Understanding atomic structure is key to chemistry, as atoms combine to form the substances that make up our world.