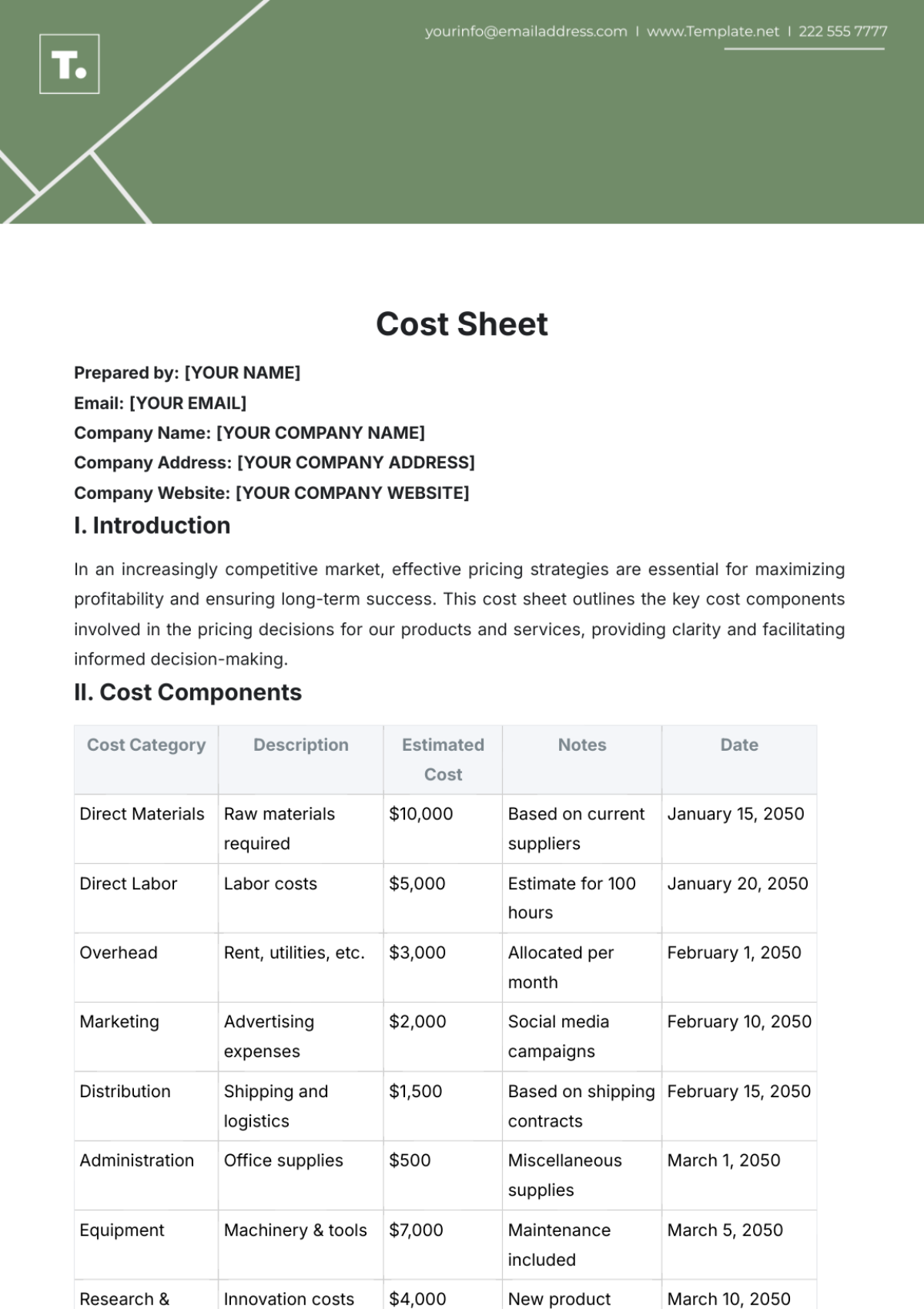
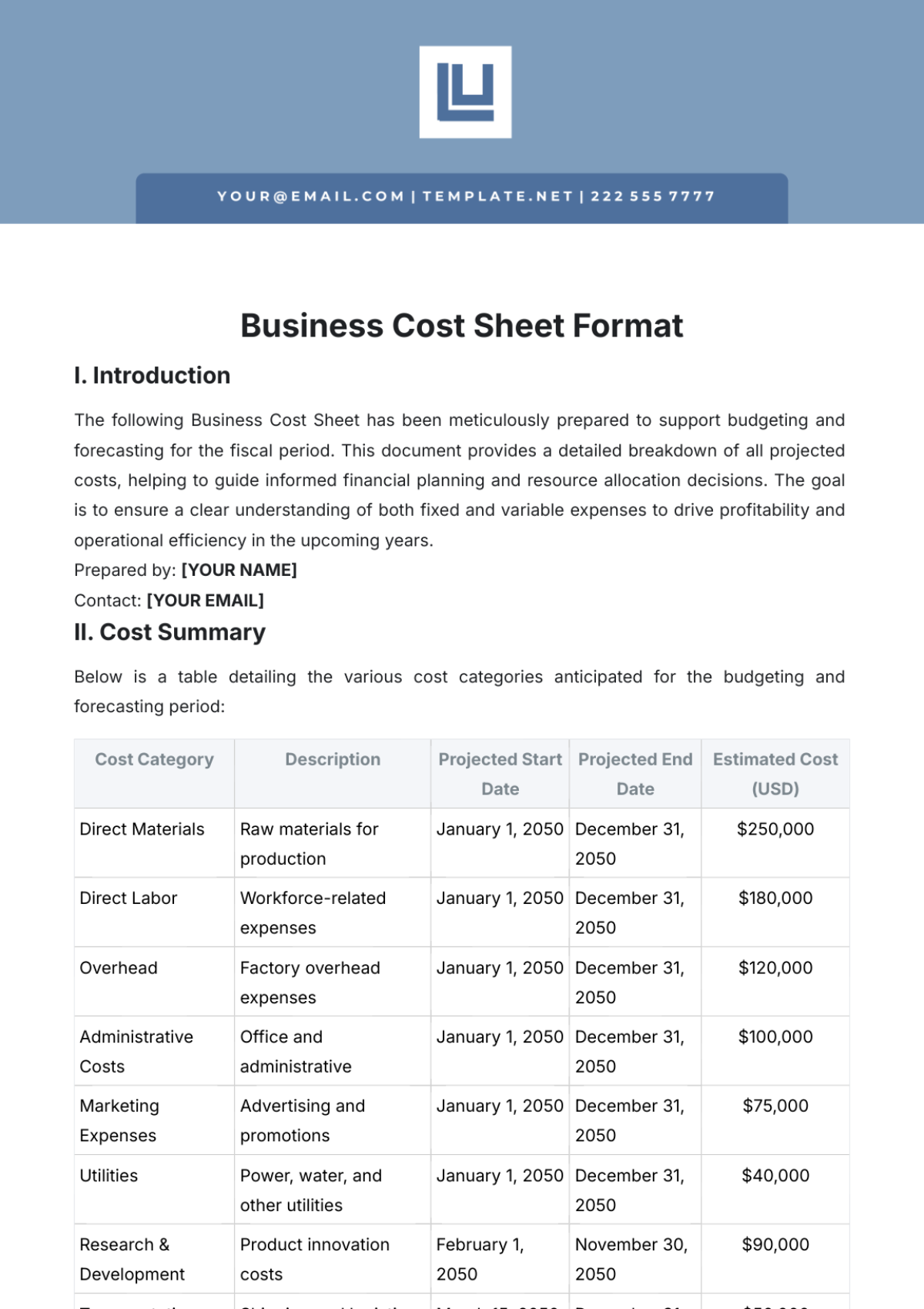
Benefit-Cost Ratio Outline
Prepared by: [YOUR NAME]
This outline provides a comprehensive framework for calculating and analyzing the Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR) for projects, policies, or initiatives. It is designed to ensure clarity and precision while covering all essential components of a cost-benefit analysis.
I. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Purpose of the Analysis:
Briefly state the objective of the analysis.
Example: "The purpose of this analysis is to evaluate the feasibility and value of [PROJECT NAME], proposed by [YOUR COMPANY NAME]."
Key Findings:
Summarize major insights, including:Total benefits.
Total costs.
Calculated BCR.
Recommendations.
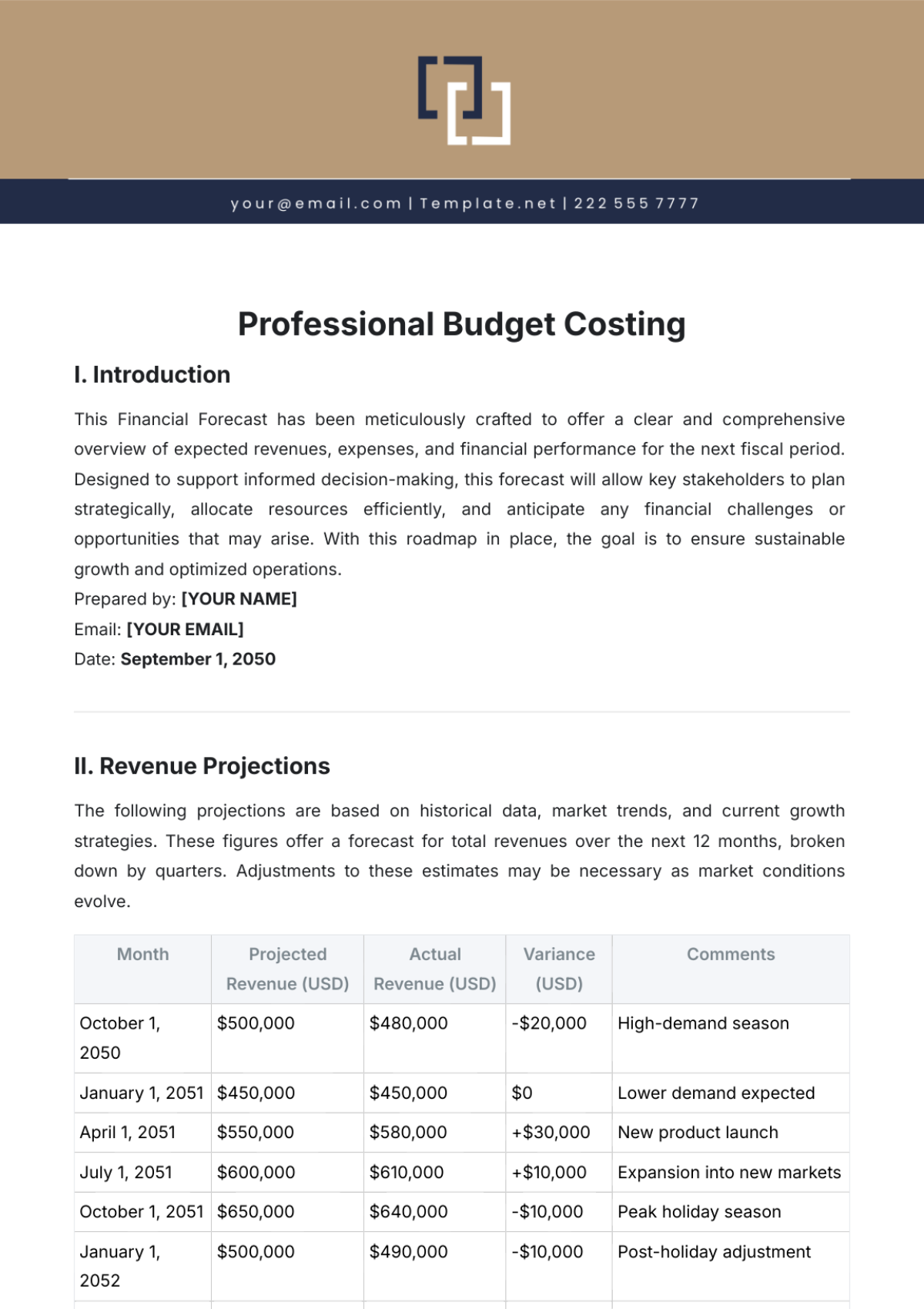
II. INTRODUCTION
Background of the Project:
Provide context, including:Objectives of the project or initiative.
Relevant stakeholders and their roles.
Purpose of the Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR):
Explain the importance of using BCR in decision-making.
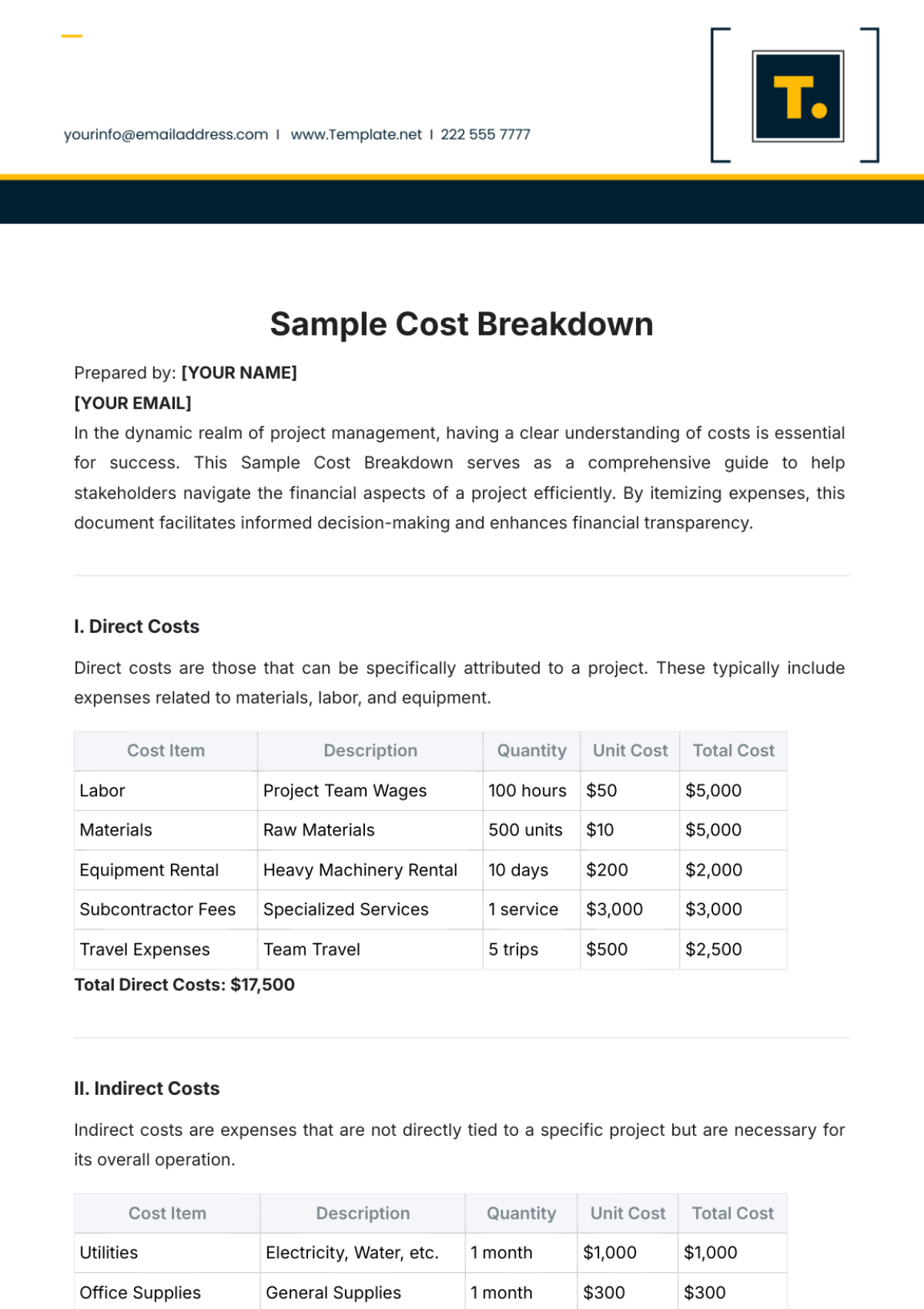
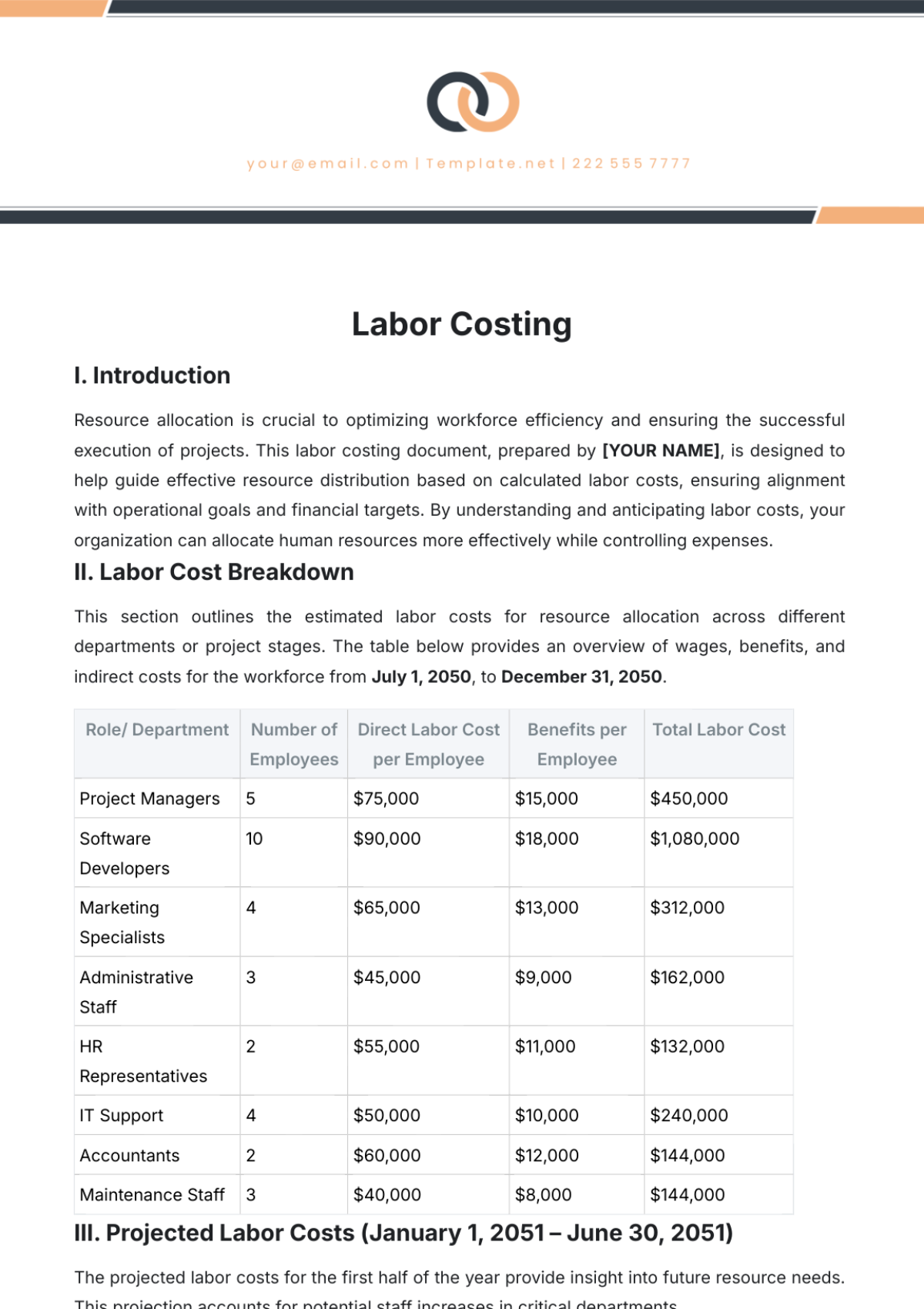
III. METHODOLOGY
Definition of BCR:
Include the formula:BCR=Total BenefitsTotal Costs\text{BCR} = \frac{\text{Total Benefits}}{\text{Total Costs}}BCR=Total CostsTotal Benefits
Scope of the Analysis:
Define the parameters, including:Timeframe (e.g., [START YEAR] to [END YEAR]).
Assumptions (e.g., discount rates, inflation rates).
Data Sources:
List all data inputs and their origins (e.g., market research, historical data, expert opinions).
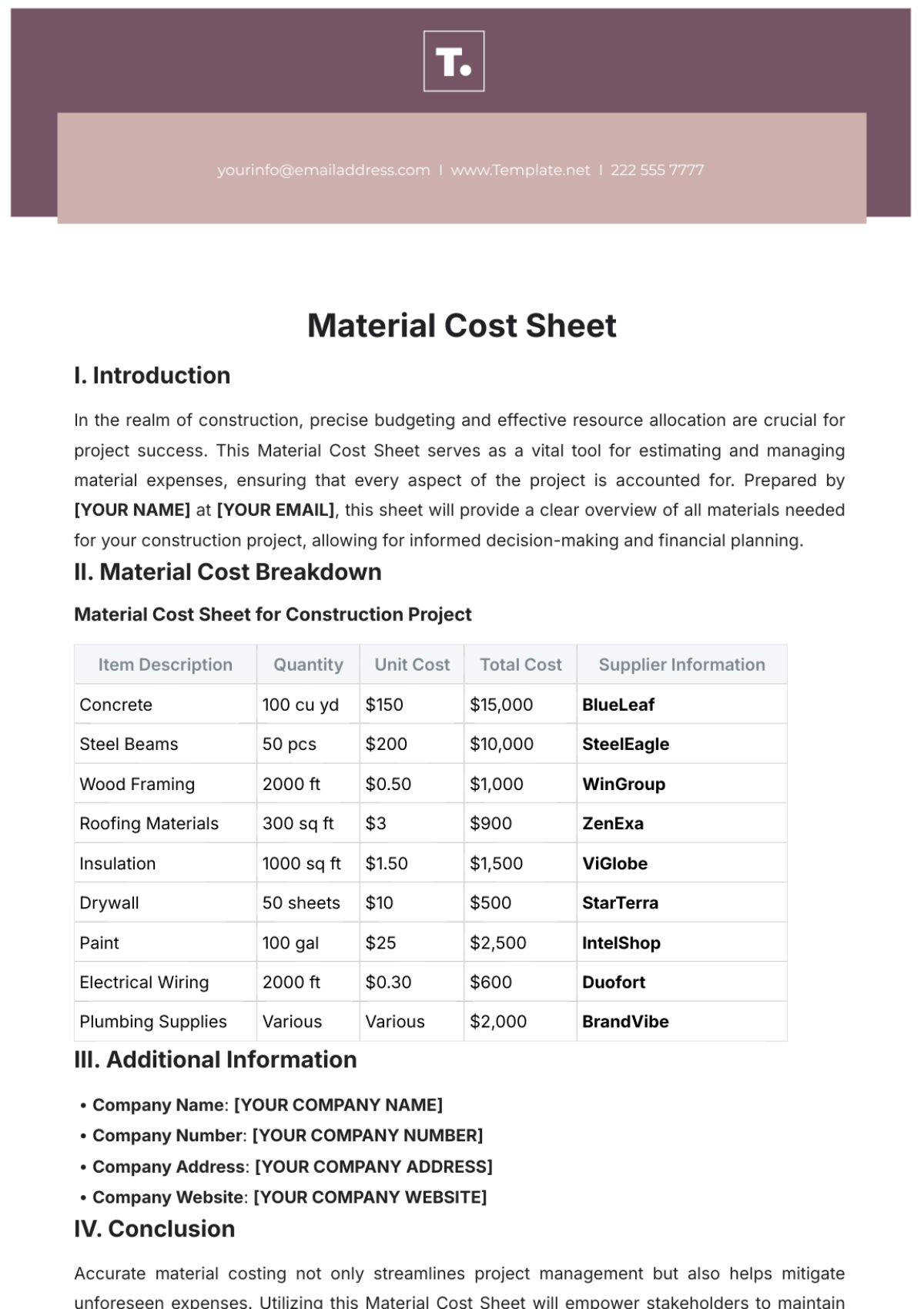
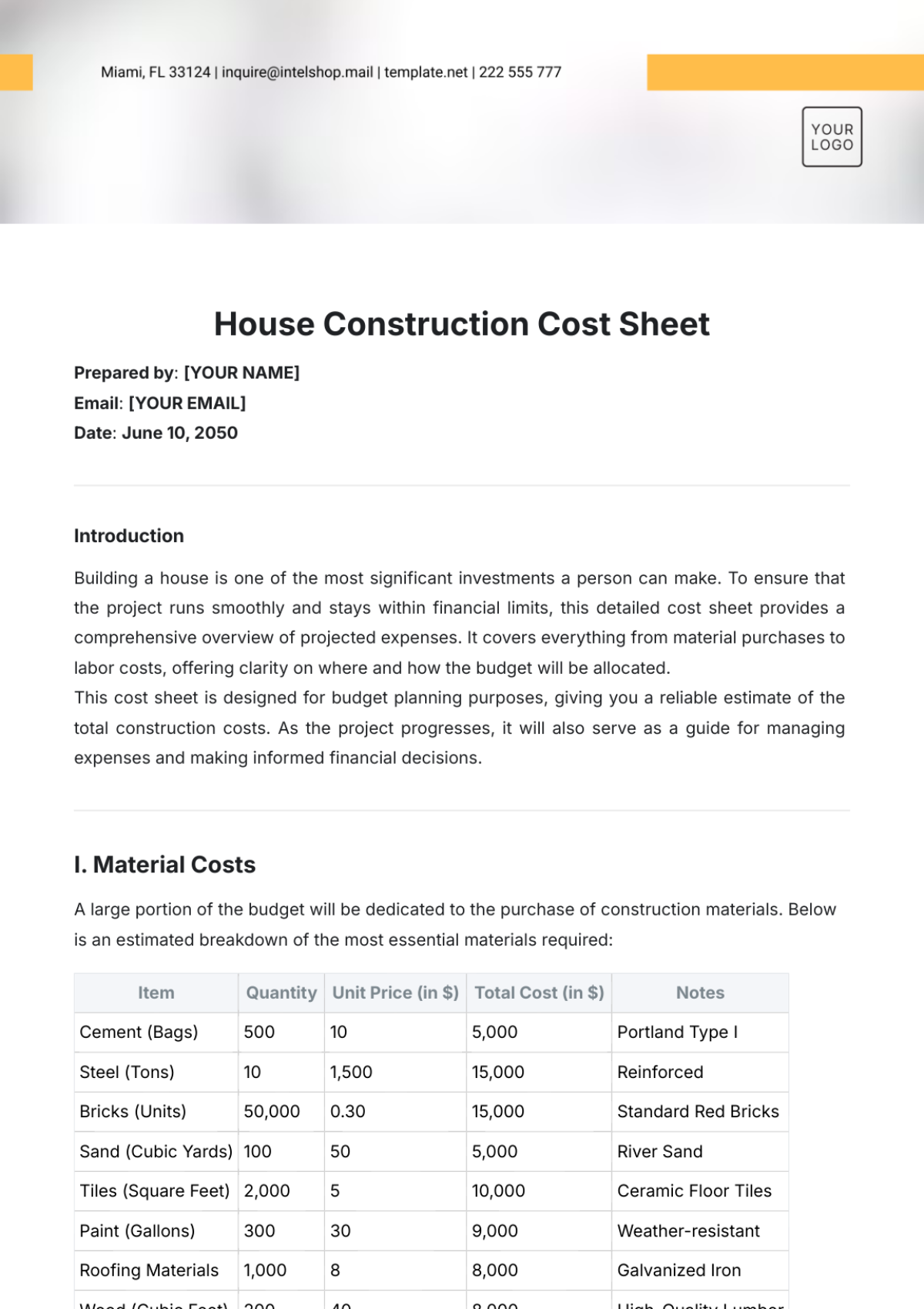
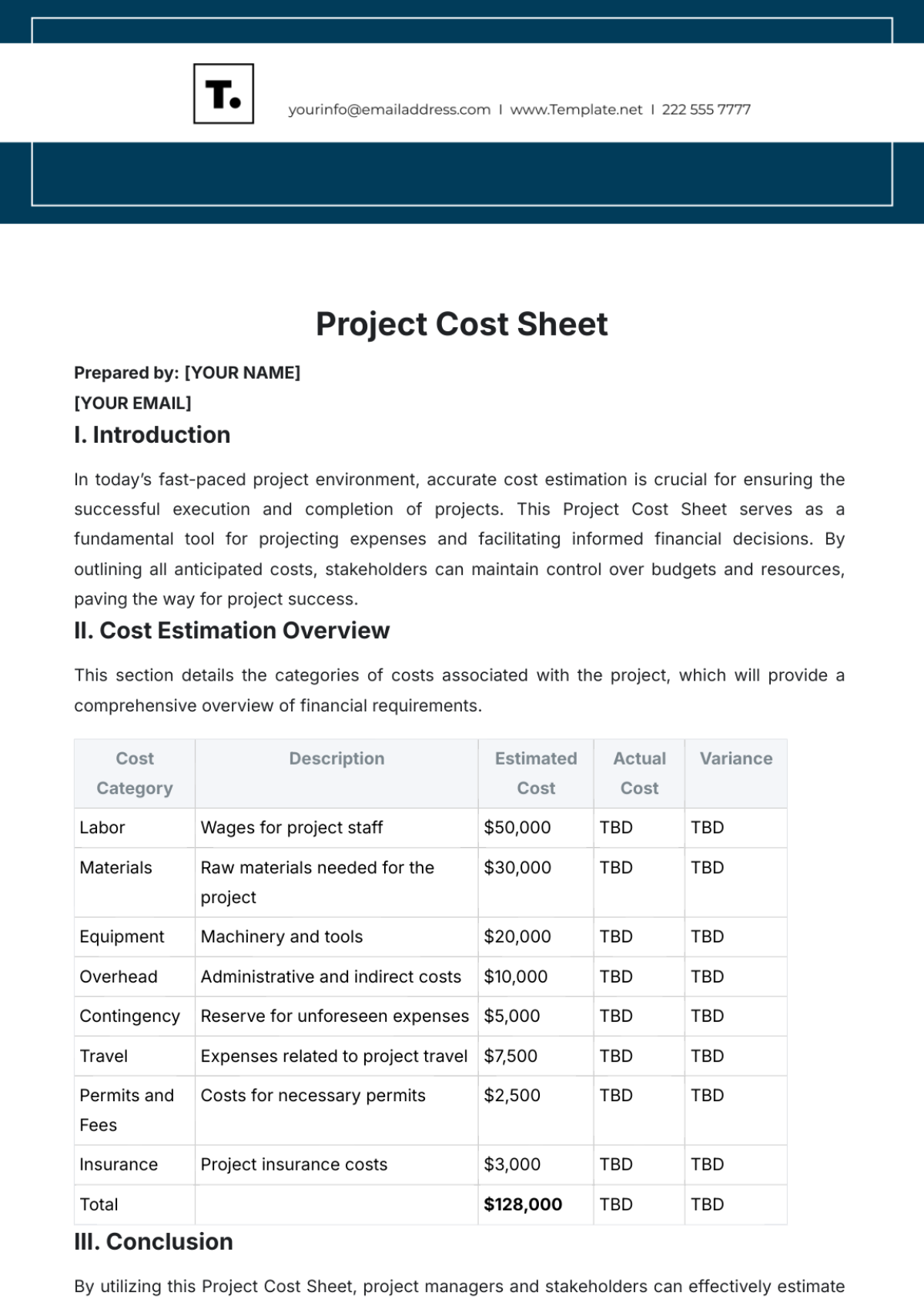
IV. COST ANALYSIS
Identification of Costs:
Capital costs ([SPECIFIC EXAMPLES]).
Operational and maintenance costs ([SPECIFIC EXAMPLES]).
Opportunity costs ([SPECIFIC EXAMPLES]).
Cost Estimation:
Provide detailed calculations and supporting evidence.
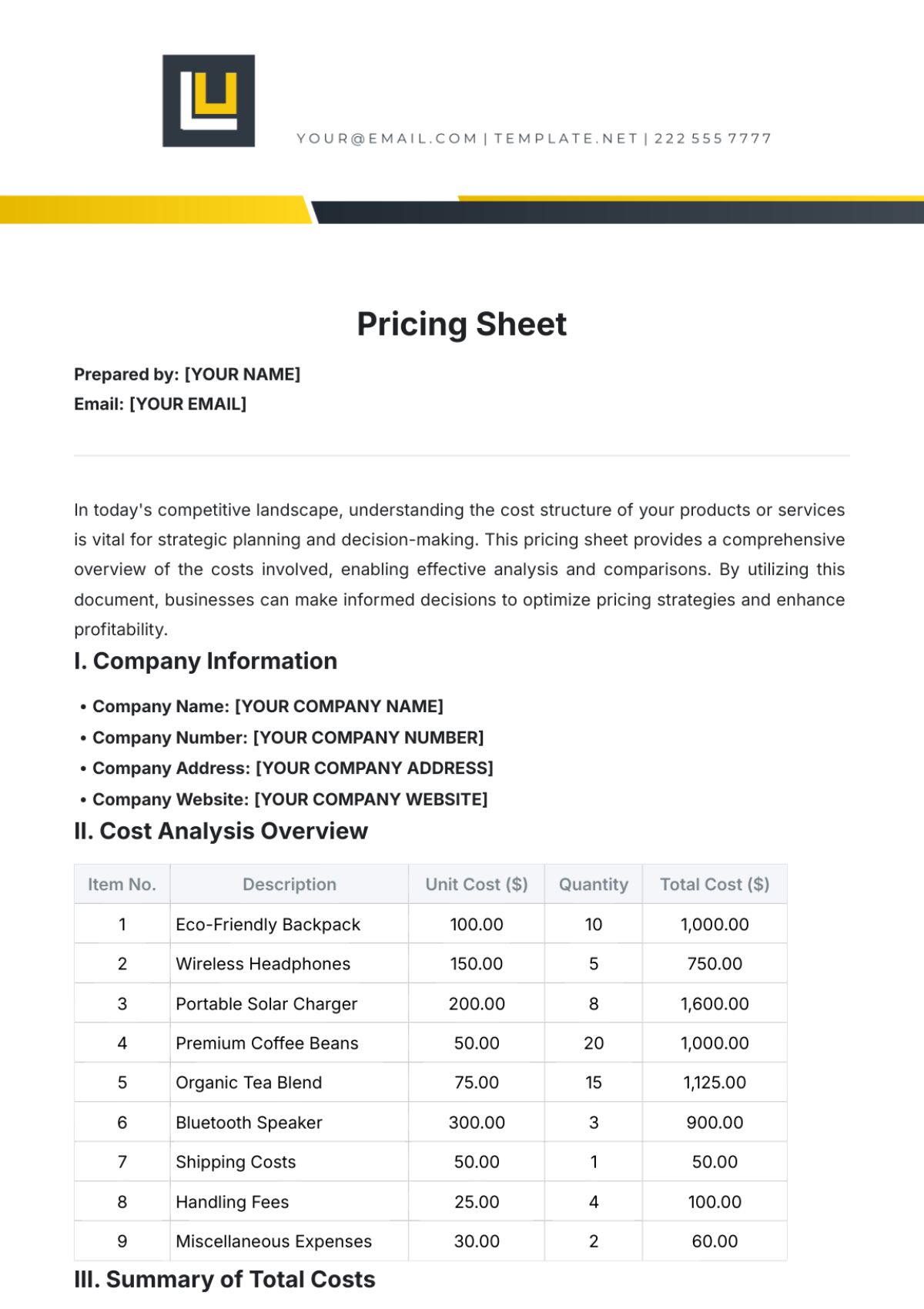
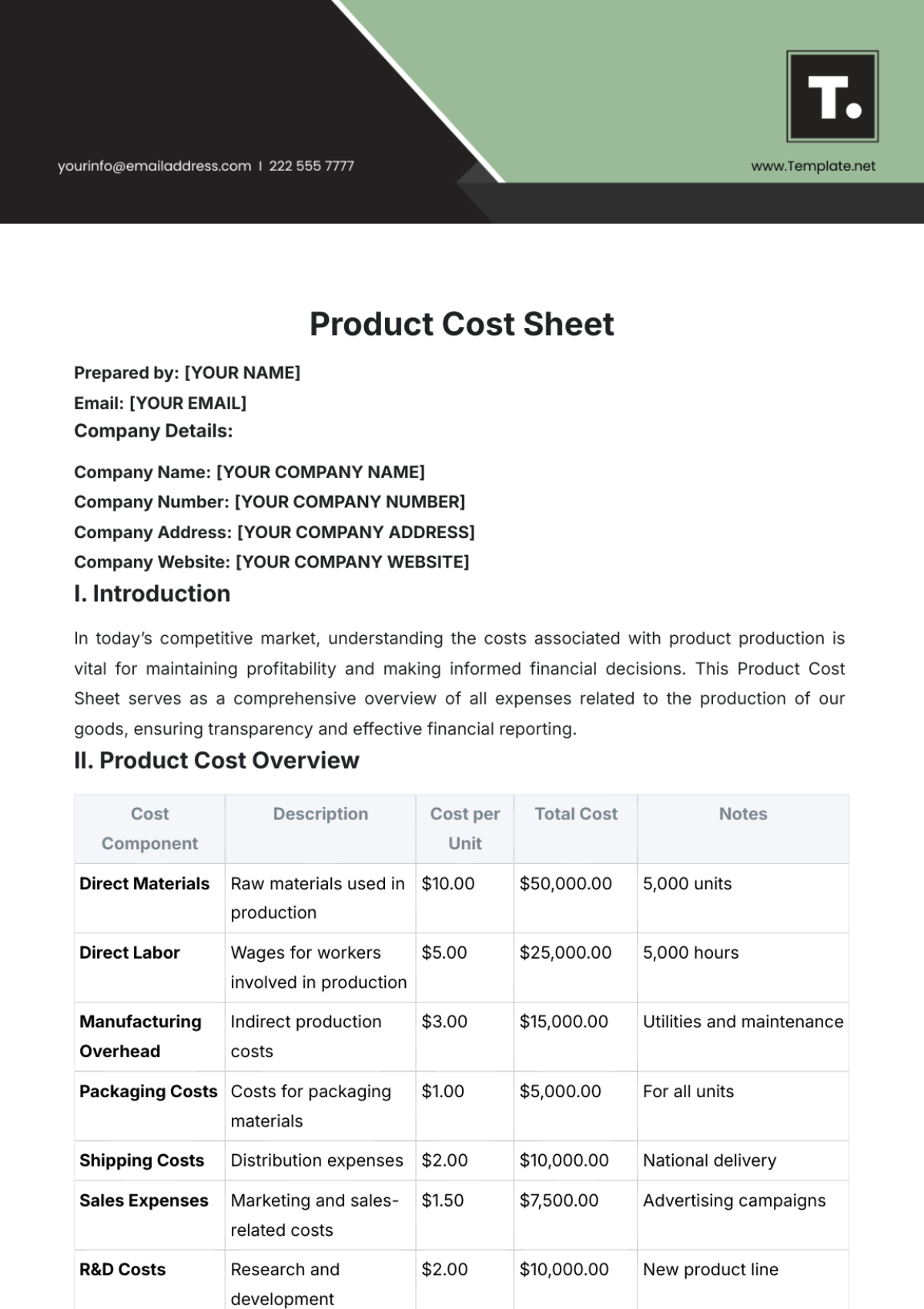
V. BENEFIT ANALYSIS
Identification of Benefits:
Direct benefits ([SPECIFIC EXAMPLES]).
Indirect benefits ([SPECIFIC EXAMPLES]).
Intangible benefits ([SPECIFIC EXAMPLES]).
Benefit Estimation:
Detail calculations and evidence supporting each benefit.
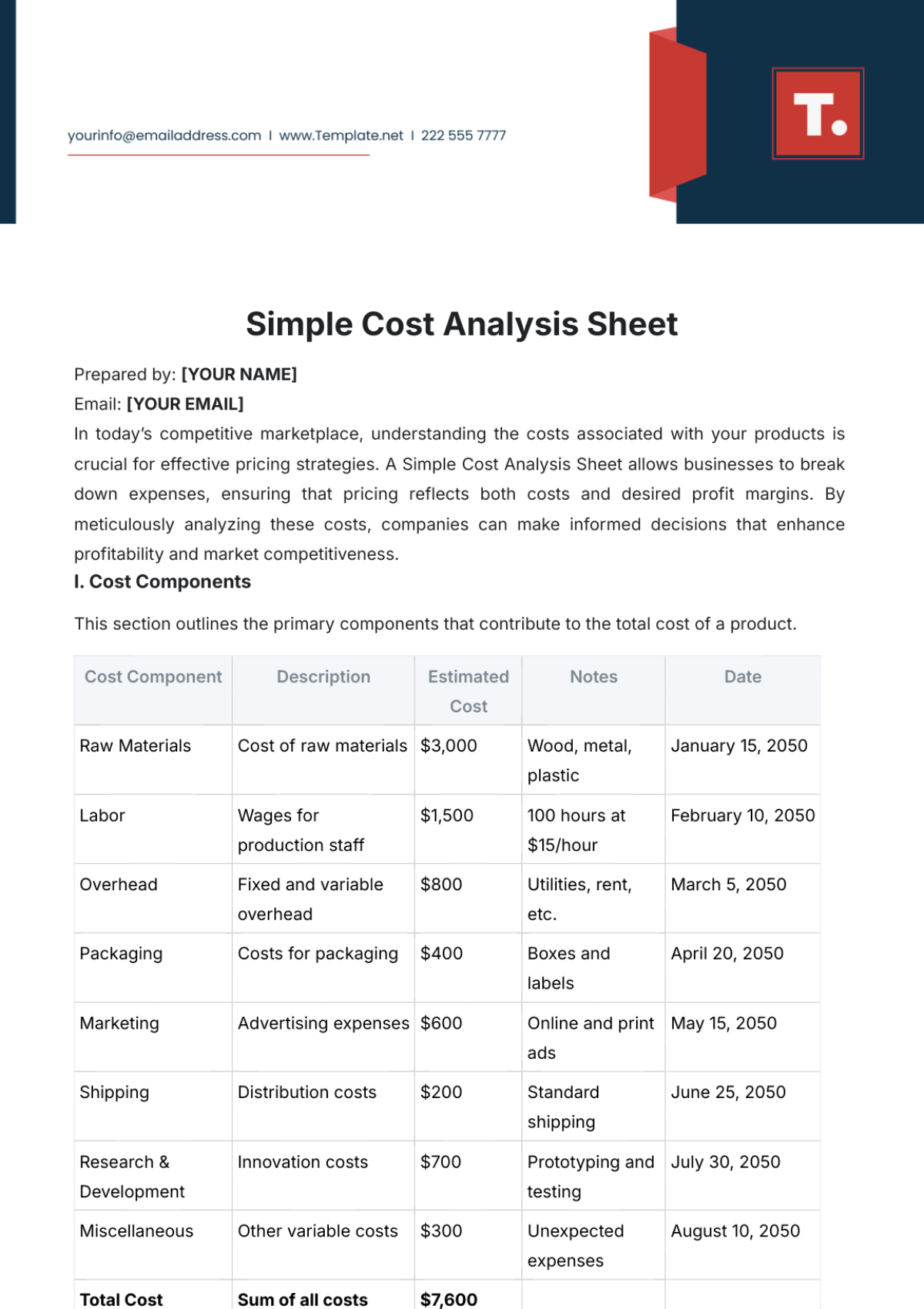
VI. BENEFIT-COST RATIO CALCULATION
BCR Formula Application:
Show the complete calculation using estimated figures.
Example:\text{BCR} = \frac{\text{Total Benefits of [PROJECT NAME] (e.g., $**[X]**)}}{\text{Total Costs (e.g., $**[Y]**)}} = [BCR VALUE]
Interpretation of Results:
If BCR > 1: The benefits outweigh the costs, making the project viable.
If BCR < 1: The costs outweigh the benefits, questioning project feasibility.
VII. SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS
Purpose of Sensitivity Analysis:
Discuss how changes in variables (e.g., discount rate, costs, or benefits) affect the BCR.
Scenarios Evaluated:
Best-case scenario.
Worst-case scenario.
Most likely scenario.
Results:
Include revised BCRs under each scenario.
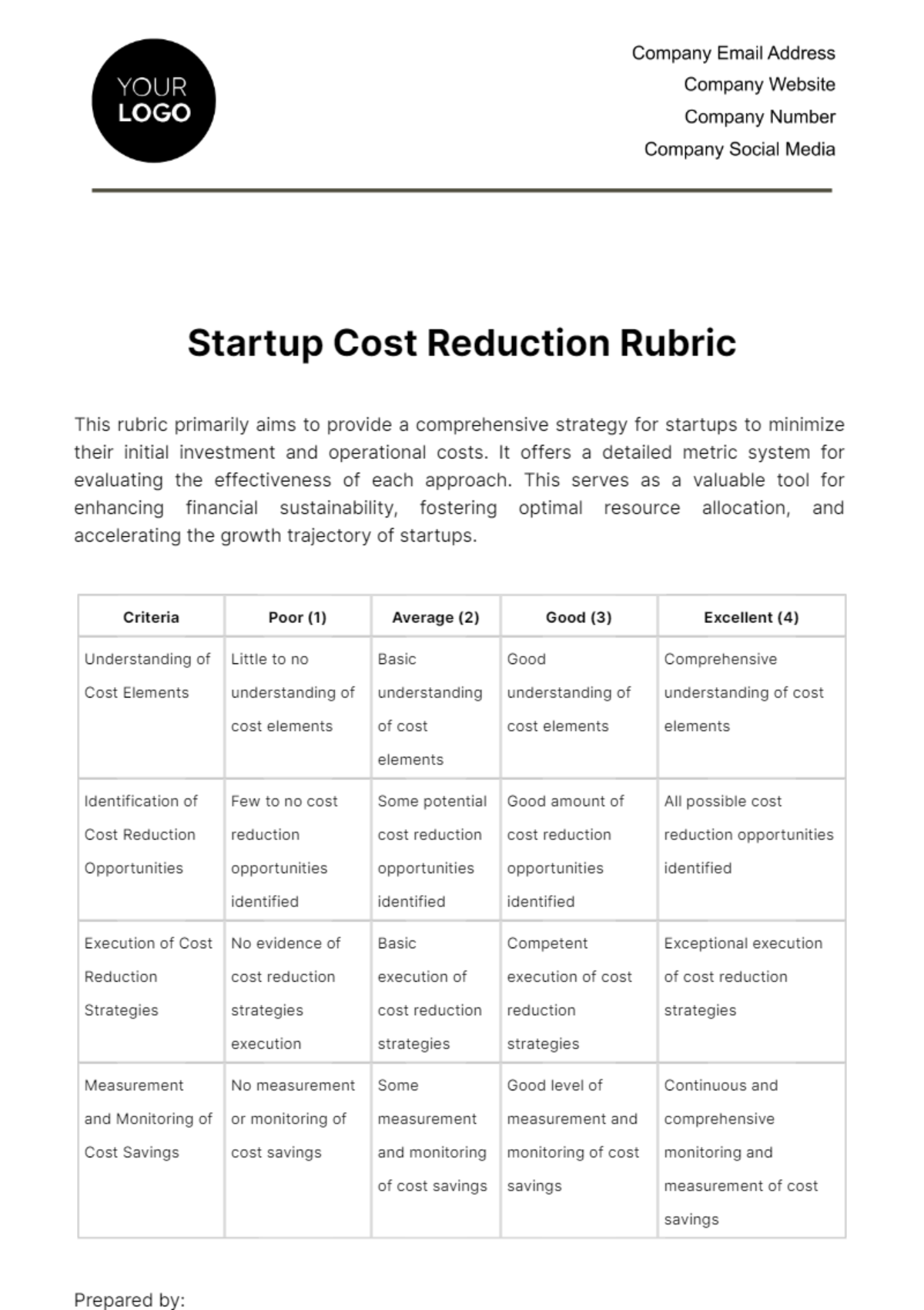
VIII. LIMITATIONS AND RISKS
Limitations of the Analysis:
Data constraints ([SPECIFIC EXAMPLES]).
Assumptions made ([SPECIFIC EXAMPLES]).
Risks:
Discuss potential risks impacting costs or benefits.
IX. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Summary of Findings:
Recap the key results, including BCR and sensitivity analysis outcomes.
Recommendations:
Provide actionable advice based on the analysis.
X. APPENDICES AND REFERENCES
Appendices:
Detailed calculations.
Additional data tables.
Graphs and charts.
References:
Cite all data sources and references used in the analysis.