Process Efficiency Gap Analysis
Prepared By: [YOUR NAME]
Date: July 1, 2050
I. Process Description
The process under analysis involves the operations of the supply chain management system within our organization. This process encompasses the planning, procurement, inventory management, and logistics stages that facilitate the seamless flow of goods from suppliers to customers. Our objective is to critically evaluate this process to identify areas that hinder maximal operational efficiency and effectiveness, thereby optimizing productivity and minimizing costs.
II. Current State Assessment
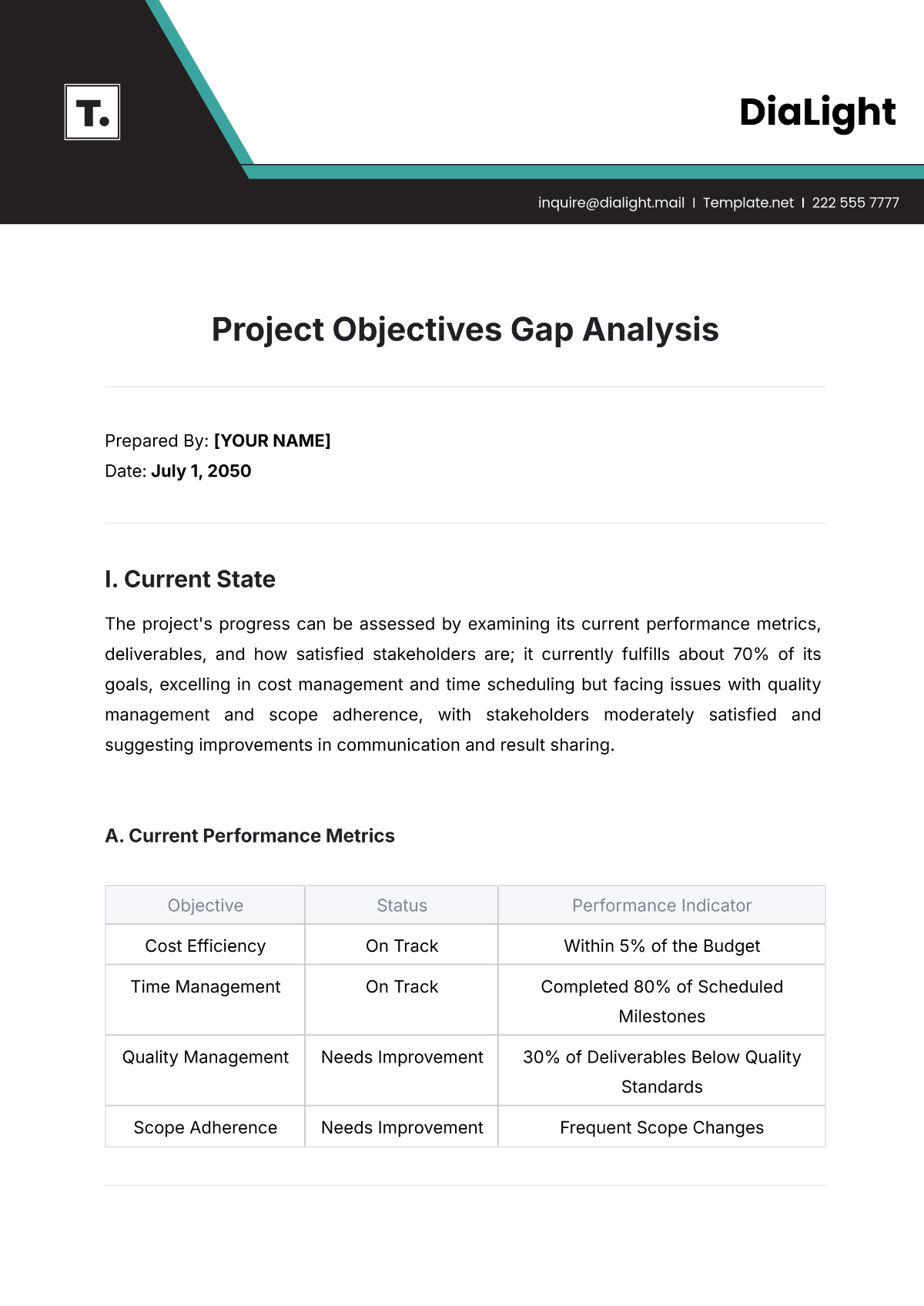
Currently, the supply chain process functions through a series of integrated steps that rely heavily on various software tools for ordering, tracking, and reporting. However, bottlenecks in communication and delay in information updates have been identified as prevalent issues. Analysis of performance metrics reveals:
Metric | Current Performance |
|---|---|
Order Fulfillment Time | 72 hours |
Inventory Turnover | 5 times per year |
Supply Chain Cost as a Percentage of Sales | 12% |
These metrics illustrate an operational framework that requires improvements, particularly in reducing lead times and enhancing inventory rotation rates.
III. Desired State
The desired state of the supply chain process involves achieving a leaner, more responsive operation with improved accuracy and connectivity across all stages. Performance targets include:
Reducing order fulfillment time to less than 24 hours.
Increasing inventory turnover to 8 times per year.
Lowering supply chain costs to under 8% of sales.
These targets align with strategic goals of competitiveness, cost-efficiency, and superior customer satisfaction.
IV. Gap Identification
The analysis identifies significant gaps between the current and desired states, primarily characterized by:
Delays in order processing and delivery schedules.
Excess materials lead to high inventory holding costs.
Under-utilization of technological tools and data analytics.
These gaps highlight the need for a strategic overhaul in process execution and resource management.
V. Root Cause Analysis
To fully comprehend the inefficiencies, a root cause analysis was conducted, identifying the following underlying issues:
Systems Integration: Poor integration between different software systems leads to miscommunication and delays.
Process Complexity: Workflows that are needlessly intricate and convoluted can lead to inefficiencies by creating obstacles and delays in processes.
Lack of Training: There is a lack of adequate training provided to staff members on the most effective practices as well as on the adoption and use of new technologies.
Vendor Performance: Varying supplier reliability contributes to inconsistent supply lead times.
VI. Action Plan
To address the identified gaps and achieve the desired state, the following action plan has been proposed:
Systems Overhaul: Implement comprehensive ERP solutions to ensure seamless integration and real-time data flow.
Process Simplification: Streamline workflows by eliminating redundancies and automating routine tasks.
Training Programs: Develop continuous training modules for staff to enhance process understanding and skillset.
Supplier Evaluation: Conduct regular performance reviews and establish a robust vendor management framework.
VII. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The success of these interventions will be measured through specific KPIs, including:
Reduction in average order fulfillment time to below target levels.
Increase in inventory turnover rates meeting annual targets.
Decreased percentage of supply chain costs relative to sales.
Improvement in supplier performance ratings.
Achieving these KPIs will signify a successful realignment of the supply chain process towards greater efficiency and customer satisfaction.