Mining Inventory Management
I. Introduction
This document outlines the inventory management processes and procedures at [Your Company Name]. It covers topics such as inventory control, stocktaking, and procurement. By following these guidelines, we can ensure optimal inventory levels, minimize stock outs, and reduce costs.
II. Inventory Control
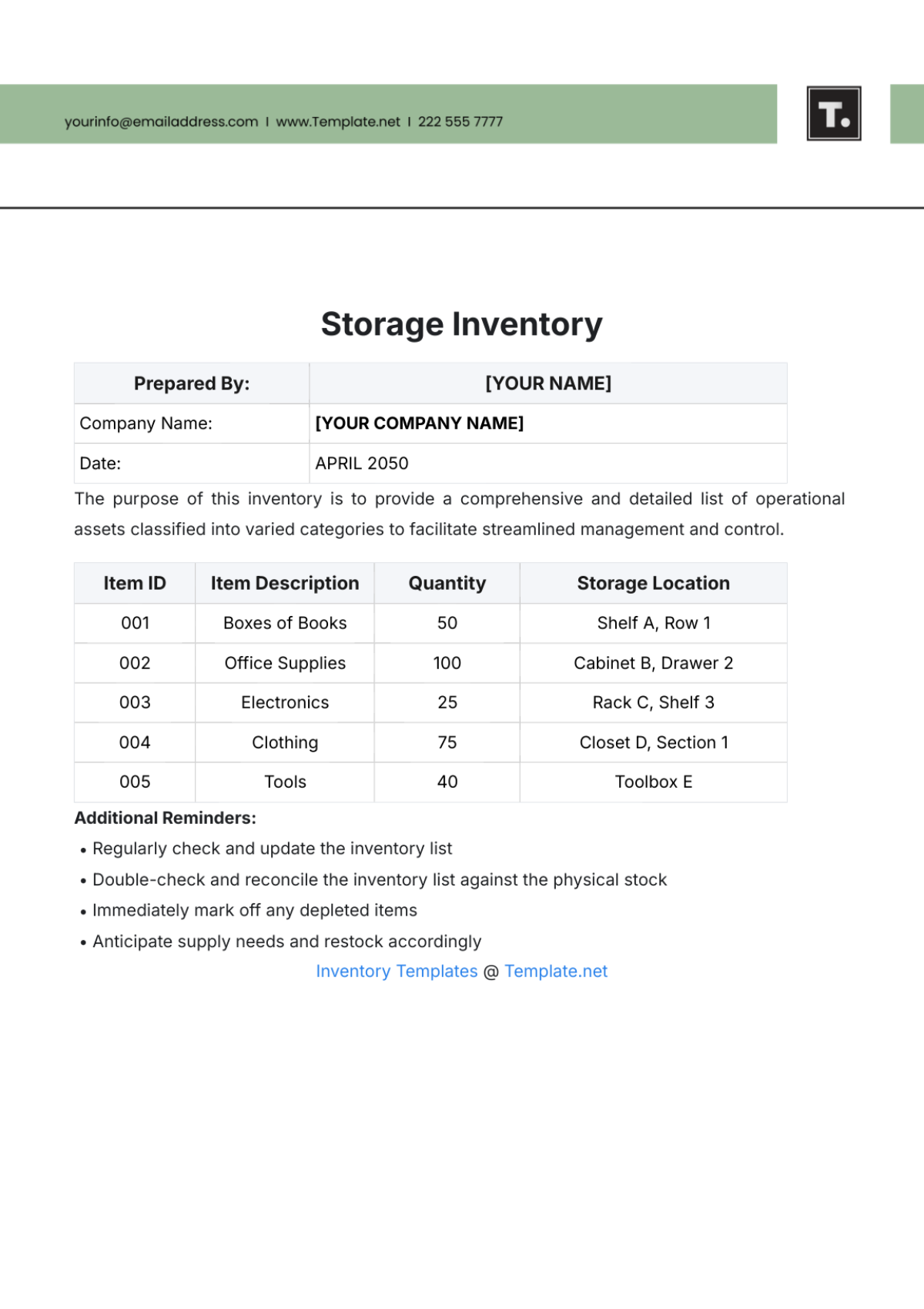
Inventory control is essential to maintain accurate records of inventory items. This section outlines the key principles and practices of inventory control at [Your Company Name].
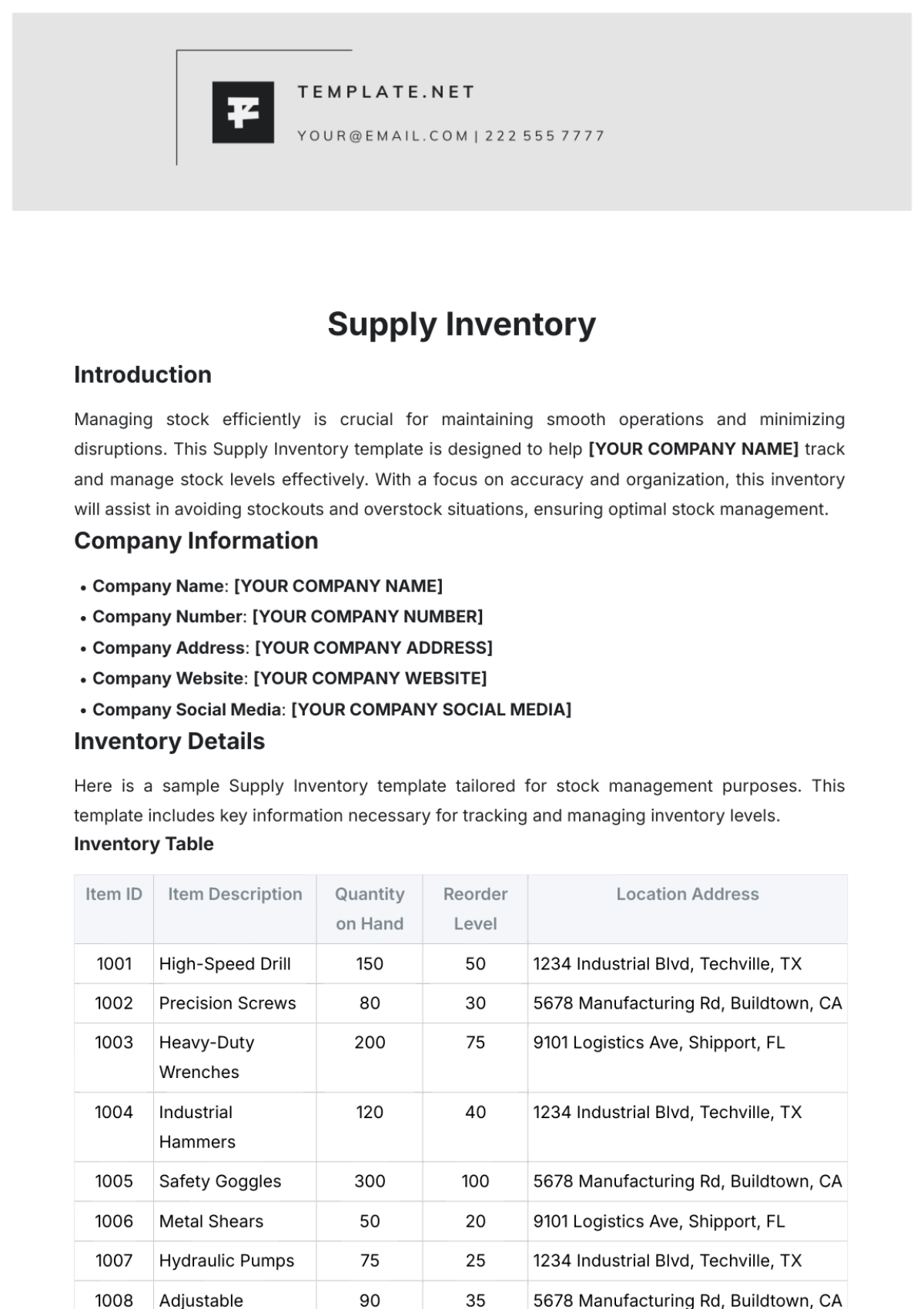
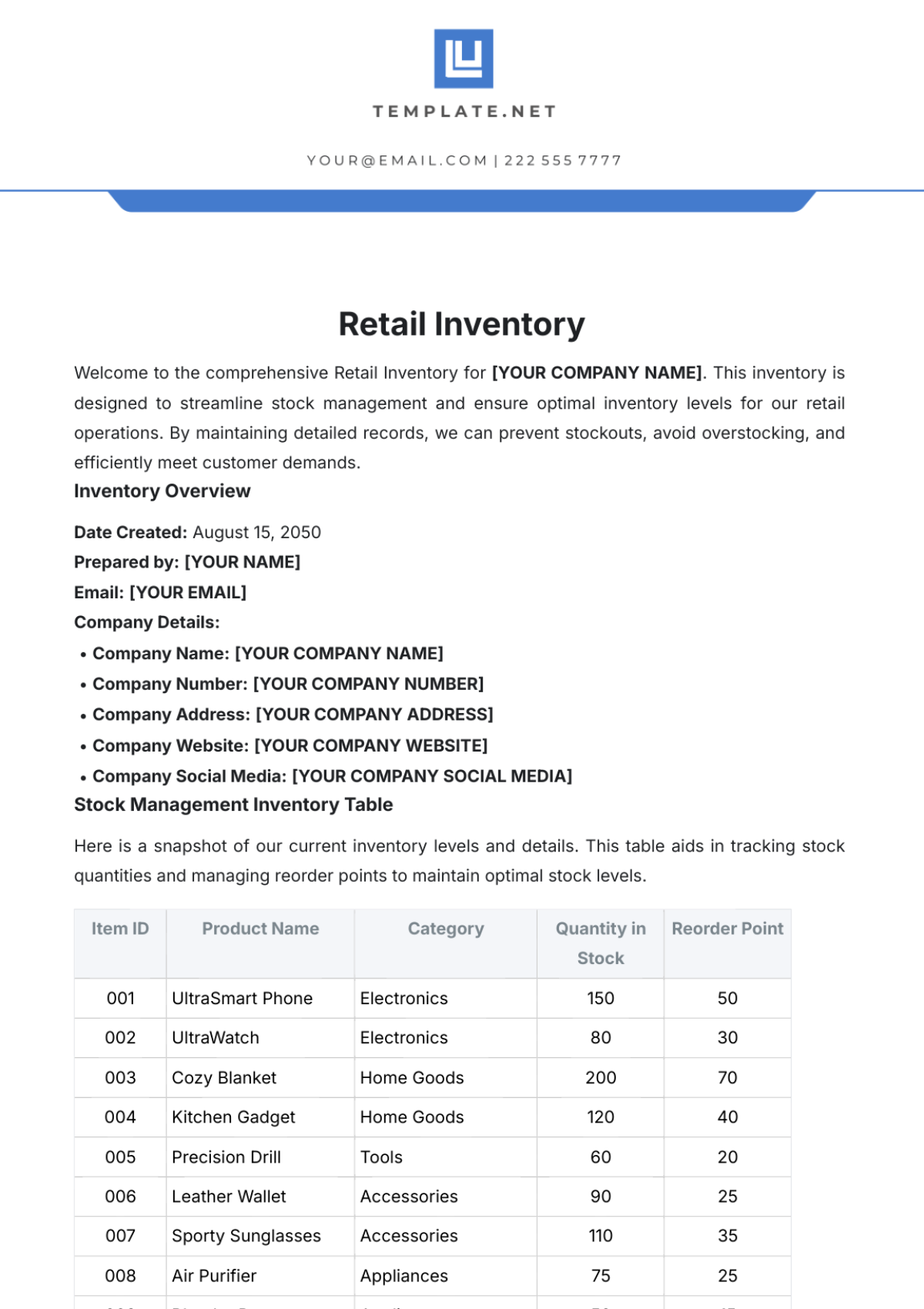
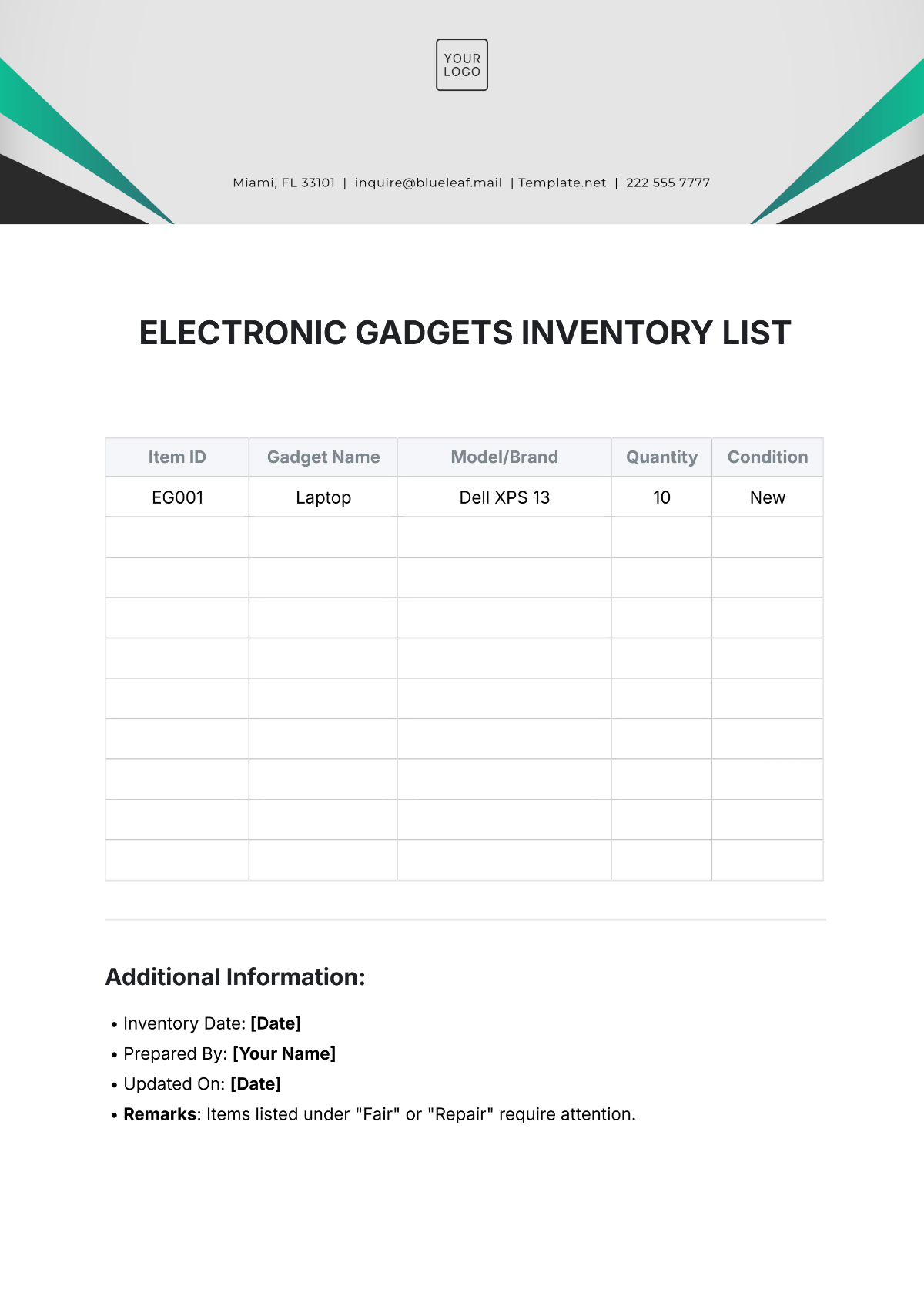
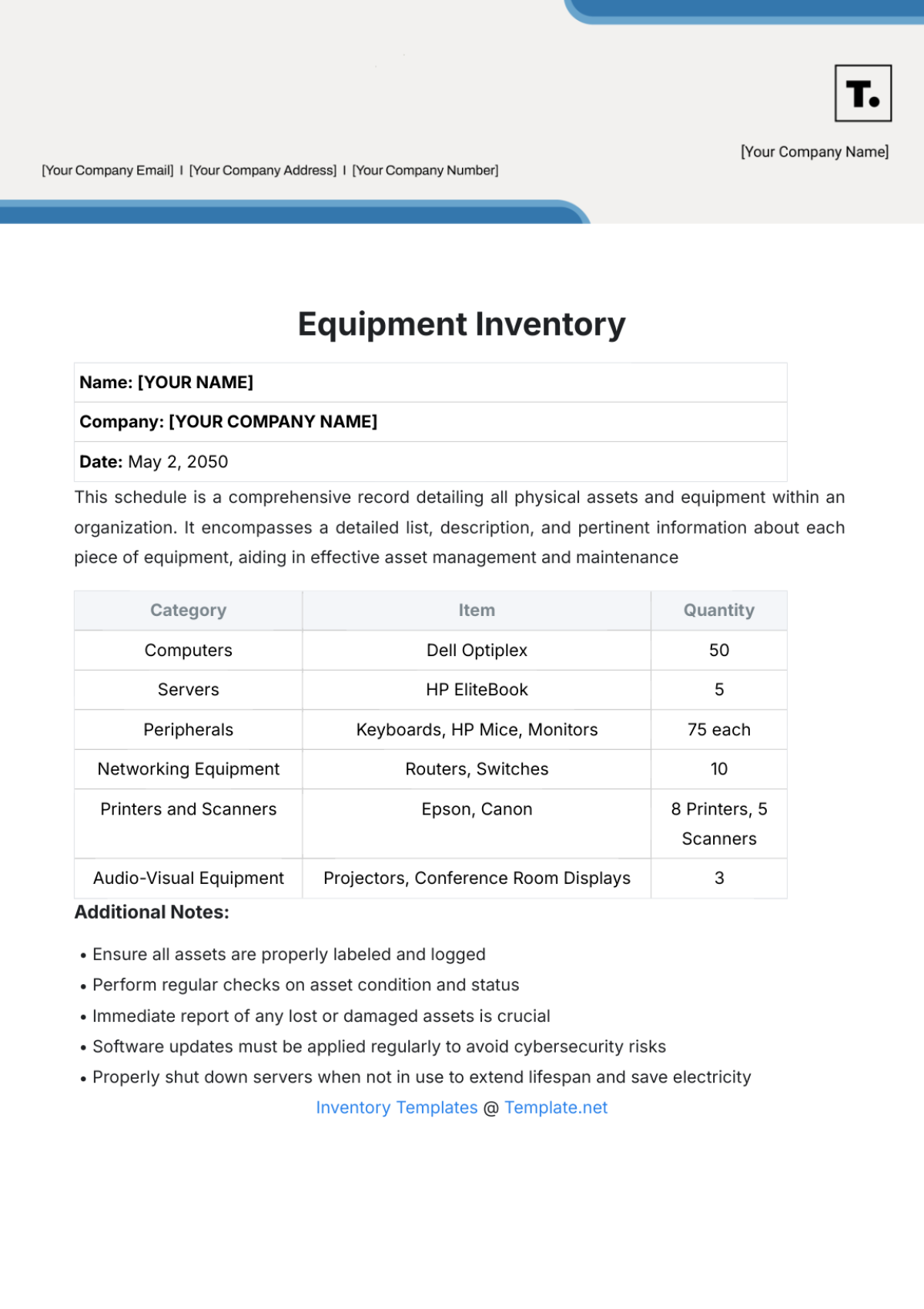
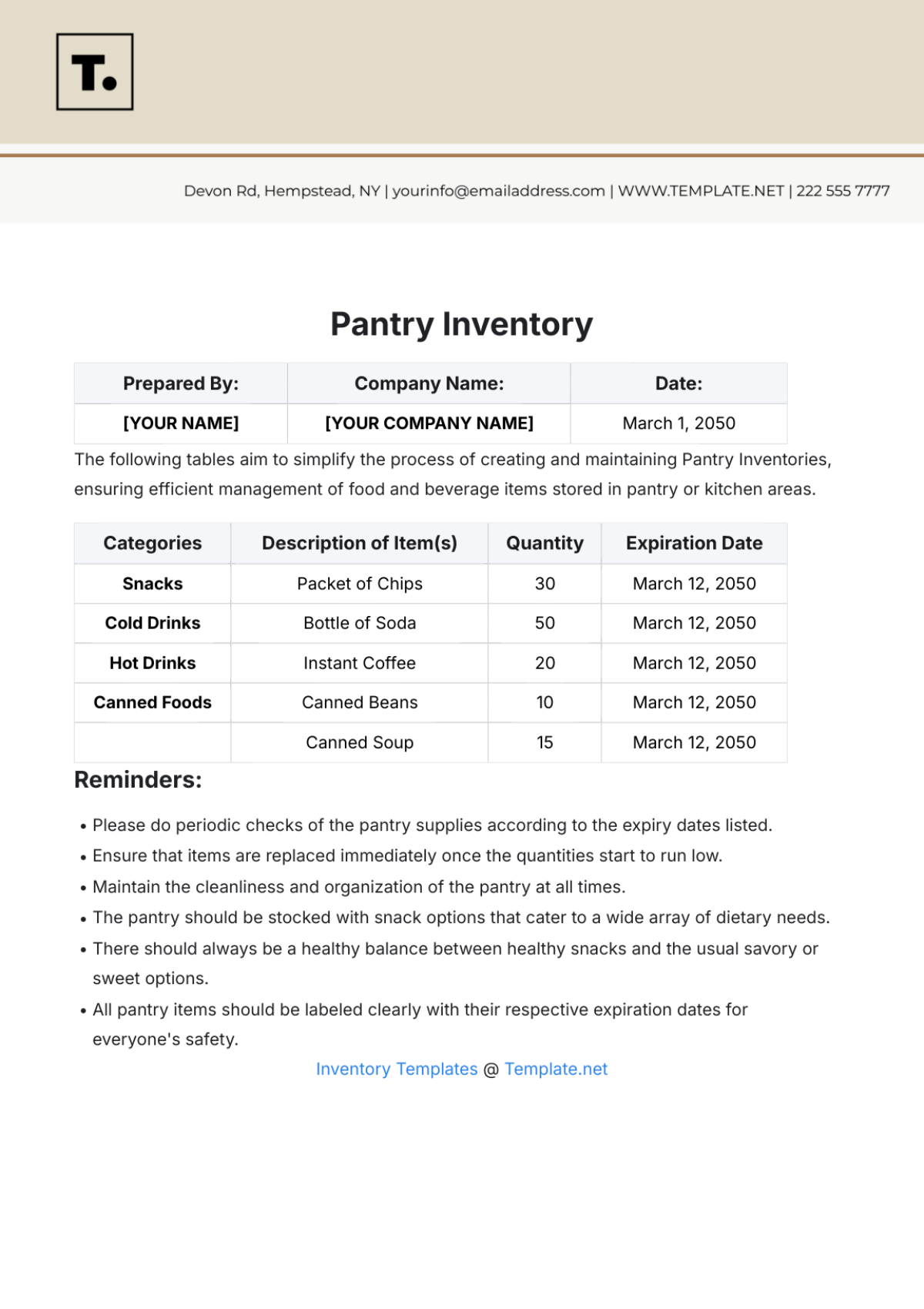
Inventory Classification: Inventory items are classified based on their usage rate, criticality, and cost. This classification helps prioritize inventory management efforts and allocate resources effectively.
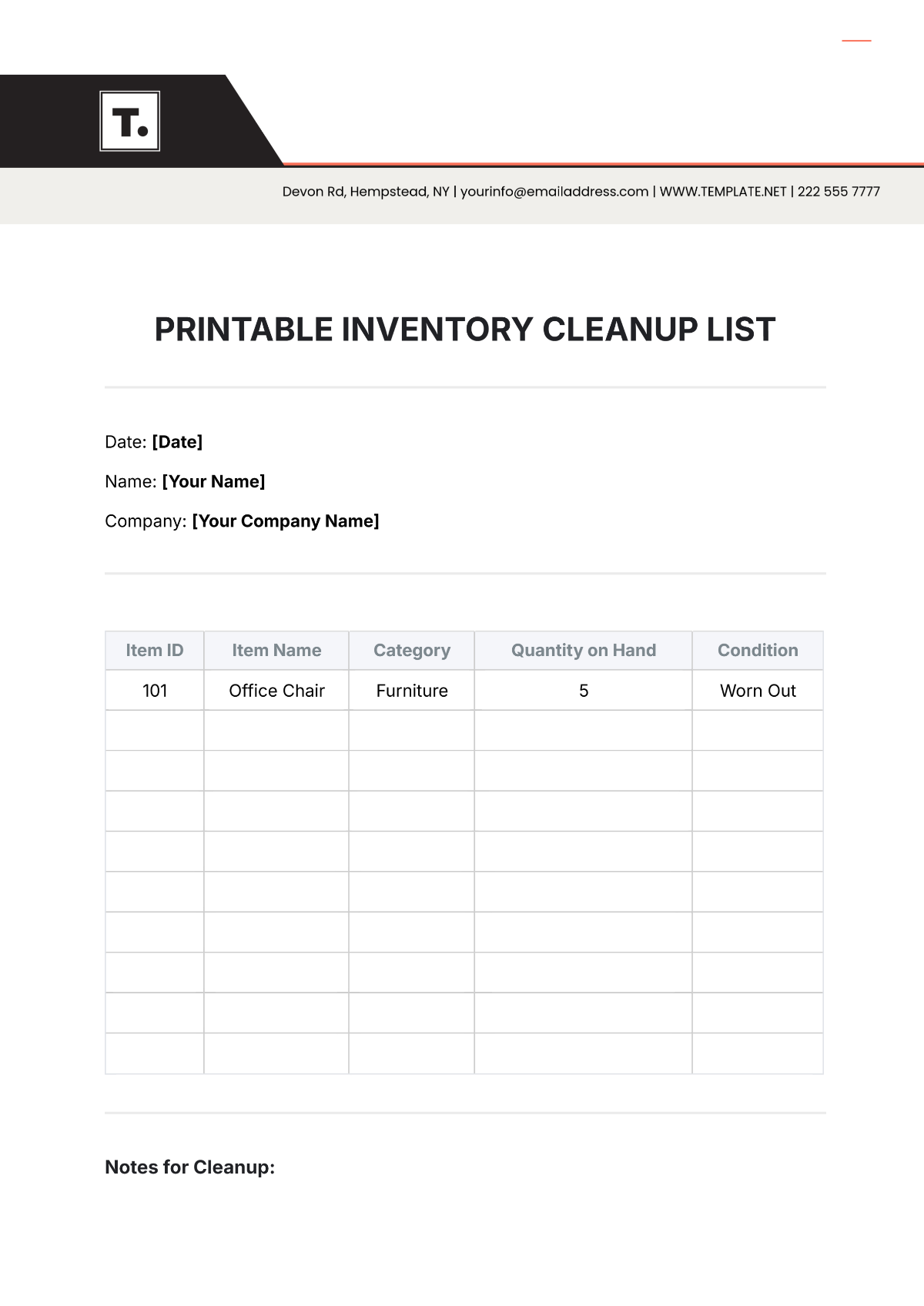
Inventory Accuracy: Regular physical stock counts are conducted to verify inventory levels and identify discrepancies. Cycle counting is implemented to count a portion of inventory items on a regular basis.
Inventory Tracking: A robust inventory management system is used to track inventory movements and maintain accurate records. Barcoding and RFID technology can be used to automate inventory tracking.
Inventory Levels: Optimal inventory levels are determined based on factors such as demand forecasting, lead times, and safety stock levels. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) analysis is used to calculate the optimal order quantity.
Inventory Turnover: Inventory turnover ratio is calculated to measure the efficiency of inventory management. A higher inventory turnover ratio indicates efficient inventory management.
III. Procurement Process
The procurement process involves sourcing, purchasing, and receiving inventory items. This section outlines the steps involved in the procurement process at [Your Company Name].
Supplier Selection: Suppliers are selected based on factors such as quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. A supplier evaluation process is used to assess supplier performance.
Purchase Orders: Purchase orders are generated for each procurement request. Purchase orders include details such as item description, quantity, price, and delivery date.
Receiving and Inspection: Incoming inventory is inspected to verify quantity, quality, and damage. Inspection reports are generated to document the inspection findings.
Inventory Receipt: Received inventory is recorded in the inventory management system. Discrepancies between the purchase order and received quantity are investigated and resolved.
Payment Processing: Payment is processed to suppliers based on approved invoices and delivery of goods.
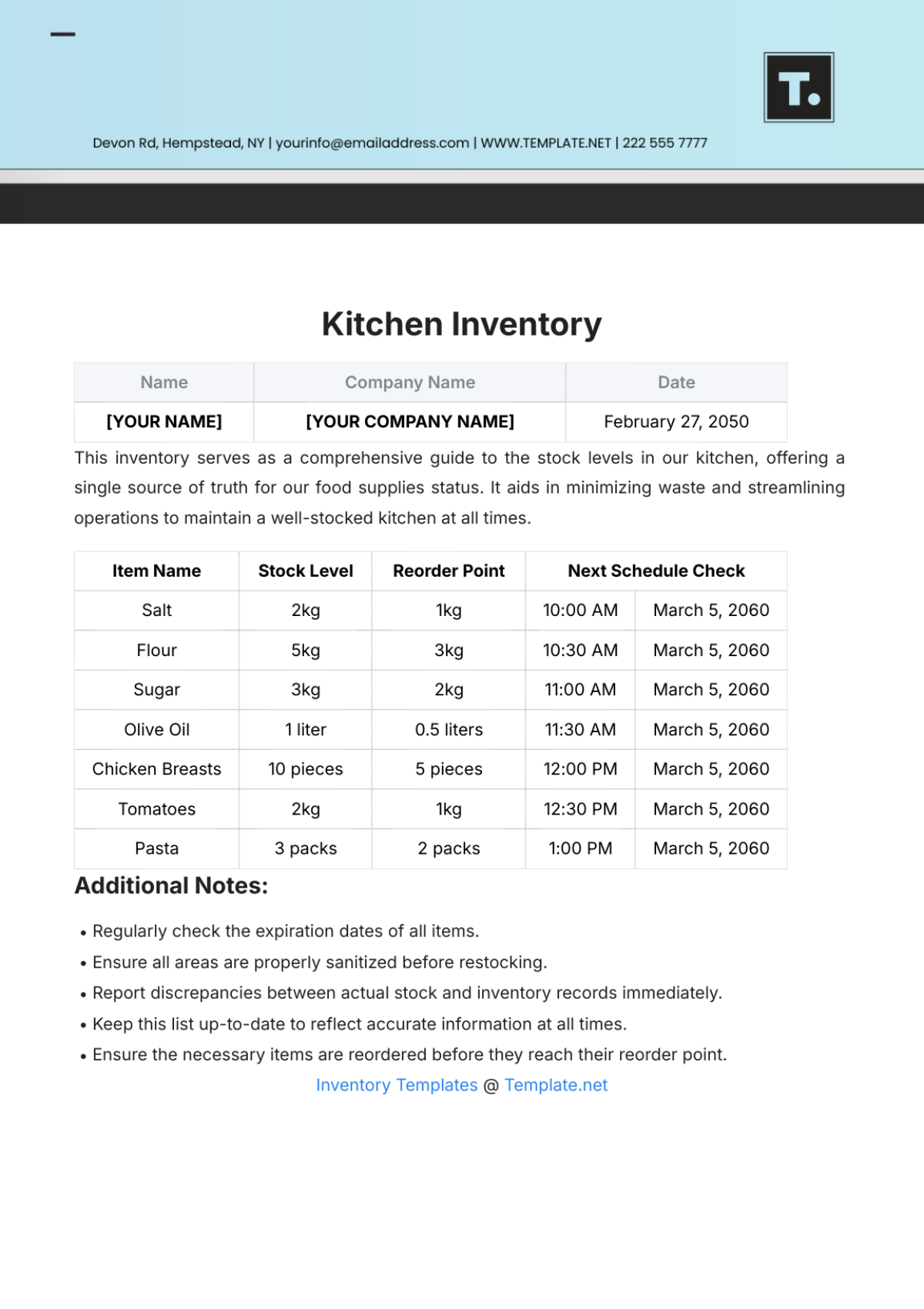
IV. Stocktaking
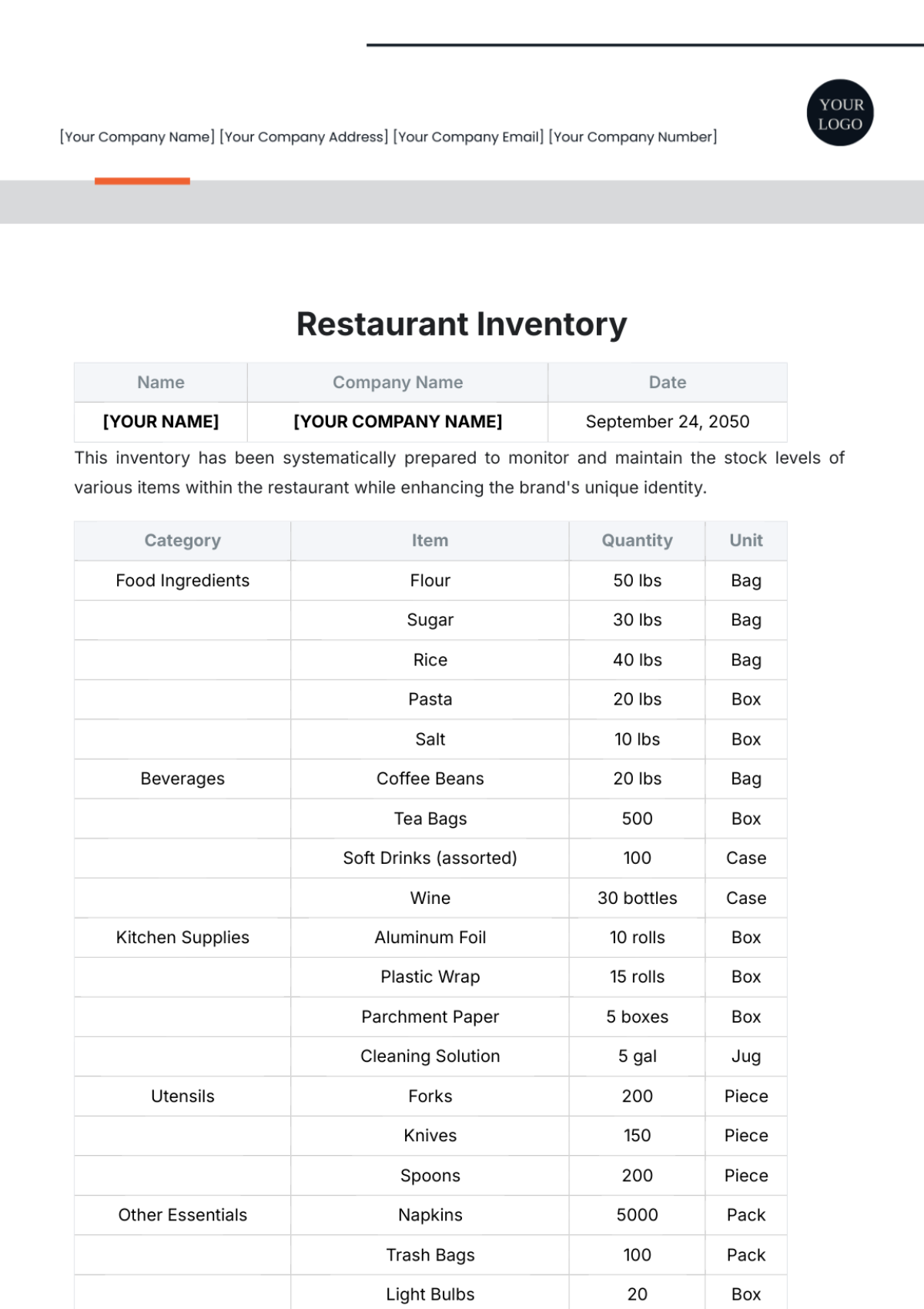
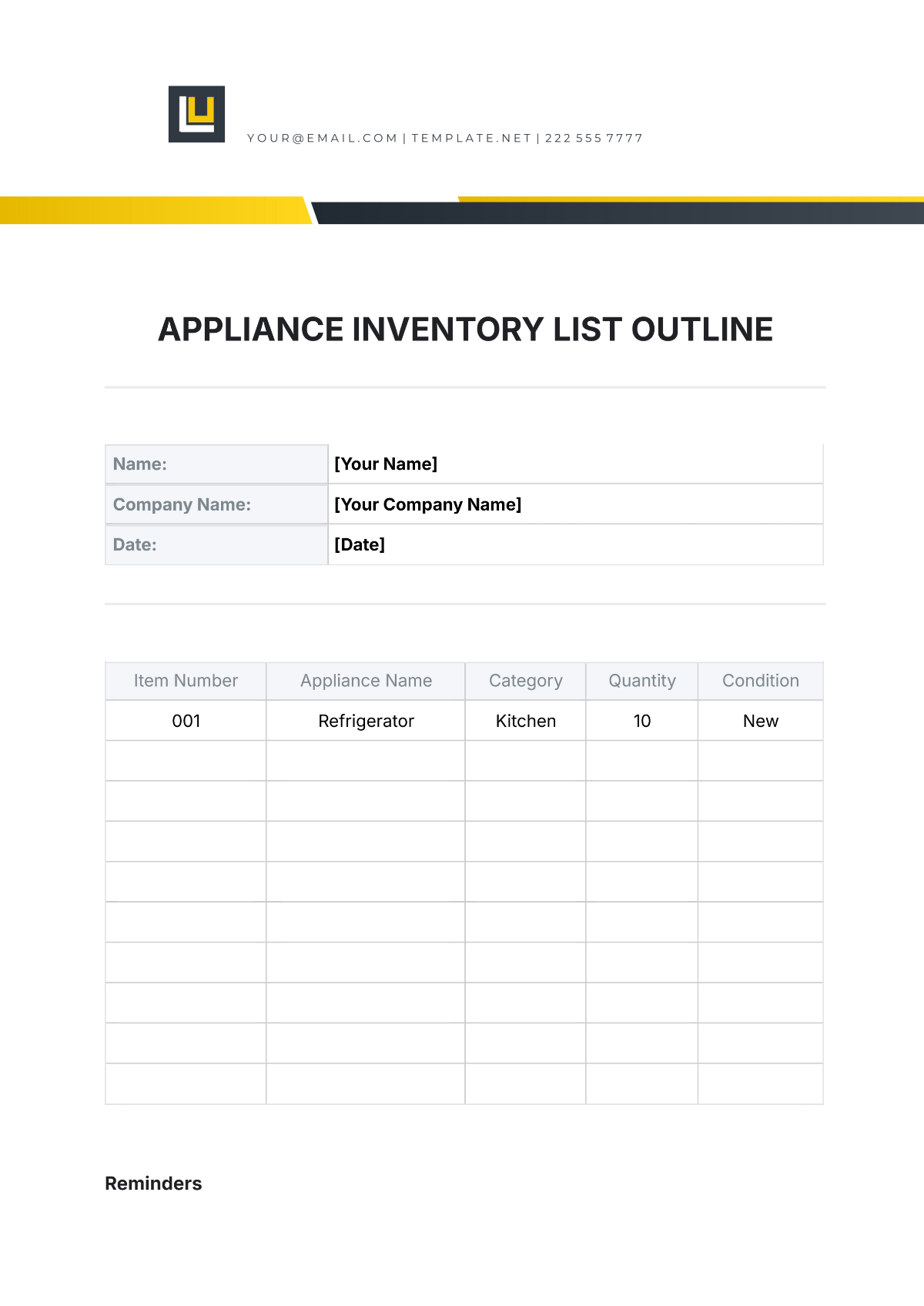
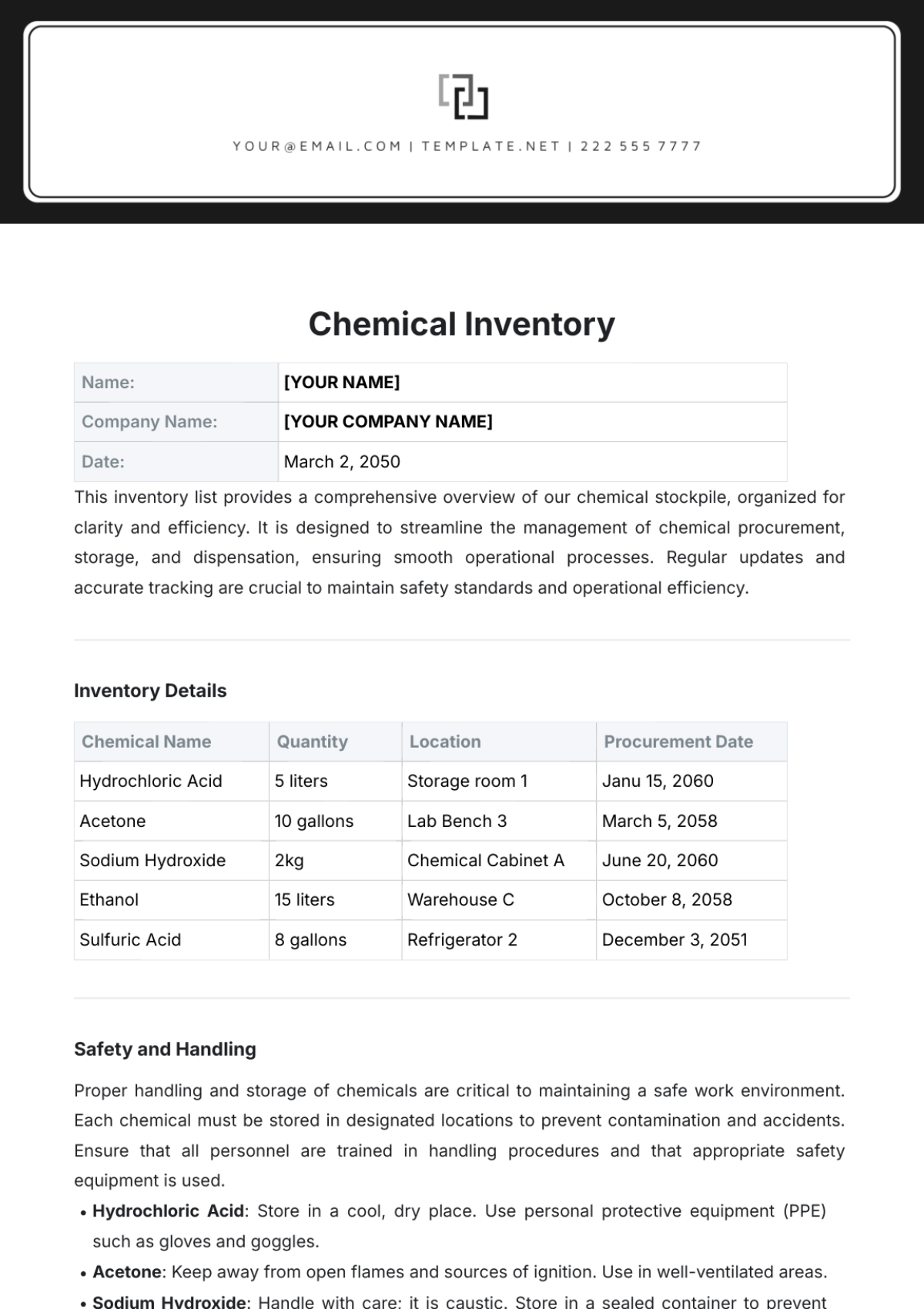
Stocktaking involves physically counting inventory items to verify their quantity and condition. This section outlines the stocktaking process at [Your Company Name].
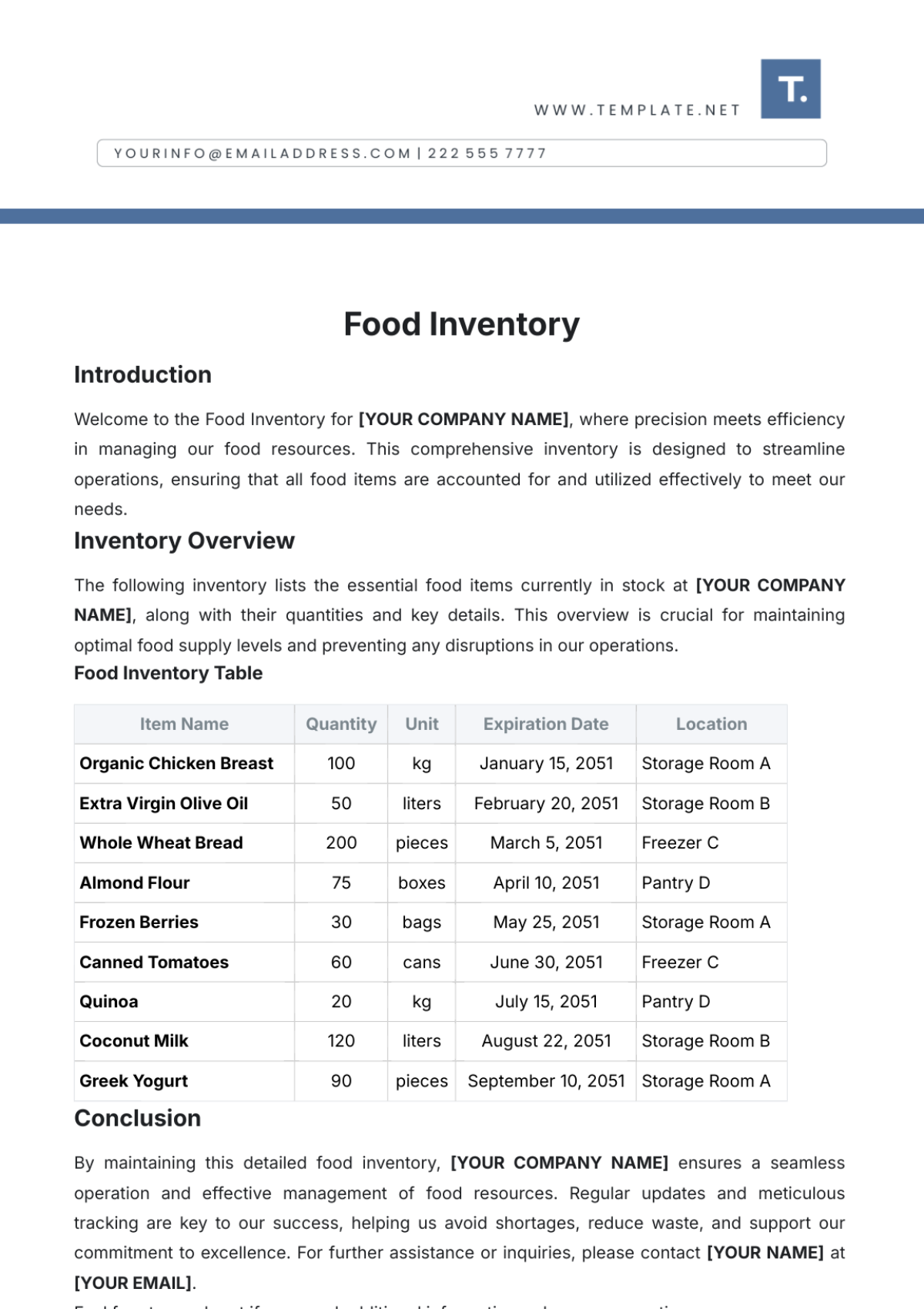
Stocktaking Frequency: Regular stocktaking is conducted to ensure inventory accuracy. The frequency of stocktaking depends on factors such as inventory turnover and criticality.
Stocktaking Procedures: A detailed stocktaking plan is developed, including a schedule and team assignments. Stocktaking teams are trained on stocktaking procedures and accuracy standards.
Stocktaking Tools and Equipment: Necessary tools and equipment, such as barcode scanners and handheld devices, are provided to stocktaking teams. Stocktaking forms and checklists are used to record inventory counts.
Stocktaking Data Entry: Stocktaking data is accurately entered into the inventory management system. Discrepancies between physical counts and system records are investigated and resolved.
Stocktaking Analysis: Stocktaking results are analyzed to identify any discrepancies, shortages, or excesses. Corrective actions are taken to address any issues identified during the stocktaking process.
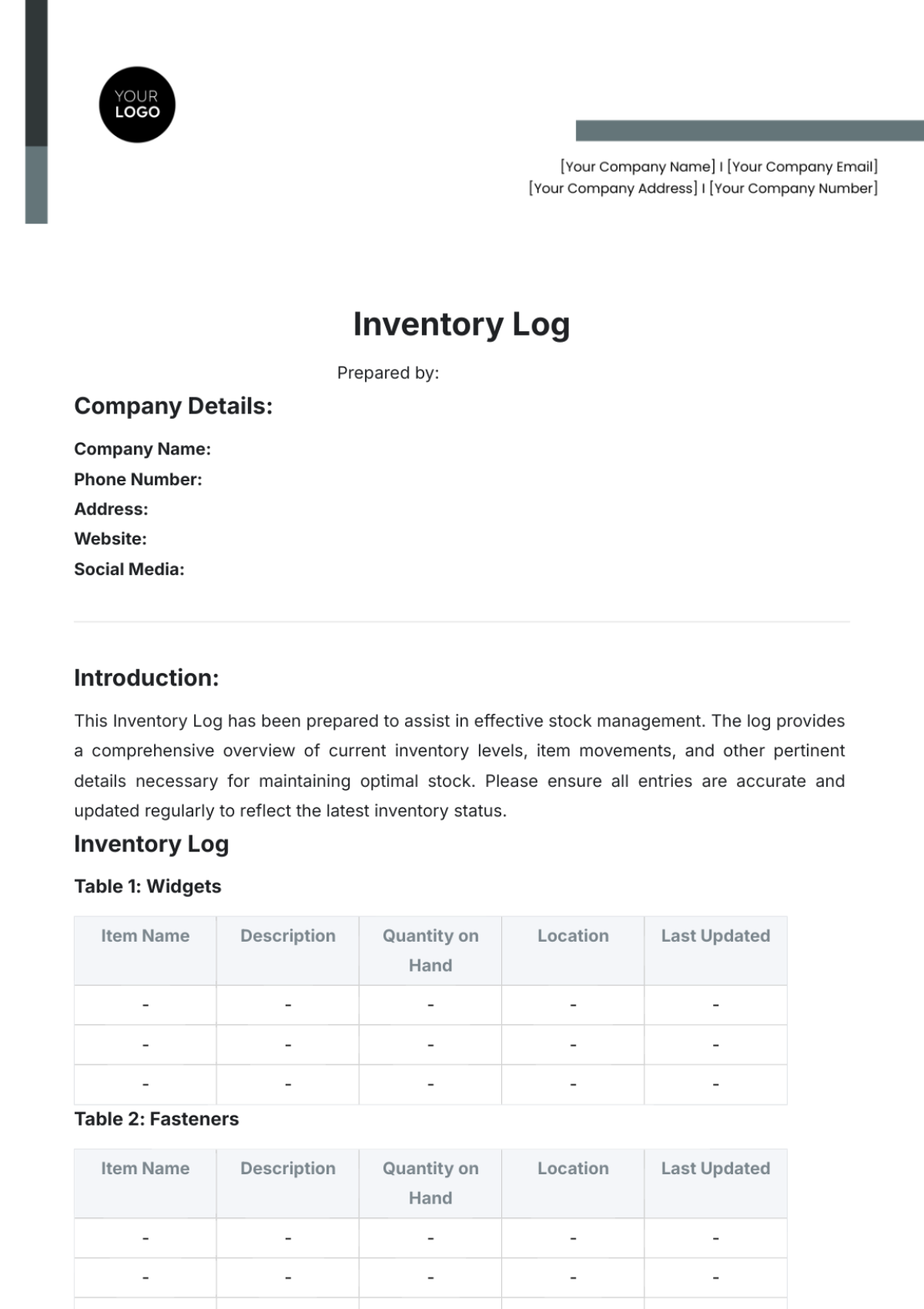
V. Inventory Reports
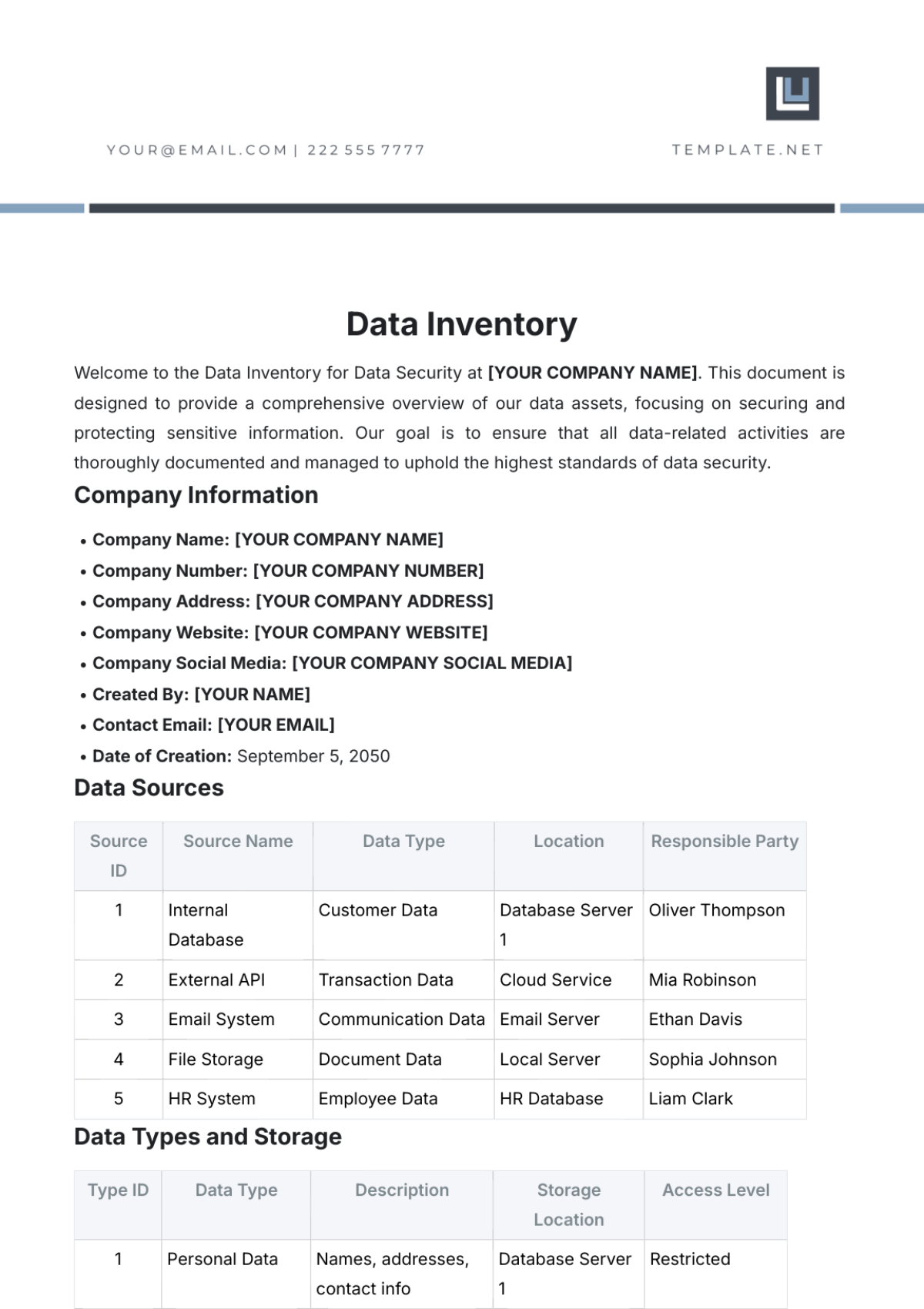
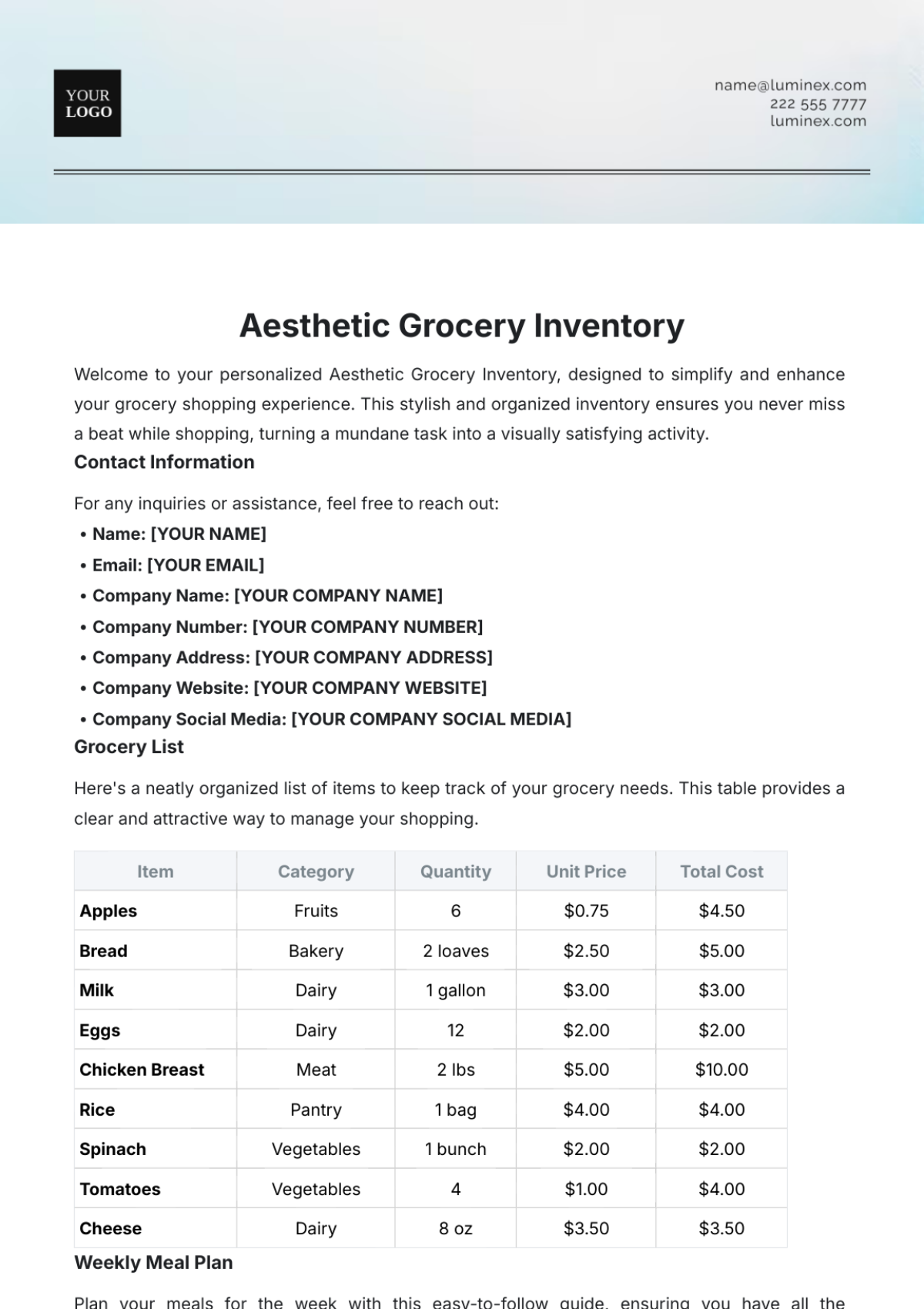
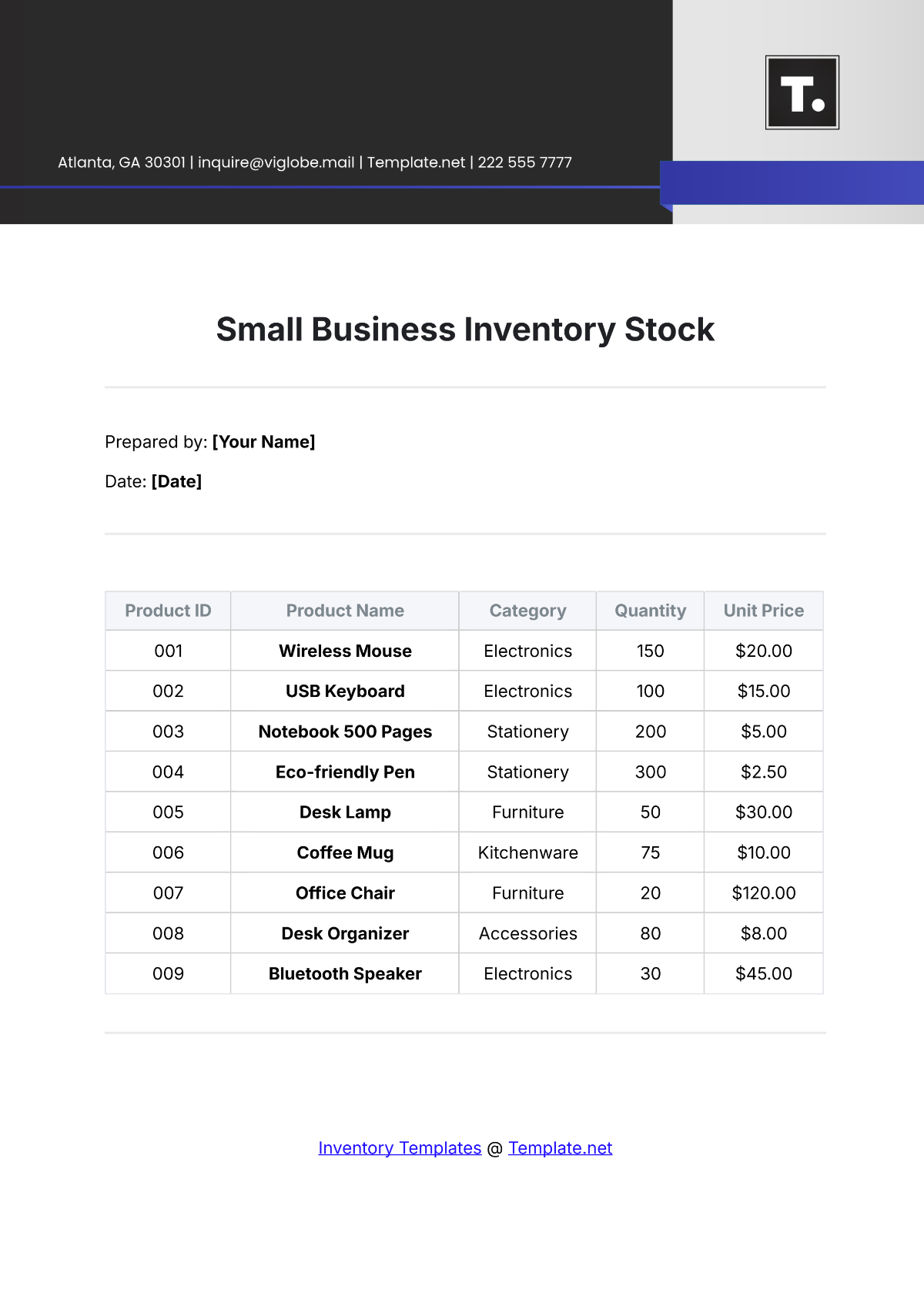
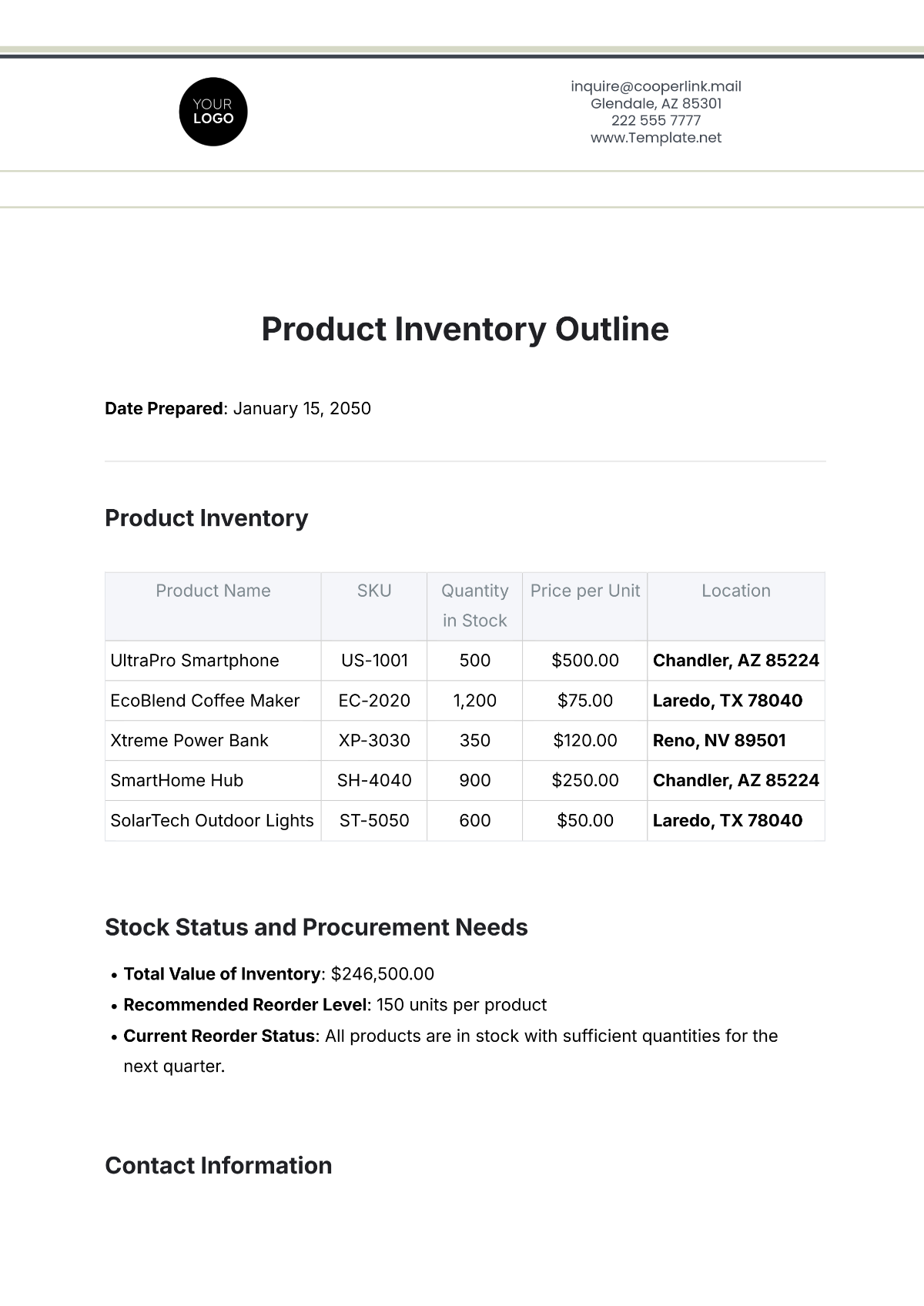
Inventory reports provide valuable insights into inventory performance and help identify areas for improvement. This section outlines the types of inventory reports generated at [Your Company Name].
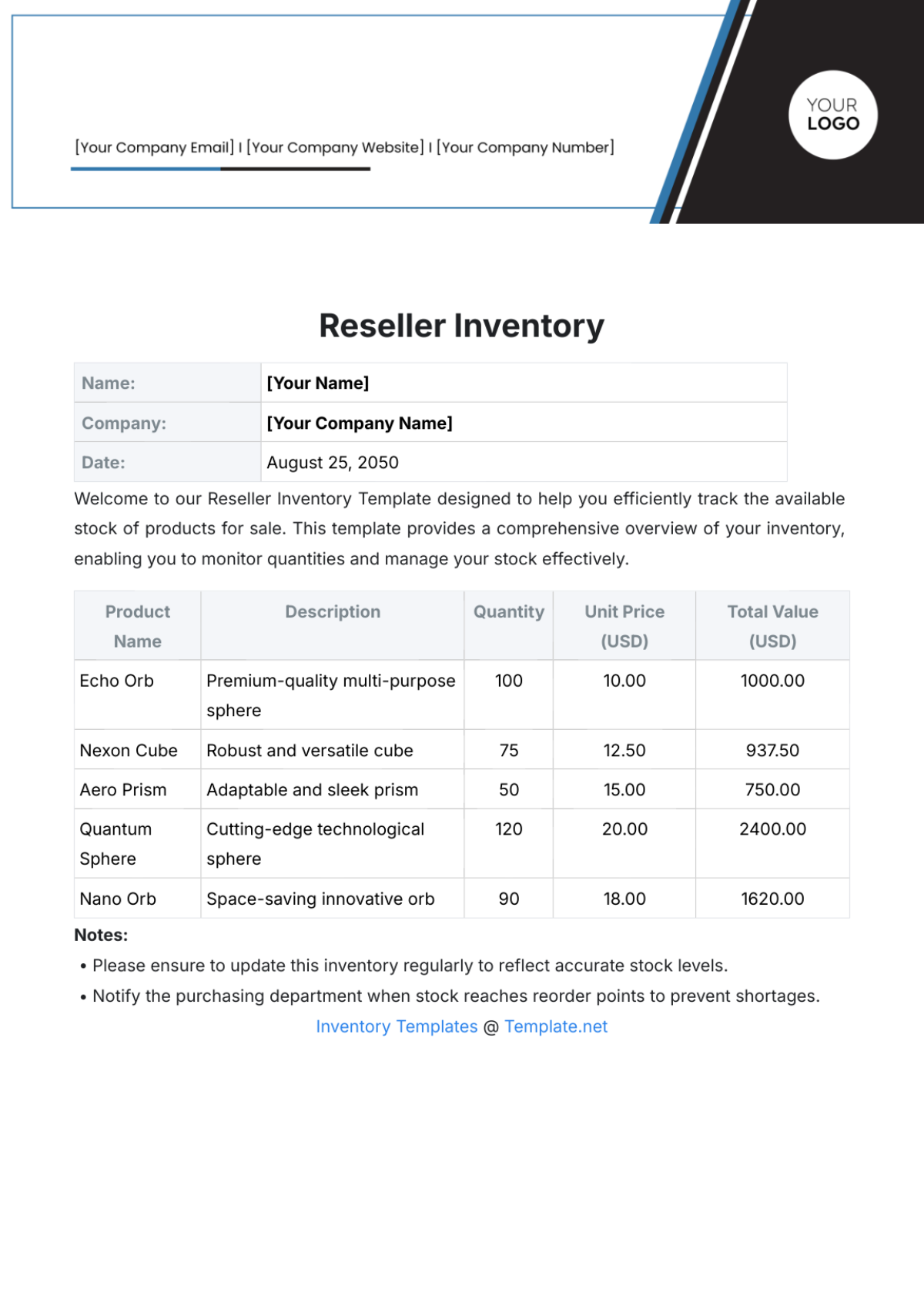
Inventory Valuation Report: This report provides the value of inventory on hand, categorized by item, location, or supplier.
Inventory Turnover Report: This report shows the rate at which inventory is sold or used.
Stockout Report: This report identifies items that have been out of stock, leading to potential lost sales.
Slow-Moving Inventory Report: This report identifies items that have not been sold or used for a long period.
Excess Inventory Report: This report identifies items that are in excess of required levels.
VI. Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization involves implementing strategies to improve inventory management and reduce costs. This section outlines some inventory optimization techniques used at [Your Company Name].
Demand Forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting helps optimize inventory levels.
Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory: JIT inventory reduces inventory holding costs by minimizing stock levels.
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI): VMI allows suppliers to manage inventory levels based on demand forecasts.
ABC Analysis: ABC analysis categorizes inventory items based on their value and usage, helping prioritize inventory management efforts.
Lean Inventory: Lean inventory principles focus on eliminating waste and reducing inventory levels.
VII. Inventory Performance Metrics
Inventory performance metrics help measure the effectiveness of inventory management practices. This section outlines some key inventory performance metrics used at [Your Company Name].
Metric | Definition |
|---|---|
Inventory Turnover Ratio | Measures the number of times inventory is sold or used during a specific period. |
Inventory Holding Cost | Represents the cost of holding inventory, including storage, insurance, and opportunity cost. |
Order Fill Rate | Measures the percentage of orders fulfilled on time and in full. |
Stock Out Rate | Measures the percentage of orders that cannot be fulfilled due to stock outs. |
Inventory Accuracy | Measures the accuracy of inventory records. |
VIII. Conclusion
Effective inventory management is essential for the success of [Your Company Name]. By following the guidelines outlined in this manual, we can ensure optimal inventory levels, minimize stock outs, and reduce costs. Regular review and updates to this manual will help maintain the effectiveness of our inventory management practices.