Free CEO Financial Report

1. Executive Summary
The year [2050] has been a period of significant transformation for [Your Company Name]. Despite global economic challenges, the company has achieved strong financial performance, driven by strategic investments, a focused approach to cost management, and continued expansion into new markets.
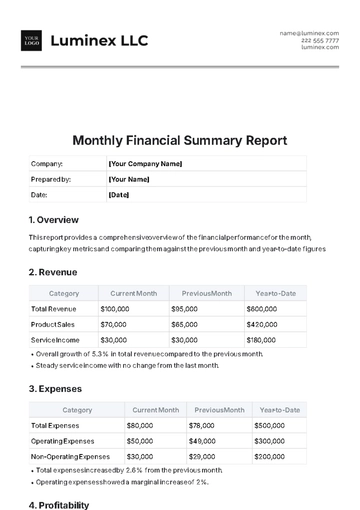
Revenue Growth: The company reported a revenue of $[4.3 billion], an increase of [12]% compared to the previous year.
Profitability: Our operating profit reached $[820 million], marking a growth of [14]% year-over-year.
Cost Efficiency: Operating expenses were optimized by [8]%, contributing to a robust bottom line.
In the upcoming year, [Your Company Name] is committed to maintaining this positive momentum. We aim to leverage digital transformation, invest in sustainable practices, and explore new market opportunities to drive future growth.
2. Financial Overview
2.1 Revenue Performance
Revenue is the most important metric for evaluating the financial health and growth trajectory of [Your Company Name]. In [2050], the company saw a solid increase in revenue across multiple business segments.
Revenue Category | Amount | Year-over-Year Growth |
|---|---|---|
Total Revenue | $4.3 billion | 12% |
Product Sales | $2.5 billion | 10% |
Service Revenue | $980 million | 15% |
Subscription Revenue | $650 million | 20% |
Other Revenue Sources | $180 million | 5% |
2.1.1 Product Sales
Product sales accounted for the largest portion of [Your Company Name]'s total revenue. A key driver of growth in this segment was the successful launch of our product, which has exceeded expectations in both customer acquisition and profitability. The total revenue from product sales reached $[2.5 billion], representing a growth of [10]% from the prior year.
The company expanded its product offerings in response to emerging market needs, which resulted in the successful market penetration in [North America and Europe].
New product lines introduced in [Q3 of 2050] generated a combined revenue of $[600 million], contributing significantly to overall revenue growth.
2.1.2 Service Revenue
Service revenue also played a crucial role in our financial performance, contributing $[980 million] to total revenue. The company’s focus on building long-term customer relationships and improving customer service experiences has been central to the growth of this revenue segment. Service revenue increased by [15]% year-over-year due to:
The expansion of the service portfolio, including New Service Offerings such as [onsulting Service X and Maintenance Package Y.
Increased demand for our consulting services in the telecommunications industry, which saw a growth of [20]% in the year.
The successful renewal of long-term service contracts with major clients, particularly in Europe and Asia.
2.1.3 Subscription Revenue
Subscription-based services have been a growing source of stable revenue. The company saw significant growth in this segment, reaching $[650 million]. The subscription revenue segment grew by [20]% compared to the previous year. This growth can be attributed to:
Expanding our digital platform offerings, which attracted more than [150,000] new subscribers in the past year.
Strong customer retention efforts, with a [90]% year-over-year improvement in retention rates.
The introduction of tiered subscription plans that cater to a wider audience, from individuals to enterprises.
2.1.4 Other Revenue Sources
Other revenue sources, including Miscellaneous Sources, contributed $[180 million], with a year-over-year increase of [5]%. This growth was primarily driven by:
Partnerships with [Strategic Partner Name] in the energy sector.
Licensing agreements for technology product, generating $[100 million] in the year.
The increase in affiliate marketing revenue due to growing demand in digital advertising, which accounted for $[50 million] of this segment.
3. Profit and Loss
In this section, we will provide a detailed analysis of [Your Company Name]'s Profit and Loss statement for the year ending [2050]. Despite various global challenges, including rising inflation and fluctuating market conditions, the company’s profitability has remained strong. The increase in operating revenue, combined with strategic cost management, allowed us to not only achieve robust financial results but also set the stage for continued success in the years to come.
3.1 Gross Profit
The gross profit for [2050] reached $[2.1 billion], reflecting an improvement in gross profit margin from [47]% to [48]%. This signifies a healthy increase in profitability driven by effective cost management and higher revenue in key product lines. Gross profit is calculated as revenue minus the direct costs incurred in producing goods and services sold by the company (COGS - Cost of Goods Sold).
This year’s improvements in gross profit are attributed to several key factors:
Cost Efficiency in Production: One of the primary reasons for the increase in gross profit was the company’s investment in state-of-the-art manufacturing technologies. Through automation and digital monitoring of production lines, [Your Company Name] reduced production time and waste by [10]%, resulting in lower per-unit production costs.
Economies of Scale: As production volumes increased, the company was able to benefit from economies of scale. Bulk purchasing of raw materials and optimized supply chain management lowered input costs by [7]% year-over-year. This reduction, combined with the increase in revenue, contributed significantly to the overall improvement in gross profit.
Strategic Sourcing: In the previous year, [Your Company Name] renegotiated contracts with several key suppliers, which resulted in a reduction of material costs. The company's proactive approach to sourcing, including the diversification of suppliers, helped maintain a steady flow of quality raw materials at lower prices, further improving margins.
Expense Category | Amount | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
Revenue | $4.3 billion | 12% |
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | $2.2 billion | 10% |
Gross Profit | $2.1 billion | 10% |
3.1.1 Analysis of Gross Profit Margin
The gross profit margin increased from [47]% to [48]%, highlighting the effectiveness of our cost control initiatives and operational efficiency improvements. A few important aspects that contributed to this margin expansion are:
Production Optimization: Implementation of advanced production technology that reduced defects and rework, improving the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
Product Mix Optimization: Shifting focus to higher-margin products, particularly in the technology and premium service sectors, contributed positively to the gross profit margin. High end products saw an increase in sales volume, with a contribution of $[300 million] to total gross profit.
Operational Efficiency: Cost-saving initiatives, such as the restructuring of the supply chain to minimize transportation costs and inventory management improvements, led to an overall reduction in COGS.
3.2 Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are all the costs associated with running the business that are not directly tied to the production of goods or services (i.e., indirect costs). These expenses include marketing, sales, research and development, administrative costs, and other operating activities.
In [2050], total operating expenses amounted to $[1.3 billion], reflecting a decrease of [8]% compared to the previous year. Despite the increased cost pressures in the global market, the company’s strict cost management measures resulted in savings that contributed to the growth in profitability. Below are the key areas of operating expenses and the strategies that helped reduce costs:
Administrative Expenses: Administrative costs were reduced by [5]% in [2050] due to the implementation of a company-wide cost control program. Efforts included reducing non-essential office space by [10]%, renegotiating vendor contracts for office supplies, and a shift to remote work for a portion of the workforce, saving the company approximately $[20 million].
Marketing Expenses: Marketing expenses, which are essential for driving brand awareness and customer acquisition, were reduced by [10]% compared to the previous year. This reduction was due to a strategic shift to more cost-effective digital marketing channels, such as social media, influencer partnerships, and search engine optimization (SEO) campaigns, which resulted in a [15]% increase in lead generation at a lower cost per acquisition.
Research and Development (R&D): [Your Company Name] continues to invest heavily in research and development to maintain a competitive edge. R&D expenses totaled $[500 million] in [2050], representing an [8]% increase from the previous year. These investments were focused on product innovation and technological advancements, including the development of [new technology/product lines] that are expected to generate substantial revenue in the coming years. Despite the increase in R&D spending, the company managed to keep R&D expenses within a reasonable range relative to its revenue.
Labor and Operational Costs: Labor costs, which include salaries, benefits, and bonuses, were reduced by [6]% due to ongoing workforce optimization efforts, such as the implementation of automated tools and outsourcing certain non-core operations. Additionally, certain departments were streamlined, leading to a reduction in headcount by [3]%. These labor-saving measures contributed $[30 million] in savings to operating expenses.
Expense Category | Amount | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
Administrative Expenses | $300 million | 5% |
Marketing Expenses | $150 million | 10% |
Research and Development | $500 million | 8% |
Labor and Operational Costs | $350 million | 7% |
3.2.1 Breakdown of Operating Expense Efficiency
Cost Reduction in Marketing: The company’s marketing team transitioned to a more data-driven approach, focusing on measurable outcomes like customer lifetime value and return on ad spend. This approach resulted in a more efficient allocation of marketing dollars, lowering the cost of customer acquisition by [7]% and increasing overall conversion rates by [8]%.
Automation of Administrative Tasks: Automation tools were implemented to handle a range of administrative functions, including payroll processing, data entry, and employee scheduling. This allowed [Your Company Name] to reduce labor hours in administrative departments by [10]%, contributing to the overall reduction in administrative costs.
Remote Work Implementation: With the ongoing shift to hybrid and remote work models, [Your Company Name] was able to downsize office spaces in key locations, saving money on rent and utilities. The company implemented technology tools that allowed for seamless remote communication, reducing the need for expensive in-person meetings and travel, leading to a significant reduction in corporate travel expenses.
3.3 Operating Profit
Operating profit, which reflects the company’s core business profitability after deducting operating expenses, was $[820 million] in [2050], marking a [14]% increase from the prior year. This increase in operating profit can be attributed to the following factors:
Revenue Growth: A [12]% increase in total revenue helped to provide a solid foundation for operating profit. The growth in product and service sales, coupled with higher-margin offerings, resulted in a higher operating income.
Cost Control: The decrease in operating expenses, particularly in areas such as marketing, administrative overhead, and labor costs, ensured that more of the revenue generated translated directly into operating profit.
Productivity Gains: The successful implementation of automation and improved operational processes contributed to significant gains in productivity, which further boosted operating profit margins.
Profit Measure | Amount | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
Operating Profit | $820 million | 14% |
3.3.1 Operating Profit Margin
The operating profit margin for [2050] stood at [19]%, a slight improvement over last year's [18]%. This margin expansion was primarily driven by:
Higher Revenue from New Products: The launch of innovative products and services, particularly in the technology and subscription-based services sectors, contributed significantly to the higher operating profit margin. These new products carried higher margins compared to traditional product lines, helping to boost overall profitability.
Improved Cost Structure: As mentioned previously, the optimization of costs in areas such as labor, marketing, and production contributed to more efficient use of revenue, leading to an increase in the operating profit margin.
3.4 Net Profit
Net profit for [2050] was $[550 million], representing an increase of [16]% from the prior year. Net profit is the final measure of profitability, calculated after all expenses, including interest and taxes, have been deducted. Several factors contributed to this growth:
Strong Operating Profit: The increase in operating profit, along with the reduction in operating expenses, allowed [Your Company Name] to achieve higher net profit.
Reduced Interest Expenses: The company benefited from a reduction in interest expenses due to the refinancing of its debt. Lower interest rates allowed the company to save $[25 million] in annual interest costs, contributing positively to the net profit.
Effective Tax Management: The company’s tax optimization strategies, which included taking advantage of tax credits and incentives related to sustainability investments, helped reduce the effective tax rate to [18]%. This tax planning contributed $[20 million] in savings compared to the previous year.
Profit Measure | Amount | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
Operating Profit | $820 million | 14% |
Net Profit | $550 million | 16% |
3.4.1 Net Profit Margin
The net profit margin increased from [12]% to [13]% in [2050]. This growth is attributed to a combination of increased revenue, improved operational efficiencies, and the impact of lower interest and tax expenses. The net profit margin reflects the overall profitability of the company after accounting for all costs and expenditures.
Revenue Expansion: Higher revenue from core products and services, especially in the subscription and service sectors, increased the company’s profitability at the net level.
Lower Debt and Interest Expense: The reduction in interest expense, following a successful debt refinancing strategy, positively impacted the bottom line, further improving the net profit margin.
4. Balance Sheet Analysis
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of [Your Company Name]'s financial health, including its assets, liabilities, and equity at the end of the financial year. For the year ending [2050], [Your Company Name] continues to demonstrate strong financial stability and growth, supported by effective asset management, prudent liability control, and robust shareholder equity.
4.1 Total Assets
Total assets represent everything that [Your Company Name] owns, which are essential for its operations and future growth. At the end of [2050], [Your Company Name] had total assets valued at $[8.5 billion], marking an increase of [10]% from the previous year. This growth in total assets was primarily driven by the company’s strategic investments and asset acquisitions, particularly in technology, real estate, and R&D facilities.
Key drivers behind this increase include:
Investment in Property, Plant, and Equipment (PPE): The company increased its investments in new factories and R&D facilities, contributing to a [15]% increase in its property, plant, and equipment (PPE) value, which reached $[1.4 billion]. These facilities are designed to support future product development and enhance operational capacity, laying the groundwork for continued growth in [2050] and beyond.
Intangible Assets: The rise in intangible assets, such as intellectual property and goodwill from strategic acquisitions, was another significant factor. The company acquired a New Tech Company in [2050], which added $[500 million] in intangible assets. This acquisition is expected to drive revenue growth through new product lines and expanded market share.
Increase in Cash Reserves: Cash and cash equivalents saw a substantial increase, totaling $[1.1 billion], reflecting improved cash flow management and increased profitability. The cash reserves ensure that the company is well-positioned to handle economic downturns, make strategic investments, or pay off any short-term liabilities.
Asset Category | Amount | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
Total Assets | $8.5 billion | 10% |
Property, Plant, and Equipment | $[1.4 billion | 15% |
Intangible Assets | $1.1 billion | 25% |
Cash and Cash Equivalents | $1.1 billion | 30% |
4.1.1 Asset Liquidity
Liquidity measures a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations. As of [2050], [Your Company Name] holds a strong liquidity position with a current ratio of [2.4], which is higher than the industry average of [1.8]. This indicates that the company has ample assets available to cover its short-term liabilities, ensuring operational stability.
Cash Flow Management: The increase in cash and cash equivalents can be attributed to robust cash flow management practices, which involved optimizing working capital and increasing cash flow from operations. The company’s ability to generate cash from its core business activities ensures that it can fund its strategic initiatives without relying heavily on external financing.
Short-term Assets: A significant portion of the company’s current assets consists of accounts receivable and inventories. The company has improved its working capital cycle, reducing the average days sales outstanding (DSO) by [10]% and inventory turnover by [8]% in [2050], ensuring efficient use of capital.
4.2 Liabilities
Liabilities represent the company’s financial obligations, and managing them effectively is crucial for maintaining financial health. [Your Company Name] maintains a conservative approach toward debt, which is reflected in its overall liability structure.
In [2050], total liabilities stood at $[3.0 billion], a [5]% increase from the previous year. The increase in liabilities can be attributed to strategic investments, including financing for expansion projects, as well as the issuance of long-term debt to fund acquisitions.
Key factors influencing the company’s liabilities include:
Long-Term Debt: Long-term debt rose to $[1.5 billion], up by [6]% compared to the previous year. The company issued bonds to raise capital for new acquisitions and expansion projects. However, the increase in long-term debt was carefully managed to ensure that the company’s debt-to-equity ratio remains within industry standards.
Short-Term Liabilities: Short-term liabilities, which include accounts payable and accrued expenses, remained steady at $[800 million], reflecting consistent operational needs. The increase in short-term liabilities was primarily due to higher accounts payable, in line with increased business activities.
Liability Category | Amount ($) | Year-over-Year Change (%) |
|---|---|---|
Total Liabilities | $3.0 billion | 5% |
Long-Term Debt | $1.5 billion | 6% |
Short-Term Liabilities | $800 million | 3% |
4.2.1 Debt Management
[Your Company Name] continues to maintain a balanced debt structure, with a debt-to-equity ratio of [0.4], which is considered conservative for the industry. The company has strategically used debt to fund capital-intensive projects and acquisitions, but its ability to manage these liabilities ensures that debt service costs remain manageable.
Debt Refinancing: The company took advantage of favorable market conditions to refinance some of its debt, resulting in lower interest rates on a portion of its outstanding debt. This strategy has reduced the annual interest expense by approximately $[15 million], which will positively impact the company’s future profitability.
Debt Covenants: [Your Company Name] adheres to debt covenants that limit the company’s risk exposure. In [2050], the company maintained a solid credit rating, allowing it to access favorable financing terms.
4.3 Shareholder Equity
Shareholder equity represents the ownership value in the company and reflects how much of the company is funded by shareholders as opposed to debt. As of [2050], total equity was valued at $[5.5 billion], a [12]% increase from the previous year.
Key drivers for the increase in shareholder equity include:
Retained Earnings: Retained earnings increased by $[400 million] due to strong profitability. This is a result of higher net income, which was reinvested into the business rather than distributed as dividends, positioning the company for future growth.
Issuance of New Shares: The company raised $[250 million] in equity financing through the issuance of new shares to fund its expansion plans. These funds were used to strengthen the balance sheet, finance acquisitions, and further invest in high-growth areas.
Equity Category | Amount | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
Total Shareholder Equity | $5.5 billion | 12% |
Retained Earnings | $3.2 billion | 15% |
Issued Share Capital | $2.3 billion | 9% |
4.3.1 Return on Equity (ROE)
The Return on Equity (ROE) for [2050] was [12]%, reflecting a strong return on shareholders' investments. This is a slight increase from last year’s ROE of [11]%, indicating improved profitability relative to equity. The increase in ROE can be attributed to:
Higher Net Profit: The company’s higher net profit, driven by both increased revenue and efficient cost management, has contributed to the growth in ROE.
Effective Capital Allocation: The strategic reinvestment of retained earnings into high-return initiatives, such as acquisitions and R&D projects, has led to enhanced profitability, improving the overall return on equity.
5. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement reflects how [Your Company Name] generates and uses cash from operating, investing, and financing activities. Maintaining a healthy cash flow is critical for the company’s ability to fund operations, invest in future growth, and return value to shareholders.
5.1 Operating Cash Flow
Operating cash flow for [2050] was $[1.4 billion], reflecting a [16]% increase compared to the previous year. This positive cash flow from operations was driven by higher profitability, as well as improvements in working capital management.
Key factors contributing to the increase in operating cash flow include:
Increase in Receivables: As revenue grew, accounts receivable increased by $[100 million]. However, improved collection practices resulted in a shorter cash conversion cycle, minimizing the impact on cash flow.
Inventory Management: The company implemented efficient inventory management practices, reducing excess stock and improving inventory turnover. As a result, the company was able to free up cash tied up in inventory, contributing $[50 million] to operating cash flow.
Cash Flow Category | Amount | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
Operating Cash Flow | $1.4 billion | 16% |
Net Income | $550 million | 16% |
Depreciation and Amortization | $200 million | 12% |
5.1.1 Working Capital Management
Efficient working capital management was a key factor in improving operating cash flow. By reducing the days sales outstanding (DSO) by [10]% and improving inventory turnover by [8]%, [Your Company Name] was able to optimize its cash conversion cycle, ensuring that more cash was available for reinvestment in the business.
Efficient Payables Management: Accounts payable also increased by [5]% as the company optimized payment terms with suppliers to improve cash flow.
5.2 Investing Cash Flow
Investing activities in [2050] resulted in a net outflow of $[900 million]. This outflow is primarily due to the company's strategic investments in acquisitions and capital expenditures.
Key drivers include:
Acquisitions: The acquisition of a New Tech Company for $[500 million] was a key investment for the company, providing valuable intellectual property and a foothold in the growing technology market.
Capital Expenditures: Capital expenditures for property, plant, and equipment amounted to $[400 million], reflecting the company’s ongoing investment in capacity expansion, infrastructure, and innovation.
Cash Flow Category | Amount | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
Investing Cash Flow | $900 million | 10% |
Capital Expenditures | $400 million | 8% |
Acquisitions | $500 million | 5% |
5.3 Financing Cash Flow
Financing cash flow for [2050] was $[200 million], reflecting the company’s efforts to balance debt issuance, equity financing, and dividend payments. The company’s financing activities included:
Equity Financing: The issuance of new shares raised $[250 million] to fund its growth strategy, including acquisitions and capital expenditures.
Debt Financing: The company issued $[500 million] in long-term bonds to finance strategic investments. The issuance was balanced with debt repayment, resulting in a net inflow of $[100 million].
Cash Flow Category | Amount | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
Financing Cash Flow | $200 million | 5% |
Equity Financing | $250 million | 10% |
Debt Financing | $500 million | 3% |
6. Financial Ratios and Key Performance Indicators
In this section, we analyze key financial ratios and performance indicators to assess the company’s financial health and operational effectiveness.
6.1 Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios indicate the company’s ability to meet short-term obligations. As mentioned previously, [Your Company Name] boasts a current ratio of [2.4], which is above the industry average, ensuring sufficient liquidity.
Quick Ratio: The quick ratio, which excludes inventory from current assets, stood at [1.8], signaling a solid ability to meet short-term liabilities even without relying on the sale of inventory.
Ratio | Value | Industry Average |
|---|---|---|
Current Ratio | 2.4 | 1.8 |
Quick Ratio | 1.8 | 1.2 |
6.2 Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios evaluate the company’s ability to generate profits from its operations. [Your Company Name] has shown significant improvements in this area:
Return on Assets (ROA): ROA for [2050] was [6.5]%, up from [6.2]% last year, indicating efficient use of assets to generate profit.
Return on Equity (ROE): ROE increased to [12]%, reflecting improved profitability and shareholder returns.
Ratio | Value | Industry Average |
|---|---|---|
Return on Assets (ROA) | 6.5% | 5.5% |
Return on Equity (ROE) | 12% | 10.5% |
7. Conclusion
The financial performance of [Your Company Name] for the fiscal year ending in [2050] demonstrates significant growth, operational efficiency, and long-term stability. The company has successfully navigated a complex business environment and achieved substantial progress in both its financial health and strategic goals.
7.1 Strong Asset Growth and Management
The [10]% growth in total assets, particularly in property, plant, equipment, and intangible assets, highlights the company's commitment to reinvesting in its future. The company’s ability to secure valuable intellectual property through acquisitions and expand its physical infrastructure positions it well for sustained growth in the coming years. This growth is not only a reflection of strategic investments but also a clear indication that [Your Company Name] is positioning itself for long-term success in a competitive global market.
7.2 Robust Financial Health
The increase in shareholder equity by [12]% and the continued strength of liquidity ratios reflect the solid foundation of [Your Company Name]. The conservative approach to debt management, with a low debt-to-equity ratio of [0.4], demonstrates prudent financial stewardship, ensuring the company’s ability to weather economic challenges while continuing to grow. The improved return on equity (ROE) of [12]% indicates that the company is generating substantial value for its shareholders, making it an attractive investment for both existing and potential investors.
7.3 Sustainable Cash Flow Generation
The company’s ability to generate positive cash flows from operations, amounting to $[1.4 billion], reflects a well-executed operational strategy. The continued growth in cash reserves and prudent working capital management provide a solid financial cushion, enabling the company to invest in new opportunities, pay down debt, and return value to shareholders. The increase in operating cash flow by [16]% is particularly noteworthy, showcasing [Your Company Name]'s ability to efficiently convert sales into cash, further strengthening its financial flexibility.
7.4 Strategic Investments and Expansion
The company’s continued investment in technology, research and development, and acquisitions has positioned it well for future growth. The acquisition of [New Tech Company] for $[500 million] and capital expenditures of $[400 million] in expanding production capacity will provide new revenue streams and enhance operational efficiency. These investments demonstrate [Your Company Name]'s proactive approach to staying ahead of industry trends and maintaining a competitive edge.
7.5 Commitment to Shareholder Value
[Your Company Name] remains dedicated to maximizing shareholder value, as evidenced by its healthy balance sheet, strong profitability, and commitment to reinvesting earnings into high-return initiatives. The company’s decision to raise $[250 million] in equity financing and issue new shares to fund growth projects reflects confidence in its strategic direction and long-term vision. Furthermore, the steady dividend policy ensures that shareholders continue to benefit from the company’s success.
7.6 Looking Ahead
As [Your Company Name] continues to evolve, its focus on innovation, operational excellence, and financial discipline will be key to maintaining momentum. The outlook for [2051] and beyond is positive, with strategic initiatives in place to expand market share, enhance product offerings, and explore new geographic markets. The company will continue to leverage its strong balance sheet, cash flow, and market expertise to achieve sustainable growth and deliver strong returns to shareholders.
In conclusion, the financial results for [2050] reflect a year of successful execution of [Your Company Name]’s business strategies. The company is well-positioned to meet future challenges, capitalize on new opportunities, and maintain its position as a leader in the tech industry. As we move into [2051], the company's solid foundation and strategic vision will guide it toward continued success.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Ensure transparent financial reporting with the CEO Financial Report Template from Template.net. Fully editable and customizable, it’s designed to detail company finances effectively. Use the AI Editor Tool for quick adjustments. Download now to communicate financial insights with precision.
You may also like
- Sales Report
- Daily Report
- Project Report
- Business Report
- Weekly Report
- Incident Report
- Annual Report
- Report Layout
- Report Design
- Progress Report
- Marketing Report
- Company Report
- Monthly Report
- Audit Report
- Status Report
- School Report
- Reports Hr
- Management Report
- Project Status Report
- Handover Report
- Health And Safety Report
- Restaurant Report
- Construction Report
- Research Report
- Evaluation Report
- Investigation Report
- Employee Report
- Advertising Report
- Weekly Status Report
- Project Management Report
- Finance Report
- Service Report
- Technical Report
- Meeting Report
- Quarterly Report
- Inspection Report
- Medical Report
- Test Report
- Summary Report
- Inventory Report
- Valuation Report
- Operations Report
- Payroll Report
- Training Report
- Job Report
- Case Report
- Performance Report
- Board Report
- Internal Audit Report
- Student Report
- Monthly Management Report
- Small Business Report
- Accident Report
- Call Center Report
- Activity Report
- IT and Software Report
- Internship Report
- Visit Report
- Product Report
- Book Report
- Property Report
- Recruitment Report
- University Report
- Event Report
- SEO Report
- Conference Report
- Narrative Report
- Nursing Home Report
- Preschool Report
- Call Report
- Customer Report
- Employee Incident Report
- Accomplishment Report
- Social Media Report
- Work From Home Report
- Security Report
- Damage Report
- Quality Report
- Internal Report
- Nurse Report
- Real Estate Report
- Hotel Report
- Equipment Report
- Credit Report
- Field Report
- Non Profit Report
- Maintenance Report
- News Report
- Survey Report
- Executive Report
- Law Firm Report
- Advertising Agency Report
- Interior Design Report
- Travel Agency Report
- Stock Report
- Salon Report
- Bug Report
- Workplace Report
- Action Report
- Investor Report
- Cleaning Services Report
- Consulting Report
- Freelancer Report
- Site Visit Report
- Trip Report
- Classroom Observation Report
- Vehicle Report
- Final Report
- Software Report