Free Defense Expense Report

I. Introduction
Defense expenditures are a crucial aspect of national security, ensuring the ability to protect the country from external threats and maintain internal stability. With the growing complexity of global security challenges, it is vital for [Your Company Name] to continue investing in its defense capabilities, modernizing military assets, and preparing for potential conflicts in both conventional and non-traditional domains. This comprehensive report provides an in-depth analysis of the defense spending for [Your Company Name] in 2050, detailing expenditure categories, funding sources, trends, challenges, and future projections. It also explores how investments in innovation, technology, and partnerships are shaping the future of defense spending.
The year 2050 witnessed an [8%] increase in total defense expenditures, reflecting an ever-evolving threat landscape and the importance of strategic investments in maintaining an edge over adversaries. The report serves as an important tool for understanding how the defense budget is allocated, the key focus areas, and how resources are being optimized to enhance operational capabilities.
II. Summary of Defense Expenditures
A. Total Expenditure Overview
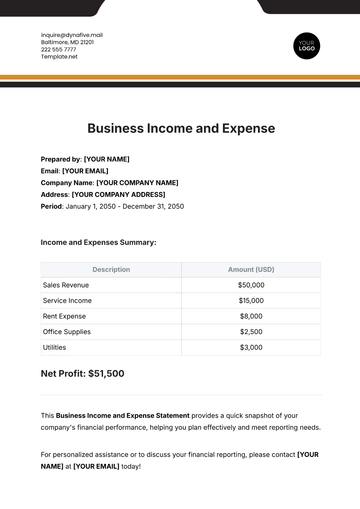
In 2050, [Your Company Name] allocated a total of $[2,500,000,000] for defense expenditures, which represented a significant increase from the previous year's budget of $[2,300,000,000]. This increase was driven by several factors, including the rising costs associated with technological advancements, personnel requirements, and the expansion of military operations. Defense spending has become a critical part of [Your Company Name]’s broader strategy to maintain national security, and the allocation for 2050 reflects a continued commitment to both defense readiness and modernization.
The table below provides a detailed breakdown of the expenditures by category, highlighting how resources were distributed across various aspects of defense operations. This helps to illustrate the priority areas and the level of investment made in each sector.
Category | Amount ($) | Percentage of Total |
|---|---|---|
Personnel Costs | 900,000,000 | 36% |
Equipment and Modernization | 750,000,000 | 30% |
Research and Development | 400,000,000 | 16% |
Operations and Maintenance | 350,000,000 | 14% |
Strategic Alliances | 100,000,000 | 4% |
This allocation provides a clearer picture of how [Your Company Name] focused its defense budget. Personnel costs remained the largest expenditure, while significant amounts were also allocated to modernization efforts to ensure military capabilities are on par with emerging threats.
III. Breakdown of Defense Expenditures
A. Personnel Costs
Personnel costs remained a critical component of the overall defense expenditure in 2050, accounting for $[900,000,000], or [36%] of the total budget. This category includes the salaries, benefits, and training costs of military personnel and civilian employees working within the defense sector.
Salary and Benefits
In total, $[650,000,000] was allocated to pay salaries and benefits for active-duty military members, civilian employees, and contractors working in the defense sector. This accounted for [26%] of the overall defense budget. Compensation packages for military personnel were adjusted to account for inflation and the increased cost of living, ensuring that service members are well-supported. Additionally, veteran support and pension schemes were funded to maintain the long-term welfare of former personnel.Training Programs
To enhance the effectiveness of the military, $[250,000,000] was spent on advanced training programs. These programs included specialized combat training for ground forces, aerial tactics for pilots, and cyber defense training to ensure that personnel are equipped to handle modern warfare challenges. As threats evolve, it has become increasingly important to train personnel in new combat techniques and technologies, preparing them for various scenarios, including cyber warfare and AI-assisted combat environments.Breakdown by Rank
The allocation of personnel expenses was also broken down by military rank and role. The table below shows the distribution of funds for different ranks and personnel types.Rank
Number of Personnel
Expense ($)
Senior Officers
1,500
150,000,000
Mid-level Officers
4,000
250,000,000
Junior Officers
8,000]
200,000,000
Civilian Staff
10,000
300,000,000
As shown, the majority of expenses were attributed to mid-level officers and civilian staff, which are critical to maintaining the operational readiness and effectiveness of defense strategies.
B. Equipment and Modernization
In 2050, $[750,000,000] was allocated to equipment and modernization efforts, representing [30%] of the total defense expenditure. The need to modernize existing systems and acquire new technologies has been critical as global military operations are increasingly influenced by technological advances in warfare.
Acquisition of Advanced Weapons Systems
A large portion of the equipment budget, totaling $[500,000,000], was dedicated to the acquisition of new, advanced weapons systems. This included cutting-edge technologies such as AI-driven unmanned combat vehicles, hypersonic missiles, and advanced radar systems. These investments were made to ensure that [Your Company Name]’s military capabilities remain at the forefront of defense technology, providing a strategic advantage over potential adversaries. Specific items purchased included:[50] AI-driven unmanned combat vehicles: $[200,000,000]
[20] Hypersonic missile systems: $[150,000,000]
Advanced radar systems: $[150,000,000]
Maintenance of Existing Assets
In addition to acquiring new technologies, $[250,000,000] was allocated for the maintenance and upgrades of existing military assets. These upgrades ensured that older systems remained operational and effective, while also integrating newer technologies. Maintenance efforts included both routine inspections and extensive retrofitting of equipment to meet modern operational requirements.Fleet Expansion
To ensure strategic and logistical mobility, $[100,000,000] was spent on expanding the naval and aerial fleets. This included the acquisition of new ships, aircraft, and drones, allowing [Your Company Name] to maintain a strong presence in key strategic regions.
C. Research and Development (R&D)
R&D is essential for ensuring that [Your Company Name] remains at the cutting edge of defense technology. In 2050, $[400,000,000] was spent on R&D efforts, which accounted for [16%] of the total defense budget. This included the development of advanced technologies such as quantum computing, AI-based systems, and space defense mechanisms.
Emerging Technologies
A major focus of the R&D budget was on emerging technologies with the potential to revolutionize warfare. This included quantum computing systems, which could significantly enhance encryption and cybersecurity, as well as AI-driven platforms that could automate many aspects of military operations. $[200,000,000] was allocated to the development of these technologies, ensuring that [Your Company Name] stays ahead of adversaries in these rapidly evolving fields.Collaboration with Academic Institutions
Collaborations with leading universities and research centers were also a critical part of the R&D strategy. $[100,000,000] was spent on joint initiatives with over [15] institutions to develop new technologies in areas such as cyber defense and autonomous vehicles. These partnerships are essential for accelerating innovation and staying ahead of global technological trends.Prototype Testing
To ensure that new technologies are viable for operational use, $[100,000,000] was spent on prototype testing and evaluation. This included rigorous field trials for hypersonic vehicles and underwater drones, as well as testing the performance of AI systems in simulated combat environments.
D. Operations and Maintenance
Operational readiness is crucial for maintaining defense capabilities, and in 2050, $[350,000,000] was allocated for operations and maintenance. This category accounted for [14%] of the total defense budget and was focused on keeping military units and equipment ready for immediate deployment.
Operational Readiness
Maintaining high levels of operational readiness involved a variety of activities, including simulated combat exercises, logistics support, and supply chain management. These efforts ensured that troops were prepared for both traditional combat and modern challenges, such as cyber warfare and asymmetric conflicts.Base Infrastructure
Infrastructure improvements at key defense bases also played a role in maintaining operational capabilities. A total of $[100,000,000] was spent on expanding and upgrading bases, ensuring that they could accommodate new technologies and provide modern facilities for personnel.Emergency Reserves
Emergency reserves are crucial for unexpected operational requirements, and in 2050, $[50,000,000] was allocated to cover unforeseen costs that may arise during operations. This funding was set aside for situations such as unexpected military engagements or the need for rapid deployment of resources.
E. Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances and international collaborations are increasingly important in ensuring global stability and enhancing defense capabilities. In 2050, $[100,000,000] was spent on forging partnerships with allied nations, enabling joint defense initiatives and cooperative military exercises.
Joint Defense Programs
Through joint programs, [Your Company Name] and its allies engaged in shared defense initiatives, including intelligence-sharing, technology development, and coordinated military operations. A total of $[60,000,000] was allocated to these programs.International Peacekeeping
As a member of global peacekeeping efforts, [Your Company Name] contributed $[40,000,000] to various international peacekeeping missions, including those led by the United Nations. These missions focus on maintaining stability in regions experiencing conflict and preventing the spread of violence.
IV. Funding Sources
Defense expenditures are primarily funded through various sources, each contributing to different aspects of national security operations. Securing adequate and sustainable funding for defense ensures that [Your Company Name] remains well-equipped to address the evolving threats of the future. Below are the main funding sources for [Your Company Name]'s defense budget in 2050, reflecting the strategic decisions made to sustain military readiness and technological advancement.
A. Government Allocations
The largest portion of [Your Company Name]'s defense funding comes from government allocations, which amounted to $[2,000,000,000] in 2050. These funds come directly from the national budget and are authorized by the government to meet defense priorities. The allocations are used for a variety of purposes, including maintaining the readiness of armed forces, funding R&D programs, and acquiring new defense systems.
In 2050, government allocations represented a significant portion of the total defense expenditure, accounting for [80%] of the overall budget. Given the increasing security threats across multiple domains, the national government recognized the need to enhance defense capabilities, thus allowing for higher appropriations in the defense sector. Furthermore, the budget for defense is often reviewed annually, with adjustments made based on geopolitical developments and emerging security concerns.
B. Private Sector Contributions
In addition to government funding, private sector contributions play a vital role in enhancing the defense sector's capabilities. For the year 2050, private sector partnerships provided $[300,000,000] in funding. This support often comes from collaborations between defense contractors, technology firms, and research institutions that are engaged in providing specialized defense equipment and technologies.
Private sector involvement primarily focuses on research and development, particularly in areas such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, robotics, and cybersecurity. Through public-private partnerships, [Your Company Name] has been able to leverage the expertise of cutting-edge tech companies to push the envelope in military innovation. These partnerships also allow for cost-sharing when it comes to developing advanced technologies, which is crucial in a landscape of rapid technological change.
C. International Aid
International aid is another crucial funding source for defense expenditure, though it accounts for a smaller portion of the overall defense budget. In 2050, international aid contributed $[200,000,000], primarily from allied nations and regional defense organizations such as NATO. These contributions are made to support joint defense operations, peacekeeping missions, and shared research projects aimed at countering common security threats.
One major benefit of international cooperation in defense is the pooling of resources for mutual benefit. For example, funding received from NATO and allied countries was used for multinational training programs, joint military exercises, and shared intelligence operations. Such collaborative efforts not only enhance [Your Company Name]'s defense capabilities but also foster stronger relationships between allied nations.
V. Trends in Defense Spending
A. Rising Costs of Modernization
As technological advancements continue to reshape warfare, one of the most notable trends in defense spending is the rising cost of modernization. In 2050, [Your Company Name] saw a dramatic shift towards high-tech military systems, including AI-driven platforms, autonomous weapons, and quantum-based communications systems. These modern systems require substantial investments not only in initial acquisition but also in long-term maintenance and upgrades.
The rapid pace of technological innovation in the defense sector means that modernization is an ongoing process rather than a one-time expenditure. The growing sophistication of military technology demands regular investment in both hardware and software updates to keep defense systems competitive. For example, the acquisition of AI-powered drones and hypersonic weapons systems in 2050 required substantial upfront costs, but these systems will continue to require investment in the form of software upgrades, cybersecurity patches, and training programs for personnel to use them effectively.
B. Focus on Cybersecurity
Another growing trend in defense spending is the increasing focus on cybersecurity. As the digital battlefield expands, the need to secure military networks, command and control systems, and communication lines becomes ever more critical. Cyberattacks targeting military infrastructure, weapons systems, and even critical national infrastructure have become more sophisticated, and defense budgets have shifted to address these vulnerabilities.
In 2050, [Your Company Name] allocated a significant portion of its R&D budget to cybersecurity initiatives. This included investments in advanced encryption technologies, cyber defense training programs, and the establishment of dedicated cyber warfare units. Additionally, the defense sector has increasingly adopted AI-driven cybersecurity solutions that use machine learning to detect and respond to threats in real-time.
C. Shift Towards Automation
The shift towards automation in defense spending is another key trend that reflects broader technological and operational changes. In 2050, investments in unmanned systems, including drones and autonomous vehicles, saw an exponential increase. These systems are used in a wide range of military operations, from surveillance and reconnaissance to combat missions.
Automation offers several benefits, including reducing the risk to human personnel, enhancing operational efficiency, and enabling new types of missions that would have been previously impossible. Unmanned systems can operate in environments that are too hazardous for humans, such as during chemical warfare, biological threats, or in hostile territory.
VI. Challenges
A. Budgetary Constraints
Despite significant government allocations and partnerships with the private sector, budgetary constraints remain one of the most pressing challenges for defense spending in 2050. Although the defense budget saw an increase, it is unlikely that future increases will keep pace with the growing costs of modernizing military systems and addressing emerging threats.
As defense needs become more complex, the government faces tough choices about where to allocate funds. Rising defense costs must be balanced with other national priorities, such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. To address these budgetary constraints, [Your Company Name] has implemented cost-cutting measures, including prioritizing critical projects, streamlining procurement processes, and leveraging more cost-effective technologies.
B. Talent Retention
As technological capabilities expand, there is an increasing need for specialized talent within the defense sector. In 2050, talent retention has become one of the most significant challenges faced by [Your Company Name]'s defense agencies. With the rapid expansion of new technologies, such as AI, quantum computing, and cybersecurity, there is a growing demand for highly skilled professionals who can develop, implement, and maintain these complex systems.
However, the private sector offers lucrative career opportunities for these specialized professionals, making it difficult for government agencies to compete in terms of salary and benefits. To address this issue, [Your Company Name] has focused on enhancing its recruitment and retention programs by offering competitive compensation packages, professional development opportunities, and the promise of meaningful work in national security. Additionally, partnerships with universities and technical schools have been established to develop a pipeline of future defense talent.
C. Technological Adaptation
One of the significant challenges of defense spending in the 2050s is the need to rapidly adapt to new technologies while maintaining existing operational capabilities. While technological advancements provide numerous opportunities, the pace at which new technologies are developed often outstrips the ability of defense agencies to integrate them fully into their systems.
The integration of emerging technologies requires substantial investments in research, development, and testing to ensure they meet operational needs. Additionally, personnel must be trained in using new systems, and existing infrastructure must be upgraded to accommodate these changes. The challenge lies in balancing innovation with the practicalities of military operations, ensuring that new technologies complement rather than replace traditional defense capabilities.
VII. Expense Data
A. Allocation by Categories
Below is a comprehensive breakdown of the defense budget allocation by category for 2050.
Category | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
Personnel Costs | 900,000,000 |
Equipment and Modernization | 750,000,000 |
Research and Development | 400,000,000 |
Operations and Maintenance | 350,000,000 |
Strategic Alliances | 100,000,000 |
B. Percentage Growth in Key Areas
In addition to budget allocation, here is a breakdown of growth rates for key areas of defense spending in 2050.
VIII. Conclusion
The defense expenditure report for 2050 illustrates the forward-thinking and strategic approach of [Your Company Name] to address the rapidly evolving security landscape. With a sharp focus on modernization, personnel readiness, and international collaboration, [Your Company Name] has ensured that its defense capabilities remain strong and adaptive to future challenges.
Despite significant challenges such as rising costs, talent retention issues, and technological integration hurdles, the defense sector is making substantial strides toward creating a more efficient, secure, and advanced military infrastructure. Continued investments in research and development, particularly in cybersecurity, AI, and automation, will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the years to come.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Track your expenditures with the Defense Expense Report Template from Template.net. This editable and customizable template simplifies expense tracking for defense projects. Tailor it easily with the AI Editor Tool to meet your financial reporting needs. Download today to maintain accurate financial records.