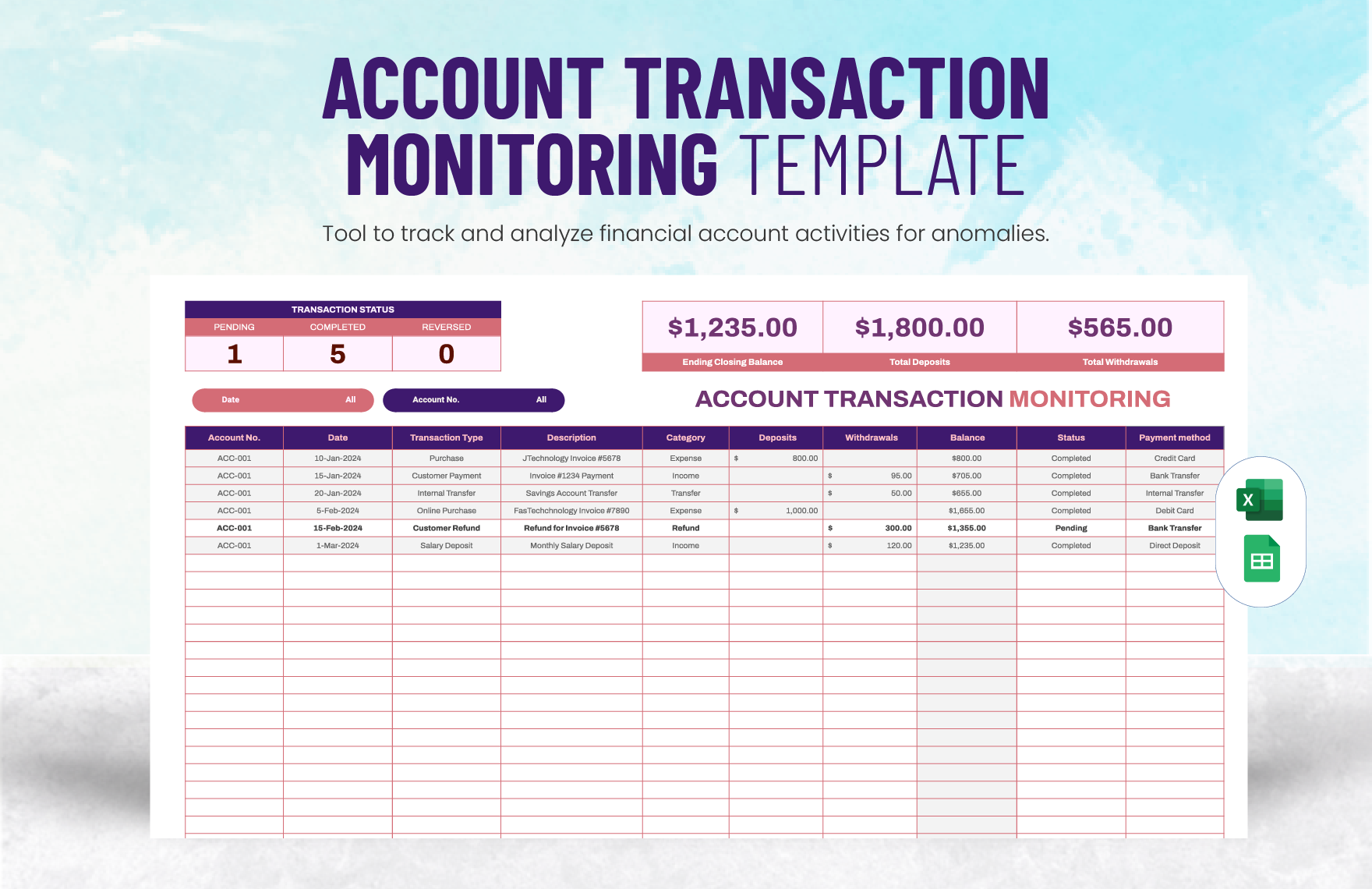
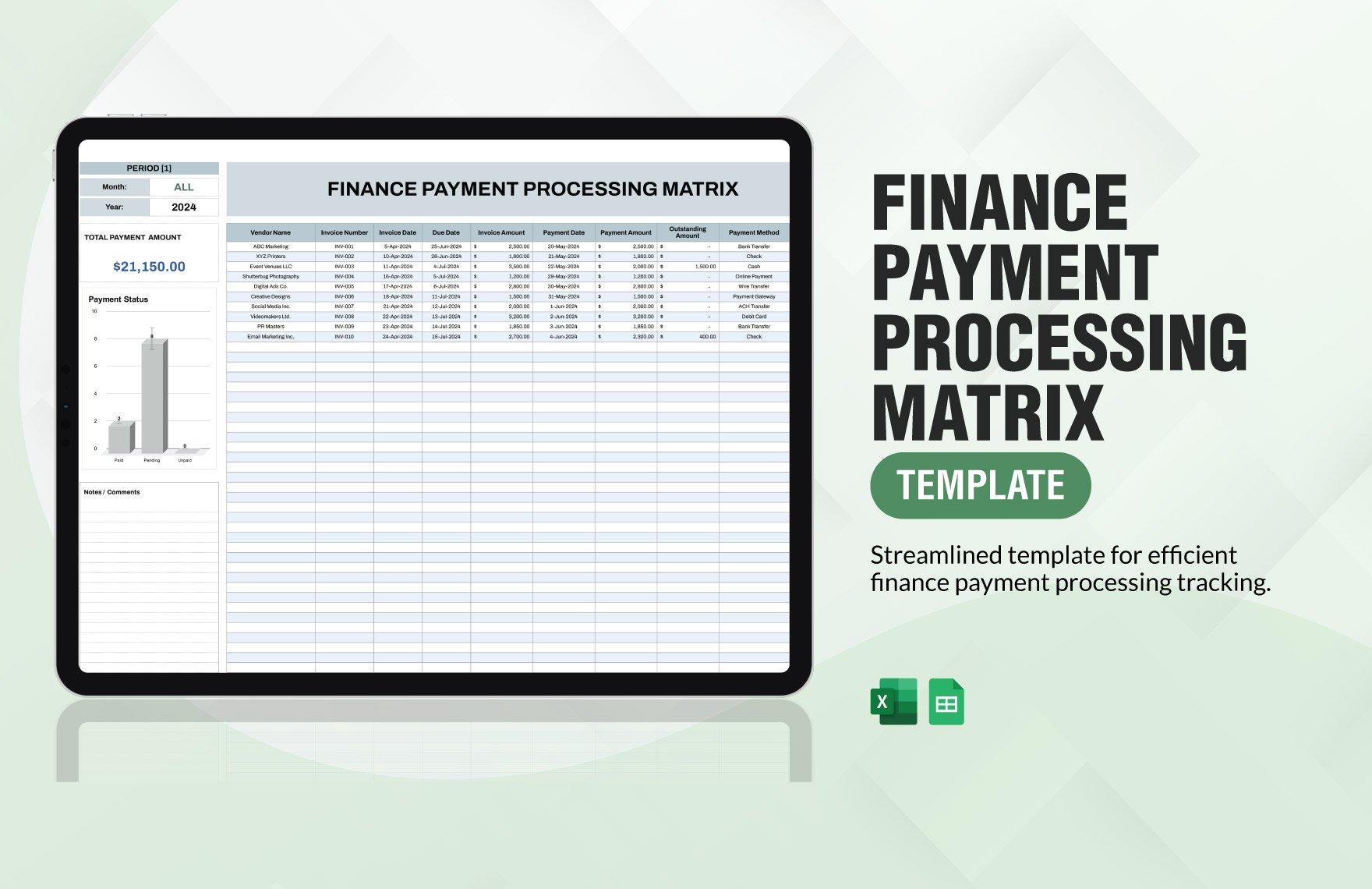
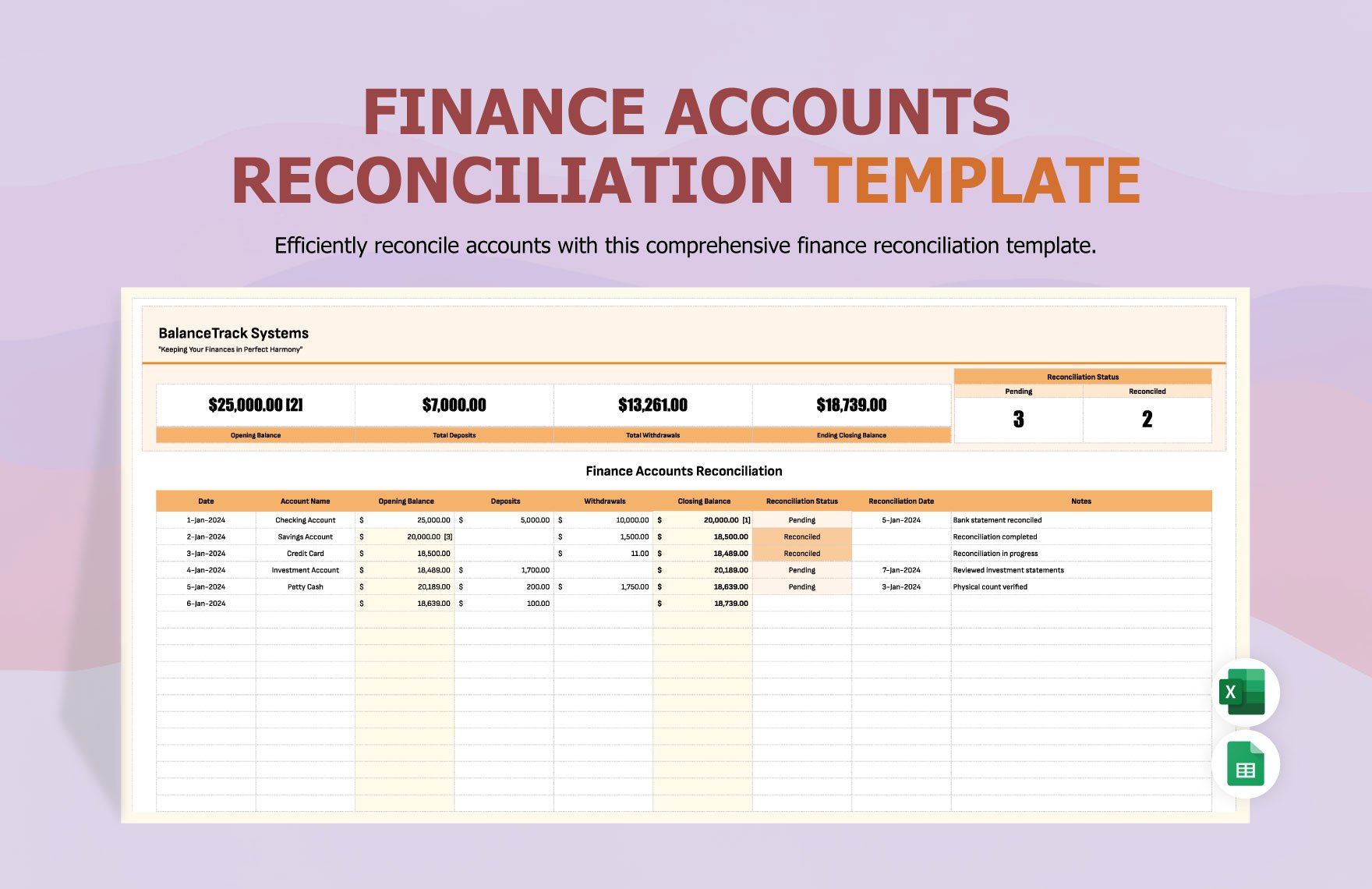
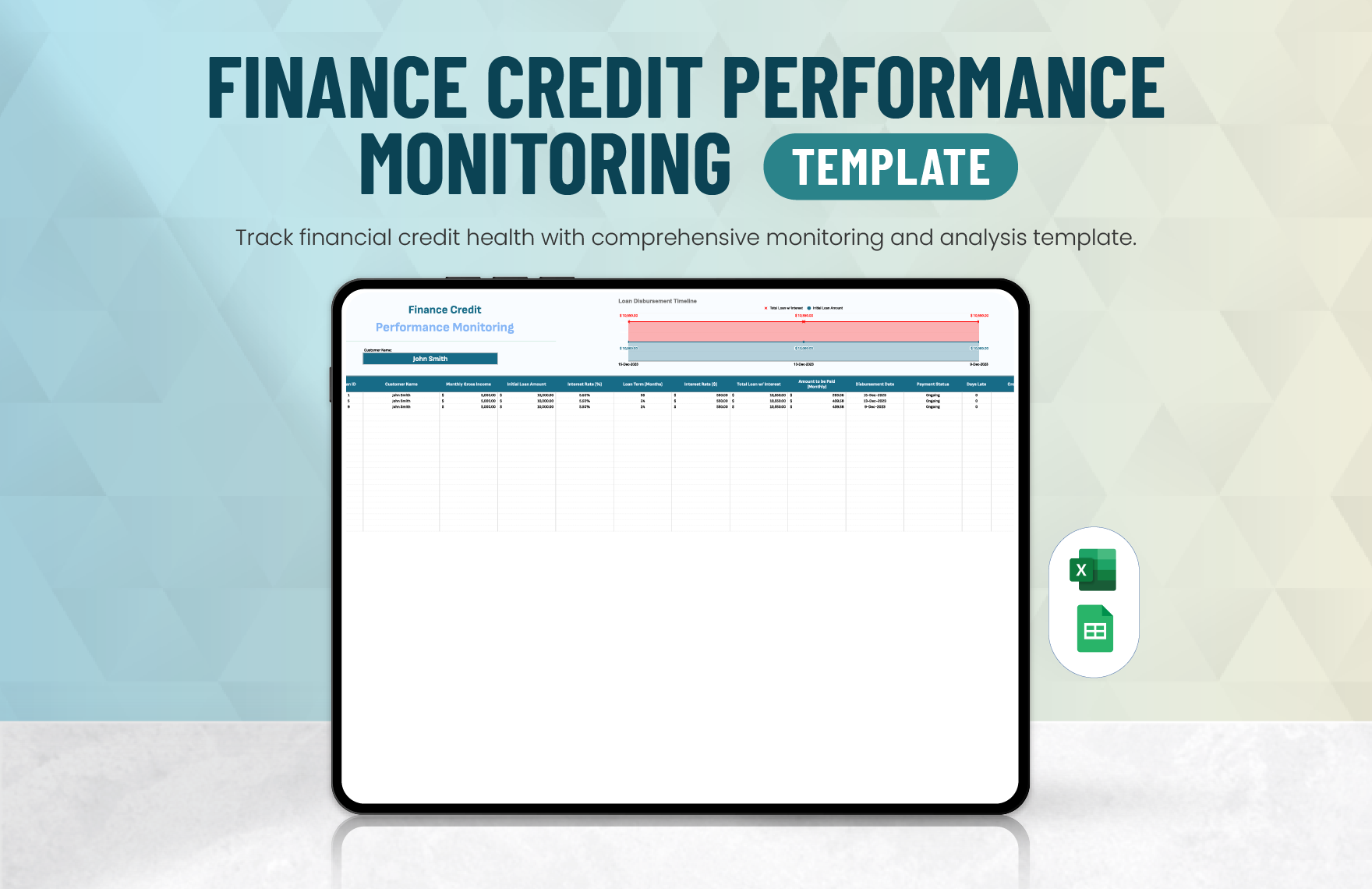
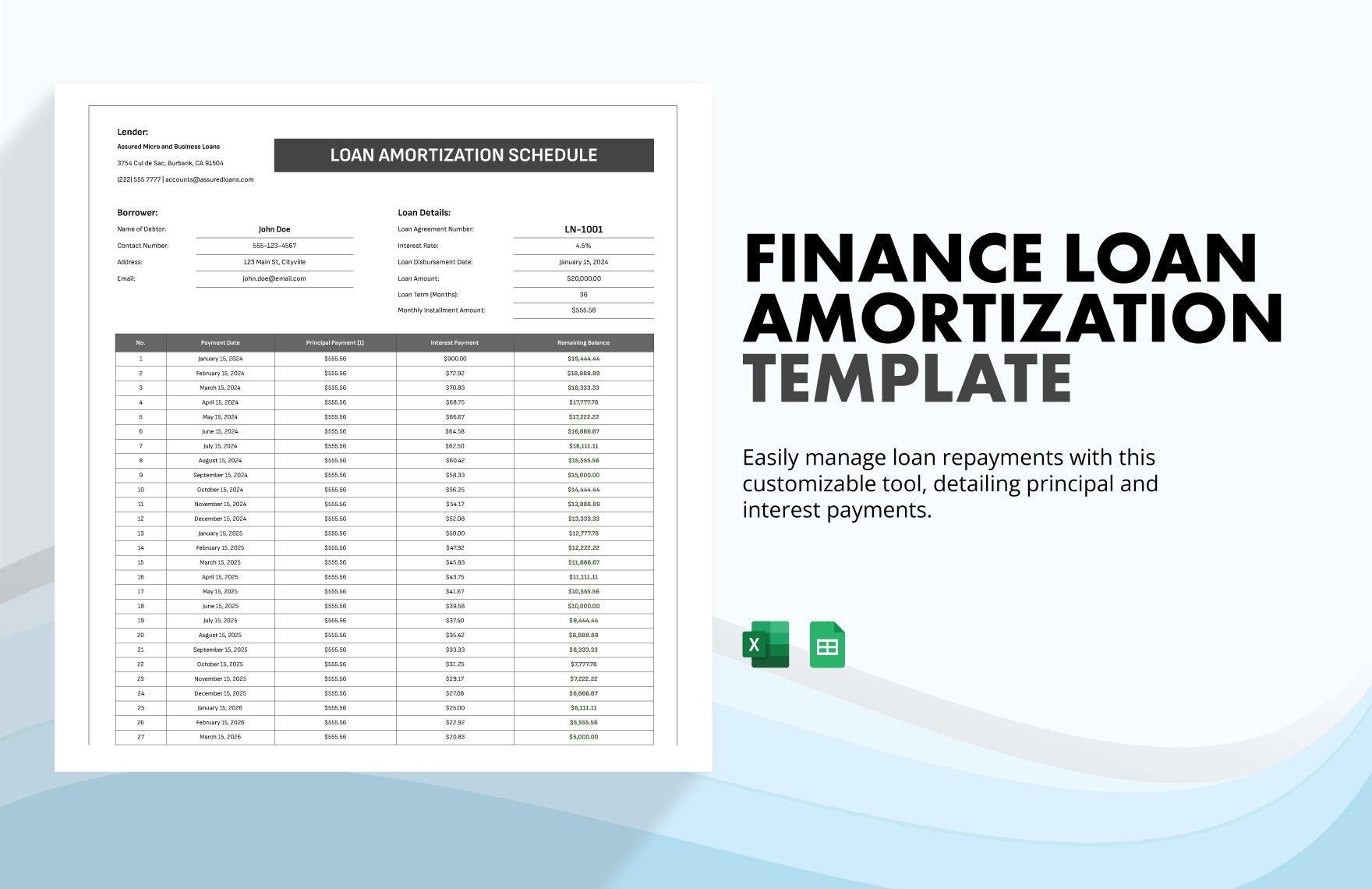
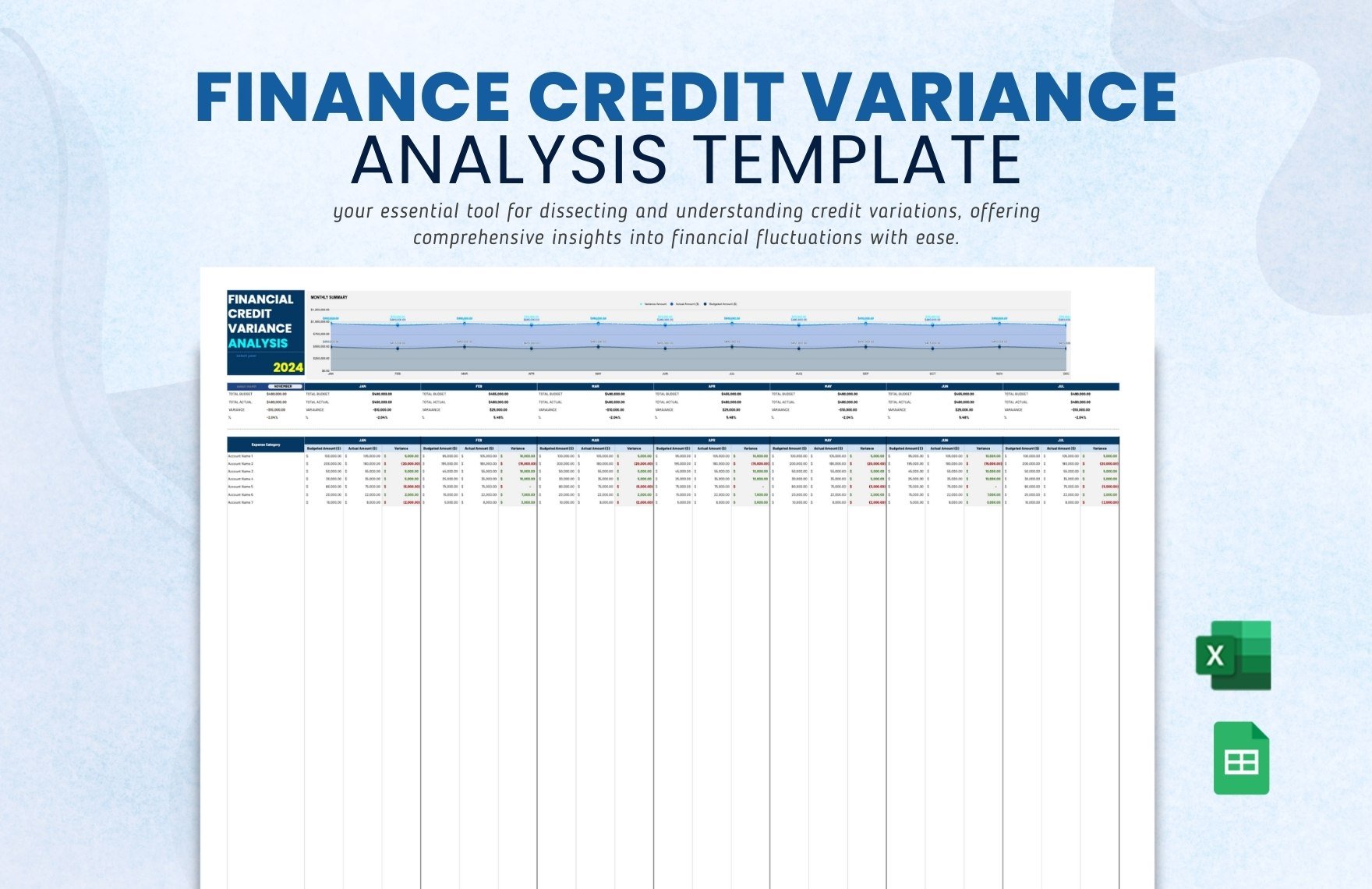
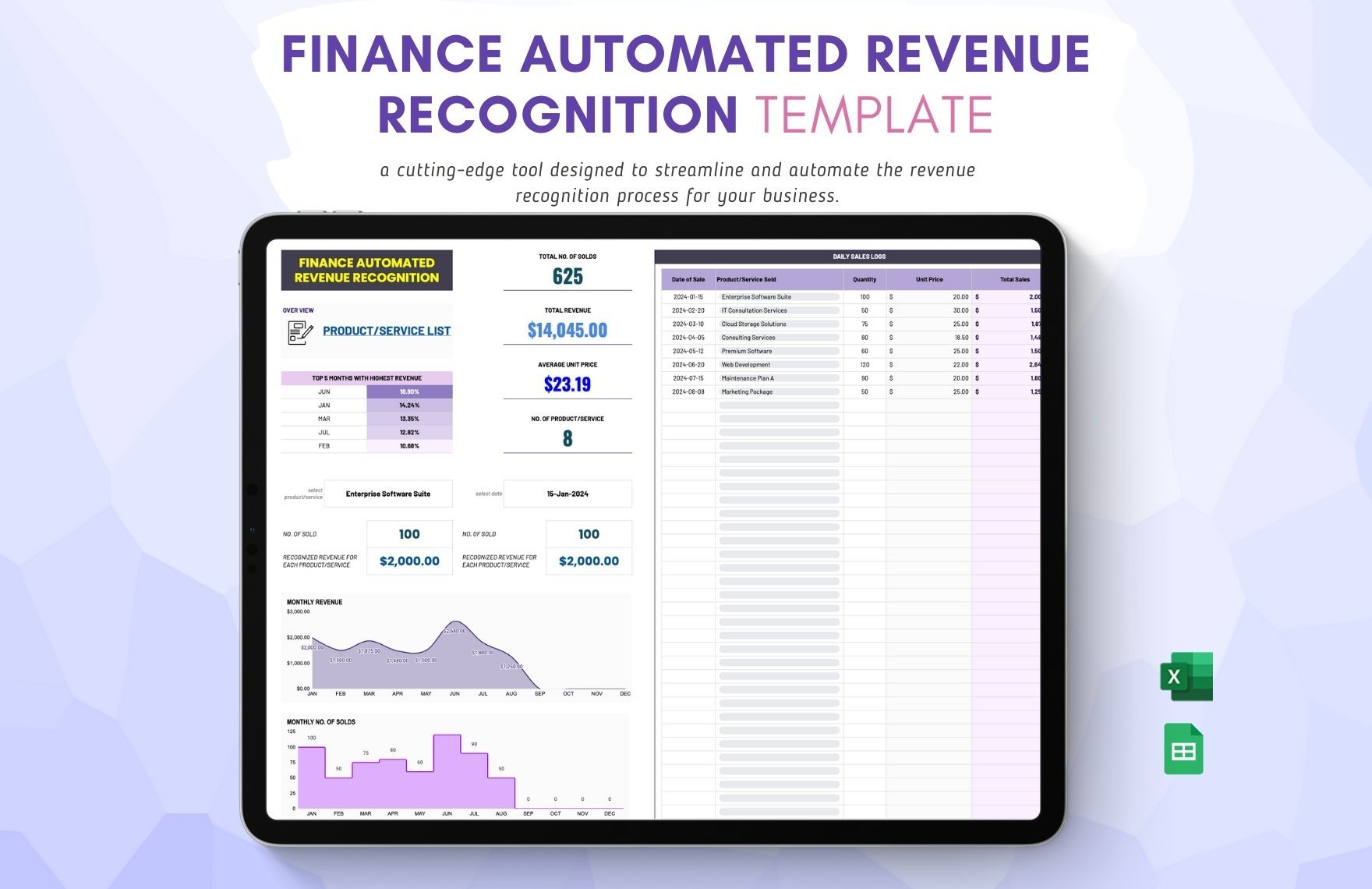
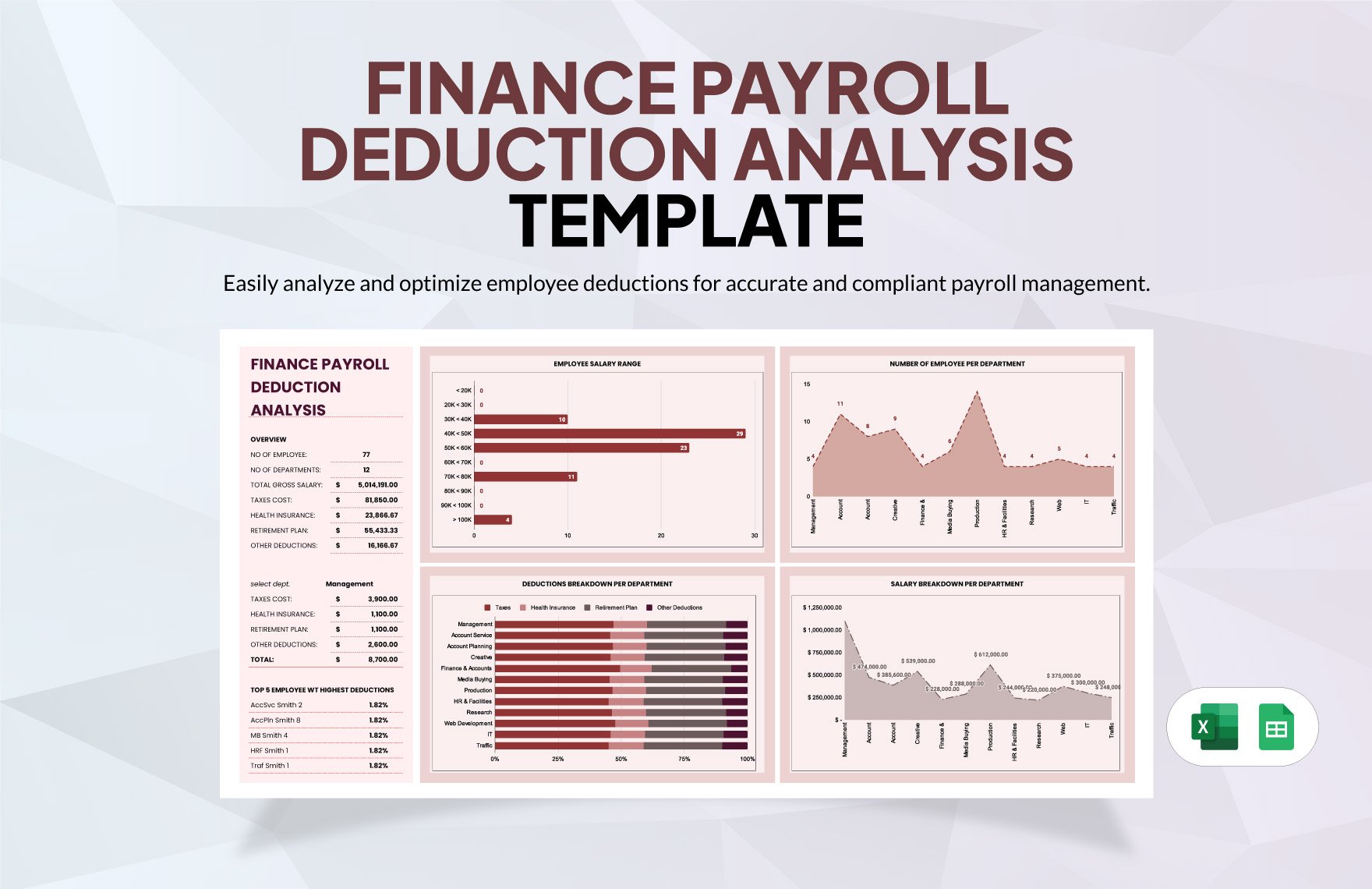
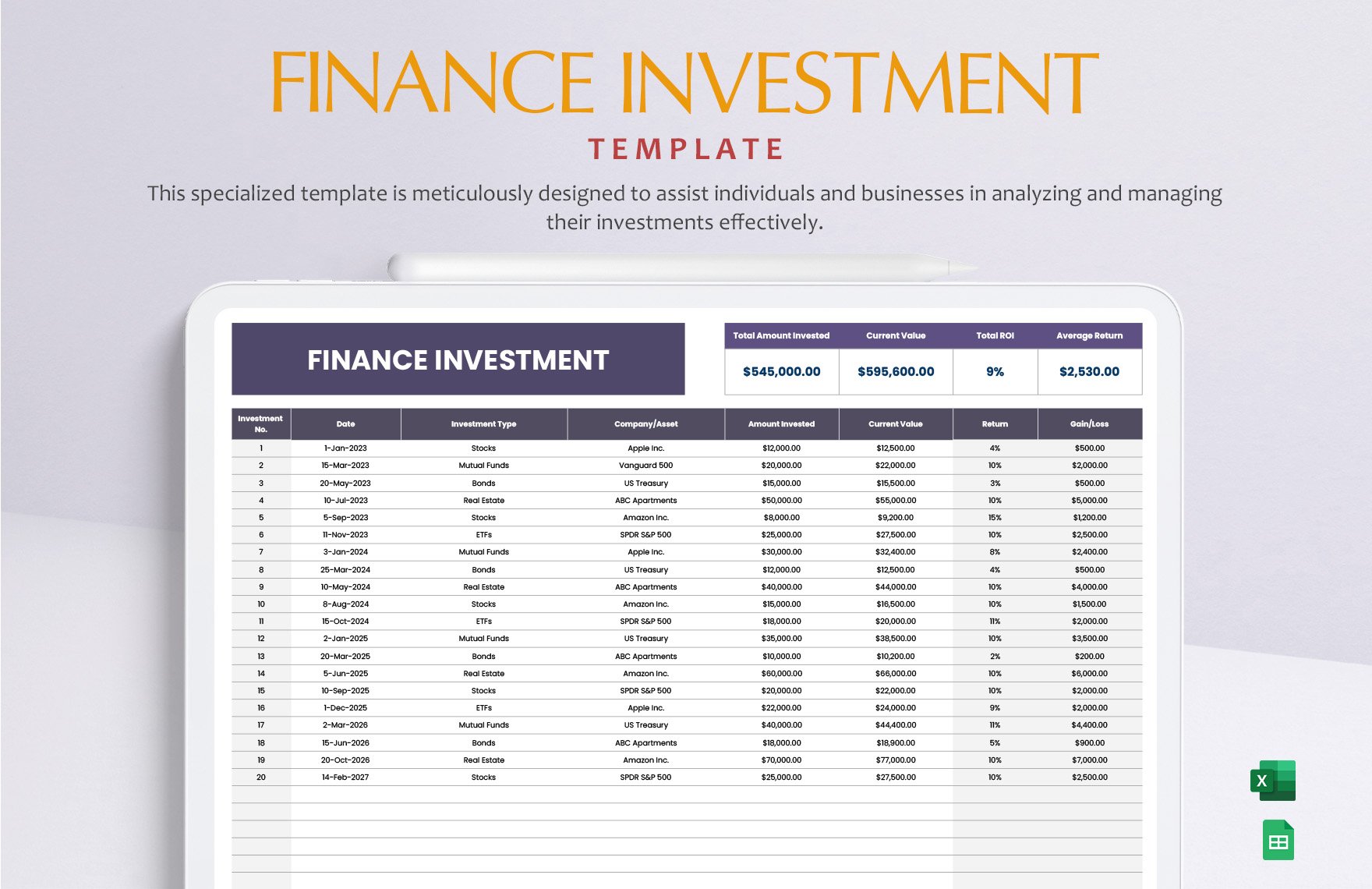
Creating the complete set of financial statements—income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, statement of changes in equity, and notes to financial statements—requires a lot of time and effort. Thankfully, we have financial statement templates that are available in Google Sheets file format in store for you! Through our well-formatted and 100% customizable templates, you will surely save time and effort and skip the hassle of starting from scratch because our templates are ready-made and content ready. All you need to do is modify the content to fit your current needs. Download any of our financial statements in Google Sheets today and maximize their benefits!
How to Make Financial Statements in Google Sheets?
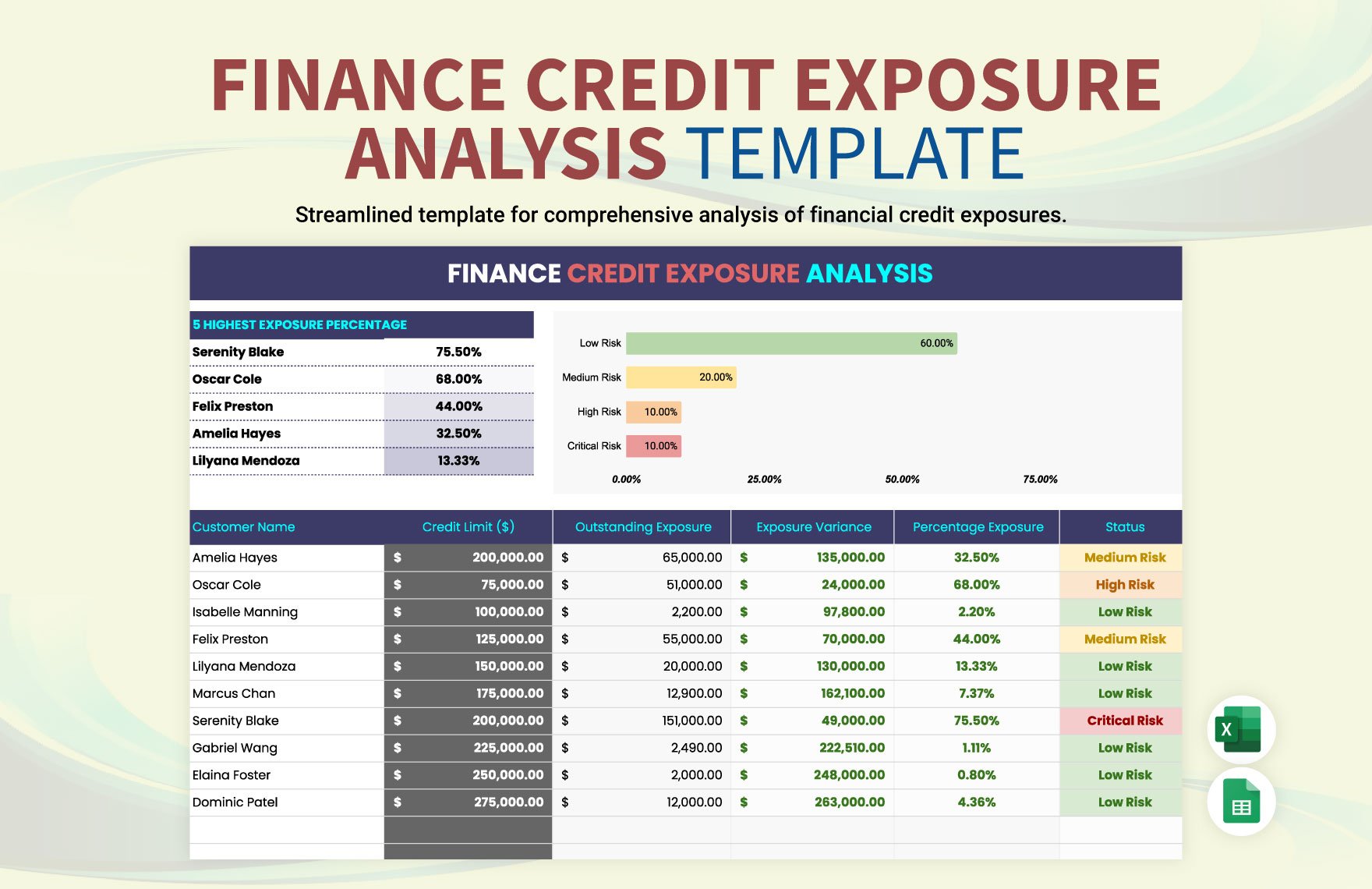
Financial statements reflect the company's health and potential for earnings, hence used not only by the internal management of the company but also by investors, creditors, market analysis, and other interested parties. Before you can create any of the financial statements, you need to undergo several steps that would help you identify each business transaction correctly and post it to the appropriate account. An error in the financial statement, although can be fixed with correcting entries, can greatly affect the decision-making of the internal and external users of the financial statements. For this reason, we can help you create financial statements with ease through the following simple steps.
1. Analyze the Business Transactions
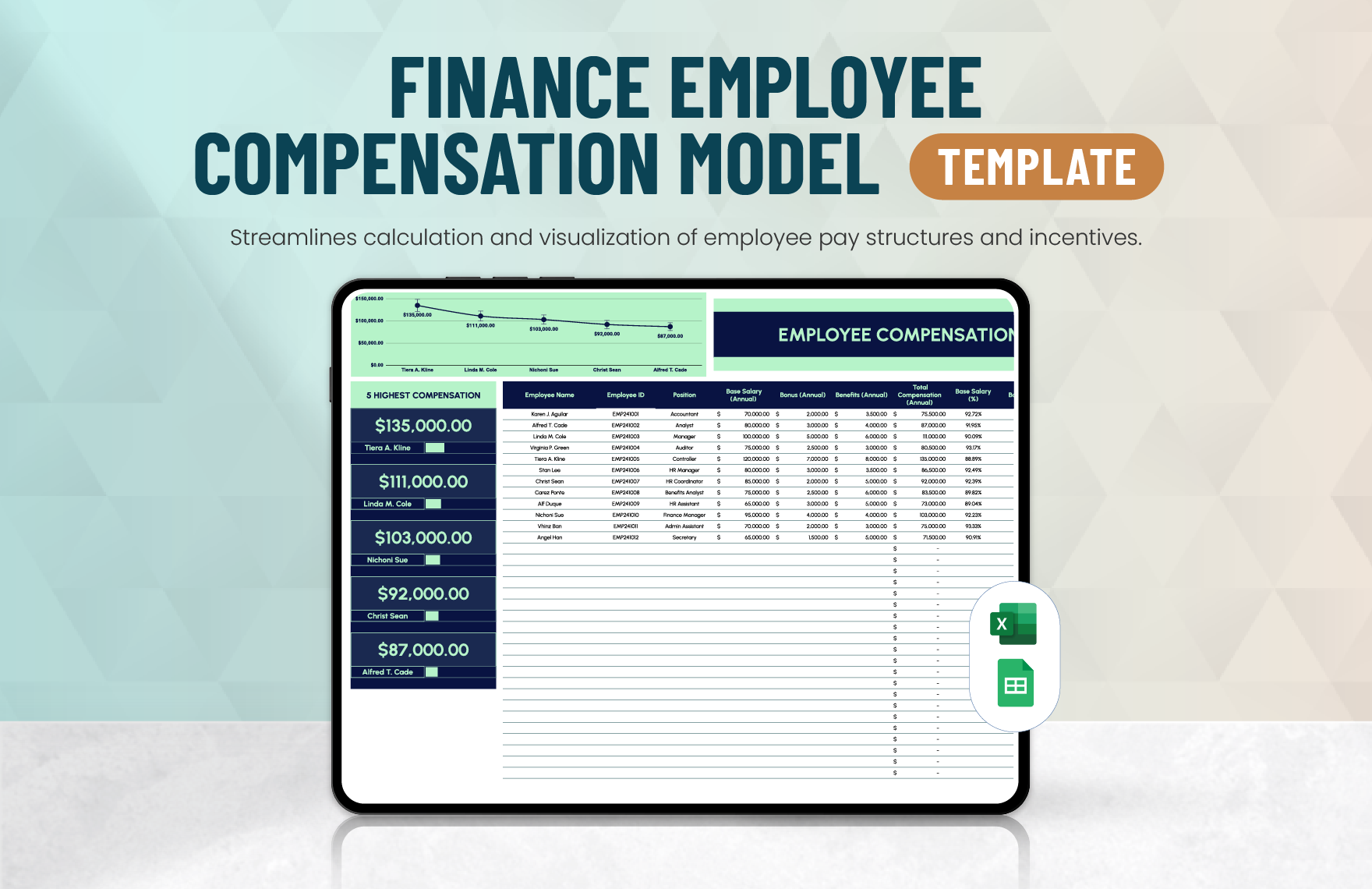
Firstly, you must analyze each business transaction and include in the accounting process only those that pertain to the business entity. Prepare the source documents, the original record which contains the detail that supports the transaction. Then, after your analysis, determine the accounts affected in the transaction and the amounts to be recorded.
2. Create a Journal Entry
In your journal, the book of original entry, record each business transaction using the double-entry bookkeeping system, that is, through debit and credit. Note that the transactions must be recorded in chronological order and as they occur.
3. Post to the Ledger
The ledger, also known as the books of final entry, is a collection of accounts and the changes made to each account in the current accounting period. Now that you have recorded each transaction in the journal, you can easily post all the transactions to the ledger to determine their ending balances.
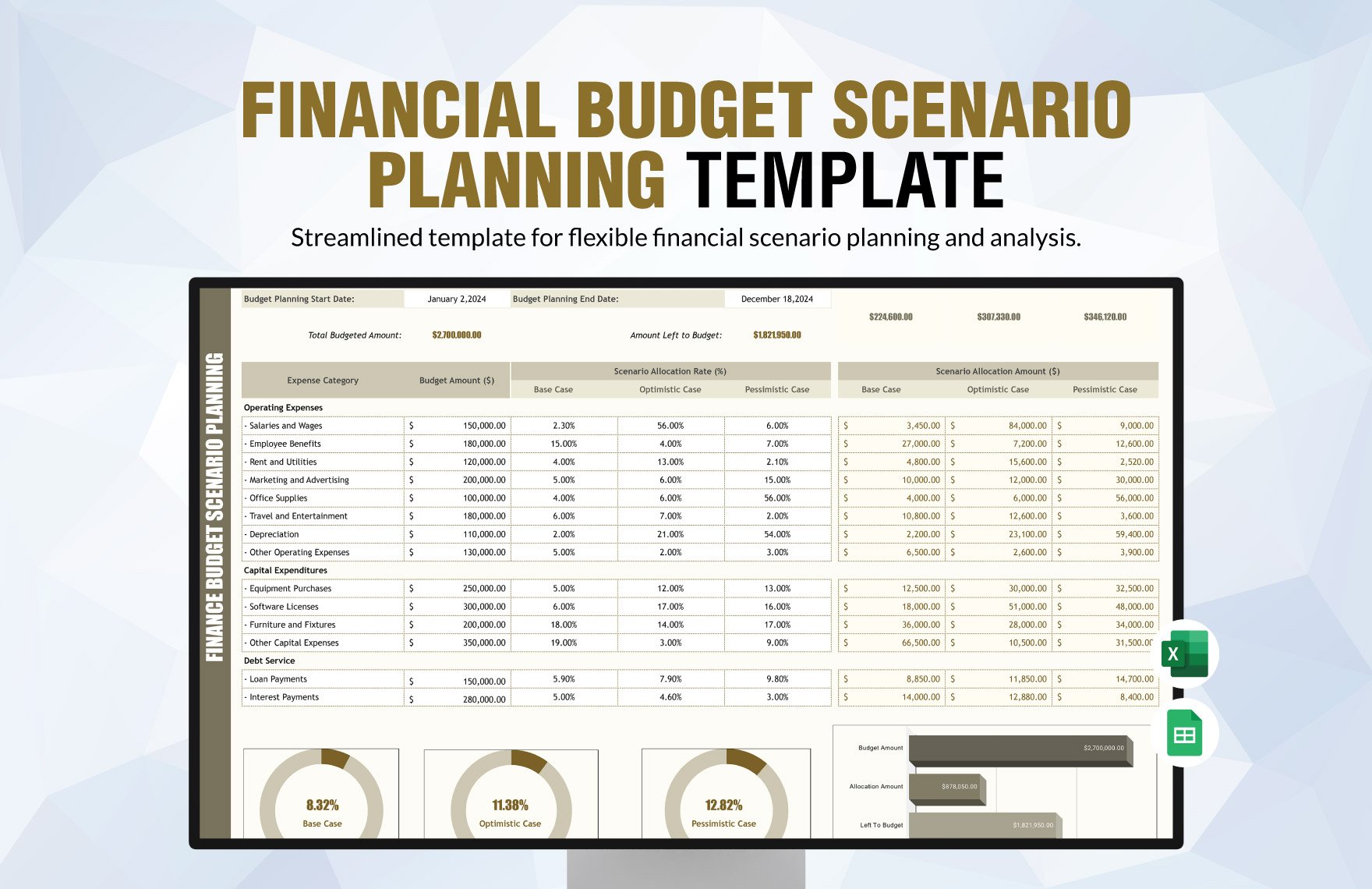
4. Create an Unadjusted Trial Balance
Preparing the unadjusted trial balance is important to test the equality of the debits and credits. This can be done by listing all account balances from the ledger and arranging them in one report. Afterward, all debit balances are added and all credit balances are also added. Total debits must equal total credits. Correcting entries must be immediately made when errors are discovered.
5. Record Adjusting Entries
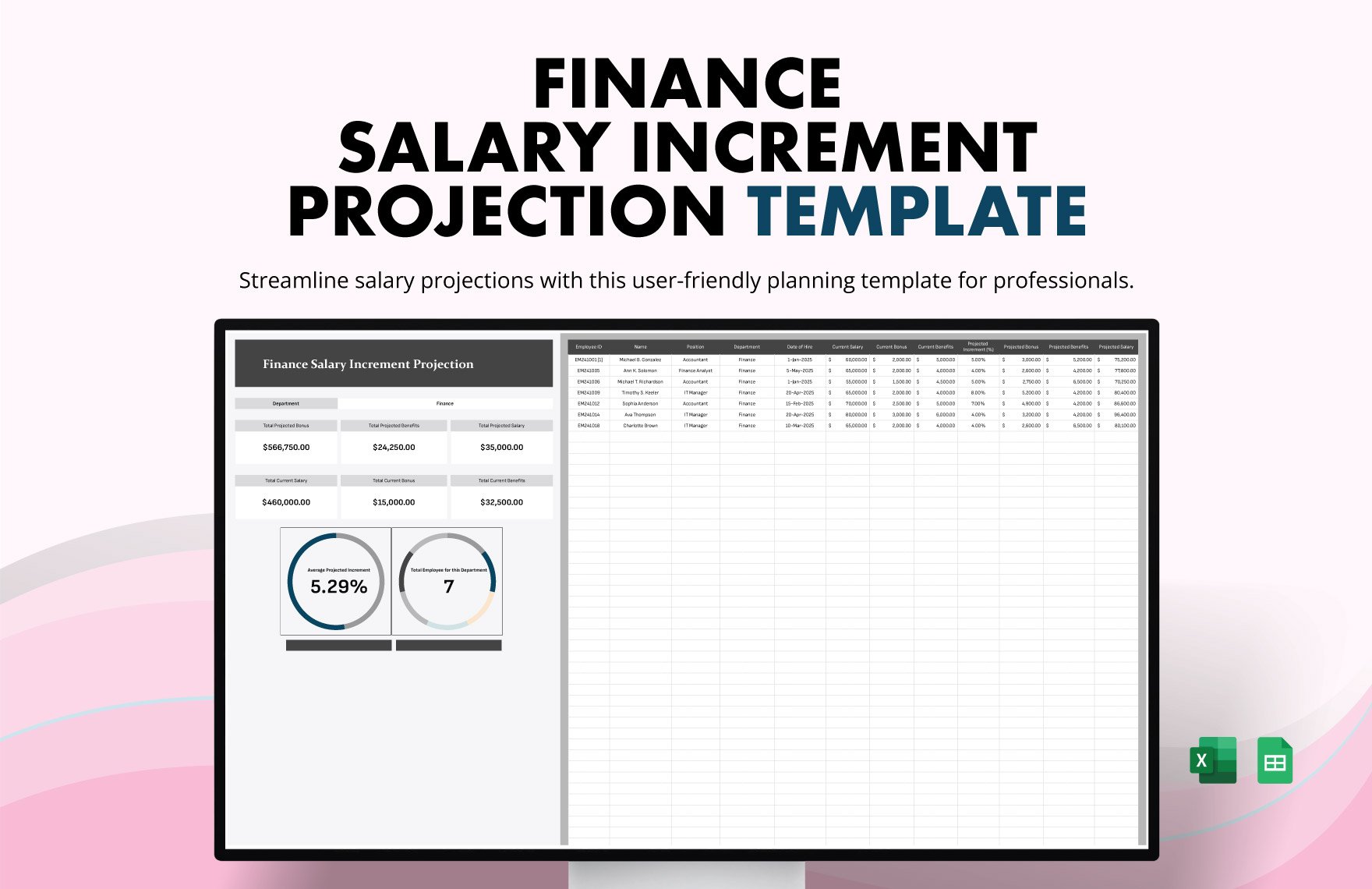
Adjusting entries are needed to update several accounts before they are posted in the financial statements. For example, some expenses may have been incurred but not yet recorded in the journals and some income may have been earned but not recorded in the books. Adjusting entries are made for accrued income and expenses, deferrals, prepayments, depreciation, and allowances.
6. Prepare the Adjusted Trial Balance
Reflect all the adjusting entries in the unadjusted trial balance to come up with the adjusted trial balance. This is important because it tests the equality of debits and credits after reflecting the adjusting entries.
7. Make the Financial Statements
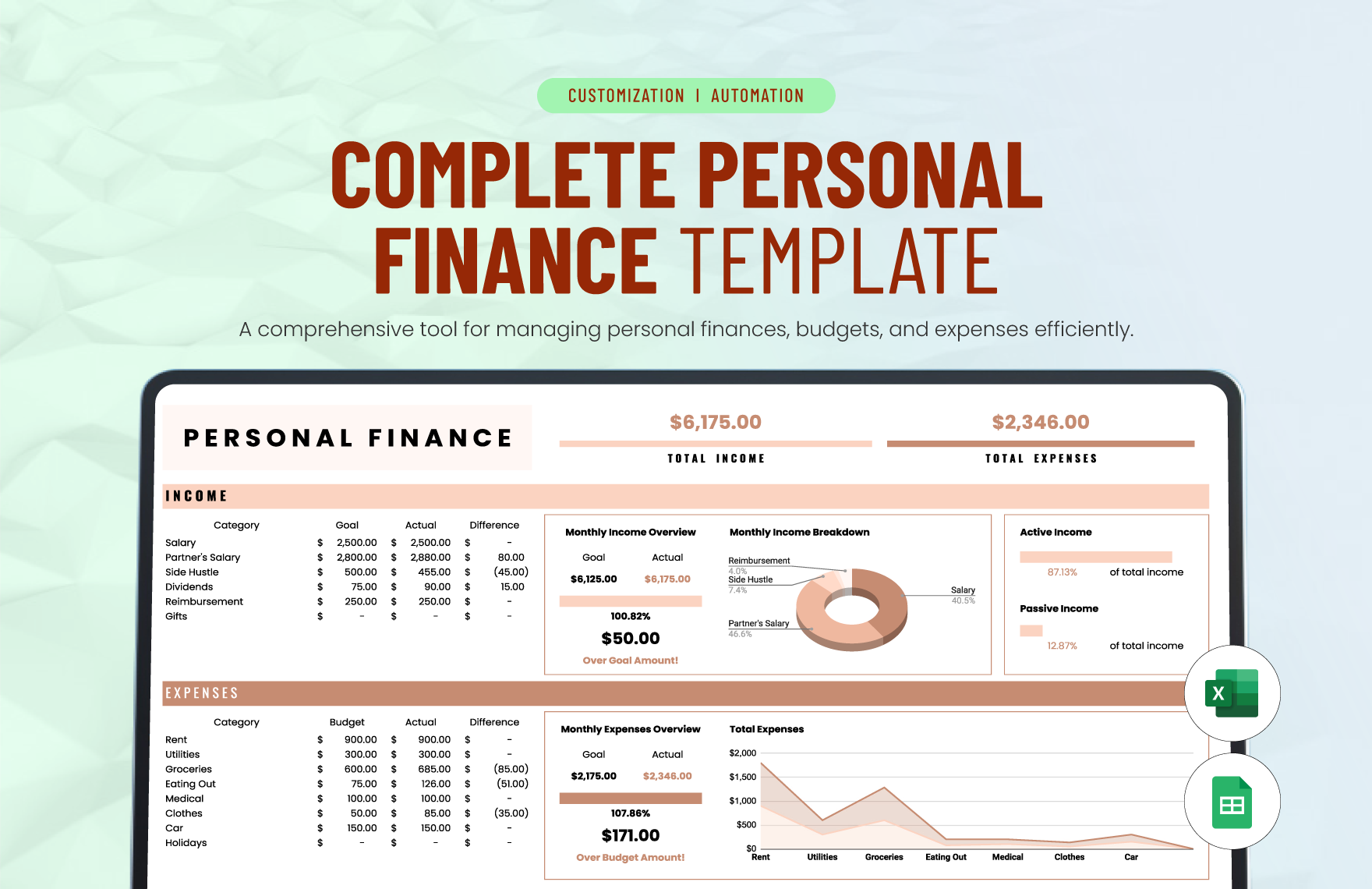
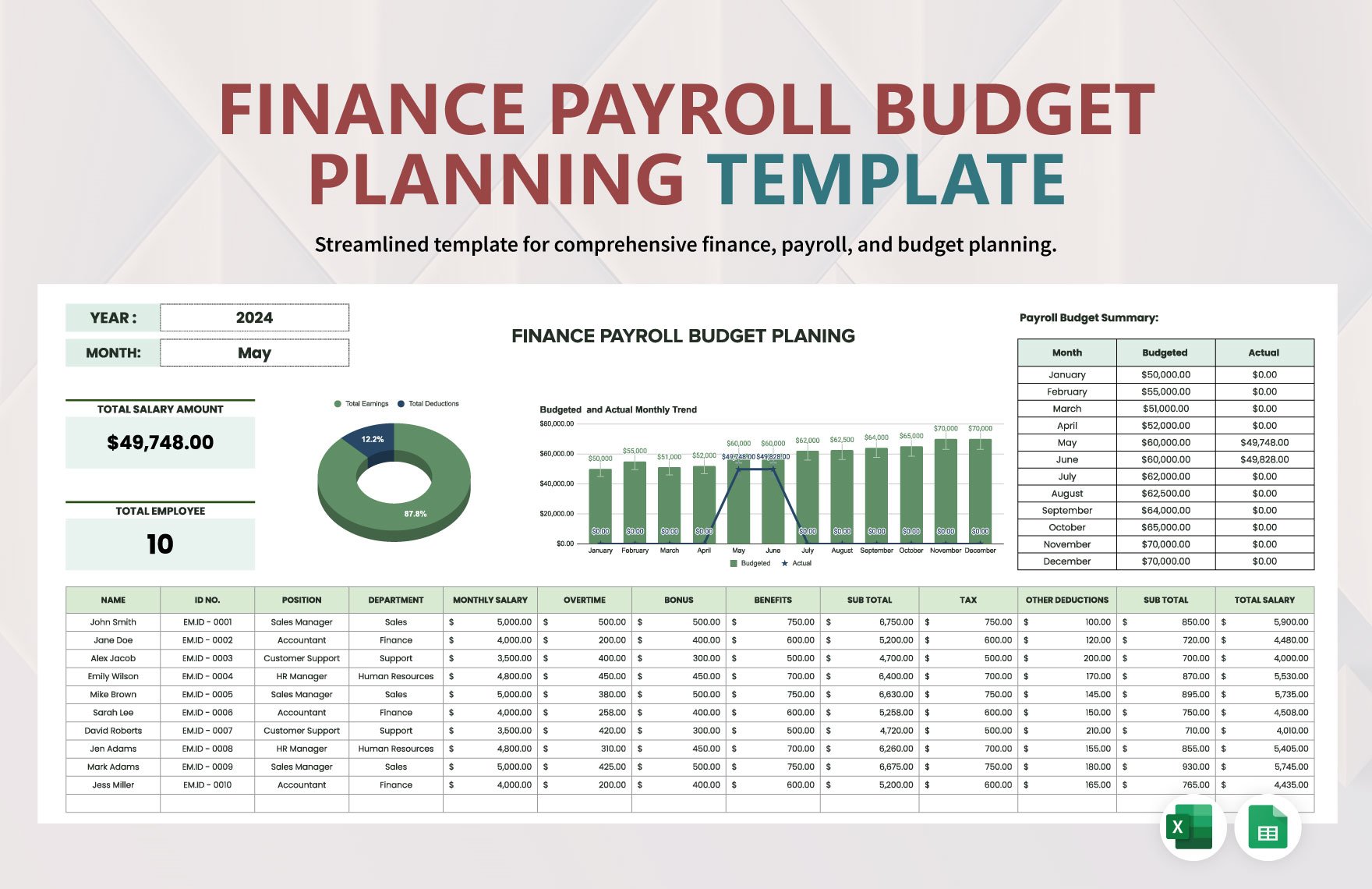
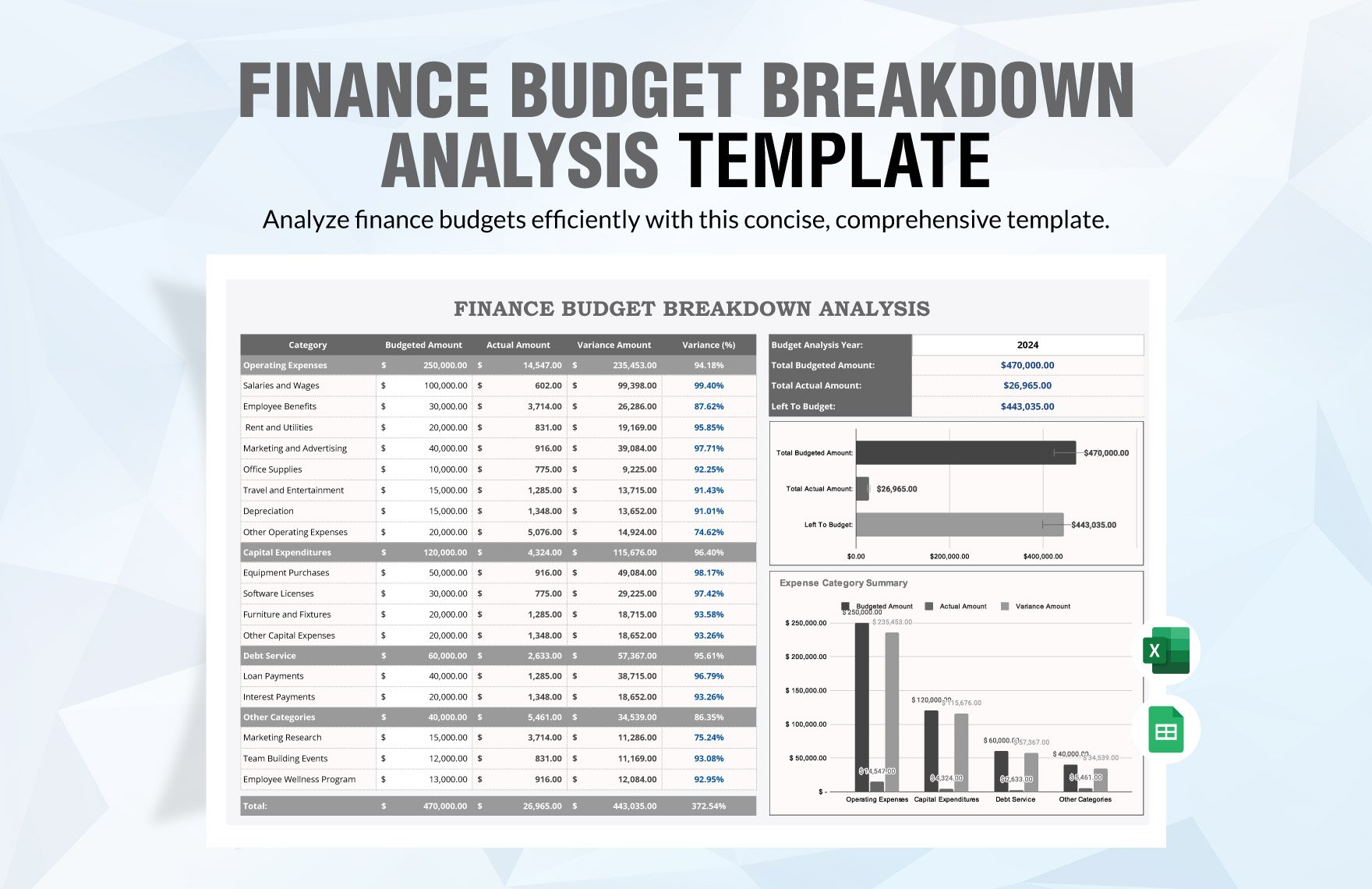
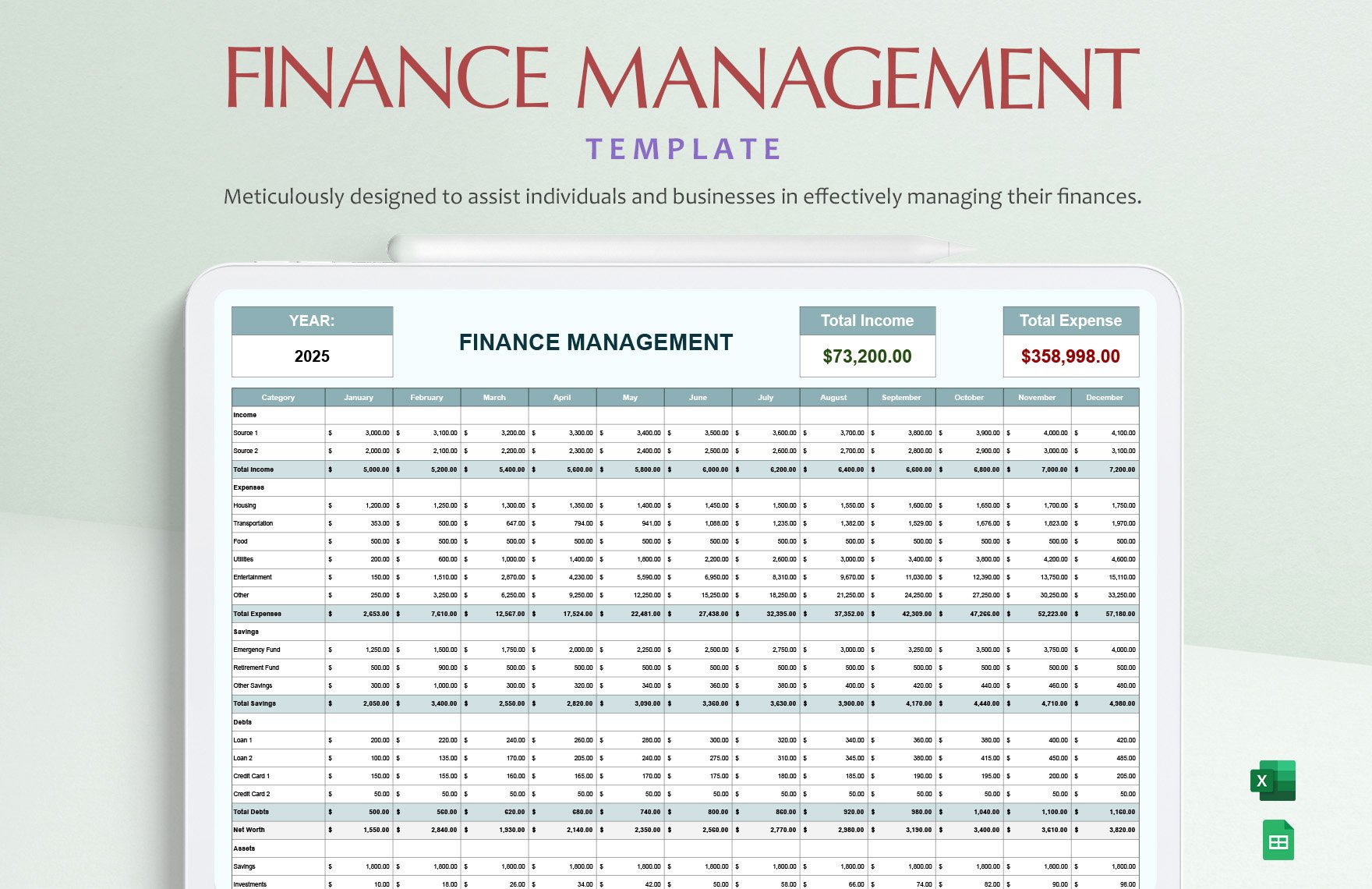
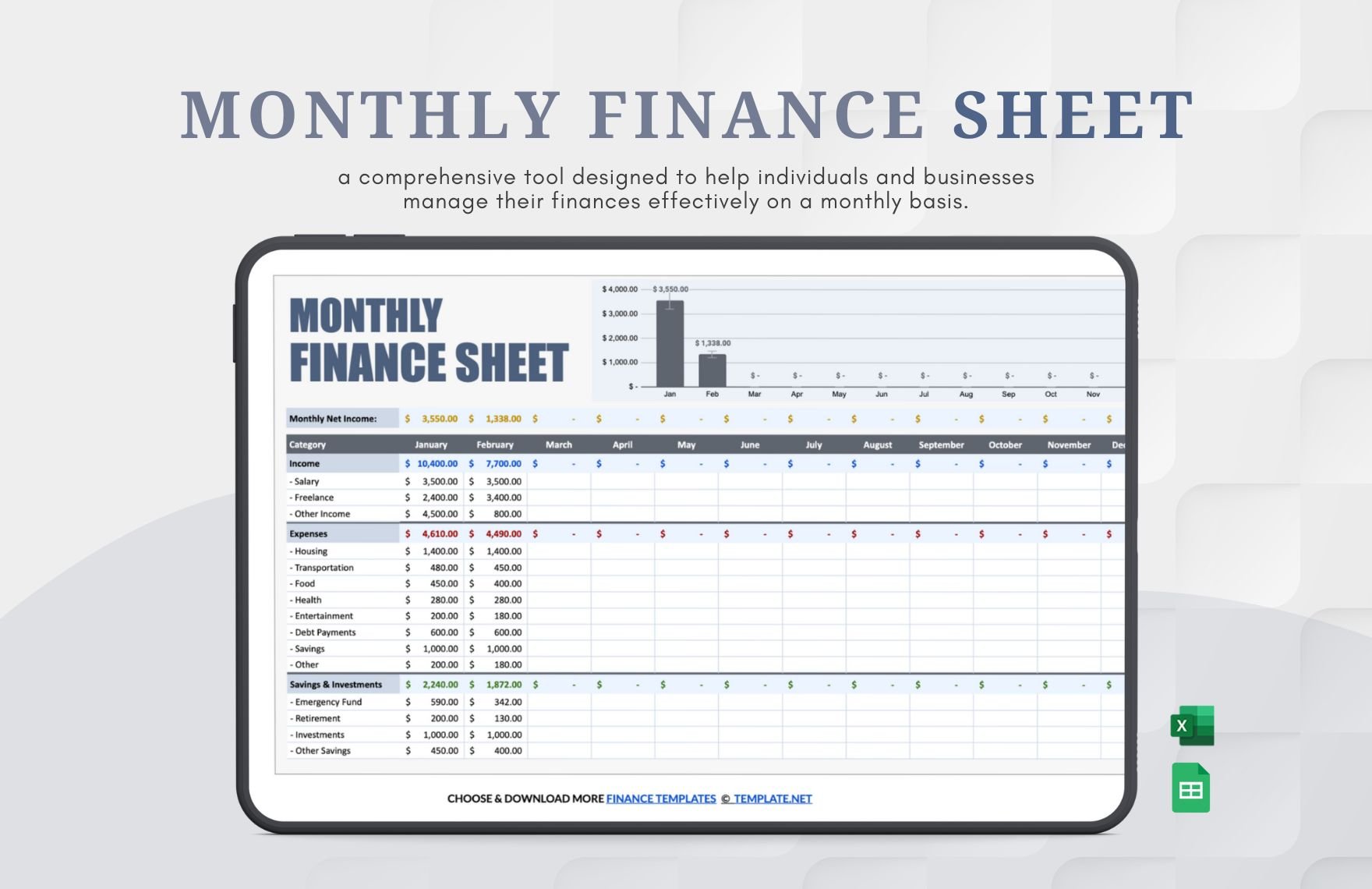
Now that you have already set the adjusted trial balance, you can now prepare the complete set of financial statements, that is, statement of comprehensive income or income statement, statement of financial position or balance sheet, statement of changes in equity, statement of cash flows, and notes to financial statements.
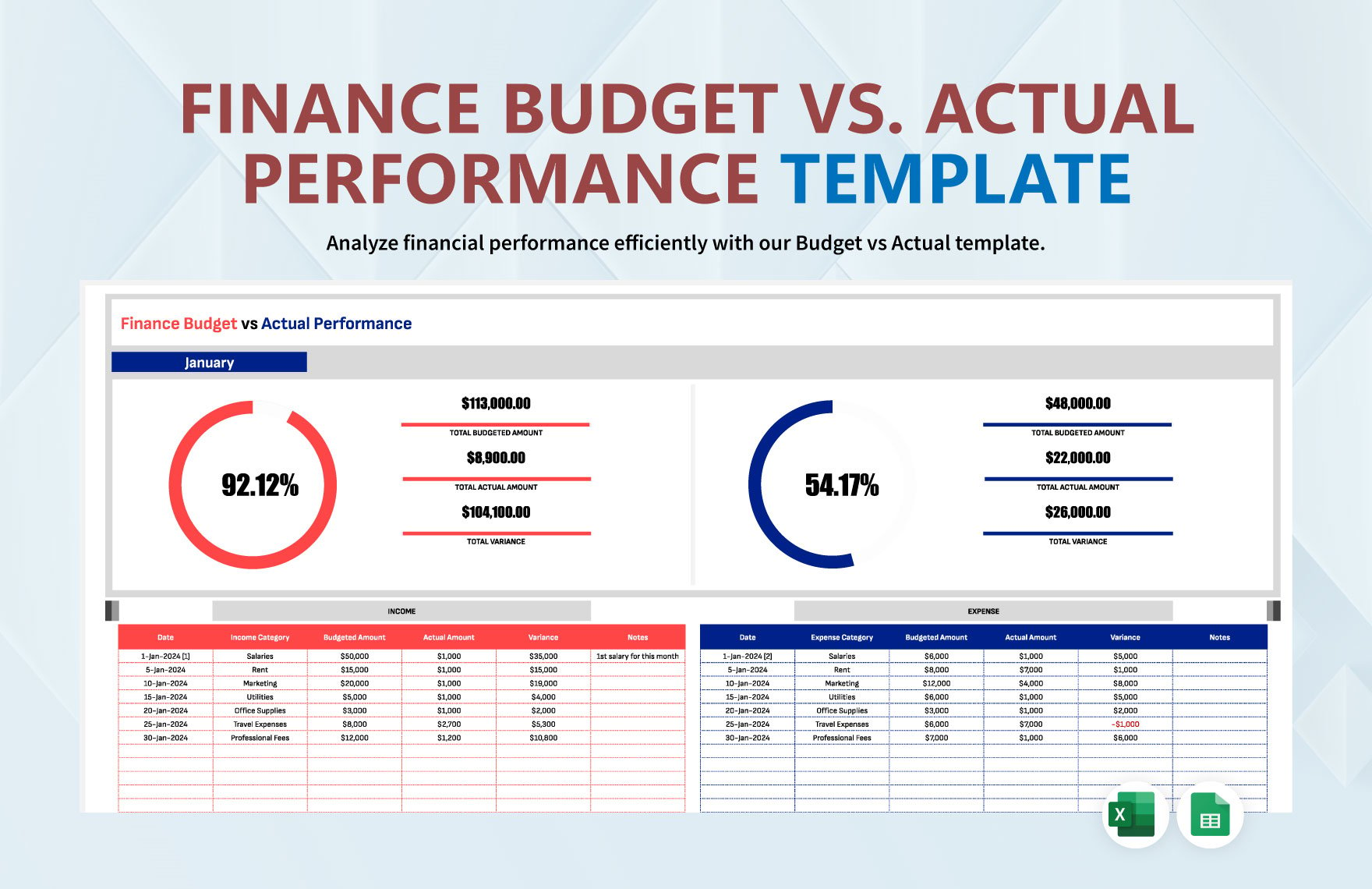
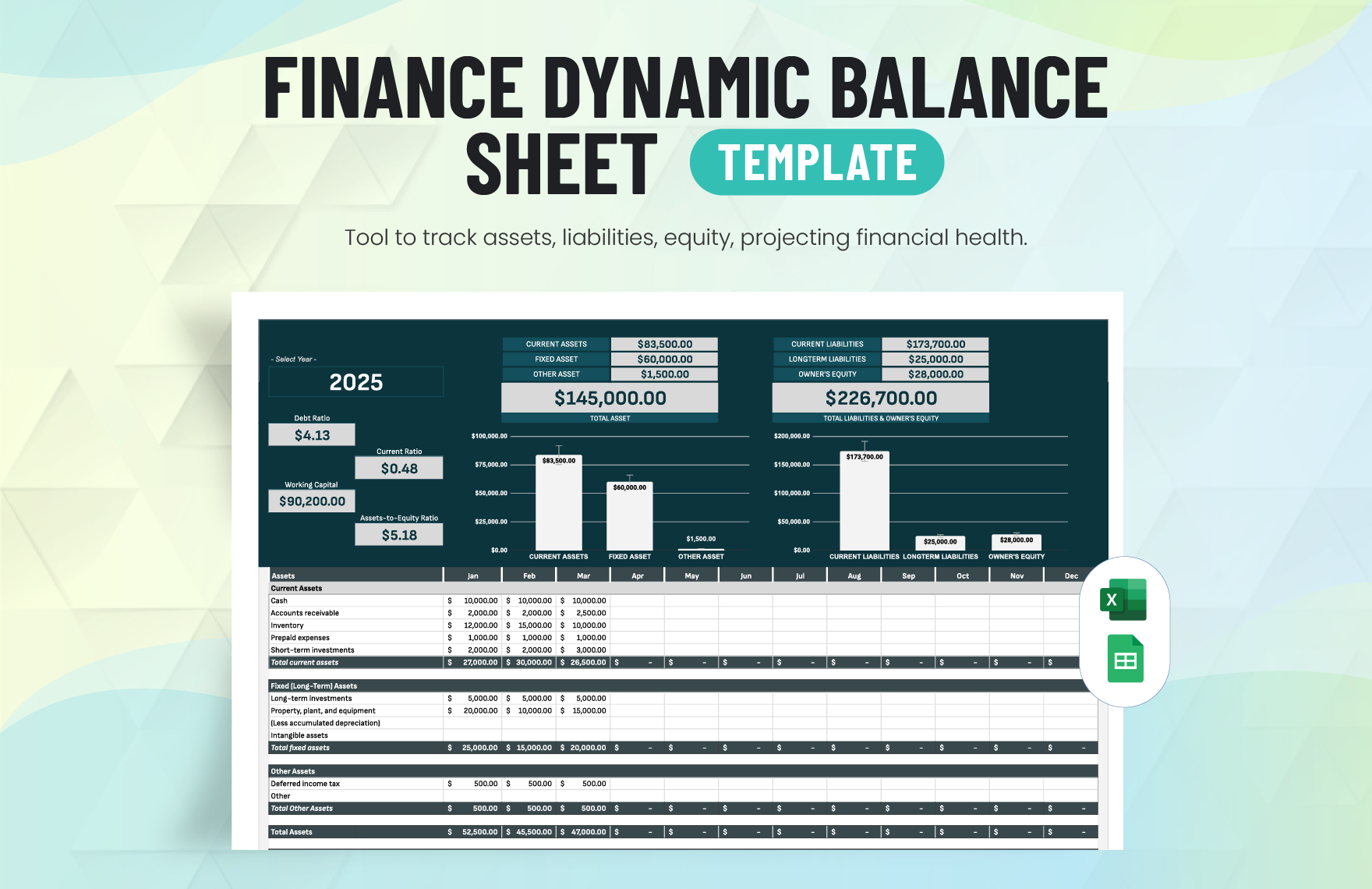
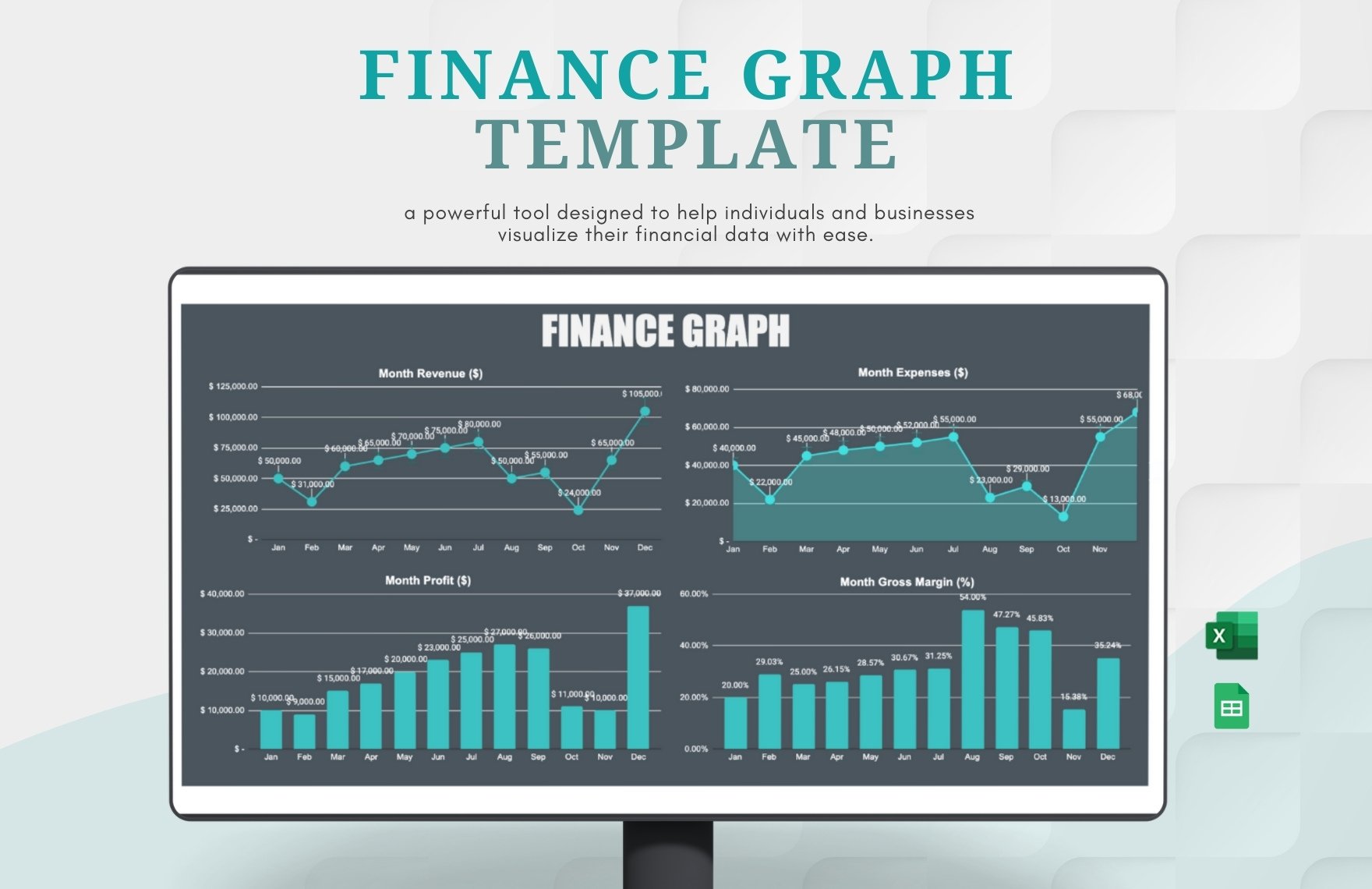
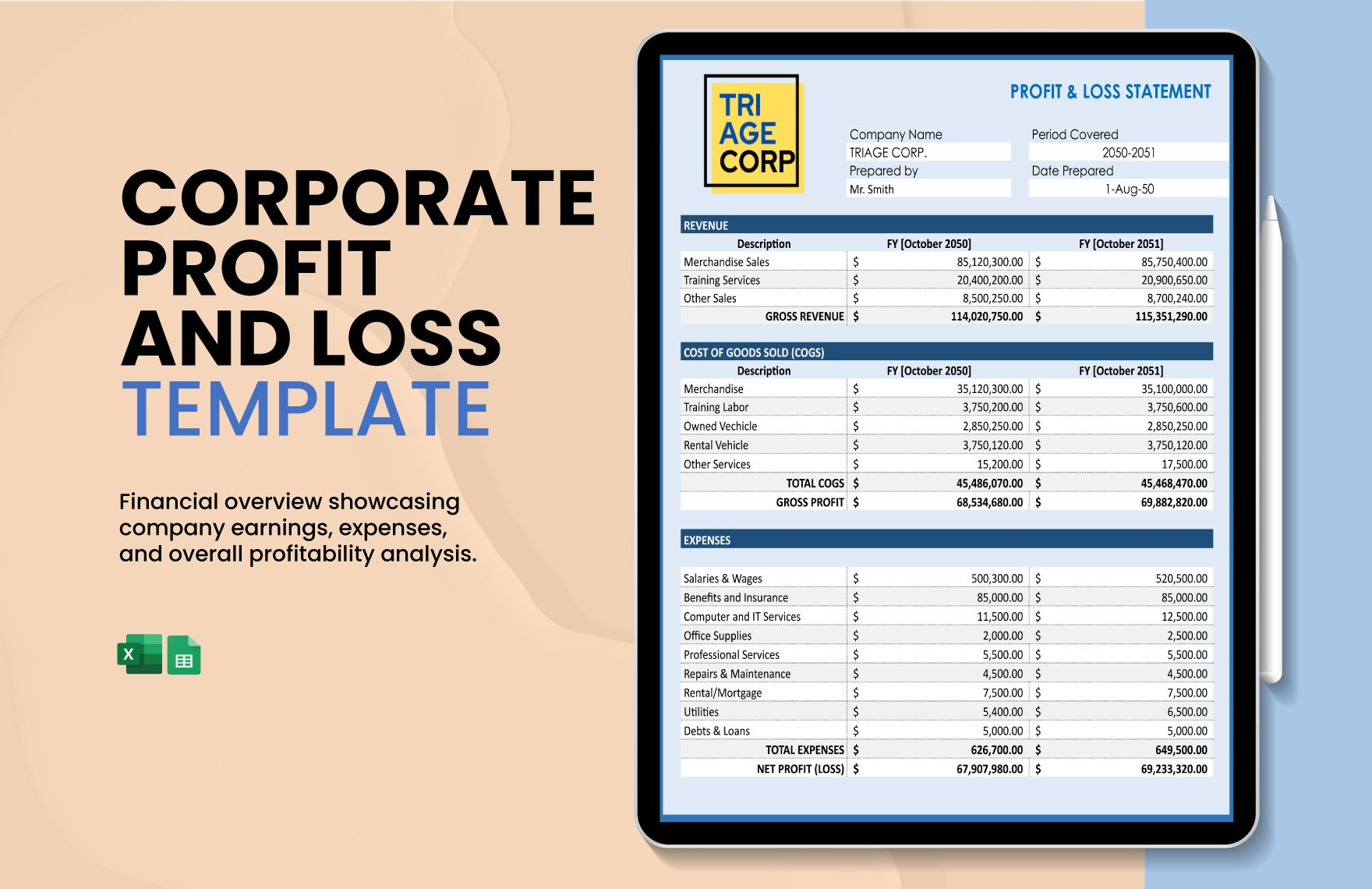
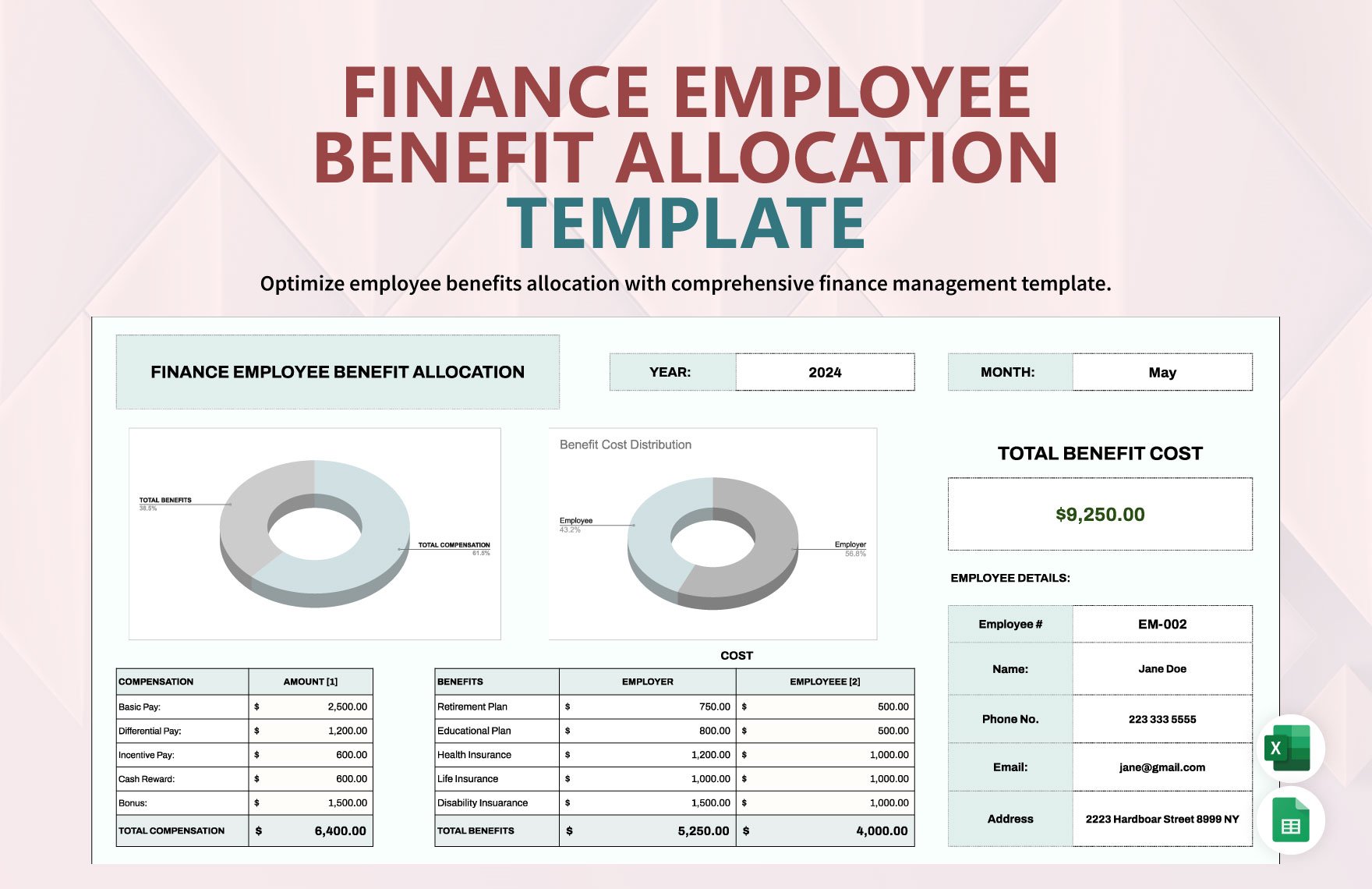
The income statement presents income, expenses, and profit or loss for the period. The balance sheet contains the company's or individual's assets, liabilities, and equities. The statement of changes in equity reflects the entity's beginning equity balance, the changes that affect the equity, and the ending equity balance. The statement of cash flows summarizes cash and cash equivalent inflow and outflow by categorizing the cash transactions into operating, investing, and financing activities. Lastly, the notes to financial statements provide disclosures and additional information pertaining to the company's operations and financial position.
8. Prepare the Closing Entries
Closing entries are made for temporary or nominal accounts to prepare the system for the next accounting period. These accounts include income, expense, and withdrawal accounts. They are closed to a summary account and then closed further to the appropriate capital account.
9. Prepare the Post-Closing Trial Balance
Finally, prepare the post-closing trial balance by listing only the real accounts since the nominal accounts are already closed at this point. It is prepared to test the equality of debits and credits after closing entries are made.