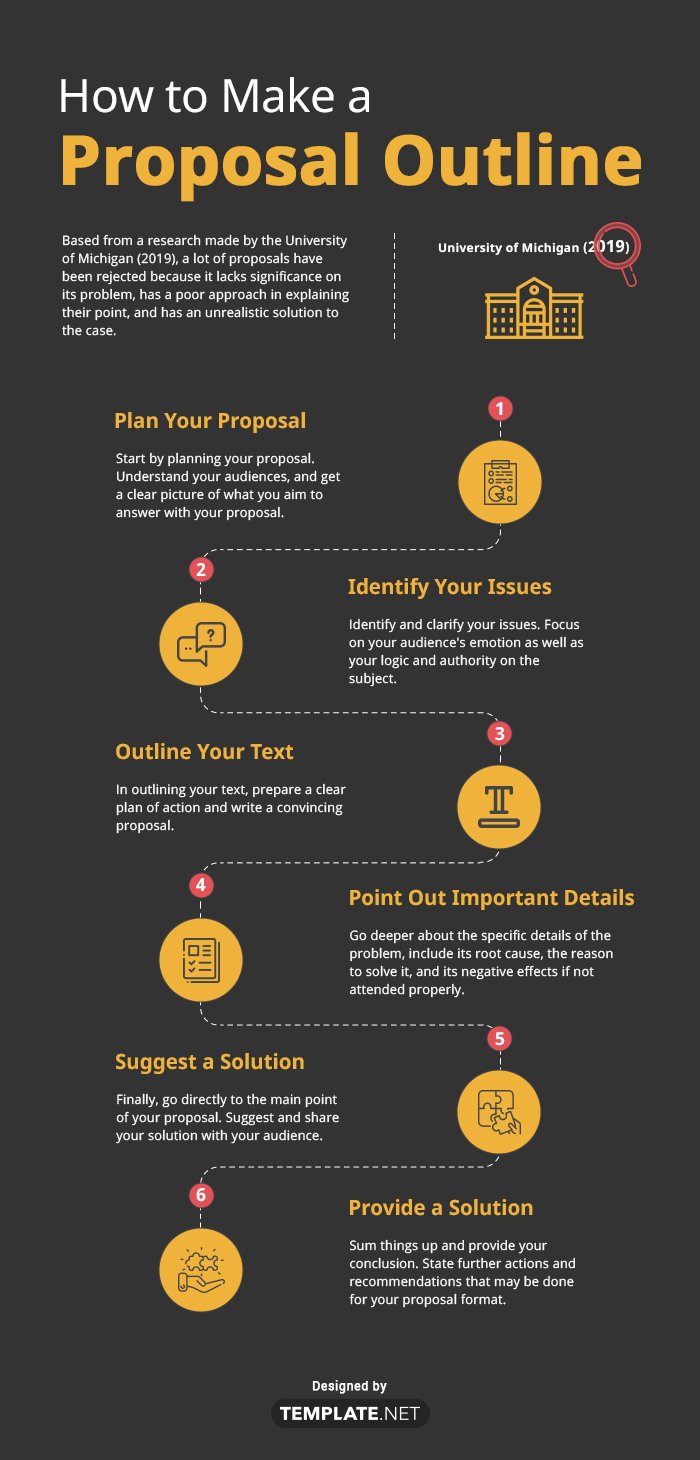
A proposal won't be accepted until you do intensive research about it and state its importance to the group. Based from a research made by the University of Michigan (2019), a lot of proposals have been rejected because it lacks significance on its problem, has a poor approach in explaining their point, and has an unrealistic solution to the case.
1. Plan Your Proposal
Start by planning your simple proposal. Understand your audiences, and get a clear picture of what you aim to answer with your proposal. Who's going to read it? Who will benefit from my proposal? How can I motivate them to make the necessary decisions upon reading my proposal? Keep these questions in mind when you plan your topic. Use the right words and tone to convince them. Keep your proposal brief but accurate, remove unnecessary information and be consistent with your topic.
2. Identify Your Issues
Identify and clarify your issues. In order to convince them about the current issue, you need to convey the situation to your audience with sufficient expertise and authority to deal with the issue. Focus on your audience's emotion as well as your logic and authority on the subject. Concentrate on the logic of your proposal to appeal the rational thinking of your audience but don't overshadow it with the rest of the persuasion methods. You must also include your audience's emotions and your high understanding of the issue to convince them.
3. Outline Your Text
In outlining your text, prepare a clear plan of action and write a convincing business proposal template. Provide your introduction, main body, and conclusion. Start off with an introduction that is straight to the point and directly address your problem. Do not repeat information that is already known by your audience, instead refer to the information they already know and expand it.
4. Point Out Important Details
Now that your audience has a broader knowledge about your business project proposal, start to address the problem. Go deeper about the specific details of the problem, include its root cause, the reason to solve it, and its negative effects if not attended properly. It is useful to add some forecasting if the problem is not addressed as early as possible and add some external sources to back your explanation.
5. Suggest a Solution
Finally, go directly to the main point of your proposal. Suggest and share your solution with your audience. Mention the long-term and short-term advantages and benefits of your solution. Include the budget proposal and time it needs for your audience to spend because this is a great factor for them to decide if they will approve your proposal or not.
6. Provide a Solution
Sum things up and provide your conclusion. State further actions and recommendations that may be done for your proposal format. Once you're done drafting your proposal, proofread it and edit it for further changes. You may hire a professional editor to edit it for you.