FREE 9+ Quantitative Research Templates in PDF | MS Word | Pages
Quantitative research is characterized by collecting quantifiable metrics and conducting statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques as a systematic analysis of phenomena. Quantitative analysis uses quantitative techniques to gather information from current and prospective customers and carry out online surveys, online polls, questionnaires, etc., the findings of which can be represented in numerical form.

FREE 9+ Quantitative Research Templates in PDF | MS Word | Pages
1. Quantitative Research Analyst Resume Template

2. Quantitative Research Template
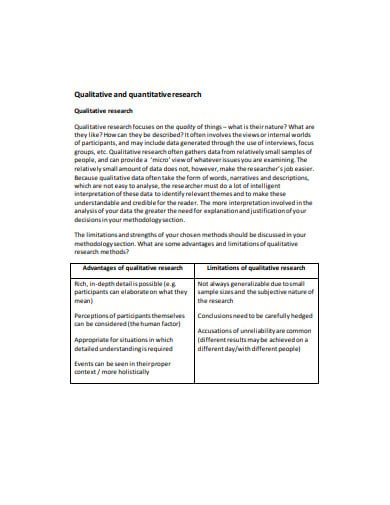 lancaster.ac.uk
lancaster.ac.uk3. Quantitative Research Report Sample
 researchrockstar.com
researchrockstar.com4. Quantitative Research Format
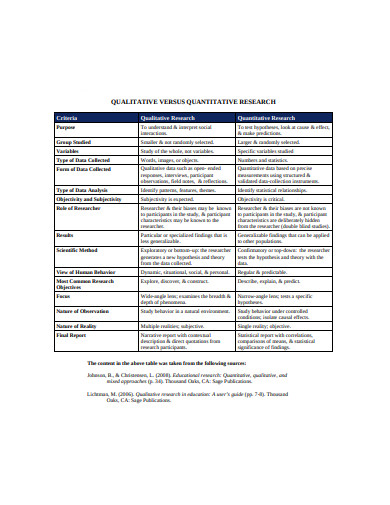 xavier.edu
xavier.edu5. Qualitative and Quantitative Research Template
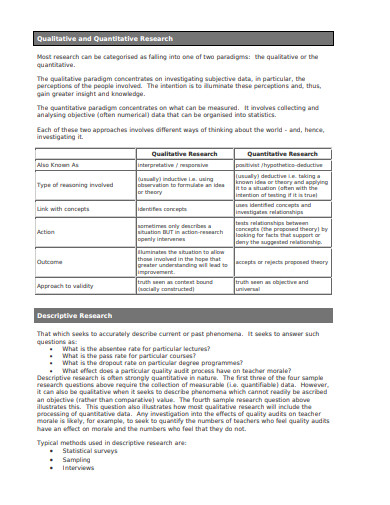 bethlehem.edu
bethlehem.edu6. Sample Quantitative Research Format
 pdx.edu
pdx.edu7. Quantitative Research Associate Position Template
 cfasociety.org
cfasociety.org8. Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods
 web.pdx.edu
web.pdx.edu9. Quantitative Educational Research Template
 leeds.ac.uk
leeds.ac.uk10. Quantitative Research Design in DOC
 secure.oregonstate.edu
secure.oregonstate.eduTypes of Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research can be conducted in two different methods:
Primary Quantitative Research Methods
The most commonly used form of performing market research is primary quantitative analysis. The distinctive feature of primary research is that the researcher focuses on specifically collecting data, rather than on data collected from previously conducted study. There are four types of research as explained in the following points:
Survey Research:
Survey Research is the most important device for all methodologies and studies in quantitative research. Surveys ask a sample of respondents questions using different types such as online polls, online surveys, paper questionnaires, web intercept surveys, etc. This sort of research can be done with a specific target market group, and can be performed with comparative analysis across multiple groups. A condition for this type of research is that the respondents sample must have members selected at random.
The two types of survey research include:
1. Cross-sectional surveys: Cross-sectional surveys are retrospective surveys carried out in circumstances where the participant aims to gather data from a target population sample at a given time point. Researchers can evaluate different variables at any given time. Data collected using this form of the survey are from individuals who represent consistency in all variables except the variables identified for the study. This one attribute will remain constant throughout the survey.
2. Longitudinal surveys: Longitudinal surveys are also retrospective surveys however, unlike cross-sectional surveys, longitudinal surveys are conducted over various time duration to detect a shift in respondent attitudes and thought-processes. This time can consist of days, months, years, or even decades. For example, the longitudinal studies will be performed by a researcher aiming to examine the shift in adolescent buying habits over 5 years.
Cor-relational Research:
There is invariability of a link between two entities. Research on correlation is undertaken to build a relationship between two tightly knit organizations and how one affects the other and what are the adjustments that are ultimately observed. This research technique is conducted to give value to the relationships that are naturally occurring, and a minimum of two different groups are needed to effectively perform this quantitative research method.
Causal-Comparative Research:
This method of analysis depends primarily on the element of comparison. Sometimes called quasi-experimental research, researchers use this quantitative research approach to establish an equation of cause and effect between two or more variables, where one variable is dependent on the other independent variable. The independent variable is defined but not controlled, and its effect is observed on the dependent variable. These variables or classes have to be defined in the natural system as they exist.
Experimental Research:
This theoretical methodology is also known as true experimentation, and is based on an idea. As the name suggests, experimental work is usually based upon one or more theories. In the past, this theory has not been proven and is merely a supposition. The analysis is done in scientific research to prove or disprove the hypothesis. This method of study is used in the natural sciences. Experimental research can have multiple theories. A theory is a statement that can be confirmed or disproved.
Primary Research methods also include data collection methodologies. This includes sampling methods such as probability and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling is of four types namely simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling, and systematic sampling. A non-probability sampling includes convenience sampling, quota sampling, snowball sampling, and judgmental sampling.
Another aspect of primary research methods includes data analysis techniques. This includes four different types of analysis namely SWOT analysis, conjoint analysis, cross-tabulation analysis, and TURF analysis.
Secondary Quantitative Research Methods
Secondary quantitative analysis or desk research is a type of research involving the use of either existing or secondary data. Existing data are compiled and collated to improve overall study effectiveness. This method includes collecting quantitative data from current sources of data such as the Internet, government resources, archives, research reports, etc. This type of research helps verify the data gathered from primary quantitative research as well as help confirm or prove or disprove previously gathered data. The following are five secondary quantitative research approaches which are popularly used:
- Data available on the internet: With the high penetration of internet and mobile apps, quantitative analysis using the internet has become increasingly straightforward. Data on most research subjects can be found online and this helps to increase the quality of primary quantitative data and to show the importance of data previously collected.
- Government and non-government sources: Secondary quantitative research may also be carried out with the help of government and non-governmental organizations concerned with market research studies. These are the most reliable and stable data.
- Public libraries: This form is now a sparsely used quantitative research tool. However, it is still a credible source of information. Public libraries have backups and collections of significant earlier research. These are a storehouse of valuable information and records which can be used to extract information.
- Educational institutions: Educational establishments perform in-depth research on different topics and are therefore an excellent source of evidence of quantitative research in the reports they write.
- Commercial information sources: One of the most easily accessible information is perhaps commercial information. Local papers, newspapers, magazines, radio stations, and television stations are a fantastic source of data for secondary quantitative research. Such sources of commercial knowledge have in-depth, first-hand information on economic trends, policy agenda, research and analysis, demographic segmentation, and so on.
FAQ’s
What are the different types of quantitative research?
Quantitative research is generally of four types. This includes cor-relational research, experimental research, descriptive research, and quasi-experimental research.
Are quantitative research and qualitative research the same?
The qualitative analysis defines abstract concepts, while empirical data is collected with the help of quantitative research. However, the significant difference lies in the type of action being taken and the sample size.
What is the importance of quantitative research?
Quantitative data helps to make informed decisions in business such as market size, demographics, and user preferences.

