Talent Pipeline Management Guide
Introduction
Overview
Welcome to the Talent Pipeline Management Guide prepared by [Your Company Name]. Talent Pipeline Management (TPM) is a strategic approach to ensuring that your organization has a consistent and reliable pool of talent to meet its current and future needs. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to effectively manage your talent pipeline, from identification to onboarding.
Purpose
The purpose of this guide is to:
Equip HR professionals and hiring managers with the tools and knowledge to build and maintain a robust talent pipeline.
Provide a structured framework for identifying, attracting, and retaining top talent.
Offer actionable insights and best practices to optimize the recruitment process.
Scope
This guide covers the following aspects of Talent Pipeline Management:
Key stages in the talent pipeline
Best practices for each stage
Workflow and operational guidelines
Monitoring and metrics for performance evaluation
Target Audience
The primary audience for this guide includes:
HR Managers
Talent Acquisition Specialists
Hiring Managers
Team Leads
C-Level Executives
Objectives
Objectives
General Objectives
The overarching objectives of Talent Pipeline Management at [Your Company Name] are:
Strategic Alignment: To align talent acquisition strategies with the overall business goals and objectives of [Your Company Name].
Operational Efficiency: To streamline the recruitment process, reducing time-to-hire and cost-per-hire.
Quality of Hire: To improve the quality of new hires, ensuring they are a good fit both in terms of skills and company culture.
Specific Objectives
Identification
To create a comprehensive database of potential candidates for various roles within [Your Company Name].
To identify skill gaps and areas where talent acquisition is needed.
Attraction
To develop and implement effective employer branding strategies.
To utilize multiple channels for job postings to attract a diverse pool of candidates.
Screening
To establish a standardized screening process that includes skill assessments and preliminary interviews.
To ensure that candidates meet the minimum qualifications for the roles they have applied for.
Interview
To conduct structured interviews that evaluate candidates based on a set of predetermined criteria.
To involve multiple stakeholders in the interview process for a well-rounded assessment.
Offer
To extend competitive job offers that include not just salary, but also other benefits and growth opportunities.
To ensure a quick turnaround time from the final interview to the job offer.
Onboarding
To provide a smooth and efficient onboarding process that helps new hires integrate into [Your Company Name] quickly.
To offer training and development programs for new hires.
Measurable Outcomes
The success of the Talent Pipeline Management strategy will be evaluated based on the following key performance indicators (KPIs):
Time-to-hire
Cost-per-hire
Quality of hire
Employee turnover rate
Employee engagement scores
Key Stages of Talent Pipeline Management
Identification
Overview
The identification stage involves recognizing the roles and skill sets that are crucial for the success of [Your Company Name]. This is the foundation upon which the entire talent pipeline is built.
Methods
Skill Gap Analysis: Conduct an analysis to identify the skills that are currently lacking within the organization.
Role Definition: Clearly define the roles that need to be filled, including job responsibilities and qualifications.
Tools
Talent Management Software
Internal Surveys
Industry Reports
Attraction
Overview
The attraction stage focuses on drawing potential candidates to [Your Company Name] through various channels and employer branding efforts.
Methods
Job Postings: Utilize job boards, social media, and company websites for job advertisements.
Networking: Leverage professional networks and events to attract talent.
Tools
Social Media Platforms
Job Boards
Networking Events
Screening
Overview
Screening involves the initial assessment of candidates based on their resumes, cover letters, and any preliminary tests or assessments.
Methods
Resume Screening: Use automated tools or manual methods to sift through resumes.
Preliminary Assessments: Conduct skill tests or personality assessments as needed.
Tools
Applicant Tracking System (ATS)
Assessment Platforms
Interview
Overview
This stage involves conducting interviews to assess the candidates' skills, experience, and cultural fit.
Methods
Structured Interviews: Use a set of predetermined questions for all candidates.
Panel Interviews: Involve multiple interviewers for a well-rounded evaluation.
Tools
Video Conferencing Software
Interview Scorecards
Offer
Overview
The offer stage involves extending a formal job offer to the selected candidates.
Methods
Compensation Analysis: Conduct market research to offer competitive salaries and benefits.
Offer Letter: Draft a formal offer letter outlining the terms of employment.
Tools
Compensation Analysis Software
Document Management System
Onboarding
Overview
The onboarding stage is crucial for integrating new hires into the organizational culture and setting them up for success.
Methods
Orientation: Conduct an orientation program to introduce new hires to the company.
Training: Provide necessary training and resources for the role.
Tools
Learning Management System (LMS)
Employee Onboarding Software
Workflow
Overview
The workflow section outlines the step-by-step process that [Your Company Name] follows in managing its talent pipeline. This serves as a practical guide for executing the strategies discussed in the previous sections.
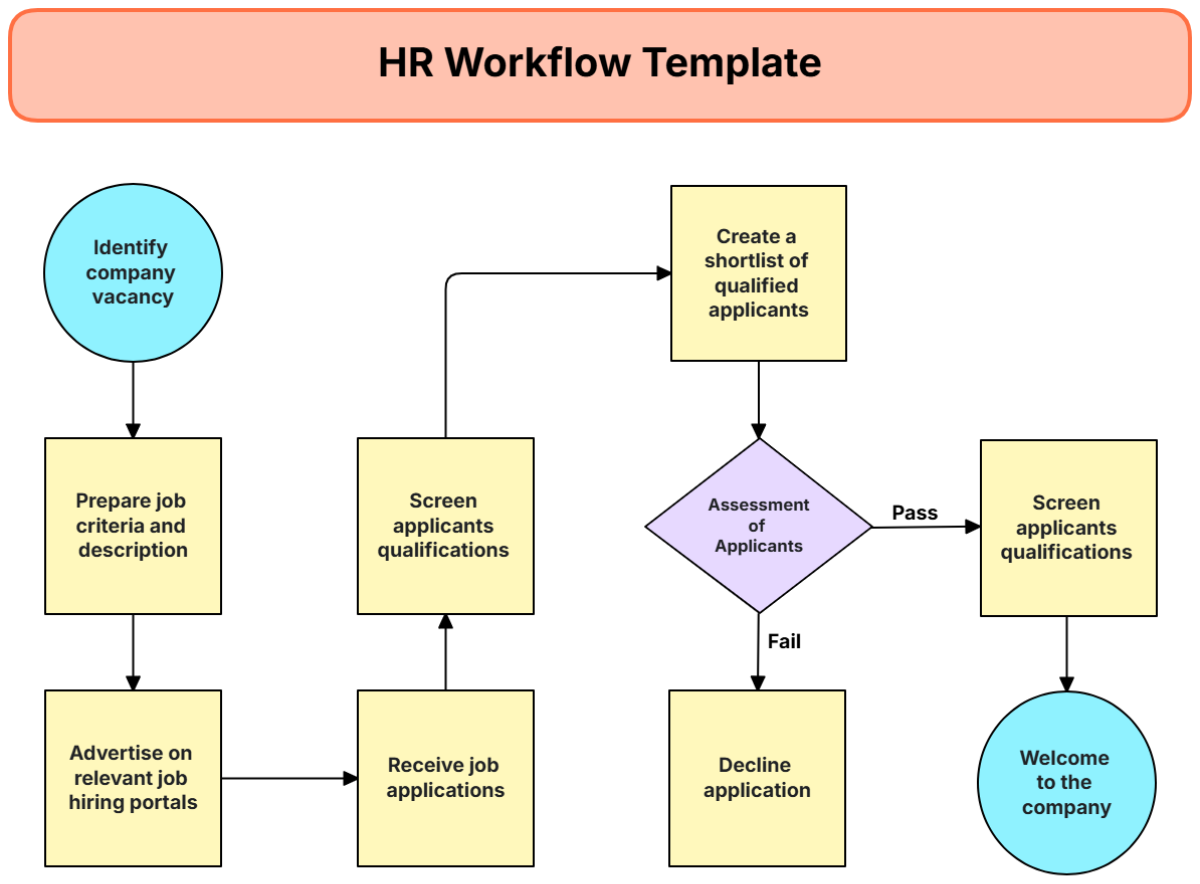
Workflow Diagram
The following flowchart provides a visual representation of the Talent Pipeline Management workflow at [Your Company Name].
Talent Pipeline Management Workflow
Workflow Steps
Identification
Conduct Skill Gap Analysis: Use internal surveys and industry reports.
Define Roles: Create detailed job descriptions.
Attraction
Develop Employer Branding: Utilize social media and other platforms.
Post Job Openings: Use multiple channels for a wider reach.
Screening
Initial Resume Screening: Use an Applicant Tracking System (ATS) for efficiency.
Conduct Preliminary Assessments: Use online assessment tools.
Interview
Schedule Interviews: Coordinate with candidates for suitable timings.
Conduct Interviews: Use structured interviews for uniform evaluation.
Offer
Prepare Offer Letter: Include all terms of employment.
Extend Offer: Use email or phone call for official communication.
Onboarding
Orientation: Introduce new hires to the company culture and policies.
Training: Provide role-specific training programs.
Workflow Automation
To streamline the workflow, [Your Company Name] uses various software tools at different stages. These include:
Applicant Tracking System (ATS): For screening and tracking applications.
Learning Management System (LMS): For onboarding and training.
HR Management Software: For overall talent management.
Roles and Responsibilities
HR Managers: Oversee the entire Talent Pipeline Management process.
Talent Acquisition Specialists: Responsible for the identification and attraction stages.
Hiring Managers: Involved in the screening, interview, and offer stages.
Team Leads: Assist in the onboarding process.
Workflow Monitoring
Regular audits and reviews will be conducted to ensure that the workflow is efficient and effective. Key performance indicators (KPIs) will be used to measure the success of the workflow.
Best Practices
Overview
This section outlines the best practices that [Your Company Name] recommends for each stage of Talent Pipeline Management. Adhering to these practices ensures a more efficient and effective process.
Identification Best Practices
Skill Gap Analysis
Involve Multiple Stakeholders: Include team leads, department heads, and HR managers in the skill gap analysis process.
Use Data-Driven Methods: Utilize analytics tools to quantify skill gaps.
Role Definition
Be Specific: Clearly outline job responsibilities, required skills, and qualifications.
Consult Existing Employees: Get input from employees who are already in similar roles.
Attraction Best Practices
Employer Branding
Consistent Messaging: Ensure that your employer brand is consistently represented across all platforms.
Employee Testimonials: Use testimonials from satisfied employees to attract potential candidates.
Job Postings
SEO Optimization: Use relevant keywords in job postings to make them easily discoverable.
Mobile-Friendly: Ensure that job postings are accessible and readable on mobile devices.
Screening Best Practices
Resume Screening
Automate Where Possible: Use an Applicant Tracking System (ATS) to automate initial screening.
Customized Screening Criteria: Tailor the screening criteria to each specific role.
Preliminary Assessments
Relevance: Ensure that assessments are directly related to the job role.
Timely Feedback: Provide candidates with feedback as soon as possible after assessments.
Interview Best Practices
Structured Interviews
Uniform Evaluation: Use a standardized set of questions for all candidates.
Multiple Interviewers: Involve multiple stakeholders in the interview process for a well-rounded assessment.
Panel Interviews
Diverse Panel: Include interviewers from different departments or roles.
Post-Interview Debrief: Conduct a debriefing session among interviewers to discuss evaluations.
Offer Best Practices
Compensation Analysis
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to offer competitive salaries and benefits.
Transparency: Be transparent about all components of the compensation package.
Offer Letter
Clarity: Clearly outline all terms of employment, including any conditional clauses.
Promptness: Extend the offer as soon as possible after the final interview to reduce the risk of losing the candidate to other opportunities.
Onboarding Best Practices
Orientation
Comprehensive: Cover all aspects of company culture, policies, and job role.
Interactive: Make the orientation interactive to engage new hires.
Training
Role-Specific: Tailor training programs to the specific needs of the job role.
Continuous Learning: Offer opportunities for ongoing professional development.
Summary of Best Practices
Best Practice | Description |
Clear Job Descriptions | Ensure that job descriptions are clear and detailed to attract the right candidates. |
Timely Communication | Keep candidates informed at every stage of the process. |
Skill Assessments | Use skill assessments to screen candidates effectively. |
Structured Interviews | Conduct structured interviews to evaluate candidates uniformly. |
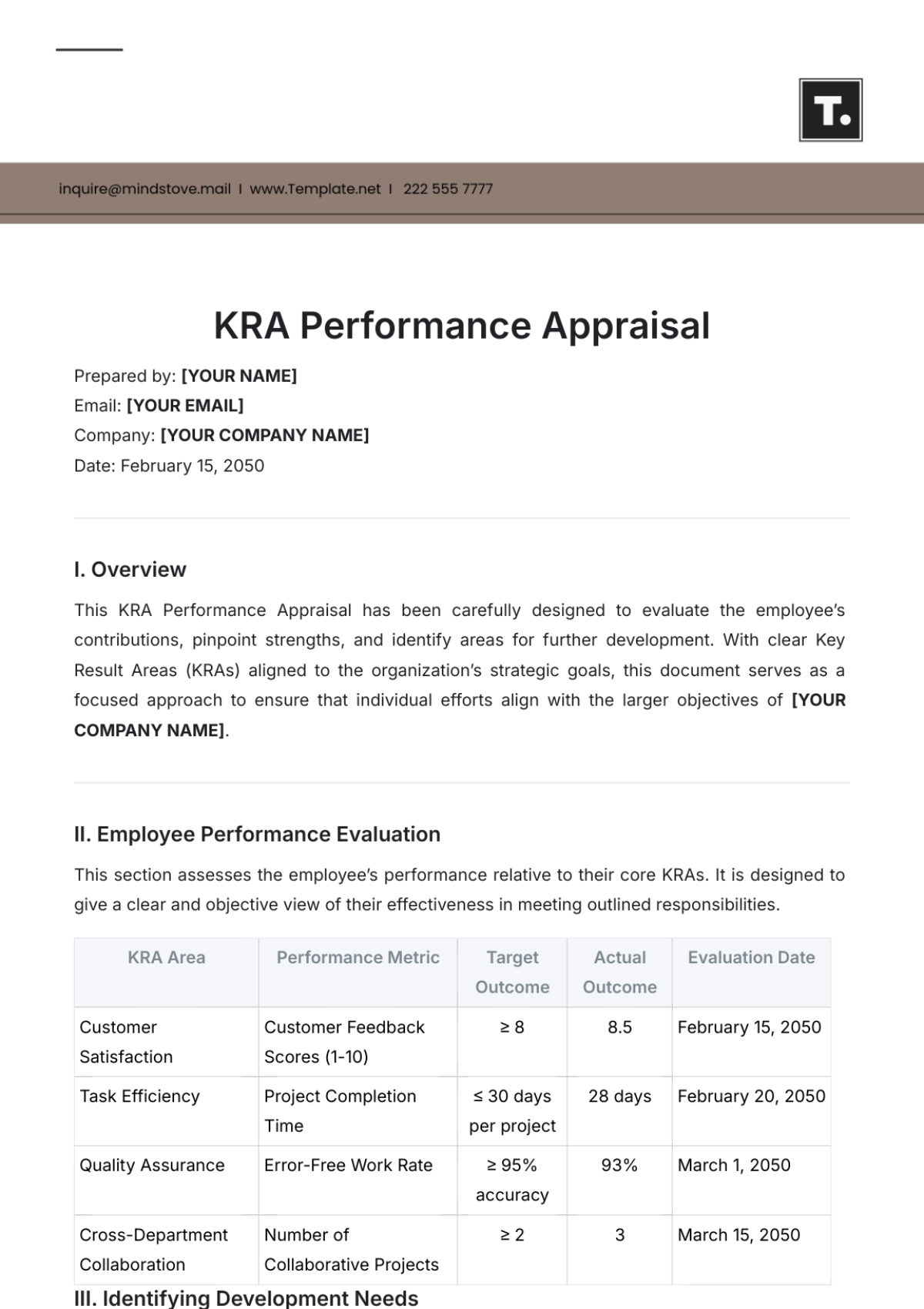
Monitoring and Metrics
Overview
Monitoring and metrics are crucial for assessing the effectiveness of your Talent Pipeline Management strategy. This section outlines the key performance indicators (KPIs) that [Your Company Name] should focus on, along with methods for tracking them.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Time-to-Hire
Definition: The average time it takes to hire a candidate from the moment the job opening is posted.
Importance: A shorter time-to-hire indicates a more efficient recruitment process.
Tracking Method: Use your Applicant Tracking System (ATS) to monitor this metric.
Cost-per-Hire
Definition: The total cost incurred in hiring a new employee, including advertising, screening, and onboarding costs.
Importance: Lowering this cost without compromising quality is a key objective.
Tracking Method: Calculate the total expenses for each hire and divide by the number of new hires.
Quality of Hire
Definition: A measure of how well a new hire performs in their role.
Importance: High-quality hires contribute more to the organization and are likely to stay longer.
Tracking Method: Use performance reviews and productivity metrics to assess this.
Employee Turnover Rate
Definition: The percentage of employees who leave the organization within a given period.
Importance: A high turnover rate can indicate dissatisfaction among employees and can be costly.
Tracking Method: Calculate the number of employees who left divided by the average number of employees, multiplied by 100.
Employee Engagement Scores
Definition: A measure of employee satisfaction and engagement.
Importance: Engaged employees are more productive and less likely to leave.
Tracking Method: Use employee surveys and feedback tools.
Monitoring Tools
Applicant Tracking System (ATS): For tracking time-to-hire and cost-per-hire.
Performance Management Software: For tracking quality of hire.
Employee Feedback Tools: For measuring employee engagement scores.
Reporting
Frequency: Monthly reports should be generated for most KPIs, with a comprehensive quarterly review.
Audience: Reports should be shared with HR managers, department heads, and C-level executives.
Format: Use charts, graphs, and tables for easy interpretation of data.
Continuous Improvement
Data Analysis: Regularly analyze the collected data to identify trends and areas for improvement.
Feedback Loop: Create a feedback loop with hiring managers and team leads to continuously refine the Talent Pipeline Management process.
Conclusion
Summary
This Talent Pipeline Management Guide serves as a comprehensive resource for [Your Company Name] to effectively manage its talent pipeline. From identification to onboarding, the guide covers key stages, best practices, and metrics for monitoring success.
Key Takeaways
Strategic Alignment: Talent Pipeline Management is not just an HR function but a strategic imperative that aligns with the overall goals of [Your Company Name].
Efficiency and Effectiveness: Following the outlined workflow and best practices can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the recruitment process.
Data-Driven Decisions: Monitoring and metrics are crucial for making informed decisions and for continuous improvement.
Recommendations
Regular Updates: The Talent Pipeline Management strategy should be reviewed and updated at least annually to adapt to changing business needs.
Stakeholder Involvement: Involve multiple stakeholders, including department heads and team leads, in the talent pipeline management process for a more holistic approach.
Employee Development: Don't just focus on hiring; invest in the continuous development of existing employees to fill future roles.
Future Scope
As [Your Company Name] continues to grow, the Talent Pipeline Management strategy may need to be scaled or modified. Future updates to this guide will include:
Advanced automation techniques
Integration with other HR functions like employee development and retention
Inclusion of remote and freelance talent in the pipeline
Final Words
Managing your talent pipeline effectively is crucial for the long-term success of [Your Company Name]. This guide aims to provide you with the tools and knowledge to achieve that. For any further queries or clarifications, please refer to the contact information provided.
Contact Information
Company Name: [Your Company Name]
Email: [Your Company Email]
Address: [Your Company Address]
Phone Number: [Your Company Number]
Website: [Your Company Website]
Social Media: [Your Company social media]
For further information, please contact [Your Name] at [Your Email].
[Your Company Logo]