Construction Project Brief
Prepared By: [YOUR NAME]
Company: [YOUR COMPANY NAME]
Date: [DATE]
Executive Summary
The [PROJECT NAME] construction project aims to construct a modern commercial office building in [PROJECT LOCATION], fostering productivity and innovation within budgetary constraints. This brief provides an overview of key project details including scope, timeline, budget, and safety considerations, facilitating efficient project execution. By prioritizing safety and regulatory compliance, we ensure a secure working environment and successful project delivery.
Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of the [PROJECT NAME] construction project. It outlines project specifics and serves as a guide for project management and execution.
Client Information
[PROJECT NAME] is a leading construction firm with a strong reputation for delivering high-quality projects on time and within budget. Their portfolio includes residential, commercial, and industrial developments across the region. [CONTACT NAME], the designated contact person, serves as the project liaison between [PROJECT NAME] and our project team. With extensive experience in construction project management, [CLIENT'S NAME] ensures effective communication and collaboration throughout the project lifecycle.
Project Team
Project Manager: [PROJECT MANAGER'S NAME]
Responsibilities:
Overseeing project planning, execution, and monitoring.
Coordinating with stakeholders to ensure project objectives are met.
Managing project schedule and budget.
Handling risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
Acting as the primary point of contact for client communication.
Design Engineer: [DESIGN ENGINEER'S NAME]
Responsibilities:
Developing project designs in compliance with regulatory standards.
Ensuring structural integrity and functionality of design solutions.
Collaborating with architects and other engineers to optimize design outcomes.
Conducting site assessments and feasibility studies.
Providing technical support during construction phases.
Construction Manager: [CONSTRUCTION MANAGER'S NAME]
Responsibilities:
Managing on-site construction activities to ensure compliance with design specifications and safety regulations.
Coordinating subcontractors and vendors to maintain project schedule and quality standards.
Implementing quality control measures and conducting inspections.
Addressing construction issues and resolving conflicts as they arise.
Ensuring adherence to budget constraints and reporting progress to the project manager.
Project Location
Location Details | Description |
|---|---|
Latitude | 33.7490° N (example) |
Longitude | -84.3880° W (example) |
Topography | Gently sloped terrain with occasional undulations |
Surrounding Area | Adjacent to the commercial district with nearby residential neighborhoods |
Accessibility | Proximity to major highways and public transportation hubs |
Utility Availability | All utilities readily available, including water, electricity, and sewage connections |
Environmental Factors | Nearby river poses potential environmental impact considerations |
Local Climate | Temperate climate with mild winters and hot summers |
Regulatory Constraints | Zoning restrictions limiting building height and setback requirements |
Nearby Communities | Residential communities may require noise mitigation measures during construction |
Unique Challenges | Historic preservation requirements for neighboring buildings |
Project Timeline
Task | Start Date | Completion Date | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
Project Planning | January 1, 2050 | March 15, 2050 | 73 days |
Site Preparation | March 20, 2050 | April 10, 2050 | 22 days |
Foundation Construction | April 15, 2050 | May 20, 2050 | 36 days |
Structural Framing | May 25, 2050 | June 30, 2050 | 37 days |
Exterior Finishing | July 5, 2050 | August 15, 2050 | 42 days |
Interior Finishing | August 20, 2050 | September 30, 2050 | 42 days |
Installation of Fixtures | October 5, 2050 | October 25, 2050 | 21 days |
Final Inspections and Handover | November 1, 2050 | December 15, 2050 | 45 days |
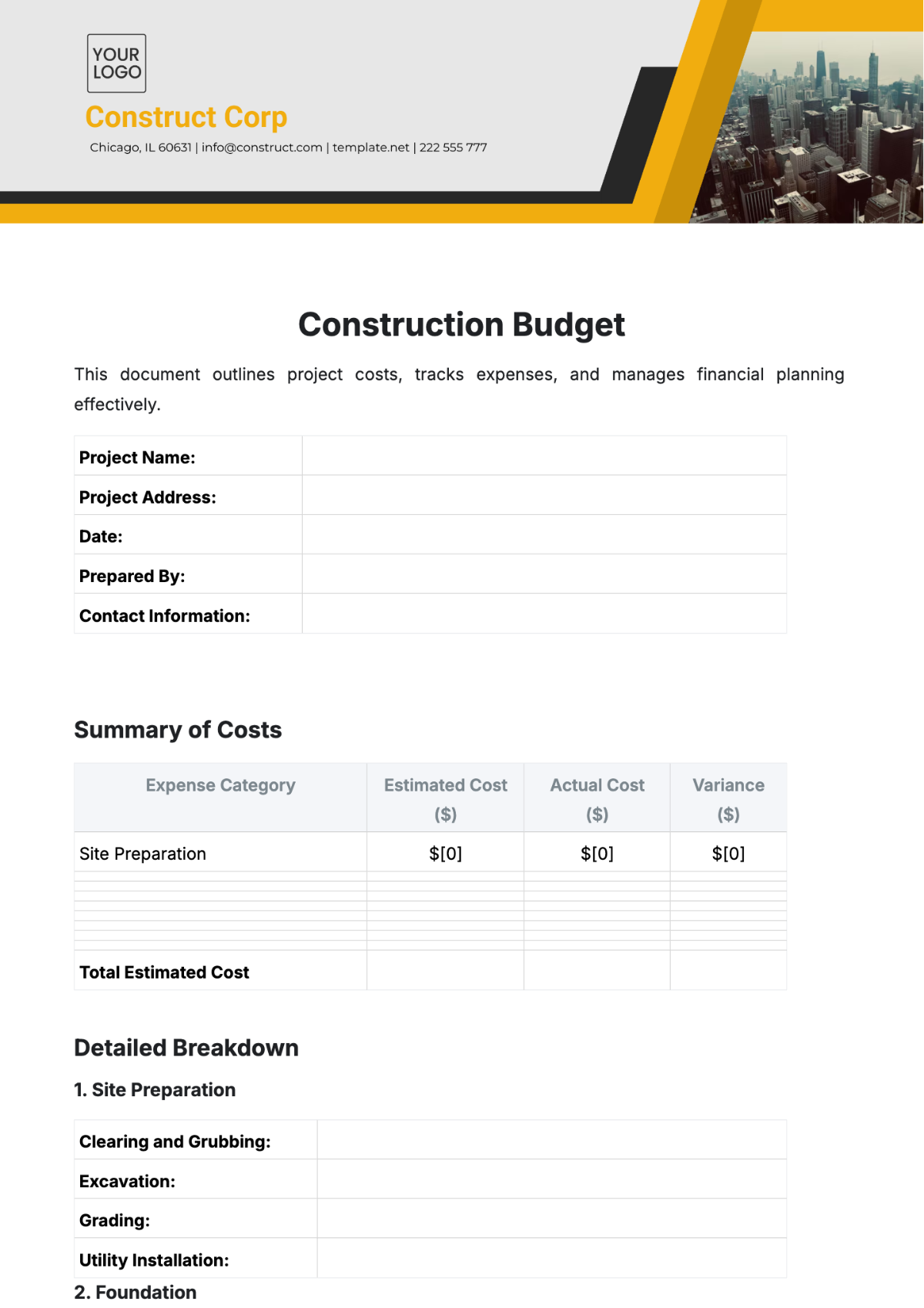
Budget
Category | Amount (USD) |
|---|---|
Total Budget | $5,000,000 |
Construction Costs | $4,000,000 |
Design Fees | $400,000 |
Contingency | $600,000 |
Site Information
Site Information | |
|---|---|
Site Area |
|
Terrain |
|
Soil Type |
|
Surroundings |
|
Urban Location |
|
Considerations |
|
Regulatory Requirements
Local Building Codes:
Compliance with [insert specific local building codes and standards] enforced by [relevant local authority] is mandatory. These codes encompass structural integrity, fire safety, accessibility, and zoning regulations.
Permitting Requirements:
Obtain necessary permits from [relevant permitting authority], including building permits, zoning permits, and environmental permits, before construction begins. Failure to secure permits may lead to legal consequences and project delays.
Environmental Regulations:
Adhere to environmental regulations outlined by [environmental regulatory agency], focusing on air and water quality protection, habitat preservation, and waste management. Conduct environmental impact assessments and implement mitigation measures as needed. Proper waste disposal and sustainable construction practices are imperative.
Design Requirements
Architectural Design
The architectural design for the [PROJECT NAME] project embodies a modern aesthetic, blending functionality with contemporary elegance. Key design elements include:
Sleek and minimalist facades complement the surrounding environment.
Open floor plans with abundant natural light to enhance the overall ambiance.
Integration of sustainable features such as green roofs or energy-efficient systems.
Emphasis on flexible spaces to accommodate various uses and adaptability over time.
Harmonious incorporation of landscaping elements to enhance the aesthetic appeal and create inviting outdoor spaces.
Structural Design
The structural design of the [PROJECT NAME] project prioritizes safety, durability, and efficiency. Specific structural requirements include:
Utilization of high-quality materials with proven structural integrity to ensure longevity and resilience.
Compliance with local building codes and regulations to meet safety standards and withstand environmental factors.
Implementation of innovative engineering techniques to optimize structural performance while minimizing construction costs.
Incorporation of seismic-resistant design principles to mitigate the risk of earthquake damage.
Collaboration with structural engineers to ensure seamless integration of architectural vision with structural feasibility.
Construction Specifications
Materials:
Foundation: Reinforced concrete with a minimum strength of 3000 psi, complying with ASTM standards.
Structural Frame: Steel beams and columns fabricated to ASTM A992 specifications.
Exterior Walls: Brick veneer over CMU (Concrete Masonry Unit) backup, with moisture barrier and insulation per local building codes.
Roofing: Standing seam metal roofing system with insulation and vapor barrier per project design.
Flooring: Polished concrete on ground level, carpet tiles in office areas, and ceramic tiles in restrooms.
Windows: Aluminum framed, low-E, double-glazed windows with tinted glass.
Doors: Solid core wood doors with commercial grade hardware.
Methods:
Excavation: Use of mechanical excavators and backhoes to excavate foundation trenches and prepare the building pad.
Flouring concrete foundation using slip-form technique for precision and efficiency.
Structural Frame: Prefabrication of steel beams and columns off-site to expedite construction and reduce on-site labor.
Masonry: Skilled masons lay bricks in a staggered pattern, ensuring proper bonding and alignment.
Roofing: Installation of standing seam metal roofing panels using mechanical fasteners for secure attachment.
Interior Finishes: Skilled tradesmen to install flooring materials according to manufacturer's specifications and industry best practices.
MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing): Coordination with MEP contractors to ensure proper installation of HVAC, electrical, and plumbing systems per design drawings and specifications.
Health and Safety Considerations
Safety Plan
The safety plan for the [Project Name] construction project prioritizes the well-being of all personnel involved. It encompasses thorough hazard identification, risk assessment, and mitigation measures to ensure a safe working environment. Key components of the safety plan include:
Hazard Identification: Comprehensive survey of the construction site to identify hazards.
Risk Assessment: Evaluation of identified hazards to determine likelihood and impact.
Mitigation Measures: Implementation of PPE, safety training, signage, and safety protocols.
Emergency Procedures
In the event of an emergency, the following procedures will be followed to ensure the safety and well-being of all personnel:
Evacuation Plan: Detailed plan with escape routes and assembly points.
Emergency Communication: Clear channels for relaying emergency information.
Emergency Response Team: Trained personnel for immediate assistance.
Emergency Equipment: Adequate provision of firefighting, first aid, and lighting equipment.
Emergency Contact Information: Display of local emergency services contact details.
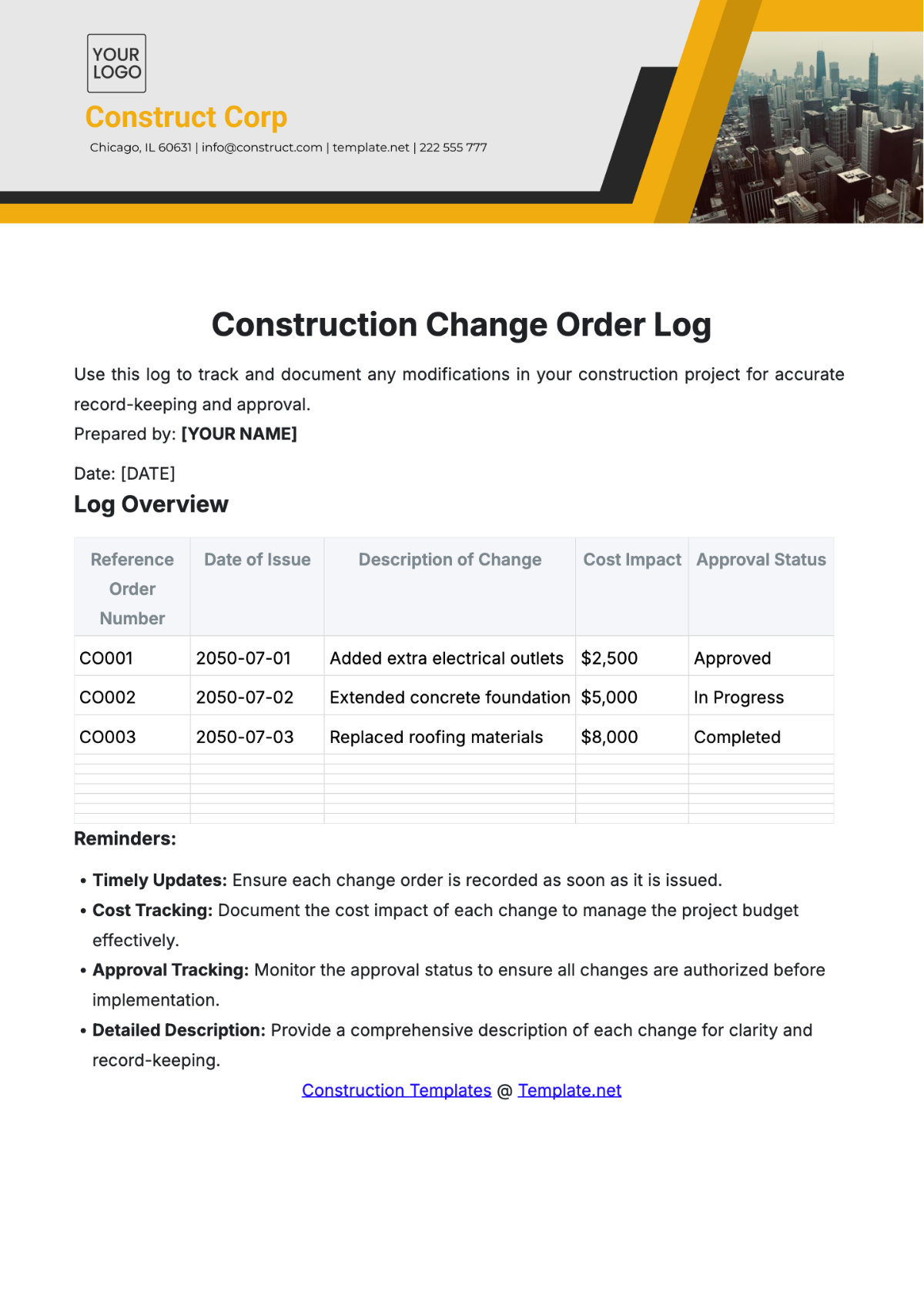
Risk Assessment
Key Risks:
Weather Delays: Unforeseen adverse weather conditions could delay construction progress.
Material Shortages: Disruptions in the supply chain may lead to shortages of essential construction materials.
Budget Overruns: Unexpected expenses or inaccurate cost estimates could result in exceeding the allocated budget.
Design Changes: Changes in project design or scope may cause delays and budget increases.
Safety Incidents: Accidents or safety violations could result in injuries, project delays, or legal liabilities.
Mitigation Strategies:
Weather Contingency Plan: Develop a contingency plan to address weather-related delays, including flexible scheduling and temporary shelter options.
Diversified Supplier Network: Establish relationships with multiple suppliers to mitigate the impact of material shortages. Maintain regular communication with suppliers to anticipate and address potential disruptions.
Budget Tracking and Reporting: Implement rigorous budget tracking mechanisms and regular reporting to identify any discrepancies early. Allocate a contingency fund to address unforeseen expenses.
Change Management Protocol: Implement a structured change management protocol to assess the impact of design changes on project timeline and budget. Prioritize changes based on necessity and feasibility.
Comprehensive Safety Training: Provide thorough safety training for all personnel involved in the project. Enforce strict safety protocols and conduct regular inspections to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with regulations.
Communication Plan
Communication Channels:
Email: Regular updates, announcements, and documentation will be communicated via email.
Meetings: Weekly progress meetings will be held to discuss project status, challenges, and resolutions.
Project Management Software: Utilization of project management software for real-time collaboration, document sharing, and task tracking.
Phone/Video Calls: Ad-hoc discussions and urgent matters will be addressed through phone or video calls.
Site Visits: Periodic site visits will be conducted to assess progress and address on-site issues directly.
Frequency of Updates:
Weekly Progress Reports: A comprehensive progress report will be provided to all stakeholders every Friday, outlining achievements, challenges, and upcoming tasks.
Monthly Meetings: Monthly meetings will be scheduled to discuss project milestones, budget updates, and any changes in scope.
Ad-hoc Updates: Immediate updates will be communicated as necessary for urgent matters, changes in schedule, or unforeseen issues.
Site Visits: Site visits will be conducted monthly to ensure alignment between project plans and on-site activities.
Approval Process
Approval Authority:
The Project Steering Committee, consisting of representatives from [Client Name], [PROJECT NAME], and relevant regulatory bodies, holds authority for project approvals. The Project Manager facilitates the approval process by presenting design proposals, budget estimates, and regulatory compliance documentation to the committee, ensuring alignment with project objectives at each stage. Upon committee approval, the project progresses through design, construction, and handover phases, with the committee providing oversight and final acceptance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comprehensive [PROJECT NAME] Construction Project Brief provides stakeholders with a clear roadmap for project success. By detailing essential project elements such as scope, timeline, budget, and safety considerations, this document ensures alignment and clarity among all parties involved. Should any questions arise or further clarification be needed, the project team is readily available to address inquiries and provide assistance. With this brief as a guide, we are poised for a collaborative and successful project delivery.