Free Workplace Strategic Incident Response Plan

I. Executive Summary
A. Overview
The [Your Company Name] Workplace Strategic Incident Response Plan is a framework made to guide our organization's response to various incidents, ensuring the safety and well-being of our employees, protecting assets, and maintaining business continuity. This plan outlines the roles, responsibilities, and procedures to be followed in the event of emergencies and critical incidents.
B. Purpose and Objectives
The primary purpose of this plan is to establish a structured and efficient response mechanism for identified risks and incidents. Objectives include minimizing the impact of incidents, safeguarding human life, ensuring communication effectiveness, and facilitating a swift recovery.
C. Key Stakeholders and Roles
Key stakeholders include members of the Incident Response Team, department heads, employees, and external partners. Roles and responsibilities are defined to ensure a coordinated effort during incident response.
II. Introduction
A. Background Information
1. Purpose
The plan is a proactive approach developed to address and manage potential risks and incidents that may affect the safety, well-being, and operational continuity of our organization. Rooted in our commitment to employee safety and corporate resilience, this plan aims to provide a structured framework for effectively responding to a diverse range of incidents.
2. Evolution of Incident Management
Building on the lessons learned from past incidents and industry best practices, [Your Company Name] recognizes the need for a continually evolving incident response strategy. The plan is a document that will be regularly reviewed, refined, and updated to adapt to changing circumstances, emerging threats, and advancements in incident response methodologies.
B. Scope and Applicability
1. Coverage
The plan is applicable to all employees, contractors, and visitors across [Your Company Name] facilities and operations. It encompasses incidents that could disrupt normal business operations, compromise safety, or pose a threat to our assets.
2. Incident Types
The plan covers a broad spectrum of incident types, including but not limited to:
a. Natural disasters
b. IT security breaches
c. Workplace violence and safety incidents
d. Health emergencies
3. Geographical Considerations
Given the geographical diversity of our operations, the plan provides flexibility for tailoring responses to location-specific risks and regulatory requirements.
C. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
1. Regulatory Landscape
[Your Company Name] is committed to adhering to all relevant local, state, and federal regulations governing incident response. The plan has been developed with a comprehensive understanding of the legal landscape to ensure compliance across jurisdictions.
2. Data Protection and Privacy
In alignment with data protection laws, the plan emphasizes the secure handling of sensitive information during incident response activities. Protocols are in place to safeguard employee and organizational data in accordance with applicable privacy regulations.
3. Industry Standards
The plan aligns with established industry standards and guidelines, reflecting our commitment to maintaining the highest levels of operational resilience and security within our sector.
4. Regular Compliance Audits
To validate ongoing compliance, periodic audits will be conducted to assess the effectiveness of the plan in meeting legal requirements and industry standards.
III. Risk Assessment and Identification
A. Risk Management Team's Analysis
Our skilled Risk Management Team, comprising experts from various departments, conducted a thorough analysis. They utilized diverse methodologies, engaging stakeholders and considering historical data and current industry trends to identify potential risks.
B. Identification of Potential Threats and Vulnerabilities
The team compiled a detailed catalog covering natural disasters, IT security threats, workplace incidents, and health-related risks. Each threat underwent careful assessment and prioritization, enabling the development of targeted response strategies.
C. Prioritization of Risks
Risks were categorized into severity levels (Low, Moderate, High), with corresponding mitigation strategies tailored to each level. Ongoing monitoring ensures adaptability to emerging threats, maintaining the plan's effectiveness in our dynamic operational environment.
IV. Incident Response Team
This section focuses on the Incident Response Team, underscoring its pivotal role in the organization's overarching security strategy. It aims to provide a detailed exposition of the team’s enhanced structure and the specific roles of its members. This approach not only aligns with best practices in incident management but also reinforces the organization's commitment to maintaining robust security protocols and safeguarding its assets and stakeholders.
A. Composition and Roles
Role | Name |
Incident Commander | [Name] |
Communication Officer | |
IT Security Lead | |
HR Representative | |
Legal and Compliance Advisor | |
Facilities Management Lead |
B. Contact Information and Communication Protocols
Detailed contact information for each team member is maintained in a secure location. Communication protocols are outlined to ensure timely and accurate information dissemination.
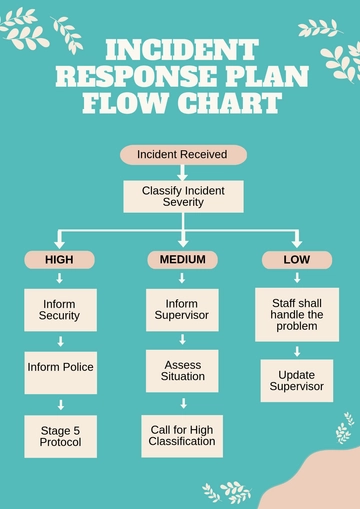
V. Incident Categories and Classification
A. Types of Incidents
1. Natural Disasters: Earthquakes, floods, storms, and other environmental events.
2. IT Security Breaches: Cyber-attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized system access.
3. Workplace Violence: Incidents involving threats, harassment, or physical harm.
4. Health Emergencies: Pandemics, infectious disease outbreaks, and public health crises.
B. Incident Severity Levels
1. Low: Minimal impact on operations and personnel.
2. Moderate: Requires a coordinated response, moderate impact.
3. High: Critical incidents with severe disruption potential.
VI. Response Procedures
A. Activation of Incident Response Team: Immediate activation triggered by severity and type of incident.
B. Communication Protocols: Established channels for internal and external communication.
C. Evacuation Procedures: Safe and orderly evacuation plans for different scenarios.
D. First Aid and Medical Response: First aid training, medical resources, and emergency medical protocols.
E. IT Security Measures: Rapid response to contain and address cybersecurity incidents.
F. Legal and Compliance Actions: Legal guidance, reporting procedures, and compliance protocols.
VII. Communication Plan
A. Internal Communication
1. Employee Notifications: Swift and clear communication to all employees using multiple channels.
2. Team Briefings: Regular updates and briefings to ensure situational awareness.
B. External Communication
Media Relations: Designated spokesperson and coordinated media response.
Public Announcements: Timely and accurate public communications to stakeholders.
C. Communication Tools and Platforms
Utilization of email, text alerts, phone trees, and designated communication platforms.
VIII. Training and Drills
A. Employee Training Programs
Regular training sessions to educate employees on incident response procedures.
B. Simulation Drills
Scheduled drills to test the effectiveness of response strategies and identify areas for improvement.
C. Evaluation and Feedback Mechanisms
Post-drill assessments and feedback loops for continuous improvement.
IX. Resource Allocation
A. Personnel
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities for Incident Response Team members.
B. Equipment and Technology
Adequate provision of tools and technologies required for incident response.
C. Financial Resources
Allocation of budget and resources to support incident response efforts.
X. Documentation and Reporting
A. Incident Reporting Procedures
1. All incidents must be reported immediately to the Incident Commander or designated team member.
2. Use the incident reporting form, detailing the nature, location, and severity of the incident.
B. Documentation Requirements
1. Maintain detailed records of incident response actions, communications, and outcomes.
2. Document lessons learned and areas for improvement after each incident.
C. Post-Incident Analysis and Reporting
1. Conduct a thorough post-incident analysis to assess the effectiveness of the response.
2. Generate incident reports summarizing key findings and recommending improvements.
XI. Continuous Improvement
A. Review and Evaluation Process
1. Conduct regular reviews of the plan to ensure its effectiveness and relevance.
2. Evaluate response actions and identify opportunities for improvement.
B. Lessons Learned
1. Capture and document lessons learned from each incident response.
2. Share insights across teams to enhance organizational learning.
C. Plan Revision and Update Schedule
1. Establish a regular schedule for plan revisions based on emerging threats and lessons learned.
2. Communicate updates promptly to all relevant stakeholders.
XII. Integration with Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plans
A. Coordination with Other Organizational Plans
1. Align the plan with broader business continuity and disaster recovery plans.
2. Ensure seamless coordination and consistency across organizational response efforts.
B. Cross-Functional Collaboration
1. Foster collaboration between incident response, business continuity, and recovery teams.
2. Conduct joint drills and training exercises to enhance overall organizational resilience.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Prepare your organization for any eventuality with Template.net's Workplace Strategic Incident Response Plan Template. This editable and customizable tool, accessible via our Ai Editor Tool, equips you to develop a comprehensive strategy for addressing emergencies effectively. Safeguard your workplace and ensure swift, coordinated responses with Template.net's innovative solutions.
You may also like
- Finance Plan
- Construction Plan
- Sales Plan
- Development Plan
- Career Plan
- Budget Plan
- HR Plan
- Education Plan
- Transition Plan
- Work Plan
- Training Plan
- Communication Plan
- Operation Plan
- Health And Safety Plan
- Strategy Plan
- Professional Development Plan
- Advertising Plan
- Risk Management Plan
- Restaurant Plan
- School Plan
- Nursing Home Patient Care Plan
- Nursing Care Plan
- Plan Event
- Startup Plan
- Social Media Plan
- Staffing Plan
- Annual Plan
- Content Plan
- Payment Plan
- Implementation Plan
- Hotel Plan
- Workout Plan
- Accounting Plan
- Campaign Plan
- Essay Plan
- 30 60 90 Day Plan
- Research Plan
- Recruitment Plan
- 90 Day Plan
- Quarterly Plan
- Emergency Plan
- 5 Year Plan
- Gym Plan
- Personal Plan
- IT and Software Plan
- Treatment Plan
- Real Estate Plan
- Law Firm Plan
- Healthcare Plan
- Improvement Plan
- Media Plan
- 5 Year Business Plan
- Learning Plan
- Marketing Campaign Plan
- Travel Agency Plan
- Cleaning Services Plan
- Interior Design Plan
- Performance Plan
- PR Plan
- Birth Plan
- Life Plan
- SEO Plan
- Disaster Recovery Plan
- Continuity Plan
- Launch Plan
- Legal Plan
- Behavior Plan
- Performance Improvement Plan
- Salon Plan
- Security Plan
- Security Management Plan
- Employee Development Plan
- Quality Plan
- Service Improvement Plan
- Growth Plan
- Incident Response Plan
- Basketball Plan
- Emergency Action Plan
- Product Launch Plan
- Spa Plan
- Employee Training Plan
- Data Analysis Plan
- Employee Action Plan
- Territory Plan
- Audit Plan
- Classroom Plan
- Activity Plan
- Parenting Plan
- Care Plan
- Project Execution Plan
- Exercise Plan
- Internship Plan
- Software Development Plan
- Continuous Improvement Plan
- Leave Plan
- 90 Day Sales Plan
- Advertising Agency Plan
- Employee Transition Plan
- Smart Action Plan
- Workplace Safety Plan
- Behavior Change Plan
- Contingency Plan
- Continuity of Operations Plan
- Health Plan
- Quality Control Plan
- Self Plan
- Sports Development Plan
- Change Management Plan
- Ecommerce Plan
- Personal Financial Plan
- Process Improvement Plan
- 30-60-90 Day Sales Plan
- Crisis Management Plan
- Engagement Plan
- Execution Plan
- Pandemic Plan
- Quality Assurance Plan
- Service Continuity Plan
- Agile Project Plan
- Fundraising Plan
- Job Transition Plan
- Asset Maintenance Plan
- Maintenance Plan
- Software Test Plan
- Staff Training and Development Plan
- 3 Year Plan
- Brand Activation Plan
- Release Plan
- Resource Plan
- Risk Mitigation Plan
- Teacher Plan
- 30 60 90 Day Plan for New Manager
- Food Safety Plan
- Food Truck Plan
- Hiring Plan
- Quality Management Plan
- Wellness Plan
- Behavior Intervention Plan
- Bonus Plan
- Investment Plan
- Maternity Leave Plan
- Pandemic Response Plan
- Succession Planning
- Coaching Plan
- Configuration Management Plan
- Remote Work Plan
- Self Care Plan
- Teaching Plan
- 100-Day Plan
- HACCP Plan
- Student Plan
- Sustainability Plan
- 30 60 90 Day Plan for Interview
- Access Plan
- Site Specific Safety Plan