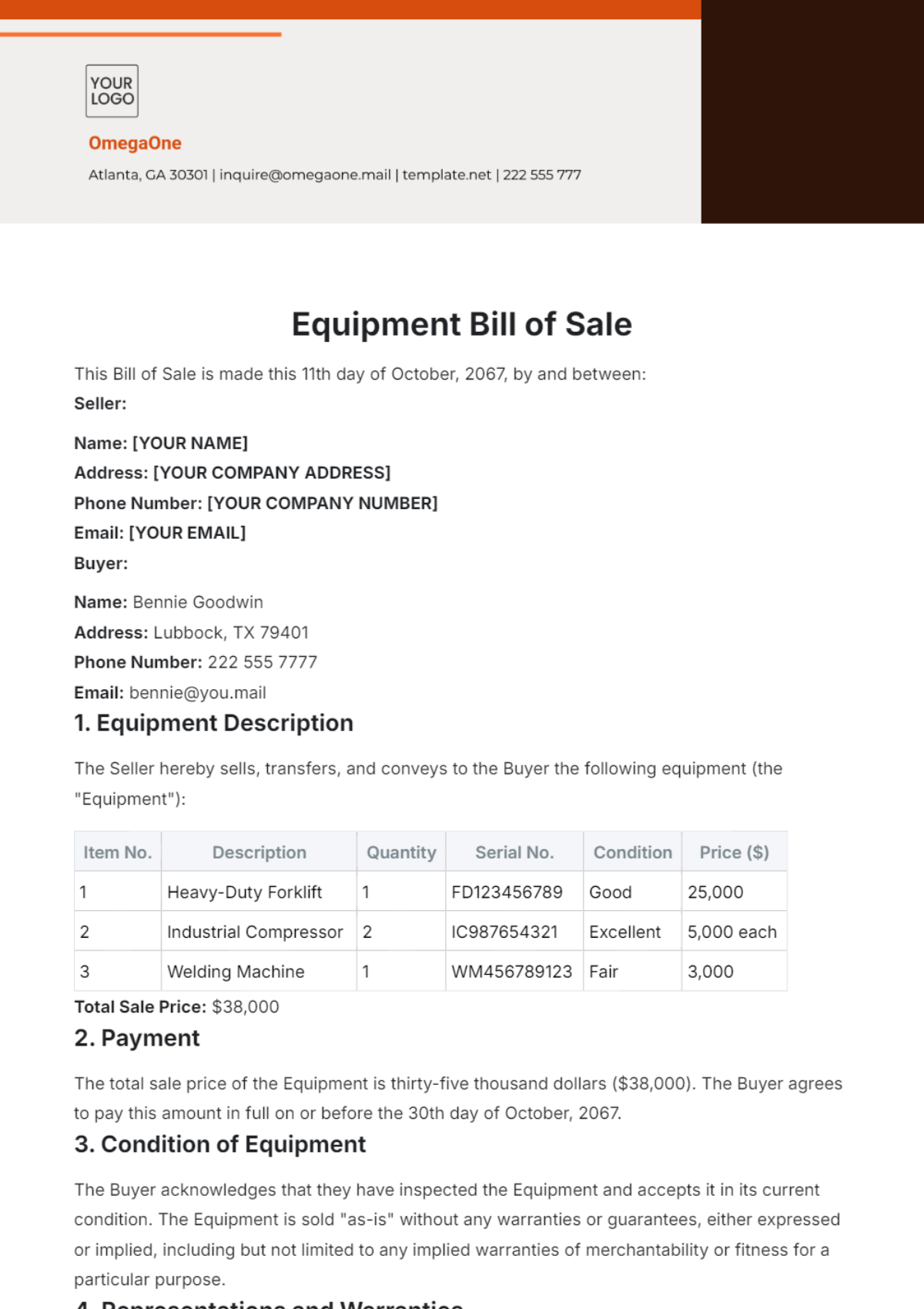
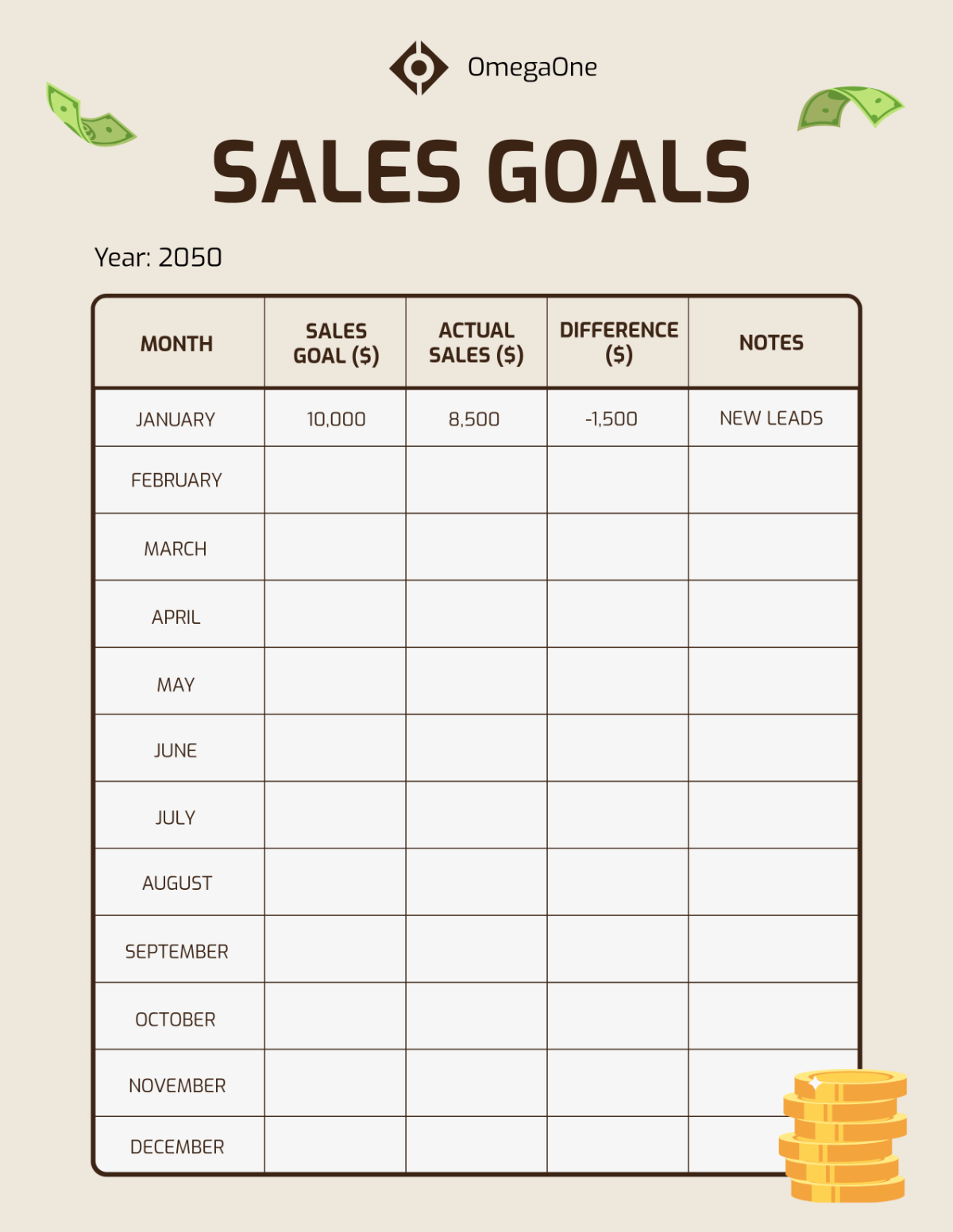
Sales SOP for Processing Customer Feedback
The Sales Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) presented here delineates the systematic approach employed by our sales department in handling customer feedback. It serves as a blueprint for efficiently receiving, scrutinizing, and resolving customer feedback. The primary aim of this procedure is to guarantee the efficient management of customer feedback, harnessing it as a valuable tool for enhancing the quality and effectiveness of our products and services.
In line with our commitment to continuous improvement, this SOP fosters a culture of proactive engagement with our customers. By adhering to this standardized process, we aim to not only respond to customer concerns promptly but also harness their insights to refine our offerings, thus promoting overall customer satisfaction and loyalty.
I. PURPOSE
The primary purpose of this SOP is to create a robust and uniform framework for the management of customer feedback, aligning all aspects of the organization towards a unified goal of enhancing customer satisfaction. By standardizing the process for handling customer feedback, it will not only guarantee consistent and prompt responses to customer concerns but also foster an environment of accountability and transparency within the sales department. Moreover, this SOP serves as a fundamental instrument in our commitment to delivering exceptional customer experiences and building long-lasting relationships.
Furthermore, this SOP plays a pivotal role in facilitating data-driven decision-making for continuous improvement. It provides a structured approach for capturing, analyzing, and deriving insights from customer feedback. These insights, once harnessed, serve as valuable inputs for product development, service enhancements, and strategic planning. The data-driven aspect ensures that we evolve in alignment with customer expectations and market dynamics, making us more agile, competitive, and customer-centric in the ever-evolving business landscape. In essence, this SOP not only embodies our dedication to customer-centricity but also acts as a compass guiding us towards a future of excellence and growth.
II. SCOPE
This SOP encompasses all activities related to the management of customer feedback within the sales department and ensures a comprehensive approach to handling various forms of feedback. It is applicable to all employees within the sales department, including sales representatives, sales managers, and support staff, who are responsible for receiving, documenting, and addressing customer feedback.
The scope of this SOP includes, but is not limited to, the following aspects:
A. Feedback Types
This procedure encompasses all varieties and types of customer feedback that may be received, such as, but not exclusive to:
Compliments: Positive feedback and praise received from customers.
Complaints: Negative feedback, grievances, and concerns expressed by customers.
Suggestions: Recommendations, ideas, and improvement proposals submitted by customers.
Inquiries: Questions, requests for information, or general queries from customers.
B. Feedback Channels
The rules and guidelines involved in the procedure are applicable to any feedback which is obtained through a variety of communication channels, to give a few examples:
Email: Feedback received via email communication.
Phone Calls: Feedback provided through telephone interactions.
Website Forms: Feedback submitted through online forms on the company website.
In-Person Interactions: Feedback gathered during face-to-face interactions with customers
C. Feedback Classification
All feedback should be classified into predefined categories for effective analysis and resolution. This includes categorization by product, service, department, or any other relevant criteria to help identify trends and areas for improvement.
D. Documentation
This SOP dictates the standardized documentation of feedback, including capturing customer details (name, contact information), date of receipt, and a detailed description of the feedback. Relevant attachments, such as invoices or support tickets, should also be recorded.
E. Analysis
The term 'it' in this context signifies the task that includes the review and the analysis of assorted feedback. This procedure is essential because it assists in identifying recurring patterns and trends. Furthermore, it is instrumental in unveiling potential areas that could benefit from enhancements. These areas of improvement could pertain to products, services, or even specific processes.
F. Resolution
Feedback resolution activities are included, emphasizing the responsibility of sales representatives and managers in addressing customer concerns or implementing improvement measures.
G. Reporting and Documentation
The SOP covers the documentation of all feedback entries and related actions, ensuring a comprehensive record for auditing, management review, and continuous improvement purposes.
H. Monitoring and Auditing
Procedures for monitoring the adherence to this SOP, including periodic audits of feedback entries, are part of the scope to ensure consistency and quality in feedback handling.
I. Collaboration
The SOP encourages cross-functional collaboration with other departments when complex issues require their expertise, promoting a coordinated approach to resolution and improvement.
III. DEFINITIONS
Customer Feedback: Any information, comments, suggestions, or complaints provided by customers regarding the products or services.
Feedback Channel: The method by which customers submit their feedback, such as email, phone, website form, or in-person communication.
Feedback Classification: The categorization of feedback into relevant categories for analysis.
Feedback Analysis: The process of reviewing feedback to identify trends and insights.
Feedback Resolution: The action taken to address customer concerns or suggestions.
Feedback Reporting: The documentation and reporting of feedback trends and actions taken.
IV. RESPONSIBILITIES
A. Sales Representatives
Our Sales Representatives play a pivotal role in ensuring a seamless customer feedback handling process. Their responsibilities include:
Attentive Feedback Reception: Sales Representatives are the frontline of customer feedback management. They are responsible for receiving feedback through various channels, such as email, phone calls, website forms, or in-person interactions. They must ensure that each piece of feedback is documented promptly and accurately.
Effective Feedback Classification: To facilitate meaningful analysis, Sales Representatives categorize feedback into predefined categories, such as product quality, service experience, pricing, and more. When necessary, they also have the flexibility to create new categories to better capture the essence of customer feedback.
B. Sales Managers
Our Sales Managers are responsible for the oversight and strategic management of the feedback handling process. Their roles encompass the following key responsibilities:
Strategic Process Oversight: Sales Managers oversee the entire feedback management process. They ensure that the process adheres to this SOP and that all feedback is handled promptly, professionally, and in alignment with our company's values.
Timely and Appropriate Responses: Sales Managers play a critical role in maintaining the quality of responses provided to customers. They ensure that every piece of feedback, whether a compliment or a complaint, receives a response that reflects our commitment to customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
C. Procedure
Receiving Customer Feedback
Customer feedback may be received through various channels, such as email, phone calls, website forms, or in-person interactions.
Sales representatives are responsible for receiving and documenting feedback using the designated feedback management system.
Classifying Feedback
Sales representatives classify feedback into predefined categories (e.g., product quality, service experience, pricing).
If feedback does not fit an existing category, they can create a new one with a brief description.
Recording Feedback
Feedback should be recorded with relevant details, including the customer's name, contact information, date, and a clear description of the feedback.
Attach any relevant documents or records to the feedback entry.
Analyzing Feedback
Sales managers periodically review and analyze feedback to identify recurring themes, trends, and opportunities for improvement.
Feedback data should be visualized through reports and charts to facilitate analysis.
Addressing Customer Feedback
Sales representatives are responsible for addressing feedback within their scope of authority.
For complex issues or those requiring input from other departments, sales managers should collaborate with the relevant teams to find solutions.
Timely responses should be provided to customers, acknowledging their feedback and informing them of any actions taken.
Reporting and Documentation
Sales managers compile regular reports summarizing feedback trends, resolutions, and improvement initiatives.
These reports are shared with the management team and relevant departments.
All feedback and related actions are documented for auditing and continuous improvement purposes.
D. Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Monitoring
The feedback handling process should be regularly monitored to ensure compliance with this SOP.
Sales managers should conduct random audits of feedback entries and responses to maintain quality.
Continuous Improvement
Feedback trends and insights should be used to drive product and service improvements.
Regular meetings and discussions should be held to address recurring issues and implement corrective actions.
V. REVISION HISTORY
Maintaining a well-documented revision history is essential to track the evolution of our Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Processing Customer Feedback. This record provides transparency, accountability, and a clear understanding of the changes made over time. Below is a snapshot of the revision history, with additional details for Version 1.0 and an explanation of how future revisions will be documented:
Version 1.0 [06-20-2050]: – Initial Release |
Summary: The initial release of this SOP marked the commencement of our structured approach to customer feedback processing. The content outlined the fundamental framework for managing customer feedback within our sales department, serving as the baseline for future improvements and enhancements. |
Version 2.0: [10-15-2050] – Enhancements and Clarifications |
Summary: In Version 2.0, various enhancements and clarifications were introduced to streamline the customer feedback handling process. These changes were made in response to practical experiences and feedback from our team. Notable updates included more detailed guidelines for feedback categorization and a refined procedure for interdepartmental collaboration. |
Version 2.0: [10-15-2050] – Enhancements and Clarifications |
Summary: In Version 2.0, various enhancements and clarifications were introduced to streamline the customer feedback handling process. These changes were made in response to practical experiences and feedback from our team. Notable updates included more detailed guidelines for feedback categorization and a refined procedure for interdepartmental collaboration. |