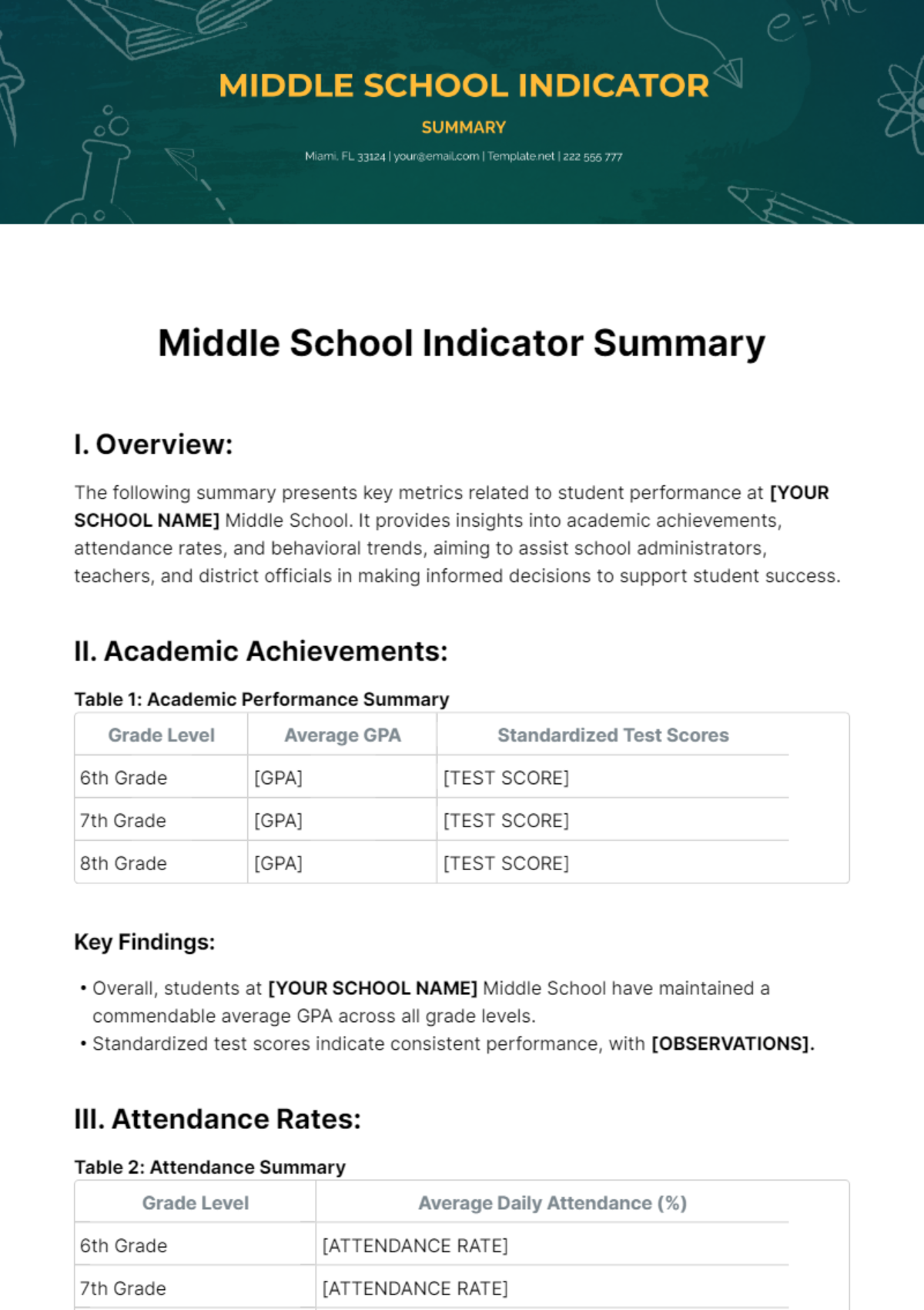
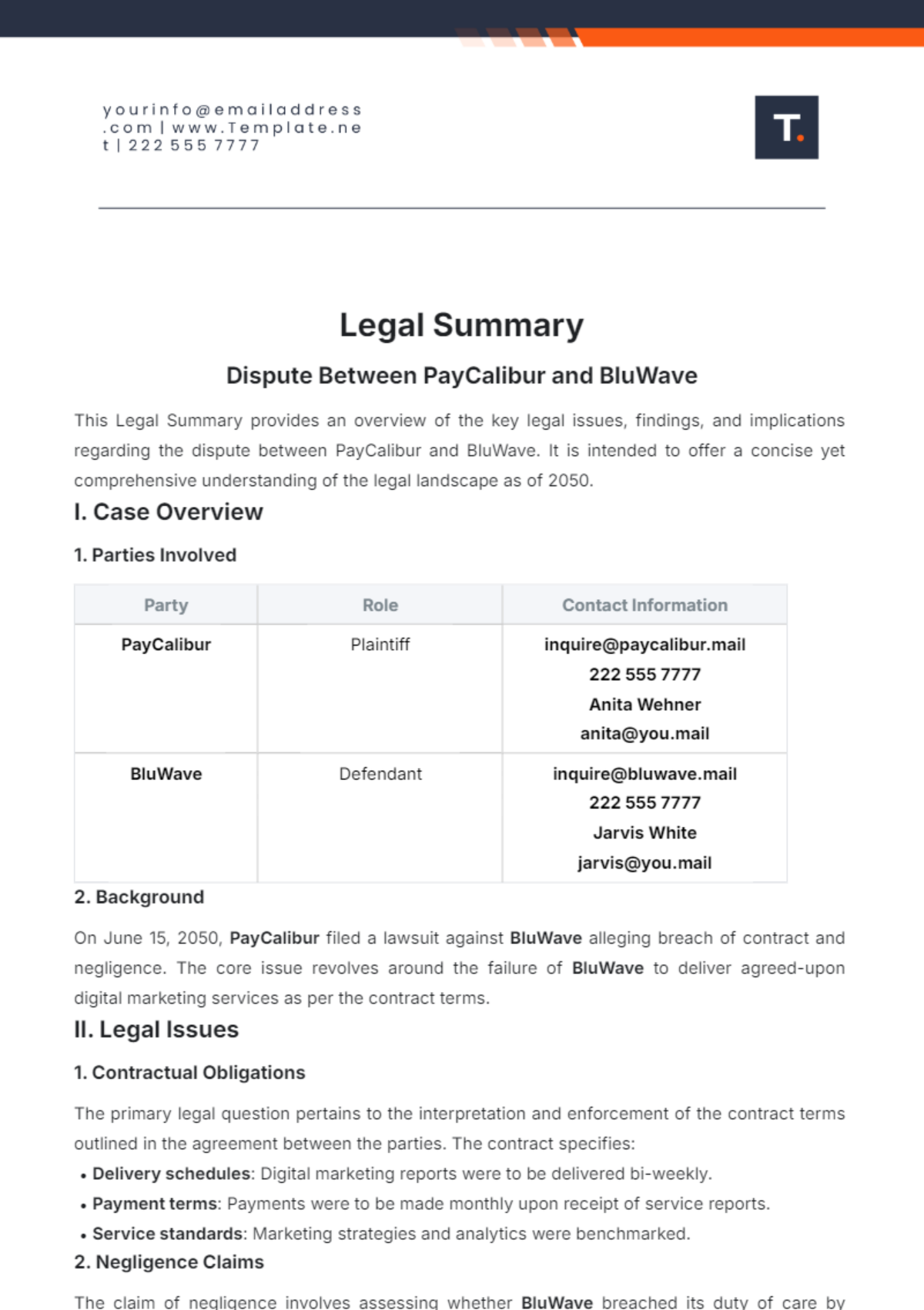
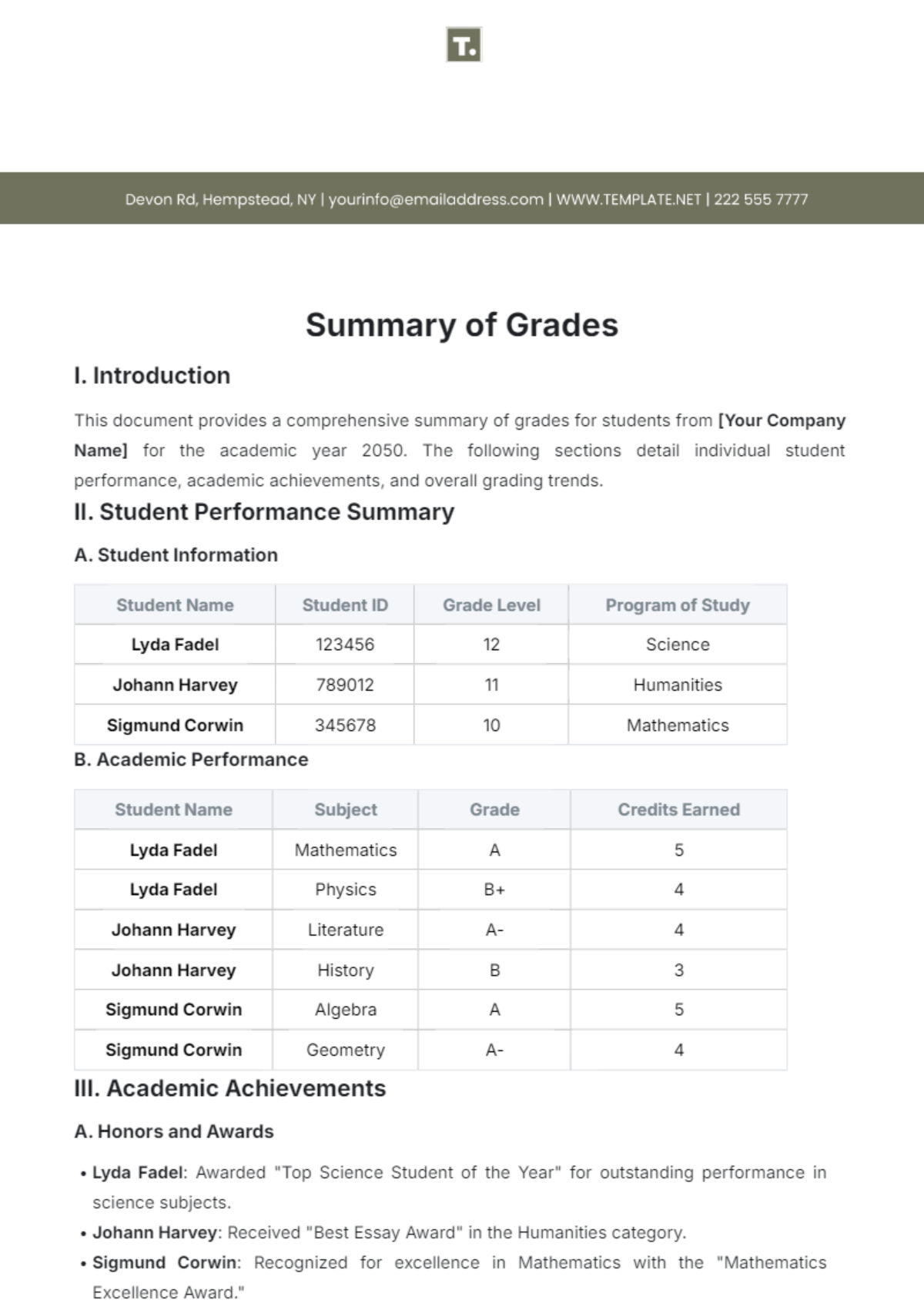
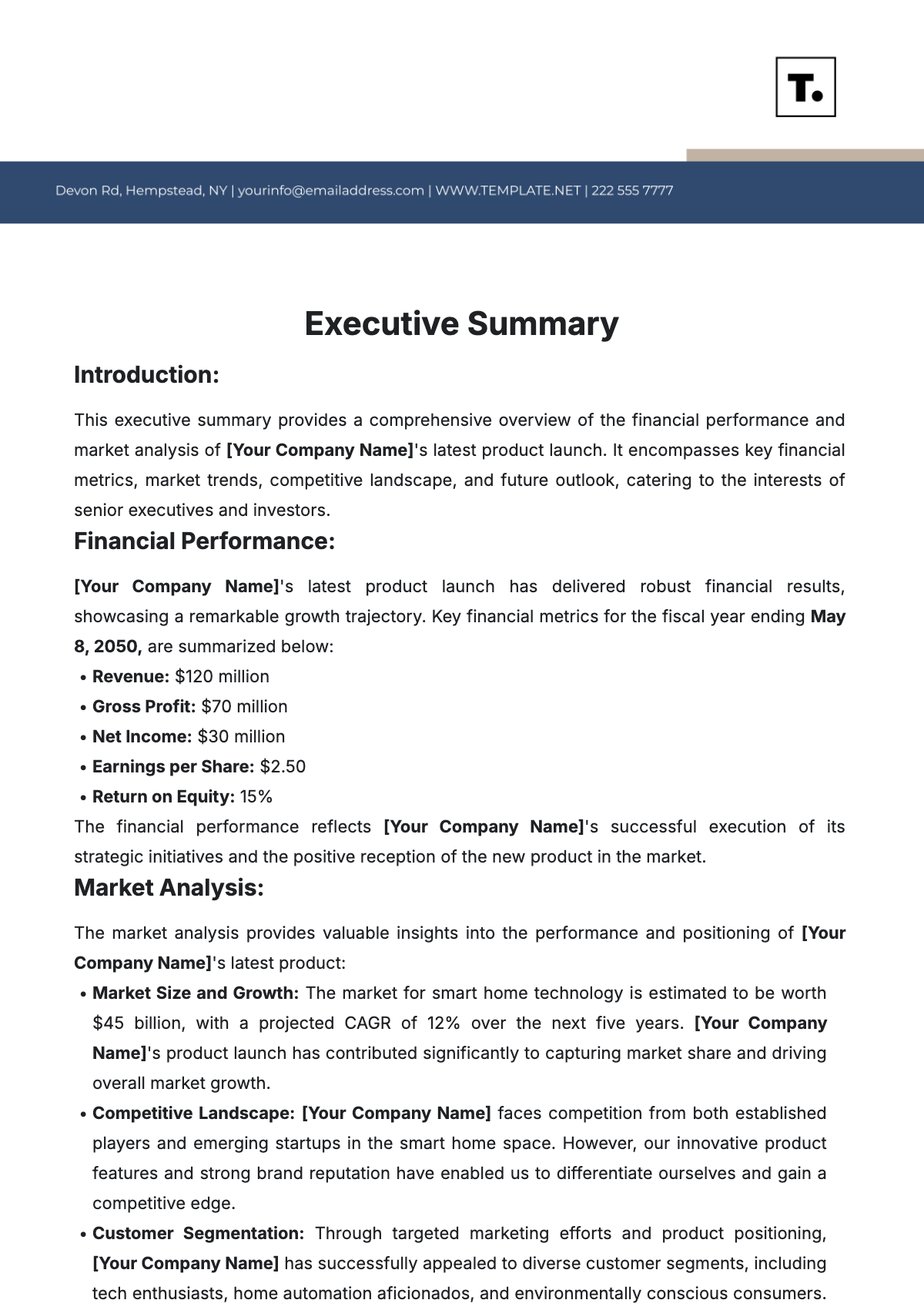
Free Subjective Summary
Introducing the Subjective Summary Template from Template.net, a versatile solution for crafting engaging summaries effortlessly. This editable and customizable template empowers users to tailor summaries to their preferences, enhancing productivity. Seamlessly edit in our Ai Editor Tool for a streamlined experience. Elevate your summarizing game with this dynamic tool.