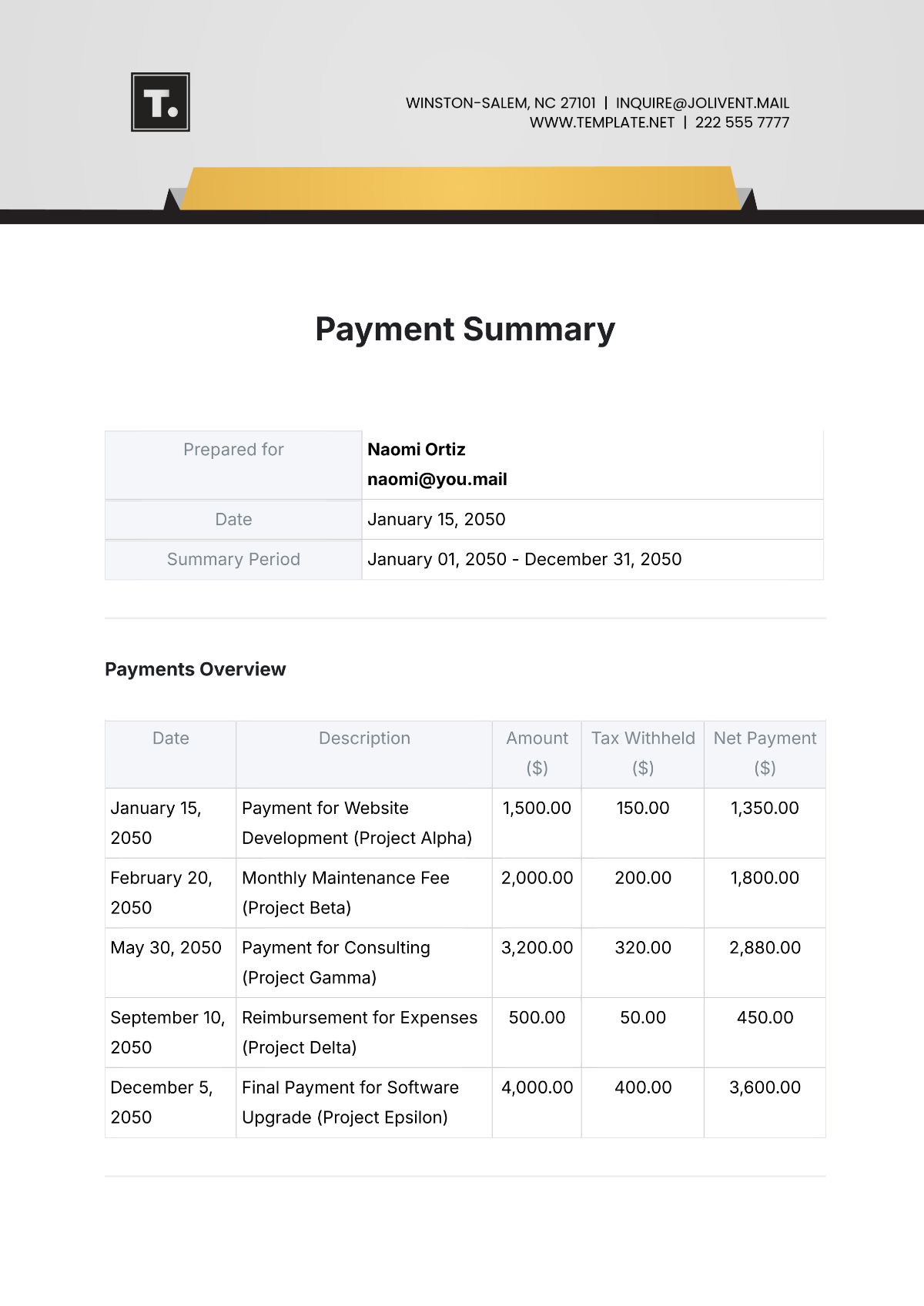
Lesson Summary
Introduction
Welcome to [LESSON TITLE], where we explore the essential concepts of physics, laying the groundwork for comprehending the world's natural phenomena. Physics, a cornerstone of scientific inquiry, investigates the properties of matter, energy, motion, and their interplay. Understanding these principles provides invaluable insight into the workings of the universe at its core.
Key Concepts:
Newton's Laws of Motion:
First Law (Law of Inertia): An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an external force.
Second Law (Law of Acceleration): The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This can be mathematically expressed as F = ma.
Third Law (Action and Reaction): For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first.
Law of Universal Gravitation:
All objects with mass attract each other with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres. Mathematically, this is represented as F = (G m1 m2) / r^2, where G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects, and r is the distance between their centres.
Principle of Conservation of Energy:
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another. This principle is crucial in understanding various phenomena such as mechanical energy, thermal energy, and electromagnetic energy.
Principle of Conservation of Momentum:
The total momentum of a closed system remains constant if no external forces act on it. This principle is applicable in analysing collisions and other interactions between objects.
Application Examples:
Principle | Example |
|---|---|
Newton's First Law | A soccer ball remains at rest on the field until a player kicks it, demonstrating the tendency of objects to maintain their state of motion. |
Newton's Second Law | Pushing a heavy box requires more force than pushing a lighter box with the same acceleration, illustrating the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. |
Newton's Third Law | When a rocket propels itself upward, the exhaust gases exert a downward force on the rocket, causing it to move upward. |
Universal Gravitation | The gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon keeps the Moon in orbit around the Earth. |
Conservation of Energy | In a roller coaster ride, the potential energy at the top of the hill is converted into kinetic energy as the coaster descends, maintaining the total energy of the system. |
Conservation of Momentum | When two billiard balls collide, the total momentum of the system before and after the collision remains the same, even if individual ball velocities change. |
Conclusion:
Mastering the fundamentals of physics lays the groundwork for understanding the dynamics of various objects and phenomena across the cosmos. By internalizing principles like [CONCEPTS], learners can cultivate a richer understanding of the natural realm and its intricate workings. Through diligent [ACTIONS], individuals can further probe into the enigmas of physics, unveiling its profound implications in our daily existence.
Summarized By: [YOUR NAME]