Student Course Summary
I. Course Details
The [COURSE TITLE] course offered by [YOUR SCHOOL NAME], [YOUR DEPARTMENT], provides a comprehensive understanding of [COURSE SUBJECT]. Throughout the semester, students delve into various aspects of the subject, including theoretical foundations, practical applications, and case studies. The course is designed to equip students with essential knowledge and skills that are crucial for [COURSE OBJECTIVES].
Course Instructor: [INSTRUCTOR NAME]
Course Duration: [DURATION]
Course Credits: [CREDITS]
II. Key Topics Covered
A. Introduction to [COURSE SUBJECT]
The course begins with an overview of [COURSE SUBJECT], exploring its historical significance, key concepts, and relevance in contemporary contexts. Students gain insight into the fundamental principles that underpin the study of [COURSE SUBJECT].
B. Theoretical Frameworks
This section delves into the theoretical frameworks that inform [COURSE SUBJECT]. Students examine prominent theories, models, and paradigms, critically analyzing their strengths, limitations, and real-world applications. Key topics include:
[THEORY 1]
[THEORY 2]
[THEORY 3]
C. Practical Applications
Here, students explore the practical applications of [COURSE SUBJECT] in various domains, such as [DOMAIN 1], [DOMAIN 2], and [DOMAIN 3]. Through case studies, simulations, and hands-on exercises, students develop problem-solving skills and apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios.
D. Research and Methodology
This section focuses on research methodologies and techniques relevant to [COURSE SUBJECT]. Students learn how to design research studies, collect and analyse data, and draw valid conclusions. Key topics include:
Research Design: Understanding different research designs and their implications.
Data Collection Methods: Exploring qualitative and quantitative data collection techniques.
Data Analysis: Using statistical tools and software for data analysis.
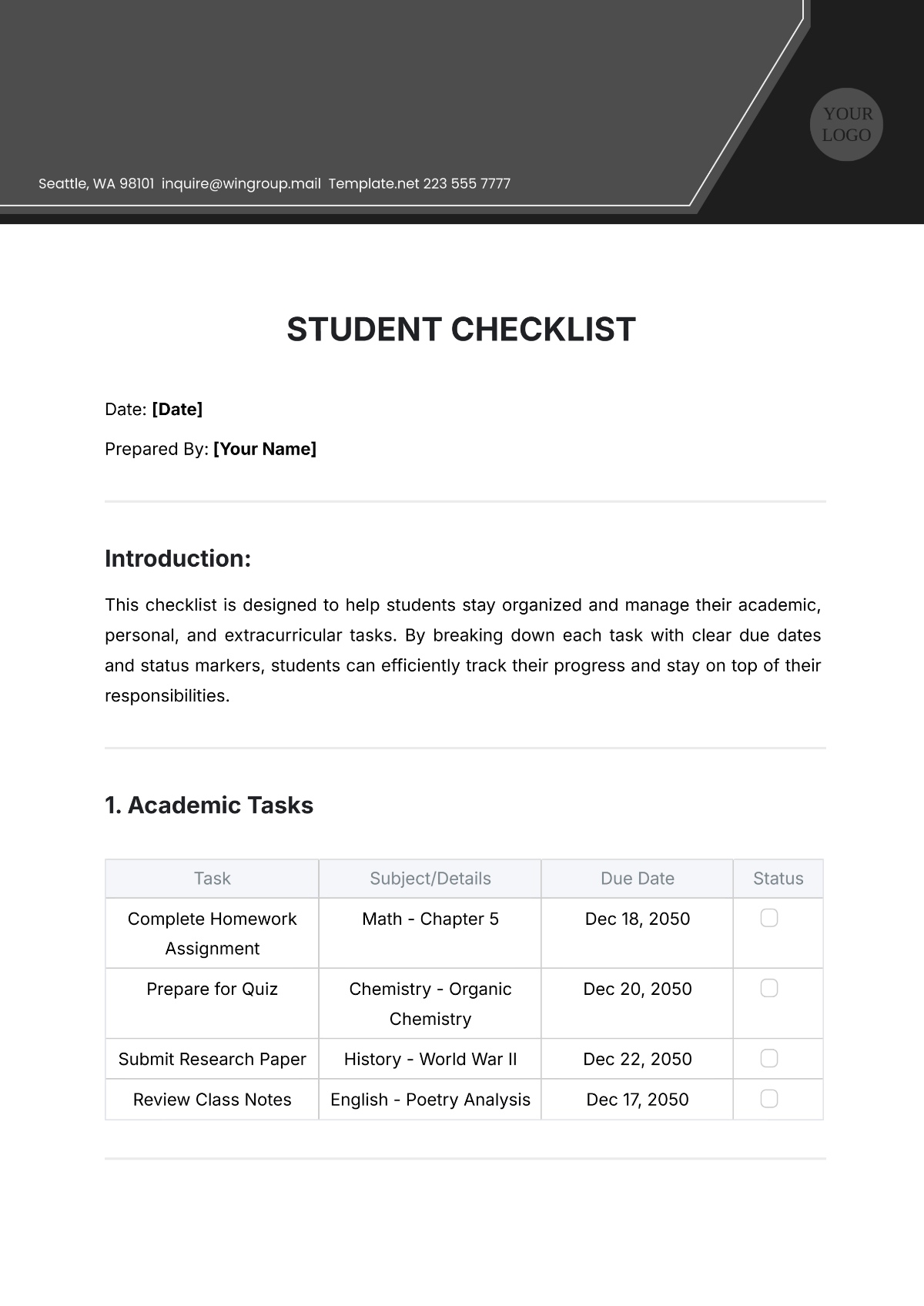
III. Assessment Methods
A. Assignments
Students are assessed through a variety of assignments, including essays, reports, and presentations. These assignments provide opportunities for students to demonstrate their understanding of course concepts and apply them in practical contexts.
B. Examinations
Formal examinations assess students' knowledge and comprehension of the course material. Exams may include multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, and essay questions, covering topics discussed throughout the semester.
C. Class Participation
Active participation in class discussions, group activities, and presentations contributes to students' overall assessment. Engaging in constructive dialogue and sharing insights enhances the learning experience for all students.
IV. Resources
A. Textbooks
Recommended textbooks and supplementary readings provide additional resources for students to deepen their understanding of [COURSE SUBJECT]. These resources cover a wide range of topics and perspectives, enriching students' learning experience.
B. Online Resources
Access to online platforms, academic journals, and databases enhances students' access to up-to-date research and scholarly articles related to [COURSE SUBJECT]. These resources support students' independent study and research endeavors.
V. Support and Assistance
A. Office Hours
[INSTRUCTOR NAME] holds regular office hours to provide additional support and clarification to students. During these sessions, students can seek guidance on course material, assignments, and any questions or concerns they may have regarding the course.
B. Tutoring Services
[YOUR SCHOOL NAME] offers tutoring services for students seeking extra assistance with [COURSE SUBJECT]. Experienced tutors provide one-on-one support, helping students with comprehension, problem-solving, and exam preparation.
VI. Feedback and Evaluation
A. Feedback Mechanisms
Throughout the course, students receive feedback on their performance through various channels, including:
Written Feedback: Detailed feedback provided on assignments and assessments.
Verbal Feedback: In-class discussions and individual feedback sessions with the instructor.
Peer Feedback: Opportunities for students to provide constructive feedback to their peers during group activities and presentations.
B. Evaluation Criteria
Clear evaluation criteria are established for assignments, exams, and class participation. These criteria outline the expectations for students and provide a transparent framework for assessment. Criteria may include:
Content: Accuracy, depth of analysis, and relevance to course objectives.
Presentation: Clarity, organization, and effective communication of ideas.
Critical Thinking: Demonstration of critical thinking skills, logical reasoning, and evidence-based argumentation.
VII. Conclusion
The [COURSE TITLE] course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of [COURSE SUBJECT] through a combination of theoretical exploration, practical applications, and critical analysis. By engaging with key topics, participating in assessments, and utilising available resources, students can enhance their knowledge and skills in [COURSE SUBJECT] and achieve the learning outcomes outlined in the course objectives.
Summarized By: [YOUR NAME]