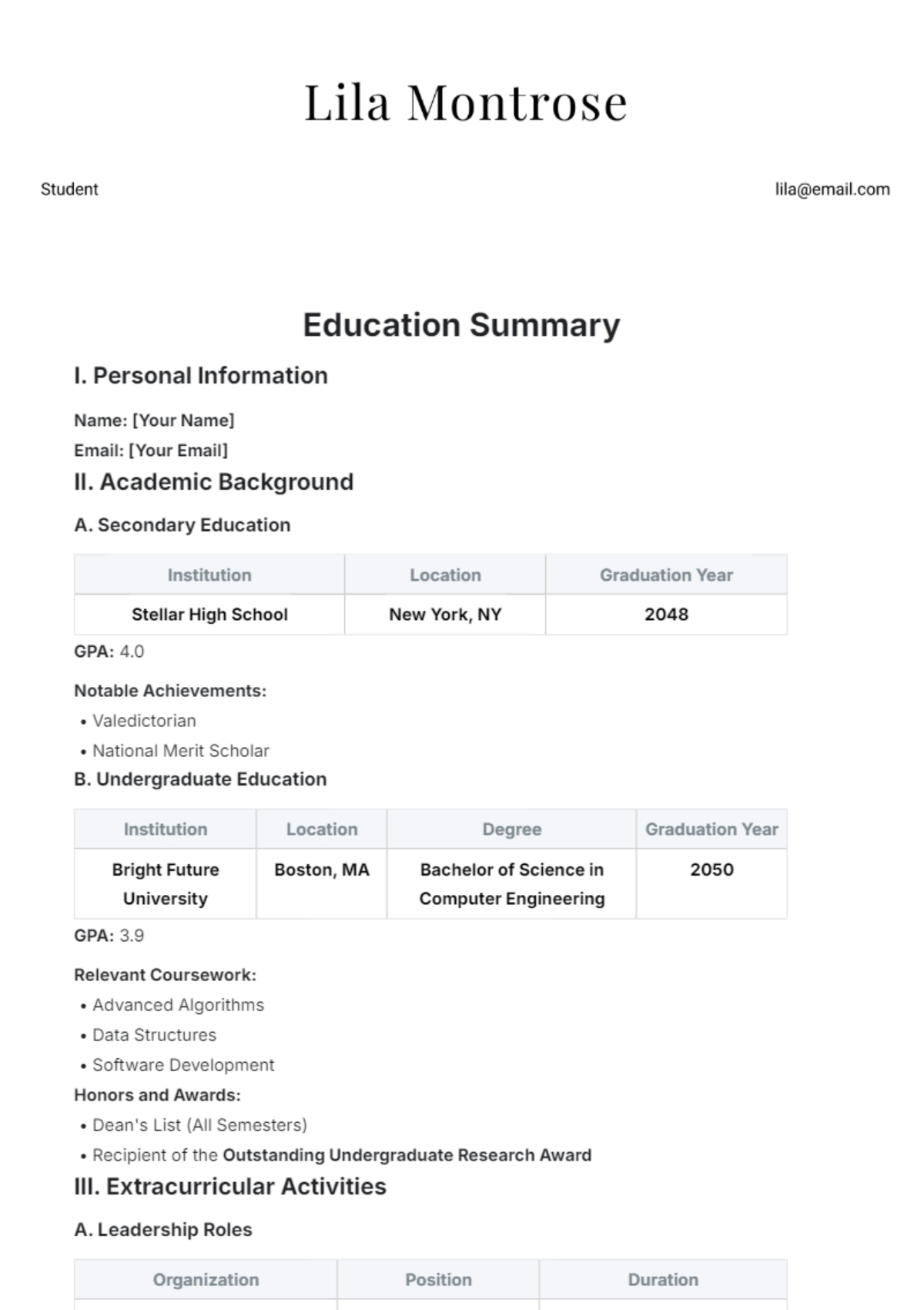
Article Review Summary
Prepared By: [YOUR NAME]
Introduction
In the realm of psychological treatments for anxiety disorders, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has emerged as a prominent and widely studied approach. This article review aims to summarize and assess recent findings on the effectiveness of CBT in treating various forms of anxiety disorders.
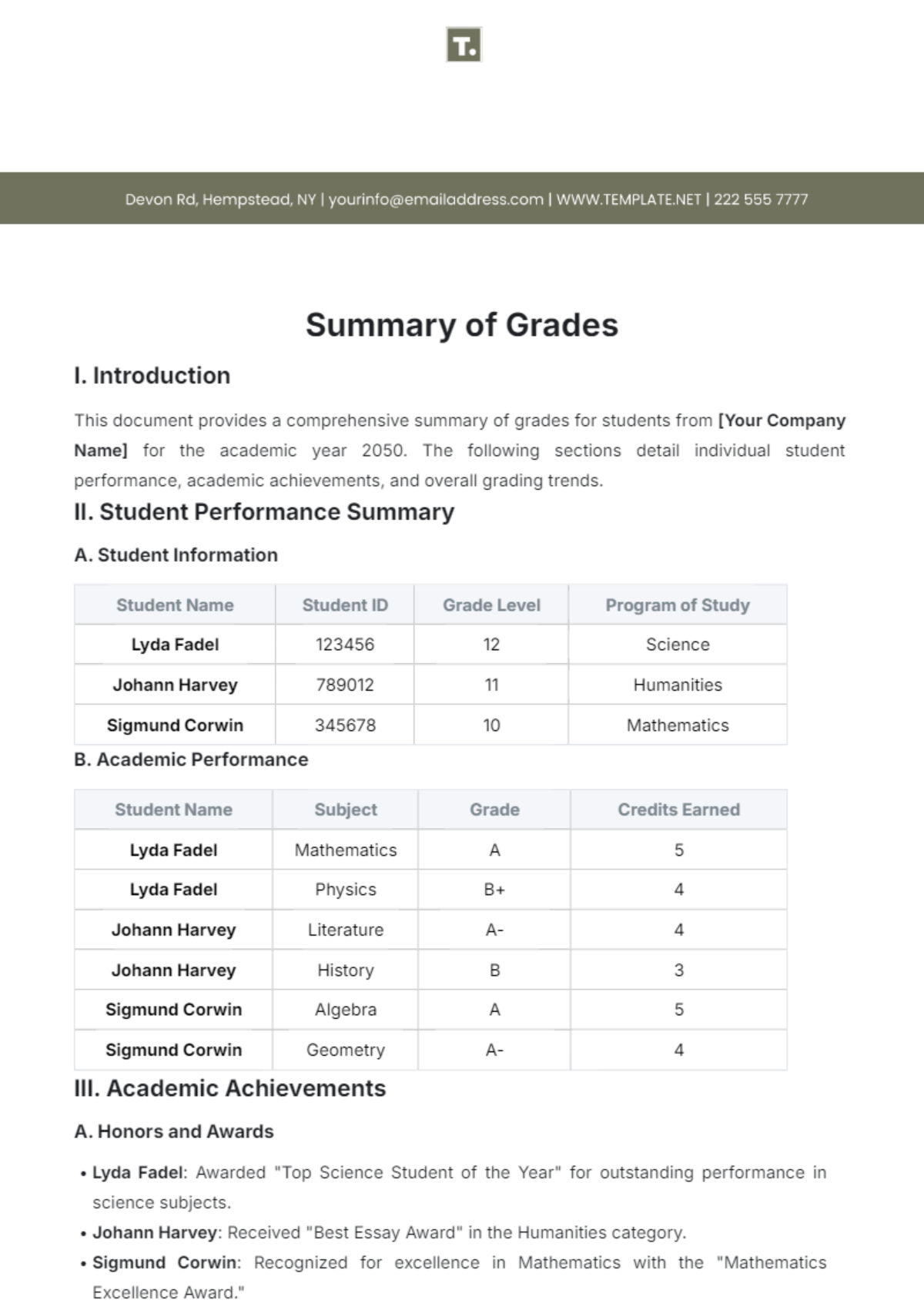
Review of Selected Articles
Study 1:
Title: [INSERT TITLE]
Authors: [INSERT AUTHORS]
Journal: [INSERT JOURNAL], [PUBLICATION YEAR]
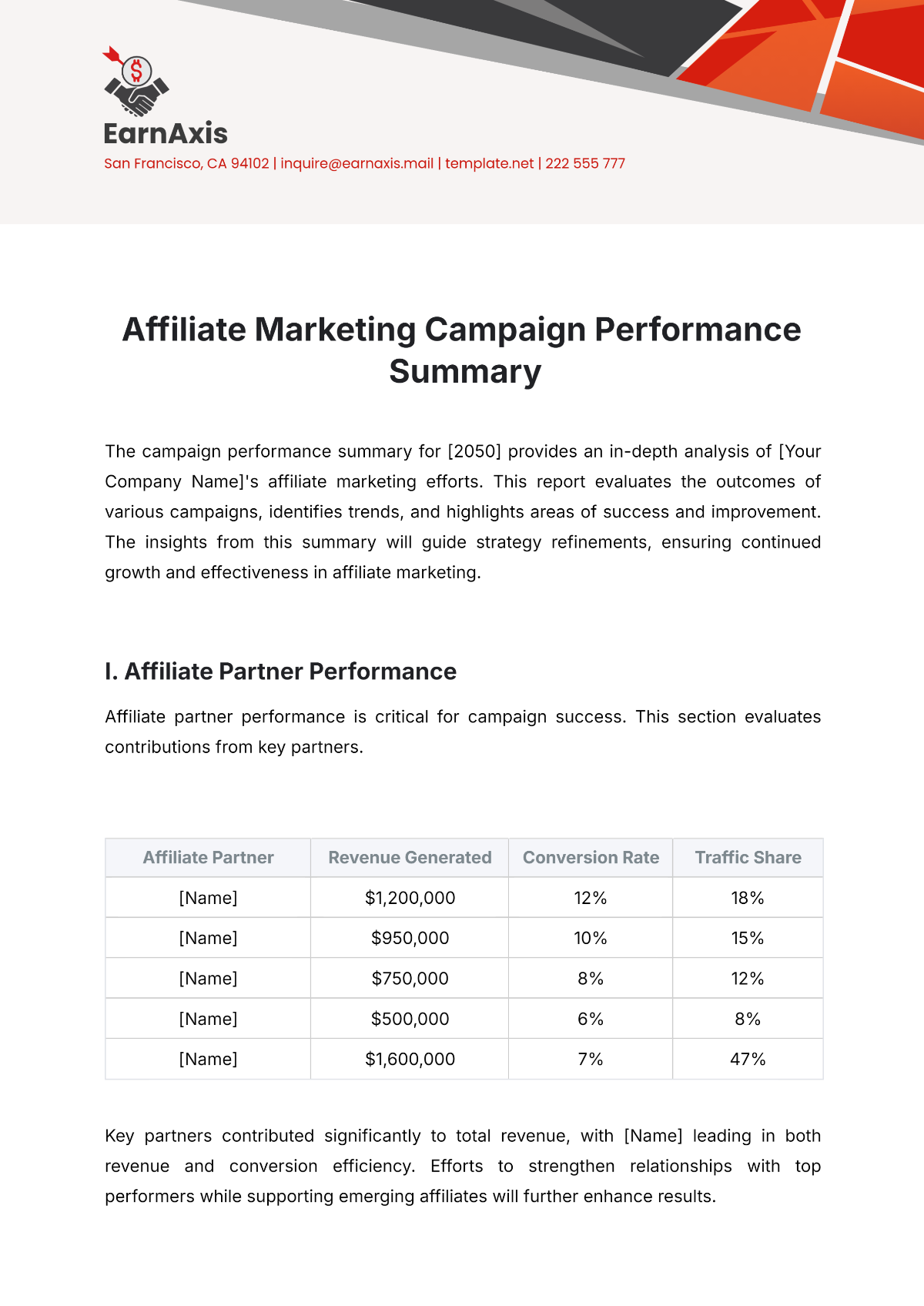
This meta-analysis investigated the efficacy of CBT in treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). The study analyzed data from [INSERT NUMBER] randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving over [INSERT NUMBER] participants. The results demonstrated a significant reduction in anxiety symptoms following CBT compared to control conditions (standardized mean difference = [INSERT EFFECT SIZE], 95% CI [INSERT CONFIDENCE INTERVAL]). See Table 1 for a summary of key findings.
Table 1: Summary of Meta-Analysis Results
Study
Effect Size (ES)
95% Confidence Interval (CI)
Overall (GAD)
[INSERT EFFECT SIZE]
[INSERT CONFIDENCE INTERVAL]
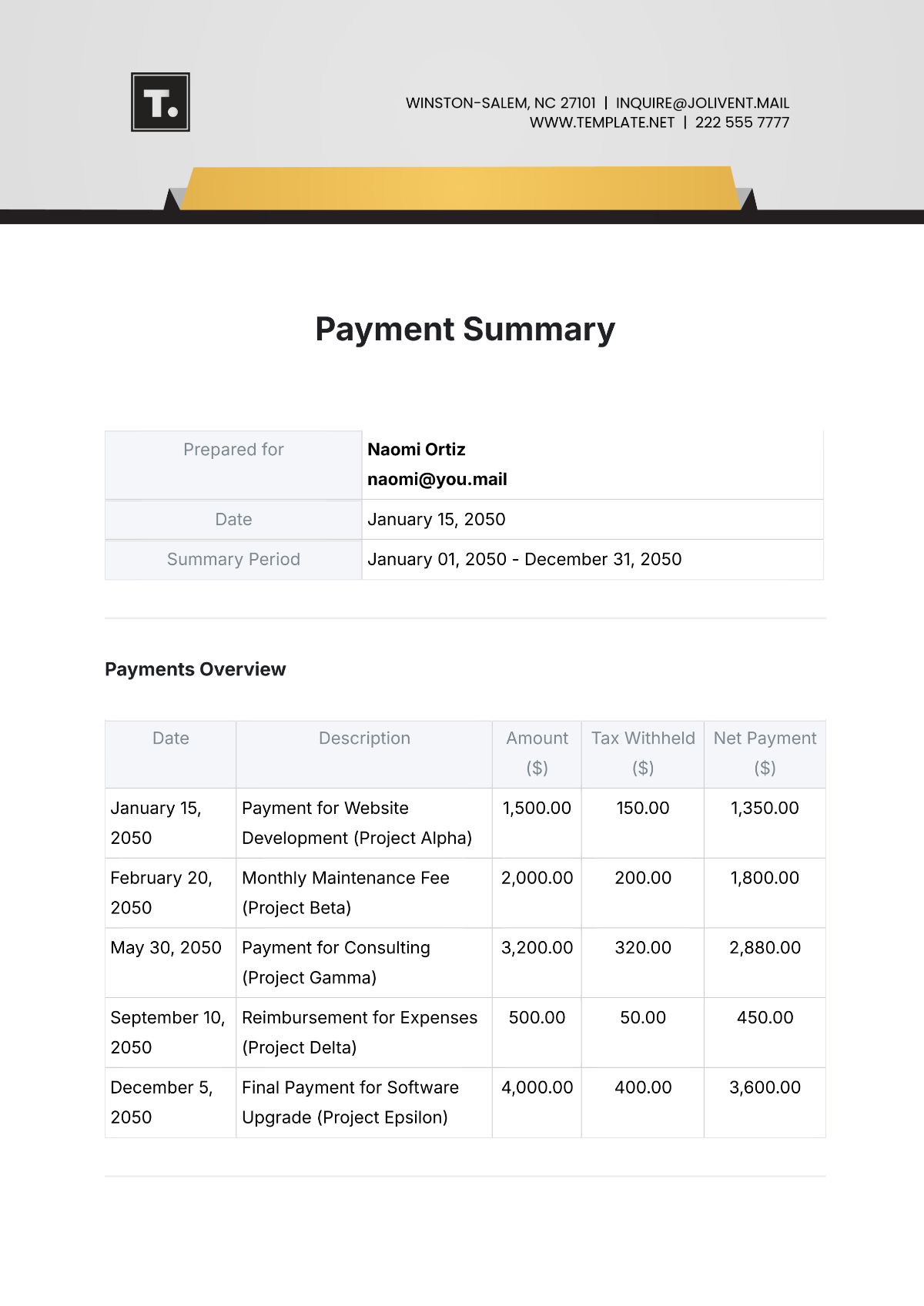
Study 2:
Title: [INSERT TITLE]
Authors: [INSERT AUTHORS]
Journal: [INSERT JOURNAL], [PUBLICATION YEAR]
This longitudinal study examined the enduring effects of CBT on social anxiety disorder (SAD). The researchers followed [INSERT NUMBER] patients over a [INSERT TIME PERIOD] period post-treatment. Results indicated that CBT not only reduced symptoms during treatment but also maintained its effectiveness over the follow-up period, with [INSERT PERCENTAGE] of participants showing sustained improvement. Refer to Table 2 for a summary of long-term outcomes.
Table 2: Long-Term Outcome of CBT in SAD
Follow-Up Period
Sustained Improvement (%)
1 Year
[INSERT PERCENTAGE]
2 Years
[INSERT PERCENTAGE]
3 Years
[INSERT PERCENTAGE]
Discussion and Conclusion
The reviewed studies collectively suggest that cognitive-behavioral therapy is highly effective in treating various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety disorder. The findings support CBT as a recommended psychological intervention due to its robust evidence base and enduring benefits post-treatment.
Implications for Research Methods Students
For students studying research methods, these articles demonstrate the importance of evidence-based practices in psychology. Conducting meta-analyses and longitudinal studies provides valuable insights into treatment effectiveness and long-term outcomes, which are essential considerations for future clinical research and practice.
References
[INSERT FIRST ARTICLE REFERENCE]
[INSERT SECOND ARTICLE REFERENCE]
Action Plan:
Incorporate CBT into clinical practice guidelines for anxiety disorders.
Encourage further research to elucidate mechanisms underlying CBT's effectiveness.
Emphasize methodological rigor in future studies evaluating treatment efficacy and long-term outcomes.
Conclusion
The reviewed studies affirm the efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in treating anxiety disorders, showing significant symptom reductions in both generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and social anxiety disorder (SAD). Meta-analyses demonstrate CBT's superiority over control conditions in GAD treatment, while longitudinal studies reveal sustained improvement in SAD symptoms over multiple years post-treatment. These findings emphasize CBT's status as a recommended intervention for anxiety disorders and highlight the importance of methodological rigor in evaluating treatment efficacy and long-term outcomes.