Grocery Store Employee Training SOP
I. Introduction
A. Purpose
The purpose of this Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is to establish a comprehensive framework for training new employees at [Your Company Name]. This SOP aims to standardize the training process across all departments, ensuring consistent performance, adherence to company policies, and alignment with operational goals. By following this SOP, new hires will gain the necessary knowledge and skills to contribute effectively to our team and deliver exceptional service to our customers.
Effective training is crucial for maintaining our high standards of customer service, operational efficiency, and compliance with health and safety regulations. This document provides detailed steps, procedures, and best practices to achieve these objectives. A well-structured training program not only helps new employees understand their roles and responsibilities but also fosters a positive work environment and supports long-term employee retention.
B. Scope
This SOP applies to all new hires at [Your Company Name], including full-time, part-time, and temporary employees. It covers various roles within the grocery store, including cashiers, stock clerks, customer service representatives, department managers, and other support roles. Each position has specific training requirements tailored to its unique responsibilities and functions.
The training outlined in this SOP encompasses a range of topics essential for job performance, from basic operational procedures to customer service excellence. It ensures that every new employee receives a thorough introduction to the company, its policies, and their specific job functions, facilitating a smooth transition into their new role and setting them up for success.
C. Responsibilities
Store Manager
The Store Manager is responsible for overseeing the implementation of the training program. This includes ensuring that all new hires complete the required training modules, monitoring the effectiveness of the training, and making necessary adjustments to improve the program. The Store Manager provides leadership and support to both trainers and new employees, ensuring that the training process aligns with company objectives and standards.
Department Managers
Department Managers are responsible for conducting role-specific training within their respective departments. They mentor new employees, provide on-the-job training, and offer feedback on performance. Department Managers play a key role in integrating new hires into their teams and ensuring that they understand the specific requirements and expectations of their roles.
Human Resources (HR)
The HR department coordinates the overall onboarding process, including organizing training sessions, maintaining training records, and ensuring that all training activities comply with company policies and legal requirements. HR provides administrative support, addresses training-related issues, and ensures that new hires are properly documented and enrolled in the necessary training programs.
New Employees
New employees are expected to actively engage in all training activities, ask questions when clarification is needed, and adhere to the guidelines provided throughout the training process. It is important for new hires to be proactive in their learning and seek assistance from trainers or managers whenever they encounter challenges or uncertainties.
II. Pre-Training Preparation
A. Training Schedule
Developing the Schedule
The training schedule should be detailed and tailored to accommodate both trainees and trainers. It should outline all specific training activities, including the dates and times for each session. This ensures that training sessions are conducted in a timely manner and that new employees can complete their training without delays.
Flexibility
Flexibility in the training schedule may be necessary to accommodate unforeseen circumstances or varying levels of trainee progress. Allowing for adjustments and additional time if needed helps ensure that all training objectives are met and that new hires receive the support they need to succeed.
B. Training Materials
Preparation of Materials
All necessary training materials should be prepared in advance to facilitate a smooth training process. This includes handbooks, job aids, checklists, and digital resources. Materials should be comprehensive, up-to-date, and designed to facilitate understanding of key concepts and procedures.
Accessibility
Training materials should be accessible to all trainees, whether in physical or digital format. Providing materials in multiple formats accommodates different learning preferences and ensures that all new hires have the resources they need. Digital resources should be easily accessible through the company’s intranet or learning management system.
C. Training Environment
Setup
The training environment should be conducive to learning. This includes setting up a designated training area equipped with necessary tools and resources, such as computers, cash registers, stockroom equipment, and other relevant technology. The environment should be organized and free from distractions to create an optimal learning experience.
Interaction and Practice
The training environment should be arranged to facilitate interaction, discussion, and hands-on practice. Opportunities for trainees to engage with trainers and practice tasks in a controlled setting are essential for effective learning and skill development.
III. Orientation Program
A. Company Overview
History and Mission
New employees should be introduced to [Your Company Name]'s history, mission, and core values. Understanding the company’s foundation, goals, and commitment to customers and employees helps new hires align with the company’s vision and fosters a sense of belonging.
Organizational Structure
Explaining the store's organizational structure helps new hires understand how different departments and roles interact and contribute to the overall success of the company. This includes introducing key departments, their functions, and the reporting lines within the organization.
B. Policies and Procedures
Employee Handbook
The employee handbook is a critical resource that outlines key policies related to attendance, dress code, code of conduct, and other important guidelines. Reviewing the handbook with new employees ensures they are aware of their responsibilities and the standards expected of them.
Health and Safety
Outlining health and safety policies is essential for creating a safe work environment. This includes reviewing emergency procedures, identifying potential workplace hazards, and explaining injury reporting protocols.
C. Employee Benefits
Compensation and Benefits
Explaining the compensation structure, including hourly wages, overtime pay, and benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and employee discounts, helps new hires understand their total compensation package.
Leave Policies
Reviewing leave policies, including vacation, sick leave, and other types of leave, ensures that new employees are aware of their entitlements and the procedures for requesting leave.
IV. Job-Specific Training
A. Cashier Training
1. Operating the Cash Register
Register Setup
New cashiers must learn how to set up and close the cash register, including initializing the register at the start of their shift, setting up the starting cash amount, and closing it out at the end of their shift. Proper setup and closure are essential for accurate cash handling and end-of-day reconciliation.
Transaction Processing
Cashiers should be trained on processing various types of transactions, including cash, credit/debit cards, and checks. This involves learning how to use the register’s functions, handle different payment methods, and process refunds or exchanges when necessary.
2. Customer Interaction
Greeting Customers
Teaching cashiers to greet customers warmly and courteously sets the tone for a positive shopping experience. Effective communication skills, including using friendly language and maintaining a positive attitude, help create a welcoming environment for customers.
Handling Complaints
Providing guidelines for handling customer complaints and escalations equips cashiers with the skills to address issues calmly and professionally. This includes listening to customer concerns, offering solutions, and involving a manager if needed to resolve more complex issues.
3. Accuracy and Efficiency
Error Prevention
Training cashiers to double-check their work, verify prices, and ensure accuracy in transactions helps prevent errors and discrepancies. Emphasizing the importance of attention to detail and careful handling of transactions contributes to overall efficiency.
Speed and Efficiency
Training on techniques to process transactions quickly while maintaining accuracy ensures that cashiers can handle high customer volumes efficiently. This includes learning how to manage multiple transactions, handle peak periods, and maintain a steady workflow.
B. Stock Clerk Training
1. Inventory Management
Stock Replenishment
Training stock clerks on procedures for replenishing shelves, including restocking items and organizing merchandise, ensures that products are available and presented attractively. This involves learning how to prioritize items, manage inventory levels, and maintain store presentation standards.
Stock Rotation
Teaching stock clerks to implement stock rotation techniques, such as first-in-first-out (FIFO), helps manage inventory effectively and reduce spoilage. Proper stock rotation ensures that older products are used before newer ones, minimizing waste and maintaining product quality.
2. Store Organization
Shelf Layout
Training on maintaining an organized shelf layout, including product placement and signage, helps enhance the shopping experience and ensure that products are easy to find. This includes learning how to arrange products according to category, brand, or promotional displays.
Pricing and Tagging
Teaching stock clerks to apply price tags accurately and make pricing changes as needed ensures that products are correctly labeled and priced. This includes training on using pricing tools, updating price tags, and verifying pricing accuracy.
3. Safety and Efficiency
Handling Equipment
Training on the safe use of equipment such as forklifts, pallet jacks, and ladders is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring efficient operations. This includes demonstrating proper handling techniques, conducting safety checks, and following maintenance procedures.
Emergency Procedures
Reviewing procedures for handling spills, breakages, and other emergencies helps stock clerks respond effectively to unexpected situations. This includes training on first aid, emergency reporting, and clean-up procedures.
C. Customer Service Training
1. Communication Skills
Effective Communication
Teaching active listening and effective communication techniques for interacting with customers helps build rapport and resolve issues effectively. This includes training on how to ask open-ended questions, provide clear explanations, and address customer needs.
Problem-Solving
Providing strategies for resolving customer issues and complaints efficiently equips employees with the skills to handle challenging situations. This includes training on how to remain calm under pressure, offer solutions, and follow up to ensure customer satisfaction.
2. Store Policies
Return and Exchange Policies
Ensuring customer service representatives understand and can explain the store’s return and exchange policies helps manage customer expectations and handle returns smoothly. This includes training on the conditions for returns, the process for issuing refunds, and handling exchanges.
Promotions and Discounts
Training on current promotions, discounts, and loyalty programs enables employees to inform customers about available deals and encourage participation in loyalty programs. This includes explaining promotional terms, applying discounts correctly, and answering questions about loyalty rewards.
3. Customer Assistance
Product Locations
Familiarizing employees with the layout of the store and the locations of various products helps them assist customers more effectively. This includes training on store navigation, product placement, and restocking procedures.
Special Services
Training on providing special services, such as gift wrapping, rain checks, and special orders, ensures that employees can offer additional value to customers. This includes demonstrating how to handle special requests and provide personalized service.
V. Department-Specific Training
A. Produce Department
1. Product Handling
Quality Control
Training on identifying and handling high-quality produce involves teaching employees how to select fresh, ripe fruits and vegetables and recognize signs of spoilage. This ensures that customers receive the best quality products and reduces waste.
Storage Requirements
Teaching proper storage techniques for maintaining freshness and preventing spoilage is essential. This includes training on temperature control, proper shelving, and handling guidelines for different types of produce.
2. Customer Service
Product Recommendations
Equipping employees with knowledge to recommend produce based on customer needs helps enhance the shopping experience. This includes training on seasonal produce, recipe suggestions, and nutritional information.
Handling Requests
Training on handling special requests, such as cutting or packaging produce, ensures that employees can meet customer needs efficiently. This includes demonstrating techniques for preparing produce and processing special orders.
B. Meat Department
1. Food Safety
Hygiene Practices
Training on hygiene practices to prevent contamination involves teaching employees proper handwashing techniques, glove use, and cleanliness standards for the meat department. This ensures a safe and sanitary environment for handling meat products.
Temperature Control
Teaching proper temperature control and storage procedures for different types of meat is essential for maintaining food safety. This includes training on refrigerator and freezer temperatures, monitoring meat quality, and handling defrosting procedures.
2. Butchering Skills
Cutting Techniques
Training on basic butchering skills and cutting techniques involves demonstrating how to properly cut and prepare different cuts of meat. This includes teaching knife skills, portion control, and presentation techniques.
Equipment Use
Demonstrating the safe use and maintenance of meat department equipment, such as saws and grinders, ensures that employees can operate machinery safely and effectively. This includes training on cleaning procedures, equipment checks, and troubleshooting common issues.
C. Bakery Department
1. Baking Techniques
Baking Procedures
Training on standard baking procedures includes teaching employees how to mix ingredients, proof dough, and bake products to perfection. This involves understanding baking times, temperatures, and techniques for various baked goods.
Decorating Skills
Teaching basic cake and pastry decorating techniques helps employees create visually appealing products. This includes training on frosting, piping, and using decoration tools to enhance the appearance of baked goods.
2. Customer Orders
Order Management
Training on managing customer orders involves teaching employees how to take orders accurately, schedule pickups, and process payments. This includes using order management systems and ensuring timely fulfillment of orders.
Special Requests
Equipping employees to handle special requests, such as dietary restrictions or custom decorations, ensures that they can meet diverse customer needs. This includes understanding dietary requirements, customizing orders, and communicating with customers effectively.
VI. Evaluation and Feedback
A. Performance Evaluation
Assessment Criteria
Establishing clear criteria for evaluating employee performance helps ensure that assessments are fair and objective. Criteria may include job knowledge, skills proficiency, customer service, and adherence to company policies.
Evaluation Process
Conducting regular performance evaluations, including both formal and informal assessments, helps track employee progress and identify areas for improvement. This includes setting goals, providing feedback, and discussing performance with employees.
B. Continuous Improvement
Ongoing Training
Implementing ongoing training and development programs helps employees stay updated on new procedures, products, and industry trends. This includes offering refresher courses, advanced training, and opportunities for professional growth.
Feedback Mechanisms
Establishing feedback mechanisms, such as surveys and suggestion boxes, allows employees to provide input on the training process and suggest improvements. This helps identify areas where the training program can be enhanced and ensures that it meets the needs of employees.
VII. Documentation and Records
A. Training Records
Record Keeping
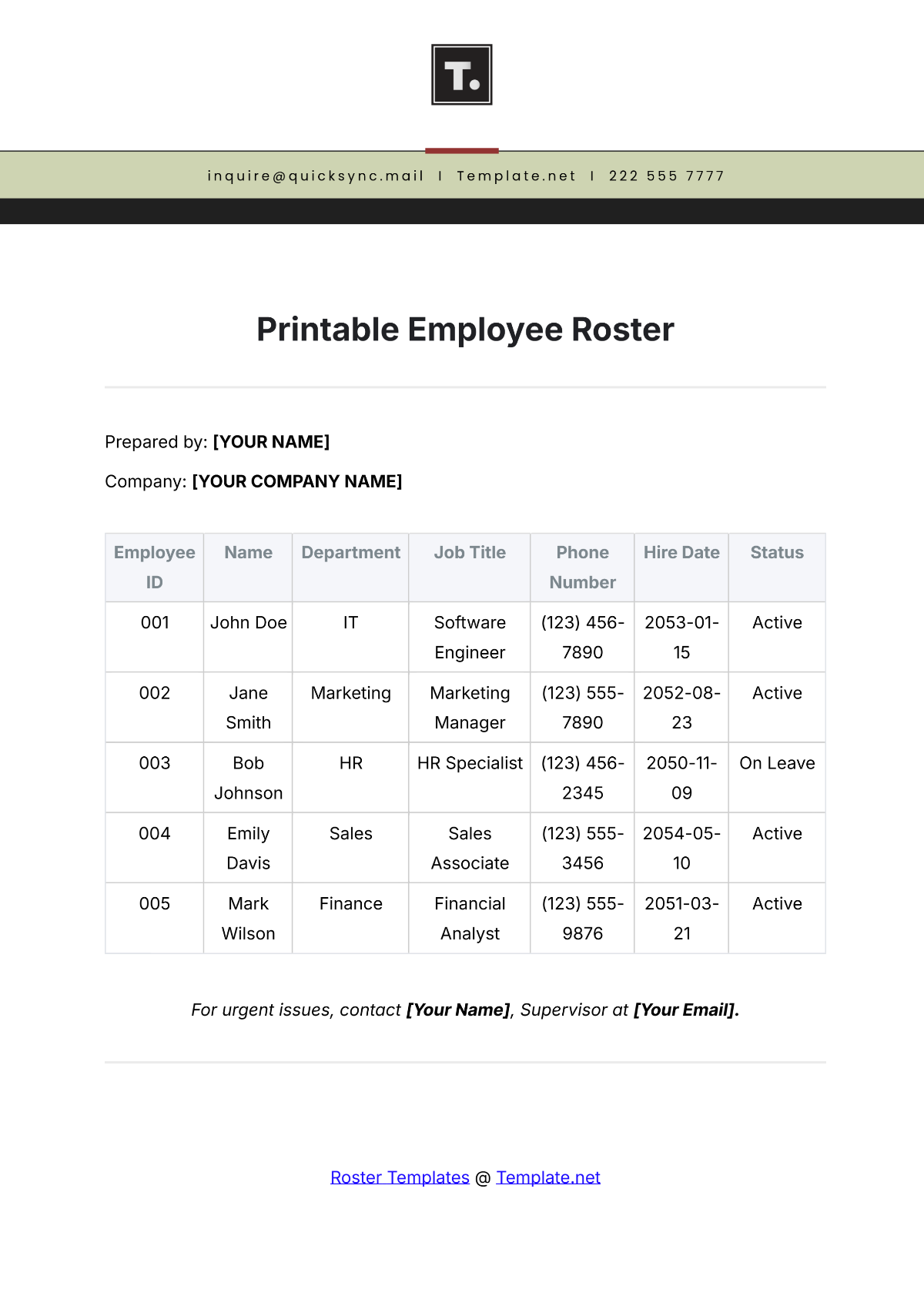
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date training records is essential for tracking employee progress and ensuring compliance with training requirements. This includes documenting completed training modules, assessment results, and any additional certifications obtained.
Access and Confidentiality
Ensuring that training records are accessible to authorized personnel only and are kept confidential protects employee privacy and maintains the integrity of the training process. This includes implementing secure storage practices and restricting access to sensitive information.
B. Training Materials
Updating Materials
Regularly reviewing and updating training materials ensures that they remain current and relevant. This includes revising content to reflect changes in company policies, procedures, and industry standards.
Archiving
Archiving outdated training materials and records helps maintain an organized system and ensures that historical data is preserved for reference. This includes storing materials in a manner that allows for easy retrieval and review when needed.