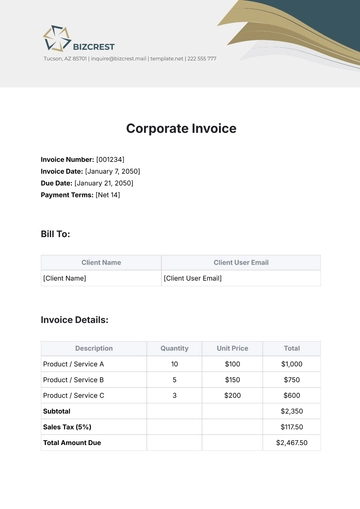
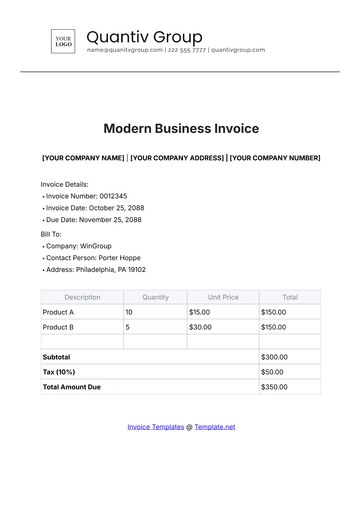
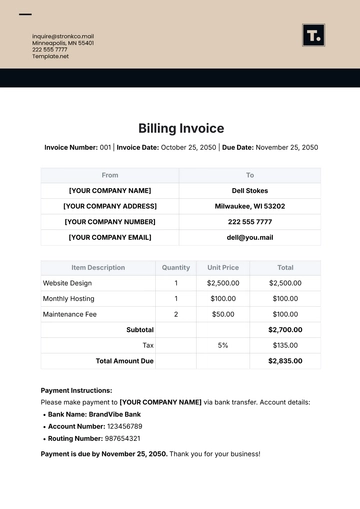
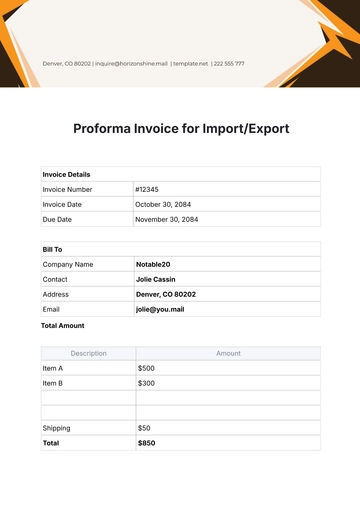
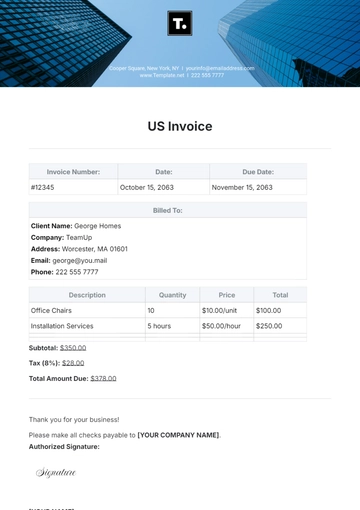
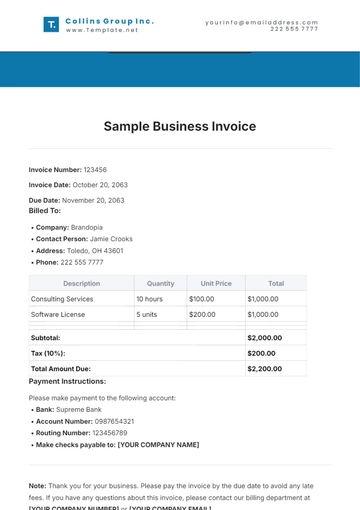
Free Financial Invoice Management

1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose
The purpose of this Financial Invoice Management template is to establish a standardized approach to managing invoices within [Your Company Name]. Effective invoice management is crucial for maintaining financial control, ensuring timely payments, and fostering positive relationships with vendors. By following the guidelines outlined in this document, [Your Company Name] aims to minimize errors, reduce payment delays, and enhance overall financial efficiency.
1.2 Scope
This template applies to all departments within [Your Company Name] involved in the processing, approval, and payment of invoices. It covers the entire invoice lifecycle, from receipt to payment, and includes guidelines for record-keeping and compliance. This document is relevant to the Finance Department, Accounts Payable Team, Department Managers, and all vendors and suppliers engaged with [Your Company Name].
1.3 Objectives
The primary objectives of this Financial Invoice Management template are:
To streamline the invoice management process, reducing processing time and errors.
To ensure compliance with financial regulations and contractual obligations.
To maintain accurate financial records for auditing and reporting purposes.
To improve vendor relationships through timely payments and transparent communication.
To leverage technology for automating and optimizing invoice management tasks.
2. Roles and Responsibilities
2.1 Finance Department
The Finance Department is responsible for overseeing the entire invoice management process at [Your Company Name]. This includes setting policies, monitoring compliance, and ensuring that all financial transactions are accurately recorded. The Finance Department also plays a key role in financial reporting, using data from invoices to generate reports that reflect the company’s financial health.
2.2 Accounts Payable Team
The Accounts Payable (AP) Team is directly responsible for processing invoices. Their duties include verifying invoice accuracy, obtaining necessary approvals, and ensuring that payments are made within agreed-upon terms. The AP Team must work closely with other departments to resolve any discrepancies or issues that may arise during the invoice approval process.
2.3 Department Managers
Department Managers are responsible for approving invoices related to their departments. They must ensure that invoices are accurate and correspond with the services or goods received. Department Managers are also accountable for managing their department’s budget and ensuring that all expenditures are within approved limits.
2.4 Vendors and Suppliers
Vendors and Suppliers are external stakeholders who provide goods or services to [Your Company Name]. They are responsible for submitting accurate invoices that comply with the terms outlined in their contracts. Vendors must also ensure that invoices are submitted on time to avoid payment delays.
3. Invoice Management Process
3.1 Invoice Receipt
Invoices can be received through various channels, including mail, email, or electronic data interchange (EDI). Upon receipt, invoices must be logged into the invoice management system to track their status and ensure timely processing. It is essential to verify that each invoice contains all necessary information, including the vendor’s details, invoice number, date, and a clear description of the goods or services provided.
3.2 Invoice Verification
Invoice verification involves checking the accuracy and validity of the invoice. This includes confirming that the goods or services were received as described, verifying the pricing and terms, and ensuring that the invoice is free from errors. Verification should also include matching the invoice against purchase orders and delivery receipts. Any discrepancies should be addressed promptly with the vendor to prevent delays in payment.
3.3 Invoice Approval
Once verified, invoices must be routed to the appropriate Department Manager for approval. Approval signifies that the goods or services have been satisfactorily received, and the expenditure is within budget. Depending on the value of the invoice, additional approvals from senior management or the Finance Department may be required. A clear and transparent approval process is critical to maintaining accountability and preventing unauthorized payments.
3.4 Payment Processing
After approval, the invoice is forwarded to the Accounts Payable Team for payment processing. Payments should be made according to the terms agreed upon with the vendor, whether it’s through check, electronic funds transfer (EFT), or another method. It is important to ensure that payments are made on time to maintain good relationships with vendors and avoid late fees.
3.5 Record Keeping and Documentation
Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential for financial transparency and audit purposes. All invoices, along with their corresponding purchase orders, receipts, and approvals, should be stored securely. Electronic storage systems can help organize and retrieve records quickly, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies.
4. Invoice Management Tools
4.1 Invoice Management Software
Utilizing invoice management software can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of the invoice management process. The software should support features like automated data entry, approval workflows, and integration with existing financial systems. Implementing such software reduces manual work, minimizes errors, and allows for real-time tracking of invoice status.
4.2 Integration with Financial Systems
Integrating invoice management software with existing financial systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or accounting software, ensures a seamless flow of data. This integration enables better financial reporting, real-time visibility into cash flow, and easier reconciliation of accounts. [Your Company Name] should prioritize software solutions that offer robust integration capabilities.
4.3 Data Security Measures
Data security is a critical aspect of invoice management, especially when handling sensitive financial information. Invoice management systems should incorporate strong encryption, secure access controls, and regular backups to protect data from unauthorized access or loss. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, should also be a top priority.
5. Monitoring and Reporting
5.1 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of the invoice management process. Important KPIs include the average time to process an invoice, the percentage of invoices processed without errors, and the rate of on-time payments. Regularly monitoring these KPIs allows [Your Company Name] to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
5.2 Regular Audits
Conducting regular audits of the invoice management process ensures compliance with internal policies and external regulations. Audits help identify discrepancies, inefficiencies, and potential risks, providing an opportunity to implement corrective actions. The Finance Department should schedule audits periodically and document findings to enhance transparency and accountability.
5.3 Exception Handling
Not all invoices will follow the standard process. Exceptions, such as disputed invoices, missing documentation, or incorrect billing, require a clear procedure for resolution. Establishing an exception-handling protocol ensures that these issues are addressed promptly and do not disrupt the overall process. The protocol should include steps for investigating the issue, communicating with the vendor, and documenting the resolution.
5.4 Continuous Improvement
The invoice management process should be continuously evaluated and refined to improve efficiency and accuracy. [Your Company Name] should gather feedback from all stakeholders, monitor industry trends, and explore new technologies that could enhance the process. Continuous improvement efforts should focus on reducing processing times, minimizing errors, and increasing automation.
6. Compliance and Legal Considerations
6.1 Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with financial regulations is a critical aspect of invoice management. [Your Company Name] must ensure that all invoice-related activities adhere to relevant laws, such as tax regulations, anti-fraud measures, and financial reporting standards. Non-compliance can result in legal penalties, financial losses, and reputational damage.
6.2 Tax Considerations
Invoices play a crucial role in tax reporting and compliance. Accurate invoice management ensures that [Your Company Name] can claim appropriate tax deductions, report income correctly, and avoid disputes with tax authorities. The Finance Department should stay updated on tax laws and ensure that invoices are stored and reported in accordance with these regulations.
6.3 Contractual Obligations
Invoices must align with the contractual terms agreed upon with vendors and suppliers. This includes adhering to payment terms, pricing, and delivery schedules. Failure to comply with contractual obligations can lead to disputes, penalties, and strained relationships with key vendors. [Your Company Name] should ensure that all contracts are carefully reviewed, and that the invoice management process is aligned with these agreements. This involves maintaining clear communication with vendors to confirm that the terms are fully understood and adhered to by both parties. Any changes or amendments to contracts should be documented and reflected in the invoice management system to avoid misunderstandings.
7. Best Practices
7.1 Standardization
Standardizing the invoice management process is essential for consistency and efficiency. [Your Company Name] should develop standardized templates for invoices, approval forms, and communication with vendors. This reduces the likelihood of errors, simplifies training for new employees, and ensures that all stakeholders follow the same procedures. Standardization also facilitates easier auditing and reporting, as all records will follow a uniform format.
7.2 Automation
Automation is a key driver of efficiency in invoice management. By automating repetitive tasks such as data entry, invoice matching, and payment scheduling, [Your Company Name] can significantly reduce processing time and minimize the risk of human error. Automated reminders and notifications can also help ensure that invoices are processed and paid on time, improving cash flow management and vendor relationships. As technology evolves, [Your Company Name] should continually explore new automation tools to further optimize the process.
7.3 Vendor Relationship Management
Strong relationships with vendors are vital for smooth invoice management. [Your Company Name] should prioritize clear and transparent communication with vendors to address any issues promptly. Establishing regular check-ins or meetings with key vendors can help resolve concerns before they escalate. Additionally, offering incentives for early payment or discounts can strengthen relationships and create opportunities for better terms in future negotiations.
8. Training and Development
8.1 Employee Training Programs
Effective invoice management requires that all employees involved in the process are well-trained and knowledgeable about their roles. [Your Company Name] should implement comprehensive training programs that cover all aspects of invoice management, including receipt, verification, approval, and payment. Training should also emphasize the importance of compliance with internal policies and external regulations. Regular refresher courses and updates on new tools or processes should be provided to ensure that employees remain proficient and up to date.
8.2 Ongoing Support and Development
Training should not be a one-time event. [Your Company Name] should offer ongoing support and development opportunities for employees to continuously improve their skills and adapt to changes in the industry. This could include access to online courses, workshops, or certifications in financial management. Encouraging a culture of continuous learning will help maintain high standards in invoice management and prepare the company for future challenges.
9. Future Considerations
9.1 Technological Advancements
The future of invoice management will be shaped by technological advancements. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and blockchain have the potential to revolutionize the way invoices are processed, verified, and stored. [Your Company Name] should actively monitor developments in these areas and consider investing in new tools that can further automate and secure the invoice management process. By staying ahead of the curve, [Your Company Name] can maintain a competitive edge and ensure that its financial operations are as efficient and secure as possible.
9.2 Scalability
As [Your Company Name] grows, its invoice management needs will evolve. It is essential to design a process that is scalable and can handle increased volumes of invoices without compromising accuracy or efficiency. This may involve upgrading software, expanding the Accounts Payable Team, or revising procedures to accommodate larger and more complex transactions. Planning for scalability ensures that the invoice management process can support the company’s growth and adapt to changing business needs.
9.3 Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in financial management. [Your Company Name] should consider adopting practices that reduce the environmental impact of invoice management, such as transitioning to paperless invoicing, using energy-efficient data storage solutions, and minimizing waste. In addition to the environmental benefits, sustainable practices can also lead to cost savings and enhance the company’s reputation with stakeholders who value corporate responsibility.
10. Conclusion
10.1 Summary
Financial Invoice Management is a critical component of [Your Company Name]'s overall financial health. By implementing a structured and standardized approach to invoice processing, [Your Company Name] can achieve greater efficiency, reduce errors, and maintain compliance with regulatory and contractual obligations. This template has outlined the key aspects of effective invoice management, including roles and responsibilities, the invoice management process, tools and technology, monitoring and reporting, and future considerations.
10.2 Next Steps
To fully implement the Financial Invoice Management system outlined in this template, [Your Company Name] should take the following steps:
Review and customize this template to align with the company’s specific needs and organizational structure.
Train relevant employees on the procedures and tools described in this document.
Implement the recommended tools and technologies to automate and streamline the invoice management process.
Establish a monitoring system to track KPIs, conduct regular audits, and continuously improve the process.
Plan for future growth and sustainability by adopting scalable and environmentally friendly practices.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Ready to streamline your invoicing process? The Financial Invoice Management Template on Template.net is your ultimate solution! This editable template helps you keep track of invoices, payments, and transactions effortlessly. Customize it to match your business needs—editable in our AI Editor Tool. Download now and take control of your finances!
You may also like
- Invoice Outline
- Creative Invoice
- Modern Invoice
- Printable Invoice
- Business Invoice
- Travel Invoice
- Rent Invoice
- Commercial Invoice
- Professional Invoice
- Restaurant Invoice
- Small Business Invoice
- Travel Agency Invoice
- Car Invoice
- Repair Invoice
- School Invoice
- Proforma Invoice
- Hotel Invoice
- Company Invoice
- Medical Invoice
- University Invoice
- Self Employed Invoice
- Accounting Invoice
- Real Estate Invoice
- Vehicle Invoice
- Consultant Invoice
- Sales Invoice
- Startup Invoice
- Cleaning Invoice
- Agency Invoice
- Legal Invoice
- Construction Invoice
- Tax Invoice
- Bakery Invoice
- Services Invoice
- Freelancer Invoice
- Rental Invoice
- IT and Software Invoice
- Cash Invoice
- Notary Invoice
- Catering Invoice
- Auto Repair Invoice
- Automotive Invoice
- Work form Home Invoice
- Photography Invoice