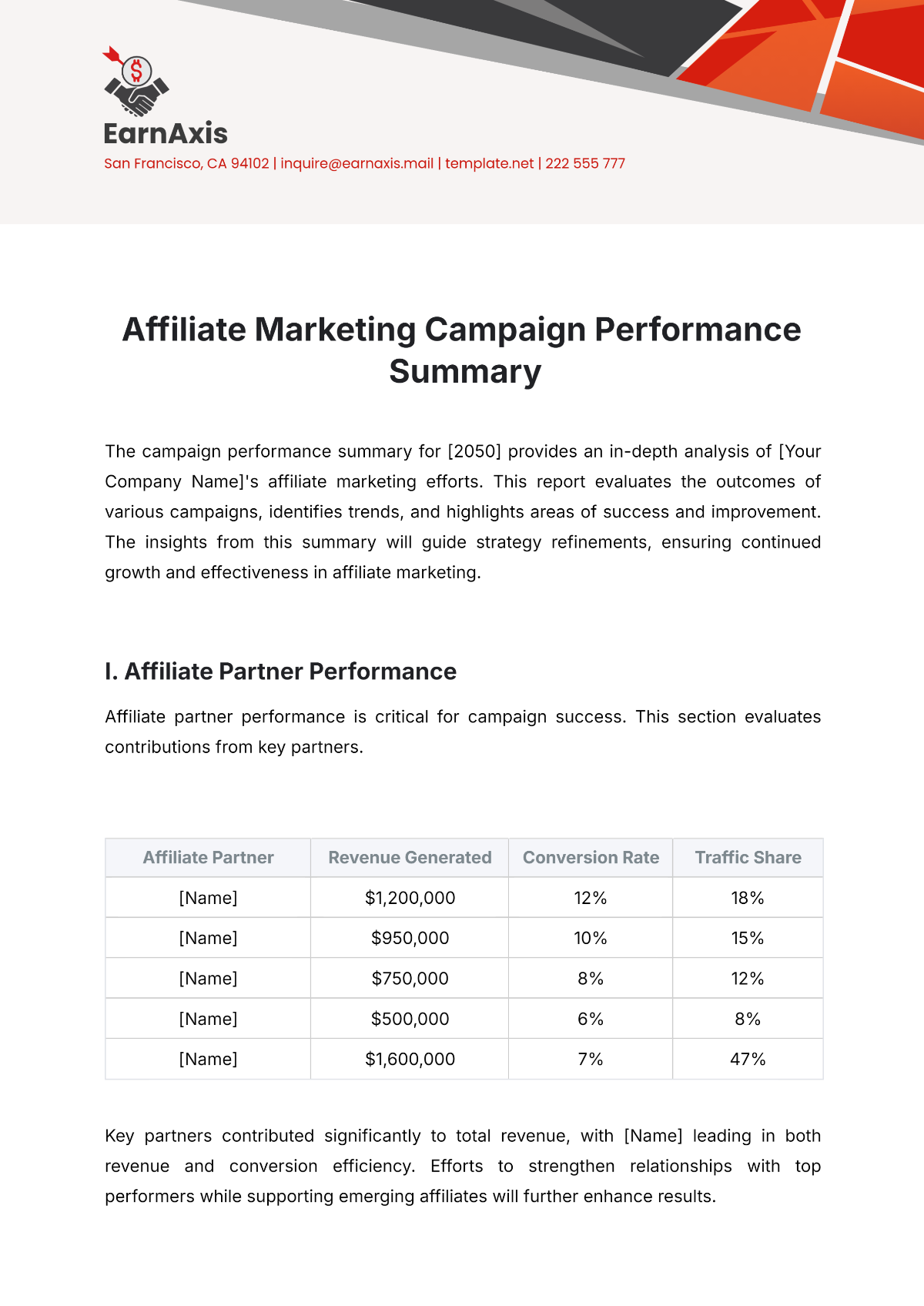
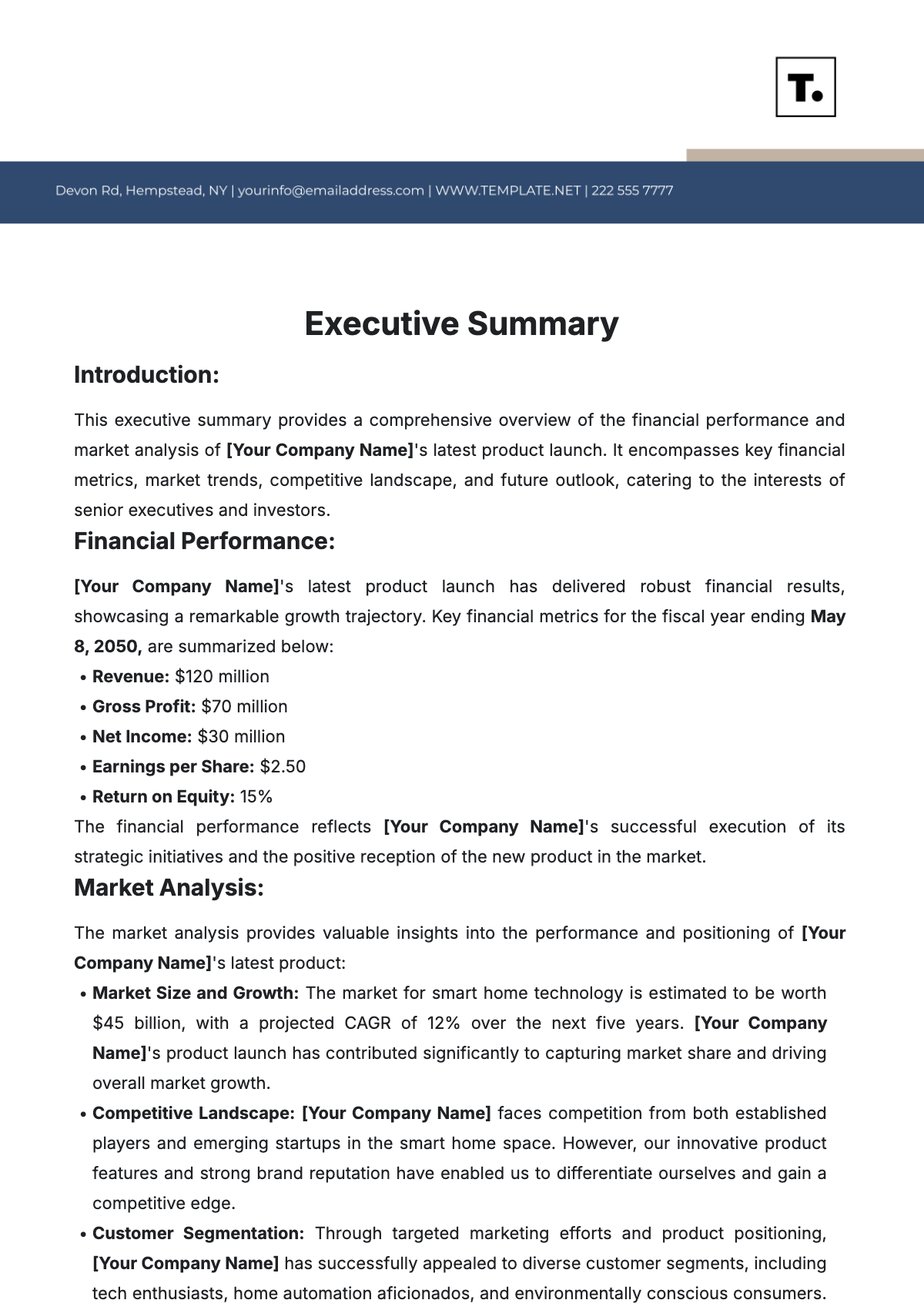
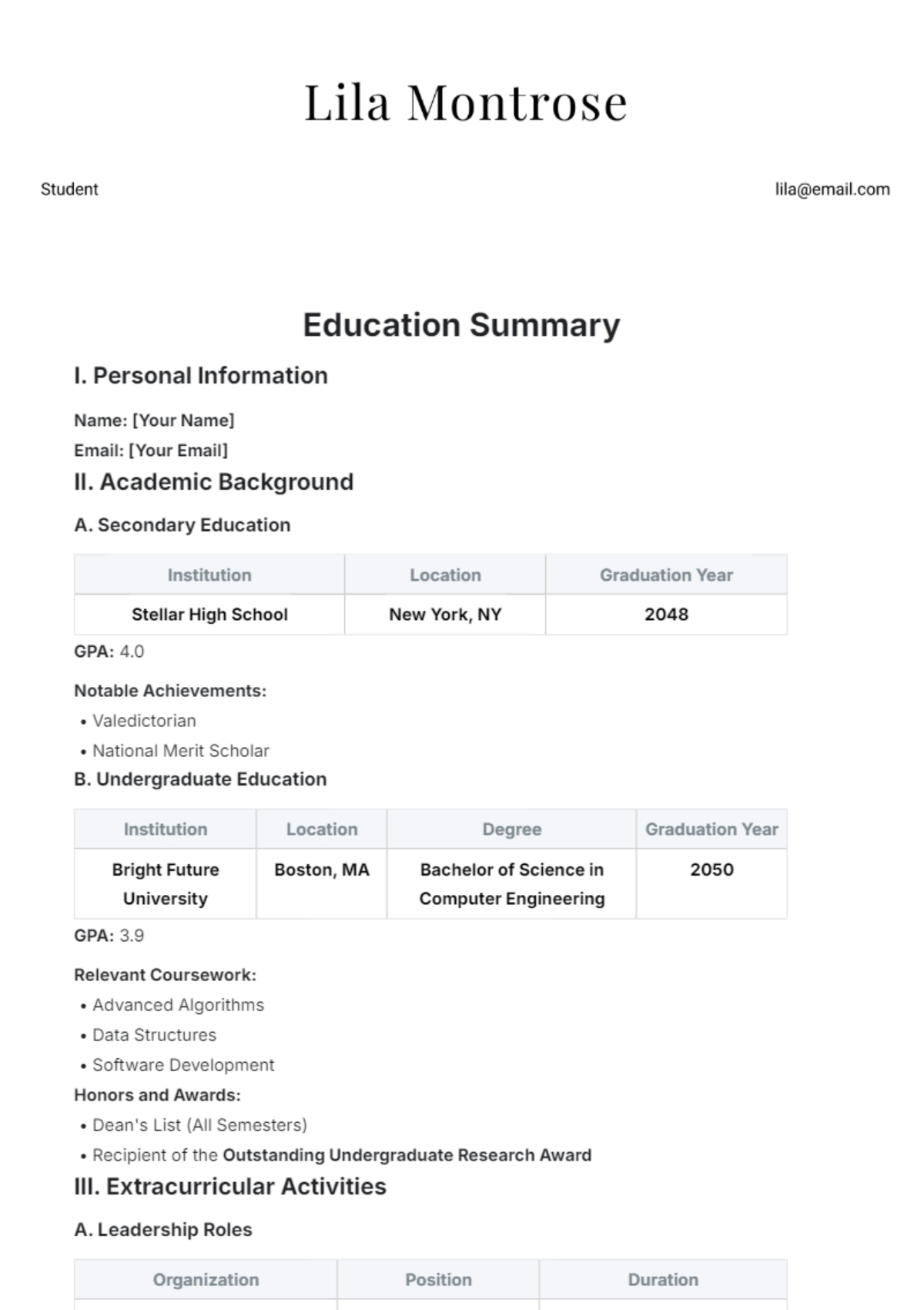
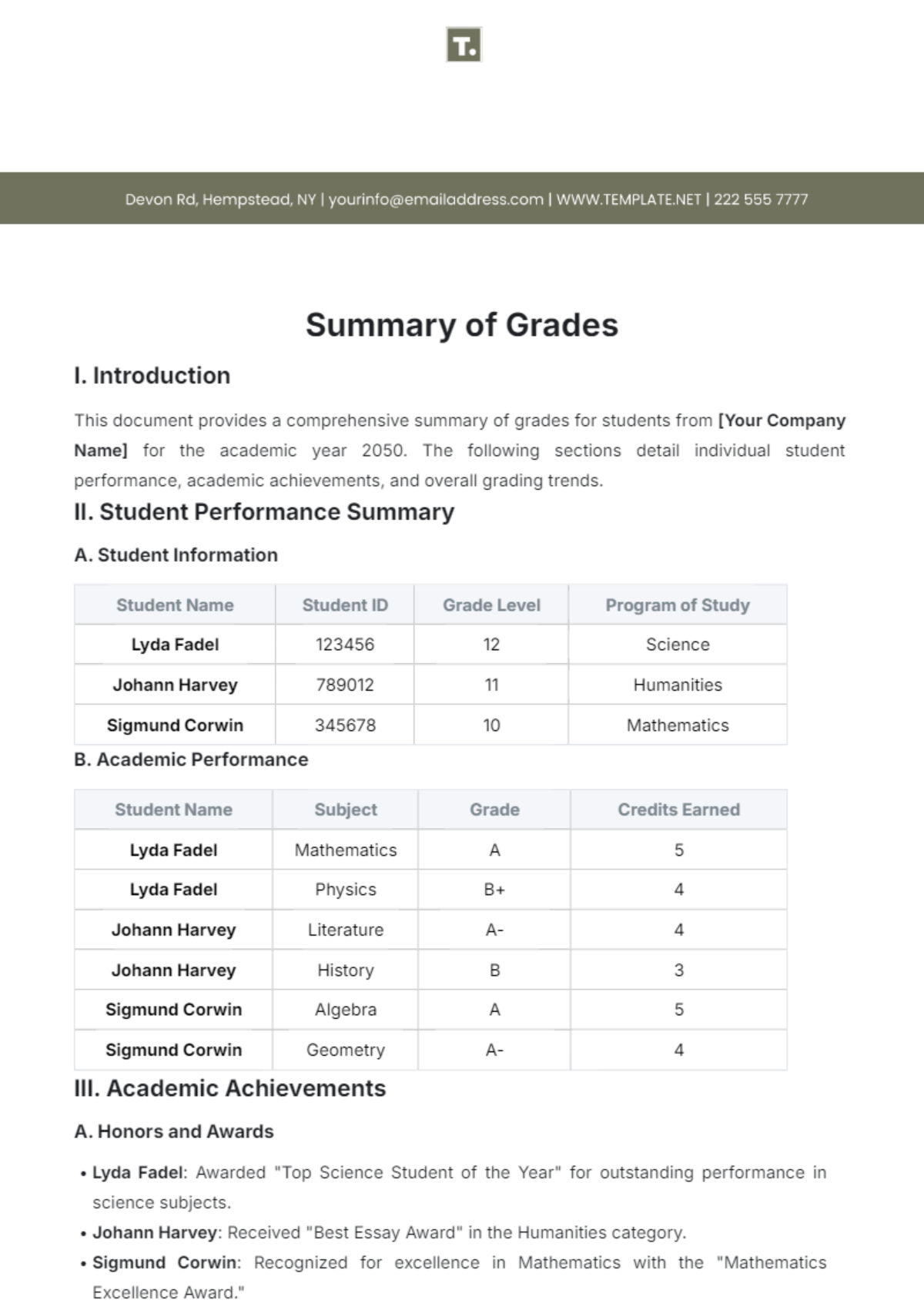
Journal Summary Article
Title: The Impact of Remote Work on Employee Productivity: A Longitudinal Study
Prepared by: [Your Name]
Date: [Date]
I. Abstract
This study investigates the influence of remote work on employee productivity from 2050 to 2051. Utilizing a mixed-methods approach, researchers gathered quantitative data through productivity metrics and qualitative feedback via surveys and interviews. The results reveal that remote work can enhance productivity for certain tasks while presenting challenges in team collaboration and communication. The study concludes with actionable recommendations for optimizing remote work practices and fostering effective virtual teamwork.
II. Introduction
With the rapid evolution of work environments in the 21st century, remote work has become a prevalent model. This study examines the effects of remote work on employee productivity, focusing on how this shift has influenced performance metrics and employee experiences over the past year. The research aims to fill existing gaps in understanding the multifaceted impact of remote work on job performance and organizational efficiency.
III. Methods
The research employed a longitudinal design, tracking 250 employees across diverse sectors from January 2050 to December 2051. Data collection involved performance metrics such as task completion rates and quality of work, along with qualitative insights obtained through semi-structured surveys and interviews. This comprehensive approach allowed for a nuanced analysis of both numerical productivity measures and employee perspectives.
IV. Results
The study demonstrated that remote work led to a 20% increase in productivity for tasks requiring focused, uninterrupted effort. Employees reported higher efficiency in completing individual assignments and projects. Conversely, challenges emerged in areas requiring team interaction, with a 12% decrease in collaborative productivity. Issues such as communication breakdowns and difficulties in maintaining team cohesion were prevalent among remote teams.
V. Discussion
The findings indicate that remote work significantly boosts productivity for individual tasks by minimizing distractions and allowing flexible work hours. However, the decline in team-based productivity highlights the need for improved virtual collaboration strategies. The study underscores the importance of investing in technologies and practices that facilitate effective communication and teamwork in a remote setting.
VI. Conclusion
Remote work can enhance productivity for tasks requiring individual focus but may complicate team-based efforts. Organizations should adopt tools and strategies to improve virtual collaboration and support employees in overcoming challenges associated with remote work. Future research should focus on developing and testing interventions to balance productivity gains with effective team dynamics in remote work environments.
VII. References
Thompson, A. (2050). Remote Work and Employee Efficiency: A Future-Oriented Review. Journal of Future Business Studies, 58(1), 45-68.
Nguyen, P., & Patel, R. (2051). Strategies for Effective Remote Team Collaboration: Insights and Recommendations. International Journal of Advanced Management, 42(3), 112-130.