Project Management Procedures
1. Introduction
This document outlines the procedures for managing projects within [Your Company Name]. It aims to ensure consistent and effective project execution, promoting successful delivery of projects on time and within budget.
2. Project Initiation
2.1. Project Proposal
Submit Project Proposal: Initiating parties must submit a detailed project proposal to the Project Management Office (PMO).
Proposal Review: The PMO reviews the proposal for alignment with organizational goals, feasibility, and resource requirements.
Approval: The proposal must be approved by the Project Sponsor and key stakeholders before proceeding.
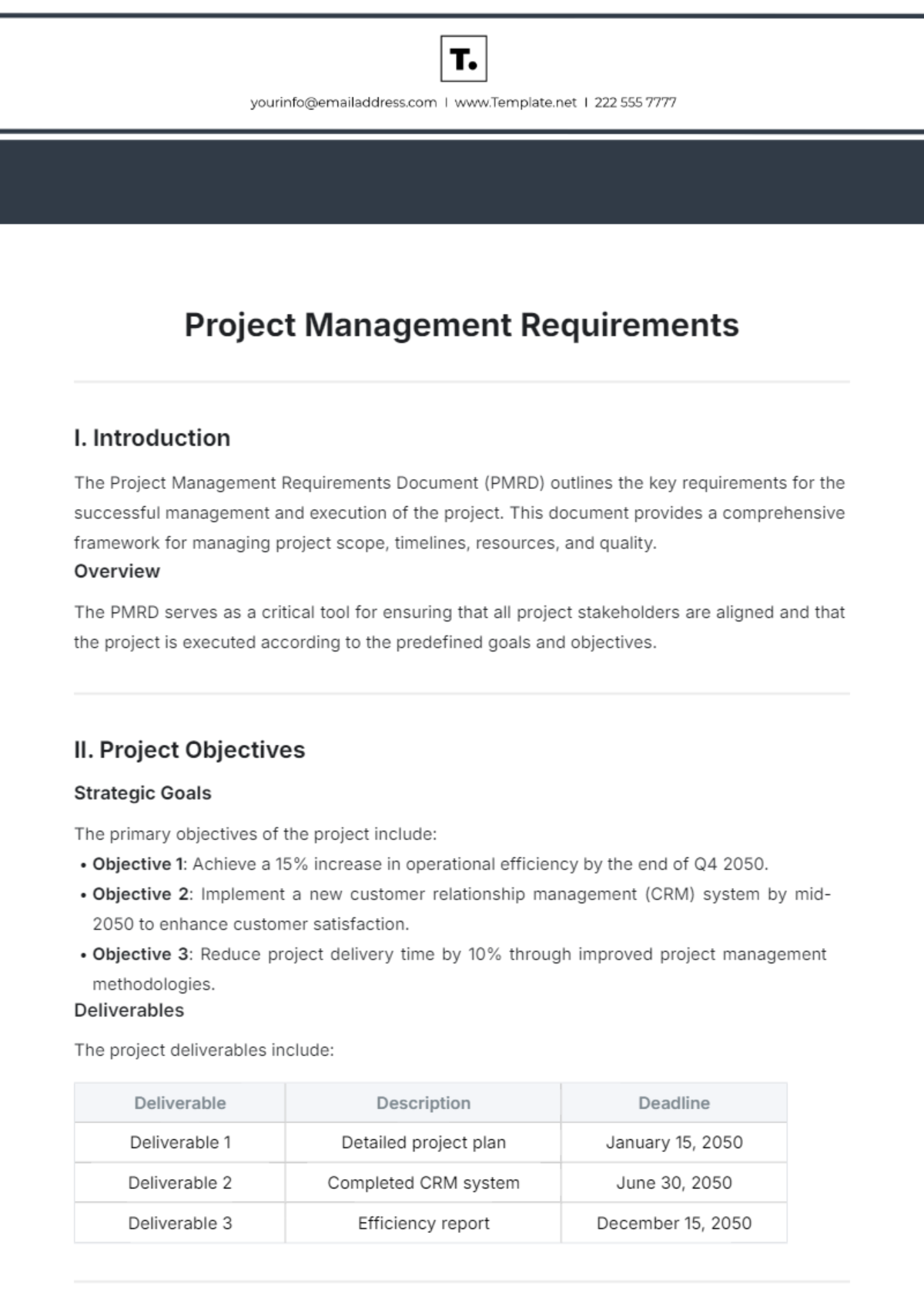
2.2. Project Charter
Create Project Charter: Develop a Project Charter that includes project objectives, scope, stakeholders, and high-level timeline.
Charter Approval: Obtain formal approval of the Project Charter from the Project Sponsor and key stakeholders.
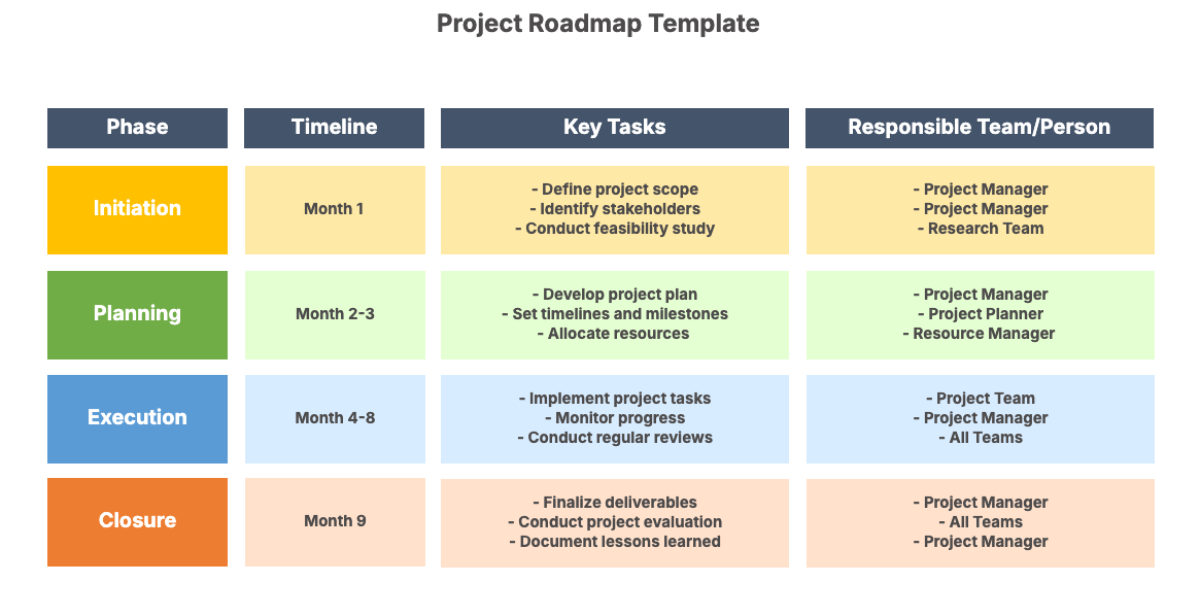
3. Project Planning
3.1. Scope Definition
Define Scope: Develop a detailed scope statement outlining project deliverables, boundaries, and constraints.
Scope Baseline: Obtain approval of the scope baseline from the Project Sponsor.
3.2. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Create WBS: Develop a Work Breakdown Structure that decomposes the project into manageable tasks and deliverables.
WBS Approval: Ensure the WBS is reviewed and approved by the Project Sponsor and relevant stakeholders.
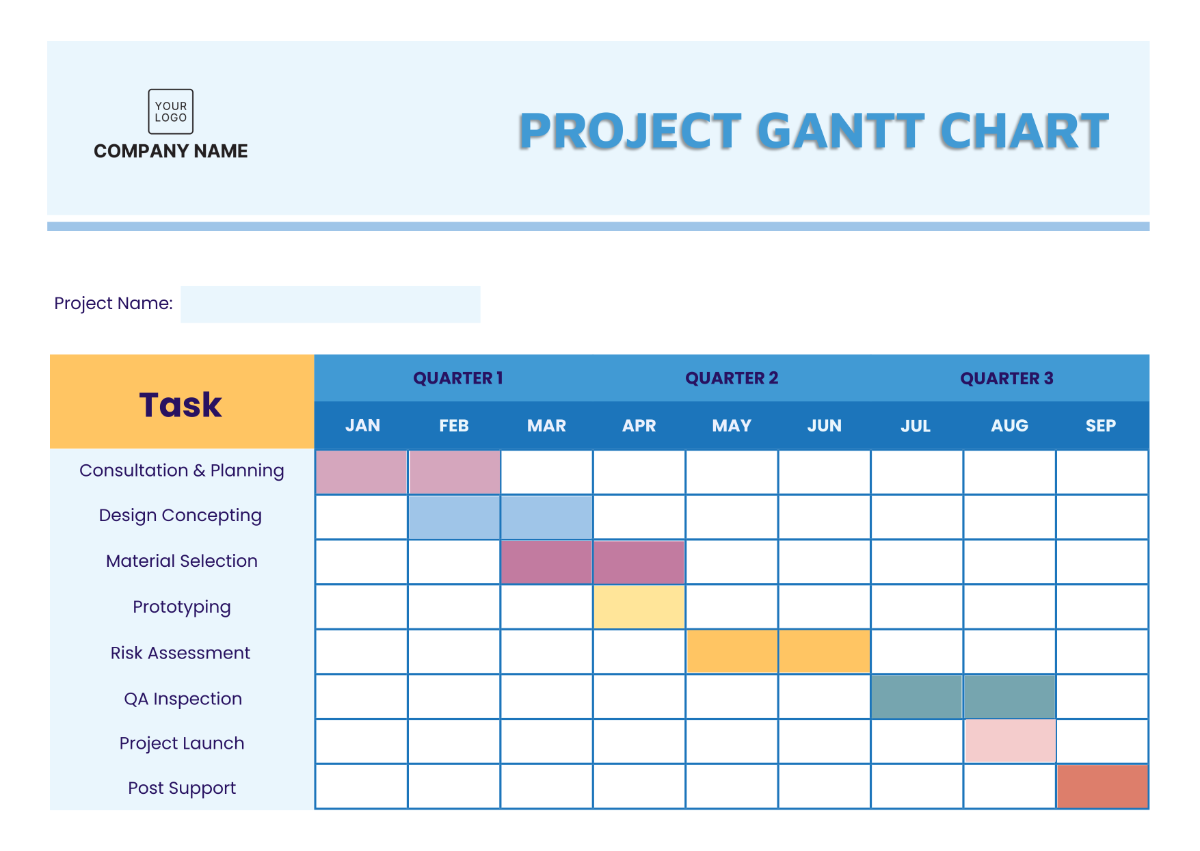
3.3. Schedule Development
Develop Schedule: Create a detailed project schedule including all tasks, milestones, and dependencies.
Schedule Review: Review and obtain approval of the schedule from the Project Sponsor and stakeholders.
3.4. Resource Planning
Identify Resources: Determine the necessary resources (human, material, financial) required for project execution.
Allocate Resources: Allocate resources based on availability and project needs, ensuring optimal utilization.
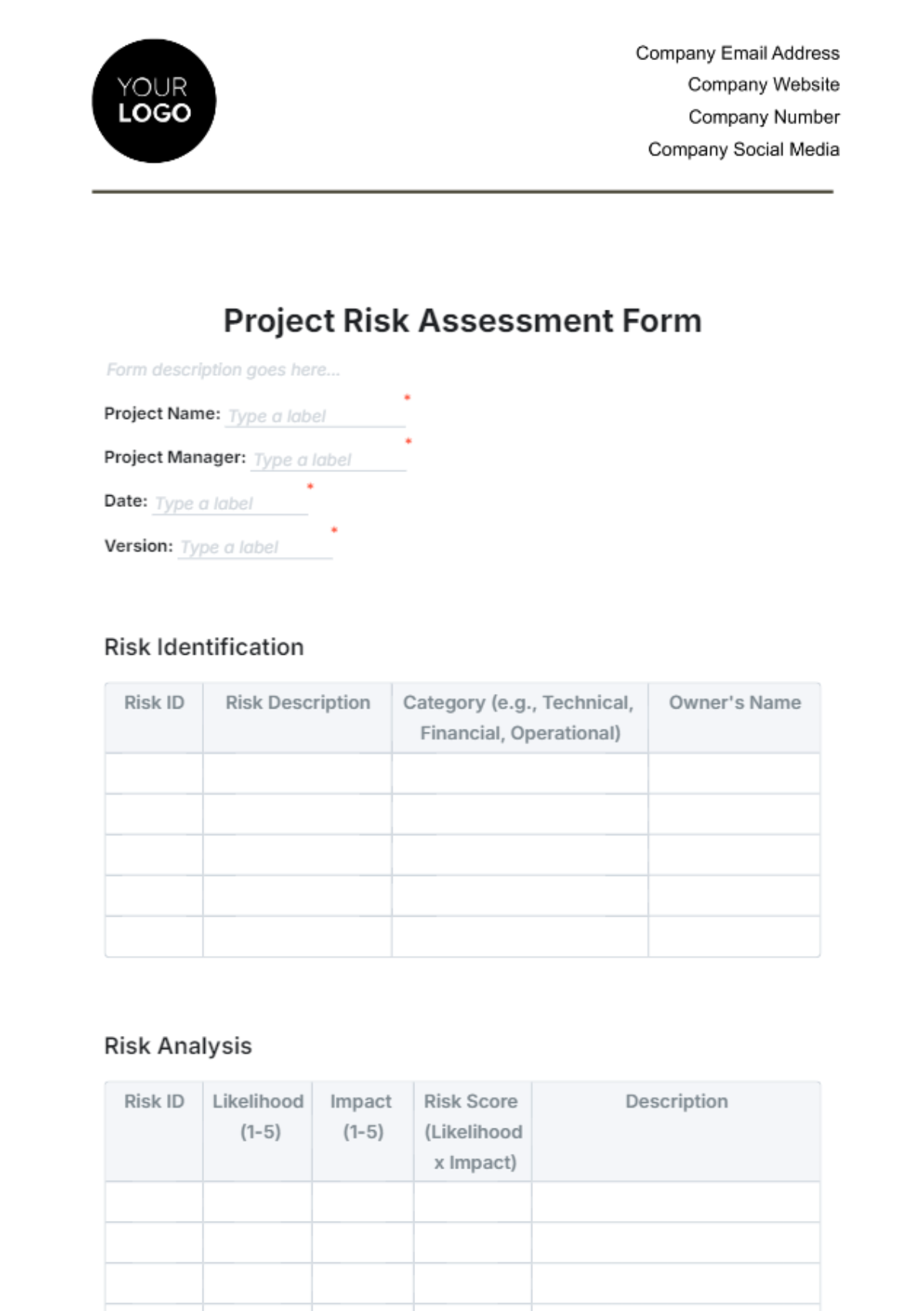
3.5. Risk Management
Identify Risks: Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential risks and their impact on the project.
Develop Risk Mitigation Plan: Create a risk management plan outlining strategies to mitigate identified risks.
Risk Monitoring: Continuously monitor and review risks throughout the project lifecycle.
4. Project Execution
4.1. Task Management
Execute Tasks: Carry out project tasks as per the project plan and WBS.
Monitor Progress: Track progress against the project schedule and scope.
4.2. Quality Assurance
Implement Quality Controls: Ensure that deliverables meet the required quality standards and specifications.
Conduct Reviews: Perform regular quality reviews and inspections to maintain standards.
4.3. Communication
Maintain Communication: Regularly communicate project status, issues, and updates to stakeholders.
Report Issues: Report any significant issues or changes in project scope to the Project Sponsor and stakeholders promptly.
5. Project Monitoring and Control
5.1. Performance Tracking
Monitor Performance: Track project performance against the project plan, including schedule, cost, and quality metrics.
Control Changes: Manage changes to the project scope, schedule, or resources through a formal change control process.
5.2. Status Reporting
Generate Reports: Prepare and distribute regular status reports to stakeholders, highlighting progress, issues, and risks.
5.3. Issue Management
Identify Issues: Detect and document any issues impacting project progress.
Resolve Issues: Implement corrective actions to address and resolve issues promptly.
6. Project Closure
6.1. Final Deliverables
Complete Deliverables: Ensure all project deliverables are completed and meet acceptance criteria.
Obtain Acceptance: Secure formal acceptance of deliverables from the Project Sponsor and stakeholders.
6.2. Documentation
Document Lessons Learned: Compile and document lessons learned throughout the project lifecycle.
Final Report: Prepare a final project report summarizing project performance, outcomes, and recommendations.
6.3. Closeout
Close Project: Complete administrative closeout tasks, including finalizing contracts and releasing resources.
Conduct Review: Perform a post-project review with the team and stakeholders to assess project success and identify areas for improvement.
7. References
[Company Project Management Framework]
[Project Management Software User Guide]
[Risk Management Guidelines]