Sales Process Methodology
I. Introduction
The Sales Process Methodology is structured to streamline sales activities, enhance customer relationships, and drive revenue growth. This methodology is critical for ensuring consistency, improving efficiency, and achieving measurable results across the sales team. Its systematic nature helps sales professionals navigate the complexities of selling while maintaining a customer-centric focus.
II. Sales Stages
Stage | Description |
|---|---|
1. Prospecting |
|
2. Qualifying |
|
3. Presenting |
|
4. Closing |
|
5. Post-Sale Follow-Up |
|
III. Key Activities
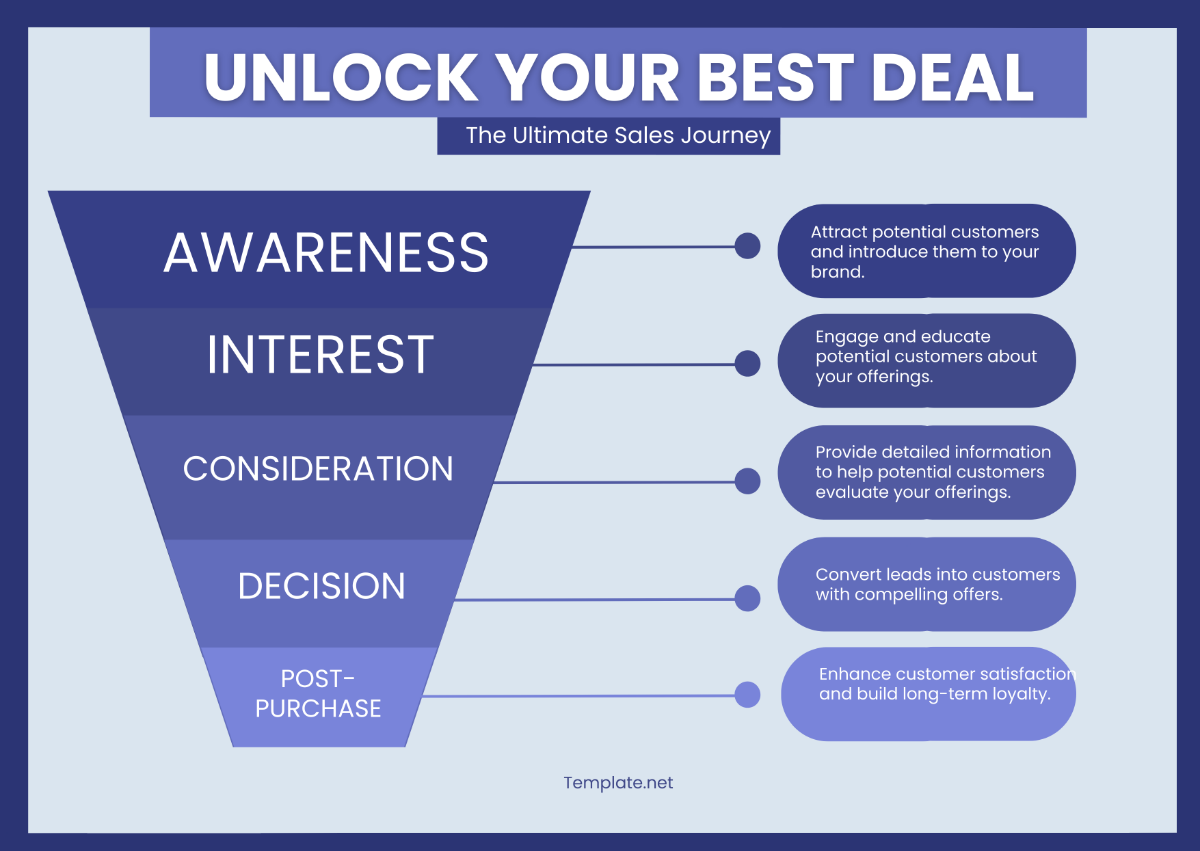
1. Prospecting
Investigate possible prospects using different avenues like social media, industry events, and recommendations.
Establish and maintain a comprehensive repository of potential leads to ensure a consistent and ongoing stream of prospective clients or customers.
Engage in proactive outreach activities, including cold calls, emails, and networking events, to connect with potential leads.
2. Qualifying
Perform introductory consultation calls to thoroughly grasp the prospect's requirements, obstacles, and objectives.
Utilize qualifying frameworks, such as BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timeline), to assess the prospect’s readiness to purchase.
Evaluate and prioritize potential leads by rigorously analyzing them against specific criteria to focus on those with the highest chance of successful conversion.
3. Presenting
Develop and deliver customized presentations and demonstrations that highlight the product or service's features and benefits tailored to the prospect's specific needs.
Evaluate the prospect's challenges and offer tailored solutions that highlight specific benefits and address their needs.
Build credibility by showcasing case studies and authentic customer testimonials. Highlight problem-solving success and measurable results to reassure potential clients.
4. Closing
Engage in tactical negotiations about pricing and conditions to achieve a fair and mutually advantageous agreement.
Promptly address any objections and questions to resolve concerns and facilitate the decision-making process effectively.
Secure formal agreements, finalize contracts, and complete all necessary paperwork to convert the prospect into a customer.
5. Post-Sale Follow-Up
Organize detailed onboarding sessions aimed at ensuring new users or clients experience a smooth transition and complete integration of the product or service.
Regularly check in with customers to monitor satisfaction and address any issues, ensuring high standards of service and strong relationships.
Identify and pursue opportunities for additional sales, upselling, or cross-selling to enhance customer value and foster long-term relationships.
IV. Tools and Resources
Effective sales processes are supported by various tools and resources designed to enhance productivity and efficiency.
CRM Software (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot): Manages customer relationships, tracks interactions, and provides insights to streamline workflows and improve engagement.
Email Marketing Tools (e.g., MailChimp, Constant Contact): Executes targeted outreach and nurturing campaigns with personalized communication and automated follow-ups.
Presentation Tools (e.g., PowerPoint, Prezi): Creates compelling sales presentations that highlight features and benefits effectively.
Analytics Platforms (e.g., Google Analytics, Tableau): Measures and analyzes sales data to provide insights into trends and performance for informed decision-making.
Communication Tools (e.g., Zoom, Slack): Facilitates timely and effective communication with prospects and team members through virtual meetings and real-time collaboration.
V. Metrics and KPIs
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are crucial for assessing the effectiveness of the sales process and pinpointing areas for improvement:
Lead Conversion Rate: Measures the percentage of leads that successfully convert into paying customers. This KPI helps evaluate the efficiency of the sales team in closing deals.
Sales Cycle Length: Tracks the average duration from the initial contact with a prospect to the finalization of a sale. This metric provides insights into the speed and efficiency of the sales process.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculates the total cost incurred to acquire a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses. It is essential for assessing the profitability of customer acquisition strategies.
Average Deal Size: This represents the average revenue generated from each closed deal. This KPI helps in understanding the value of sales and the effectiveness of upselling or cross-selling strategies.
Customer Retention Rate: Indicates the percentage of customers who continue to engage with the business over a specified period. This metric is vital for evaluating customer satisfaction and the success of relationship management efforts.
VI. Best Practices
Implementing the sales process methodology effectively requires adherence to certain best practices:
Always prioritize and integrate a customer-centric approach in every part of the organization’s operations and interactions, making the customer's needs, preferences, and satisfaction the main focus of all decisions and actions.
Consistently and methodically review, revise, and purge the lead database to maintain and uphold a high standard of data accuracy and integrity.
Leverage insights that are obtained through the careful analysis and interpretation of data to guarantee that the decisions made are both well-informed and thoughtfully considered.
Make it a priority to provide ongoing training and education for the sales team, ensuring they are consistently kept up-to-date on the newest and most effective techniques and tools available.
Encourage and facilitate cooperative efforts and effective communication among the sales team, the marketing team, and the customer service team to ensure seamless and productive interactions that benefit the organization as a whole.
VII. Training and Support
A. Initial Training
Initial Training | Description |
|---|---|
Comprehensive Onboarding Sessions |
|
Workshops and Role-Playing Exercises |
|
Detailed Training on Sales Tools and CRM Systems |
|
B. Ongoing Support
Regular Training Updates: Offer scheduled updates on new tools, market trends, and emerging sales techniques to keep the team informed and adaptable.
Knowledge Base and Online Resources: Provide access to a comprehensive knowledge base and online resources for self-paced learning and quick reference.
Personalized Coaching and Mentoring: Arrange one-on-one coaching and mentoring sessions to offer tailored guidance, address individual challenges, and support professional development.