HR Document Management
I. Introduction
A. Overview
In the rapidly evolving business landscape of 2050 and beyond, effective Human Resources (HR) Document Management is critical for the success and compliance of any organization. [Your Company Name] recognizes the importance of systematically managing HR documents to ensure efficiency, security, and accessibility. This comprehensive HR Document Management Plan outlines the policies, procedures, and responsibilities necessary for the management of HR documents throughout their lifecycle—from creation to eventual disposal.
B. Purpose
The primary purpose of this HR Document Management Plan is to establish a structured approach for the management of all HR-related documents within [Your Company Name]. This plan aims to streamline processes, enhance data security, ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, and support decision-making processes by providing easy access to accurate and up-to-date information.
C. Scope
This plan applies to all HR documents within [Your Company Name], including but not limited to employee records, recruitment documents, training materials, performance evaluations, payroll records, benefits documentation, and compliance records. It covers both physical and digital documents and applies to all departments and personnel involved in the creation, handling, and management of HR documents.
II. HR Document Management Policies
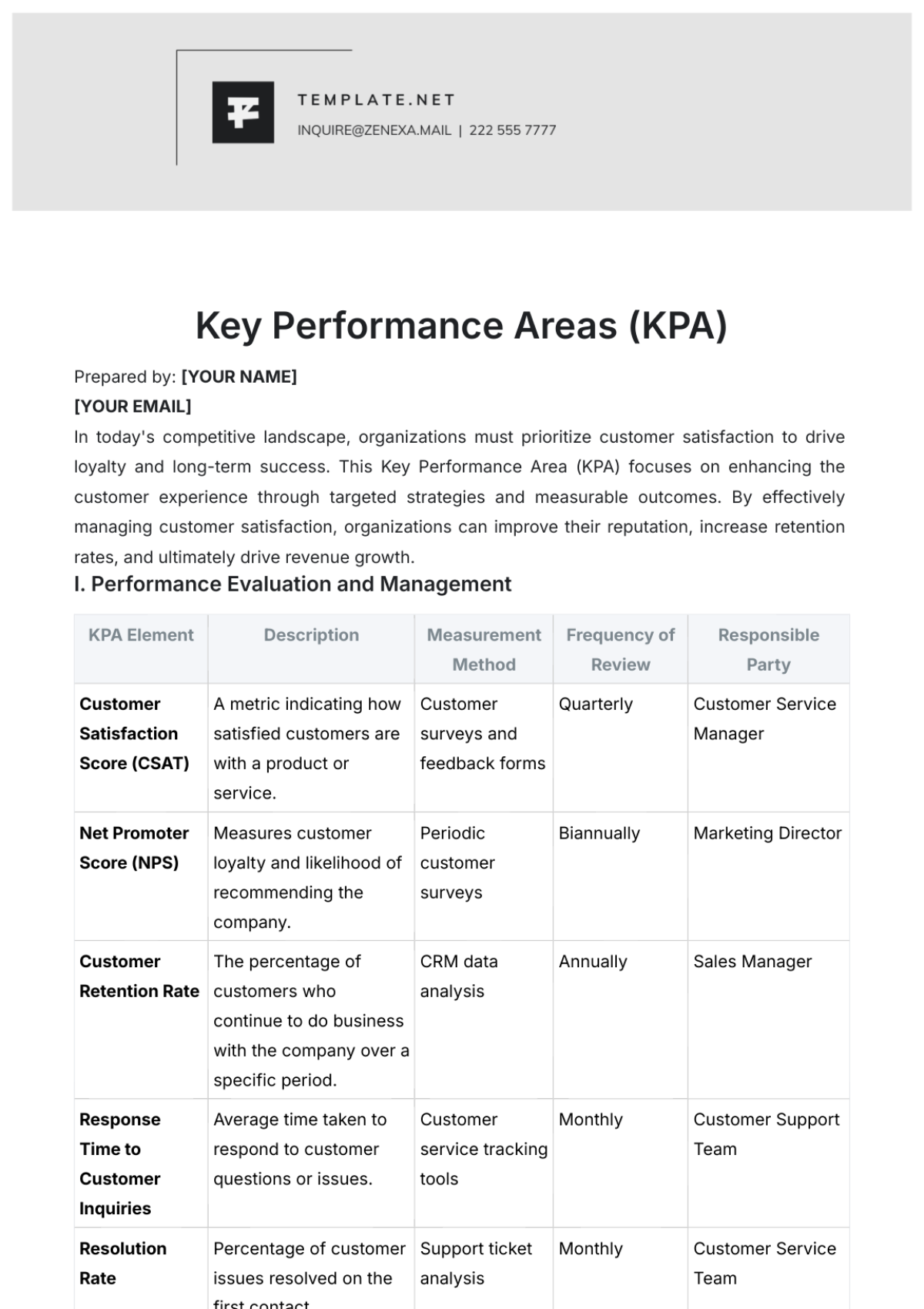
A. Document Classification
1. Types of HR Documents
HR documents at [Your Company Name] are classified into several categories, including:
Employee Records: This includes personal information, employment contracts, performance reviews, and disciplinary actions.
Recruitment Documents: Job descriptions, interview records, and onboarding documents.
Training Materials: Documents related to employee training programs, certifications, and professional development.
Payroll Records: Payroll statements, tax documents, and benefits information.
Compliance Records: Documents required for legal and regulatory compliance, such as labor law acknowledgments and safety training records.
2. Sensitivity Levels
Documents are also classified based on their sensitivity:
Confidential: Sensitive information such as employee personal data and payroll details.
Restricted: Internal documents such as performance evaluations and disciplinary records.
Public: Documents that can be shared publicly, such as job postings and general training materials.
B. Document Retention and Disposal
1. Retention Periods
[Your Company Name] has established specific retention periods for each category of HR documents, as outlined in the table below:
Document Type | Retention Period | Justification |
|---|---|---|
Employee Records | 7 years after termination | To comply with labor laws and legal requirements |
Recruitment Documents | 3 years | To maintain records of hiring decisions |
Training Materials | 5 years | For ongoing training verification and auditing |
Payroll Records | 10 years | To comply with tax regulations |
Compliance Records | 7 years | For legal compliance and auditing purposes |
2. Disposal Procedures
Disposal of HR documents is conducted in accordance with the sensitivity level of the documents. For physical documents, shredding is the preferred method of disposal, ensuring that no sensitive information is recoverable. Digital documents are permanently deleted from all systems, including backups, using secure deletion tools to prevent unauthorized recovery.
C. Document Access and Security
1. Access Controls
Access to HR documents is restricted based on the role and responsibilities of employees within [Your Company Name]. The following access controls are in place:
HR Managers: Full access to all HR documents.
Department Heads: Access to documents related to their respective departments.
Employees: Access to their personal records, performance reviews, and training records.
2. Security Measures
To protect HR documents from unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction, [Your Company Name] has implemented the following security measures:
Physical Security: HR documents are stored in locked filing cabinets in secure areas with restricted access.
Digital Security: Digital documents are stored on encrypted servers with multi-factor authentication (MFA) for access. Regular security audits and updates are conducted to ensure data protection.
III. HR Document Management Procedures
A. Document Creation and Capture
1. Standardized Document Templates
[Your Company Name] utilizes standardized templates for creating HR documents to ensure consistency and accuracy. Templates are available for common documents such as employment contracts, performance reviews, and disciplinary notices. These templates include pre-approved language and formats, reducing the risk of errors and omissions.
2. Document Capture and Filing
All HR documents, whether created electronically or on paper, are captured and filed according to the established classification system. Digital documents are uploaded to the HR Document Management System (HRDMS), while physical documents are scanned and stored electronically, with the originals securely archived.
B. Document Storage
1. Digital Document Management
[Your Company Name] relies on an advanced HRDMS to manage digital HR documents. The system allows for secure storage, retrieval, and sharing of documents, with features such as version control, audit trails, and automated retention scheduling. The HRDMS is backed up regularly to prevent data loss in case of system failures.
2. Physical Document Management
Physical HR documents are stored in a centralized location, organized by document type and sensitivity level. The storage area is equipped with fireproof cabinets and climate control to preserve document integrity. Regular audits are conducted to ensure documents are stored according to policy.
C. Document Retrieval and Use
1. Document Search and Retrieval
The HRDMS includes a powerful search function that allows authorized personnel to quickly locate and retrieve HR documents based on keywords, categories, or metadata. This ensures that documents are easily accessible when needed for decision-making, audits, or employee inquiries.
2. Document Use and Sharing
When HR documents are used or shared, [Your Company Name] ensures that the proper protocols are followed. Sensitive documents are only shared with individuals who have the appropriate clearance, and digital documents are shared using secure methods such as encrypted email or secure file-sharing platforms.
D. Document Archiving
1. Archiving Process
HR documents that are no longer in active use but must be retained for legal or historical purposes are archived. The archiving process involves transferring documents from active storage to a secure, long-term storage facility, either physically or within the HRDMS. Archived documents are indexed for easy retrieval if needed in the future.
2. Archival Maintenance
Archived documents are periodically reviewed to ensure they remain intact and accessible. Digital archives are checked for data integrity, and physical archives are inspected for signs of deterioration or damage. Any issues identified are promptly addressed to preserve the longevity of the documents.
IV. Compliance and Legal Considerations
A. Legal Requirements
1. Compliance with Labor Laws
[Your Company Name] adheres to all relevant labor laws and regulations in managing HR documents. This includes maintaining accurate employee records, ensuring the privacy of personal information, and retaining documents for the legally required periods. Regular compliance audits are conducted to verify adherence to legal standards.
2. Data Protection Regulations
In the year 2050, data protection regulations have become increasingly stringent. [Your Company Name] complies with global data protection laws, such as the Global Data Protection Regulation (GDPR 2050) and the Data Privacy Act (DPA 2050). This involves obtaining employee consent for data collection, ensuring the secure storage of personal data, and providing employees with the right to access and correct their information.
B. Risk Management
1. Risk Assessment
To mitigate risks associated with HR document management, [Your Company Name] conducts regular risk assessments. These assessments identify potential vulnerabilities in the document management process, such as the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, or loss of critical documents. Based on the assessment findings, appropriate risk mitigation strategies are implemented.
2. Contingency Planning
As part of the risk management process, [Your Company Name] has developed contingency plans to address potential disruptions to HR document management. These plans include protocols for responding to data breaches, natural disasters, and system failures. Backup procedures are in place to ensure that critical HR documents can be quickly restored in the event of an emergency.
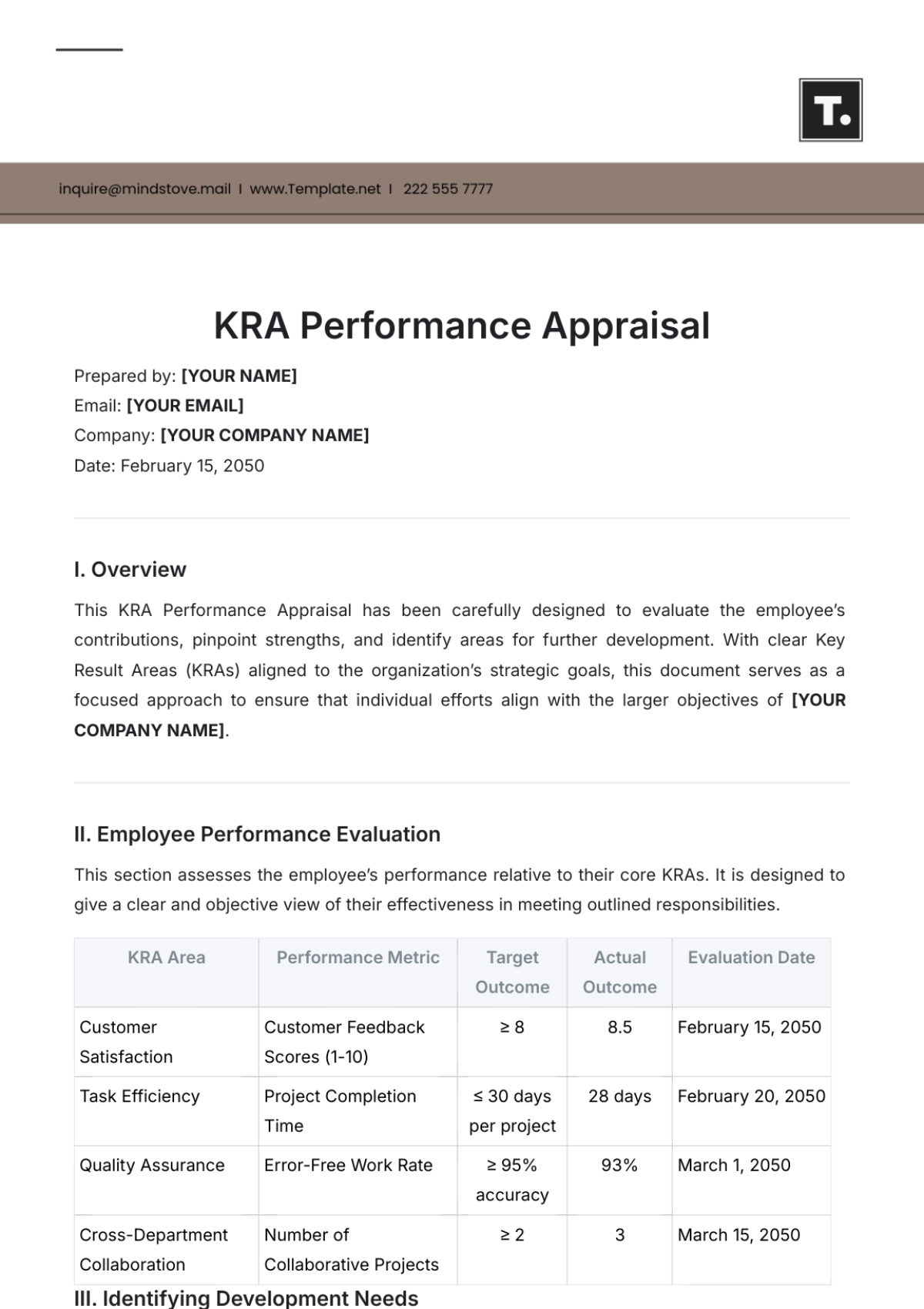
V. Roles and Responsibilities
A. HR Document Management Team
1. HR Document Manager
The HR Document Manager is responsible for overseeing the entire HR document management process at [Your Company Name]. This role includes developing and implementing document management policies, conducting regular audits, and ensuring compliance with legal requirements. The HR Document Manager also serves as the primary point of contact for any issues related to HR documents.
2. HR Staff
HR staff members are responsible for the day-to-day management of HR documents, including the creation, filing, and retrieval of documents. They must follow established procedures for handling documents and report any discrepancies or issues to the HR Document Manager. HR staff also play a key role in ensuring the accuracy and completeness of employee records.
B. IT Department
1. IT Security Specialist
The IT Security Specialist is responsible for maintaining the security of digital HR documents. This includes implementing encryption, managing access controls, and conducting regular security audits. The IT Security Specialist also collaborates with the HR Document Manager to ensure that the HRDMS is functioning properly and is protected against cyber threats.
2. System Administrator
The System Administrator is responsible for the technical maintenance of the HRDMS. This includes software updates, data backups, and troubleshooting system issues. The System Administrator works closely with the HR Document Manager to ensure that the HRDMS meets the needs of the HR department and is aligned with [Your Company Name]'s overall IT strategy.
VI. Training and Awareness
A. Employee Training Programs
1. Training Content
[Your Company Name] provides comprehensive training programs for all employees involved in HR document management. The training covers topics such as document classification, data security, legal compliance, and the use of the HRDMS. Training materials are updated regularly to reflect changes in policies and regulations.
2. Training Delivery
Training is delivered through a combination of online modules, in-person workshops, and on-the-job training. Employees are required to complete initial training upon joining [Your Company Name], with refresher courses offered annually. The HR department tracks training completion and ensures that all employees are adequately prepared to manage HR documents.
B. Awareness Campaigns
1. Ongoing Communication
To reinforce the importance of proper HR document management, [Your Company Name] conducts ongoing awareness campaigns. These campaigns include regular communication via email, newsletters, and intranet updates, highlighting best practices, policy changes, and the consequences of non-compliance.
2. Security Reminders
Security reminders are an essential component of the awareness campaigns. These reminders emphasize the importance of safeguarding HR documents, particularly in the context of digital security. Employees are encouraged to report any suspicious activity or potential security breaches to the IT department immediately.
VII. Continuous Improvement
A. Monitoring and Evaluation
1. Performance Metrics
[Your Company Name] uses a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor the effectiveness of the HR document management process. These KPIs include document retrieval times, compliance audit results, and the number of security incidents reported. Regular evaluations are conducted to assess whether the document management system is meeting its objectives.
2. Feedback Mechanisms
Employees at all levels are encouraged to provide feedback on the HR document management process. This feedback is collected through surveys, suggestion boxes, and direct communication with the HR Document Manager. The feedback is used to identify areas for improvement and to make necessary adjustments to the document management process.
B. Process Improvement
1. Continuous Improvement Initiatives
[Your Company Name] is committed to continuous improvement in HR document management. Regular process reviews are conducted to identify inefficiencies or areas where enhancements can be made. The HR Document Manager leads these initiatives, working with the HR team and IT department to implement changes that improve document management efficiency and security.
2. Technology Upgrades
As part of the continuous improvement efforts, [Your Company Name] regularly assesses the technology used in HR document management. This includes evaluating the HRDMS for potential upgrades, exploring new document management tools, and adopting the latest security technologies. By staying up-to-date with technological advancements, [Your Company Name] ensures that its HR document management processes remain robust and effective.
VIII. Conclusion
A. Summary
Effective HR document management is essential for the success and compliance of [Your Company Name] in the year 2050 and beyond. This comprehensive HR Document Management Plan provides a structured approach to managing HR documents, ensuring that they are handled securely, efficiently, and in compliance with legal requirements. By following the policies, procedures, and responsibilities outlined in this plan, [Your Company Name] can maintain the integrity of its HR records and support its long-term organizational goals.
B. Future Considerations
As [Your Company Name] continues to grow and evolve, the HR document management process must also adapt to new challenges and opportunities. This plan will be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and effective in the face of changing regulations, technological advancements, and organizational needs. By staying proactive and committed to continuous improvement, [Your Company Name] will be well-positioned to manage its HR documents effectively for years to come.